Page 178 of 2053

M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1 -- 15
D AEW OO M Y_2000
FAILURE CODES TABLE (Cont’d)
Failure
codeSee
PageDescription
401F1 -- 51Purge control valve short circuit to battery
411F1 -- 51Purge control valve short circuit to ground or open
441F1 -- 72Cooling fan (HI) relay short circuit to power
451F1 -- 72Cooling fan (HI) relay short circuit to ground or open
541F1 -- 51Purge control circuit malfunction
561F1 -- 33No.1 knock sensor signal failure
571F1 -- 33No.2 knock sensor signal failure
581F1 -- 27Camshaft position sensor signal : No.1 cylinder synchronization failure
591F1 -- 89CAN communication failure : MSR data transmission not plausible
601F1 -- 89CAN communication failure : ASR data transmission not plausible
621F1 -- 71Clutch switch defective
641F1 -- 21No ignition voltage output (No.1 ignition coil)
651F1 -- 21No ignition voltage output (No.2 ignition coil)
661F1 -- 21No ignition voltage output (No.3 ignition coil)
671F1 -- 23Crankshaft position sensor adaptation failure
681F1 -- 35Random/Multiple Misfire
711F1 -- 39Starter signal recognition failure
721F1 -- 47No.1 injector short circuit to battery
731F1 -- 47No.1 injector short circuit to ground or open
741F1 -- 47No.2 injector short circuit to battery
751F1 -- 47No.2 injector short circuit to ground or open
761F1 -- 47No.3 injector short circuit to battery
771F1 -- 48No.3 injector short circuit to ground or open
781F1 -- 48No.4 injector short circuit to battery
791F1 -- 48No.4 injector short circuit to ground or open
801F1 -- 82Oxygen sensor high voltage
811F1 -- 83Bank 1 system short term fuel trim adaptation below lean threshold
821F1 -- 82Oxygen sensor no activity detected
831F1 -- 82Oxygen sensor not lean after overrun fuel shut -- off
841F1 -- 82Oxygen sensor slow response
851F1 -- 82Oxygen sensor heater failure
861F1 -- 82Oxygen sensor heater short circuit to battery
871F1 -- 82Oxygen sensor heater short circuit to ground or open
891F1 -- 82Oxygen sensor low voltage
931F1 -- 83Bank 1 system short term fuel trim adaptation above rich threshold
961F1 -- 83Bank 1 system short term fuel trim at rich stop
971F1 -- 83Bank 1 system short term fuel trim at lean stop
981F1 -- 83Bank 1 system idle adaptation failure (above rich threshold)
991F1 -- 83Bank 1 system idle adaptation failure (below lean threshold)
1001F1 -- 83Bank 1 system learning control failure (rich, low load)
1011F1 -- 83Bank 1 system learning control failure (lean, low load)
1021F1 -- 83Bank 1 system learning control failure (rich, high load)
Page 181 of 2053

1F1 -- 18 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
IGNITION SYSTEM
This ignition system does not use a conventional distributor andcoil. It uses a crankshaft position sensor input to the
Engine Control Module (ECM). The ECM then determines Electronic Spark Timing (EST) and triggers the electronic
ignition system ignition coil.
This type of distributorless ignition system uses a‘‘waste spark” method of spark distribution. Each cylinder is paired
with the cylinder that is opposite it (1 -- 6 or 2 -- 5 or 3 -- 4). The spark occurs simultaneously in the cylinder coming up on
the compression stroke and in the cylinder coming up on the exhaust stroke. The cylinder on the exhaust stroke re-
quires very little of the available energy to fire the spark plug. The remaining energy is available to the spark plug in the
cylinder on the compression stroke.
These systems use the EST signal from the ECM to control the EST. The ECM uses the following information:
DEngine load (mass air flow sensor).
DEngine temperature.
DIntake air temperature.
DCrankshaft position.
DEngine speed (rpm).
YAA1F310
Page 183 of 2053
1F1 -- 20 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
IGNITION COIL
YAA1F240
The Electronic Ignition (EI) system ignition coil is located on the cylinder head cover. The double ended coils receive
the signal for the Engine Control Module (ECM) which controls the spark advance.
