Page 920 of 1503
Steering Column
Removal (cont'd)
8. Remove the combination switch assembly from the
column shaft.
NOTE: The combination switch can be removed by
disconnecting only the TCS sensor connector.
10. Remove the steering joint bolts and toothed lock
washers from the steering joint.
9. Remove the steering joint cover.
11. Disconnect the ignition switch connectors and
remove the column holder, then remove the steer-
ing column assembly by removing the 8 mm bolts
and flange nuts.ProCarManuals.com
Page 921 of 1503
Inspection
NOTE:
• Chec k the telescopi c mechanism , tilt mechanism , and steerin g joint bearing s or steerin g shaf t for movemen t and damage .
Replac e a s a n assembl y if damage d o r faulty .
• I f eithe r th e steerin g colum n assembl y o r TC S senso r i s removed , selec t th e appropriat e shi m an d adjus t th e distanc e
betwee n th e steerin g shaf t an d TC S sensor . Refe r t o Sectio n 1 9 fo r shi m selection .
I f th e forc e measure d i s no t withi n th e specification ,
loose n th e locknut , the n tur n th e telescopi c adjustin g
bol t unti l th e correc t forc e ca n b e obtained .
Attac
h a sprin g scal e to th e kno b o f th e telescopi c lever .
Measur e th e forc e require d to mov e th e lever .
Preload : 7 0 - 9 0 N (7 - 9 kgf , 1 5 - 2 0 Ibf )
ProCarManuals.com
Page 923 of 1503
9. Install the column covers.
NOTE: Be careful not to damage the column covers.
10. Insert the cable reel 3P connector through the col-
umn lower panel, and attach it to the column lower
panel with the connector holder. Then connect the
SRS main harness and cable reel 3P connector.
11. Install the column lower panel.
7. Install the combination switch assembly over the
column shaft.
8. Reconnect TCS sensor connector.ProCarManuals.com
Page 949 of 1503
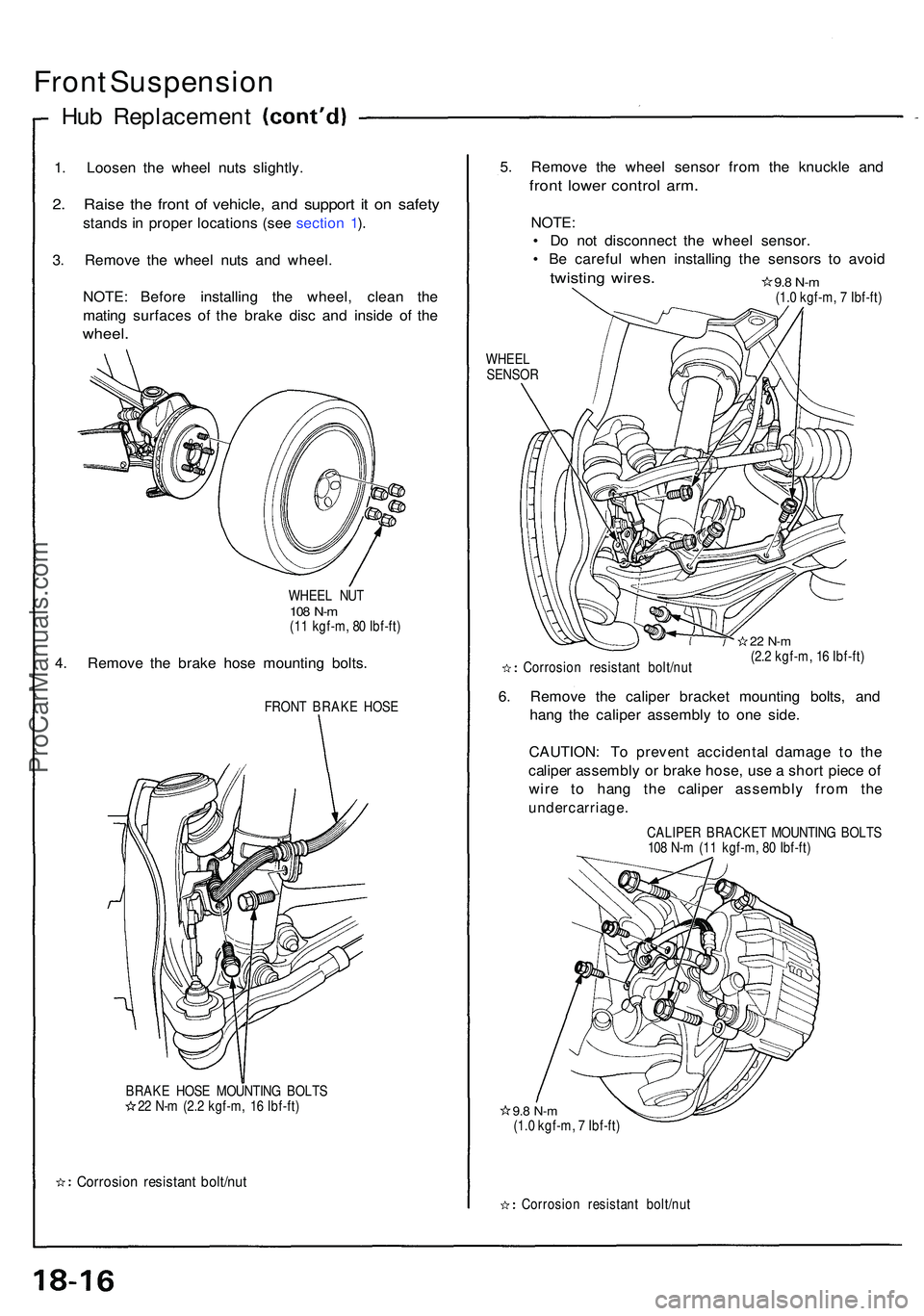
Front Suspensio n
Hub Replacemen t
1. Loose n th e whee l nut s slightly .
2. Rais e th e fron t o f vehicle , an d suppor t i t o n safet y
stands i n prope r location s (se e sectio n 1 ).
3 . Remov e th e whee l nut s an d wheel .
NOTE : Befor e installin g th e wheel , clea n th e
matin g surface s o f th e brak e dis c an d insid e of the
wheel .
WHEE L NU T108 N- m(11 kgf-m , 8 0 Ibf-ft )
4. Remov e th e brak e hos e mountin g bolts .
FRON T BRAK E HOS E
BRAK E HOS E MOUNTIN G BOLT S
2 2 N- m (2. 2 kgf-m , 1 6 Ibf-ft )
Corrosio n resistan t bolt/nu t
5. Remov e th e whee l senso r fro m th e knuckl e an d
fron t lowe r contro l arm .
NOTE :
• D o no t disconnec t th e whee l sensor .
• B e carefu l whe n installin g th e sensor s t o avoi d
twistin g wires .
WHEE L
SENSO R
Corrosio n resistan t bolt/nu t
22 N- m(2.2 kgf-m , 1 6 Ibf-ft )
6. Remov e th e calipe r bracke t mountin g bolts , an d
han g th e calipe r assembl y t o on e side .
CAUTION : T o preven t accidenta l damag e t o th e
calipe r assembl y o r brak e hose , us e a shor t piec e o f
wir e t o han g th e calipe r assembl y fro m th e
undercarriage .
CALIPER BRACKE T MOUNTIN G BOLT S
10 8 N- m (1 1 kgf-m , 8 0 Ibf-ft )
9.8 N- m(1.0 kgf-m , 7 Ibf-ft )