Each EI system ignition coil provides the high voltage to two spark plugs simultaneously;
T1/1: cylinder 2 and 5
T1/2: cylinder 3 and 4
T1/3: cylinder 1 and 6
The EI system ignition coil is not serviceable and must be replaced as an assembly.
Page 184 of 2053
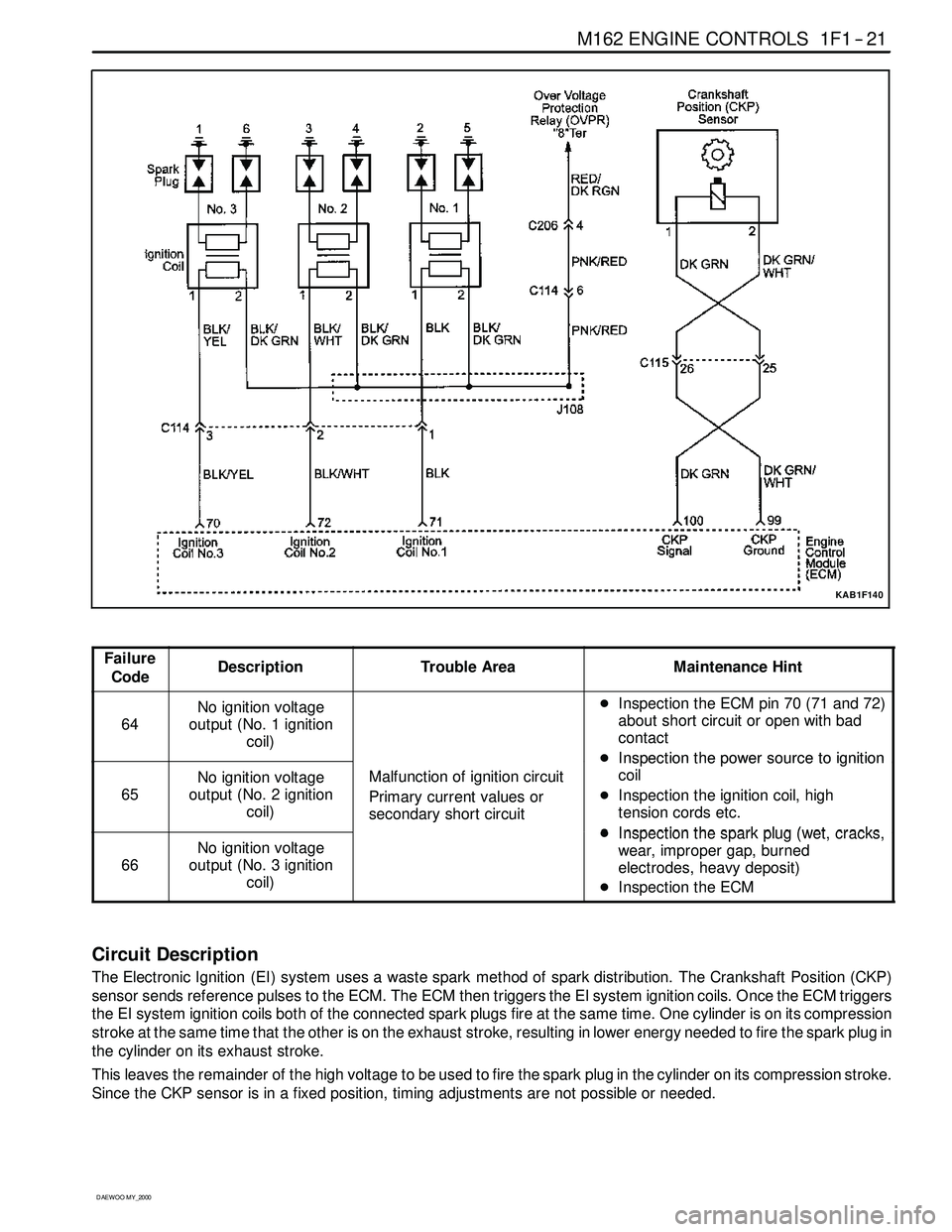
M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1 -- 21
D AEW OO M Y_2000
KAB1F140
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
64
No ignition voltage
output (No. 1 ignition
coil)DInspectiontheECMpin70(71and72)
about short circuit or open with bad
contact
DInspectionthepowersourcetoignition
65
No ignition voltage
output (No. 2 ignition
coil)Malfunction of ignition circuit
Primary current values or
secondary short circuit
DInspectionthepowersourcetoignition
coil
DInspection the ignition coil, high
tension cords etc.
DInspectionthesparkplug(wetcracks
66
No ignition voltage
output (No. 3 ignition
coil)DInspection the spark plug (wet, cracks,
wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes, heavy deposit)
DInspection the ECM
Circuit Description
The Electronic Ignition (EI) system uses a waste spark method of spark distribution. The Crankshaft Position (CKP)
sensor sends reference pulses to the ECM. The ECM then triggers the EI system ignition coils. Once the ECM triggers
the EI system ignition coils both of the connected spark plugs fire at the same time. One cylinder is on its compression
stroke at the same time that the other is on the exhaust stroke, resulting in lower energy needed to fire the spark plug in
the cylinder on its exhaust stroke.
This leaves the remainder of the high voltage to be used to fire the spark plug in the cylinder on its compression stroke.
Since the CKP sensor is in a fixed position, timing adjustments are not possible or needed.
Page 185 of 2053
1F1 -- 22 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP) SENSOR
YAA1F250
This Electronic Ignition (EI) system uses inductive or pickup type magnetic Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor. The
CKP sensor is located in the opposite side of the crankshaft pulley and triggers the pick-up wheel teeth which is
equipped 60 -- 2 teeth with a gap of 2 teeth at 360 degree spacing. This sensor protrudes through its mount to within 1.1
±0.14 mm.
The output of the sensor is a sinusoidal signal. Each tooth of the pick-up 60 -- 2 wheel generates a positive half wave.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) uses this sensor signal to generate timed ignition and injection pulses that it sends
to the ignition coils and to the fuel injectors.
Page 193 of 2053
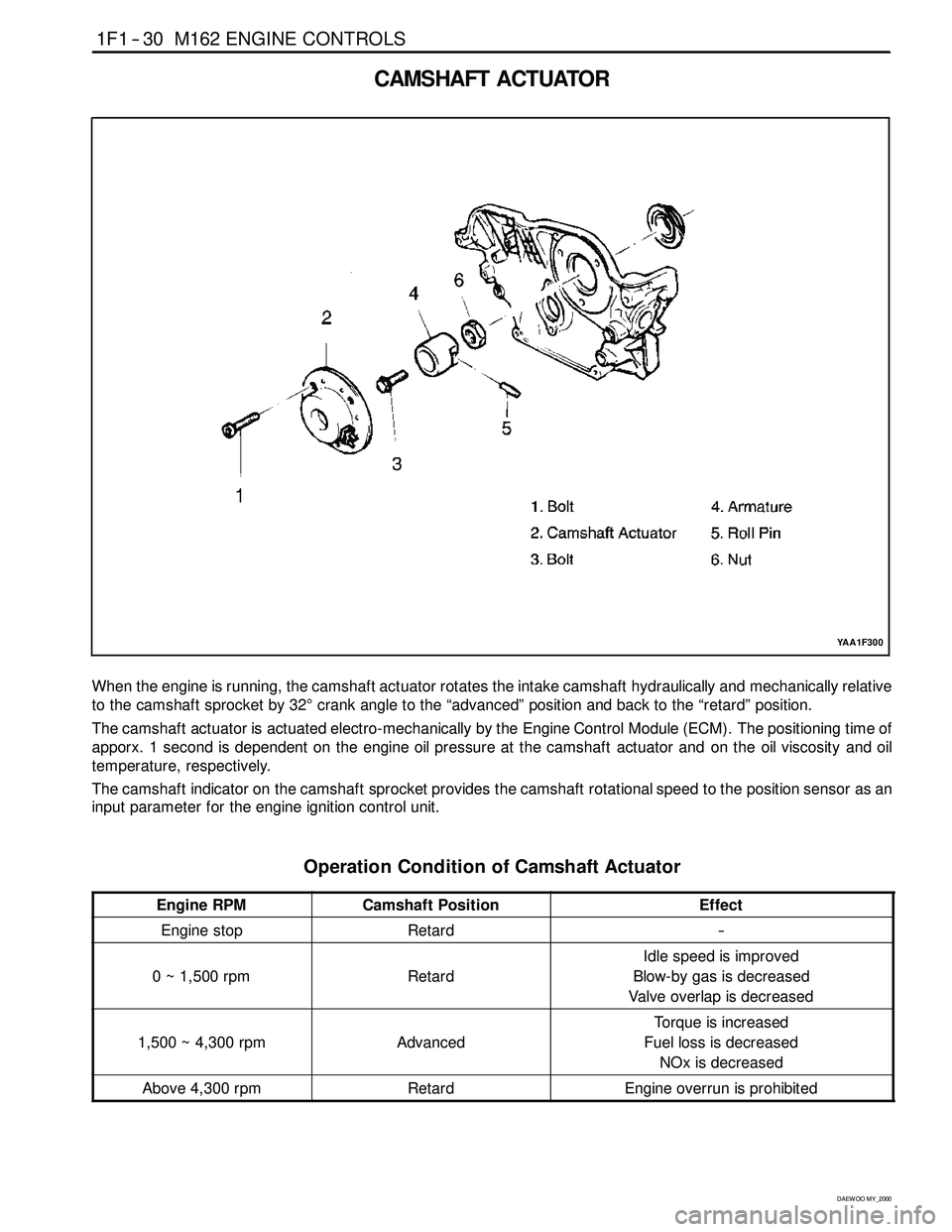
1F1 -- 30 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
CAMSHAFT ACTUATOR
YAA1F300
When the engine is running, the camshaft actuator rotates the intake camshaft hydraulically and mechanically relative
to the camshaft sprocket by 32°crank angle to the “advanced” position and back to the “retard” position.
The camshaft actuator is actuated electro-mechanically by the Engine Control Module (ECM). The positioning time of
apporx. 1 second is dependent on the engine oil pressure at the camshaft actuator and on the oil viscosity and oil
temperature, respectively.
The camshaft indicator on the camshaft sprocket provides the camshaft rotational speed to the position sensor as an
input parameter for the engine ignition control unit.
Operation Condition of Camshaft Actuator
Engine RPMCamshaft PositionEffect
Engine stopRetard--
0 ~ 1,500 rpmRetard
Idle speed is improved
Blow-by gas is decreased
Valve overlap is decreased
1,500 ~ 4,300 rpmAdvanced
Torque is increased
Fuel loss is decreased
NOx is decreased
Above 4,300 rpmRetardEngine overrun is prohibited
Page 212 of 2053

M162 ENGINE CONTROLS 1F1 -- 49
D AEW OO M Y_2000
Notice:Prepare the beaker for taking the fuel.
4. Connect the shop made cable to the injector with a firing order.
5. Connect the other end of shop made cable to the positive battery cable and negative battery cable.
6. Turn the ignition switch ON.
7. Check the injector for normal spray pattern as shown in the figure. Check injector for leaks or later drop
Injector Resistance Inspection
1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.
2. Remove the fuel injector connectors.
3. Measure the fuel injector coil resistance using a multimeter.
Specified Value
14 ~ 17Ω
Notice:Replace the fuel injector if the measured value is out of the specified values. Check the connector and wire
connection between the ECM and the injector if the measured values are normal.
Injector Pulse Width Inspection
1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.
2. Install the scan tool.
3. Turn the ignition switch ON.
4. Monitor the “INJECTION TIME” with a scan tool.
Cranking
8.0 ms
Engine Idle3~5ms
Wide Open Throttle (WOT)14 ms
Page 235 of 2053
1F1 -- 72 M162 ENGINE CONTROLS
D AEW OO M Y_2000
COOLING FAN
KAB1F290
Failure
CodeDescriptionTrouble AreaMaintenance Hint
44Cooling fan (HI) relay
short circuit to powerCooling fan short circuit to
powerDInspection the Engine Control Module
(ECM) pin 35 about short circuit or
openwithbadcontact
45
Cooling fan (HI) relay
short circuit to ground or
openCooling fan short circuit to
ground or open
openwithbadcontact
DInspection the power source
DInspection the cooling fan
DInspection the ECM
Circuit Description
Ignition voltage is supplied directly to the cooling fan relay coil. The ECM controls the relay by grounding the control
circuit. When the ECM is commanding a command ON, the voltage of the control circuit should be low (near 0 volt).
When the ECM is commanding the control circuit should be high (near battery voltage). If the fault detection circuit
senses a voltage other than what is expected, the fault line status will change causing the fault code to set.