Corrosio n resistan t bolt/nu t
9.8 N- m(1.0 kgf-m , 7 Ibf-ft )
ProCarManuals.com
Page 965 of 1503
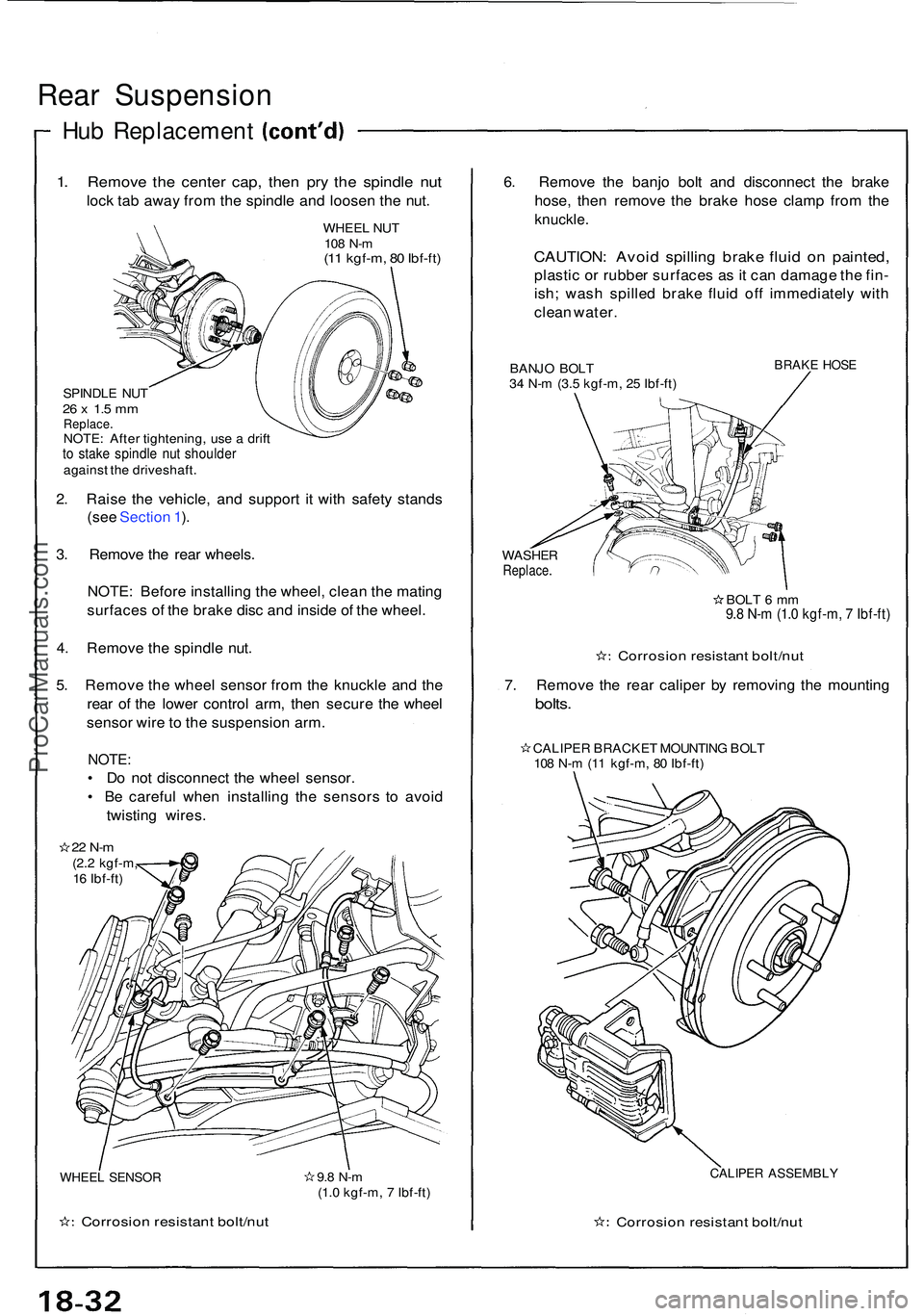
Rear Suspensio n
Hub Replacemen t
1. Remov e th e cente r cap , the n pr y th e spindl e nu t
lock ta b awa y fro m th e spindl e an d loose n th e nut .
WHEE L NU T108 N- m(11 kgf-m , 8 0 Ibf-ft )
SPINDL E NU T26 x 1. 5 m mReplace .NOTE: Afte r tightening , us e a drif tto stak e spindl e nu t shoulde ragainst th e driveshaft .
2. Rais e th e vehicle , an d suppor t i t wit h safet y stand s
(se e Sectio n 1 ).
3 . Remov e th e rea r wheels .
NOTE : Befor e installin g th e wheel , clea n th e matin g
surface s o f th e brak e dis c an d insid e o f th e wheel .
4 . Remov e th e spindl e nut .
5 . Remov e th e whee l senso r fro m th e knuckl e an d th e
rea r o f th e lowe r contro l arm , the n secur e th e whee l
senso r wir e to th e suspensio n arm .
NOTE :
• D o no t disconnec t th e whee l sensor .
• B e carefu l whe n installin g th e sensor s t o avoi d
twistin g wires .
22 N- m(2.2 kgf-m ,
1 6 Ibf-ft )
WHEE L SENSO R
Corrosio n resistan t bolt/nu t
9.8 N- m(1.0 kgf-m , 7 Ibf-ft )
6. Remov e th e banj o bol t an d disconnec t th e brak e
hose , the n remov e th e brak e hos e clam p fro m th e
knuckle .
CAUTION : Avoi d spillin g brak e flui d o n painted ,
plastic o r rubbe r surface s a s it ca n damag e th e fin -
ish ; was h spille d brak e flui d of f immediatel y wit h
clea n water .
BANJO BOL T
3 4 N- m (3. 5 kgf-m , 2 5 Ibf-ft )BRAK E HOS E
WASHE RReplace .
BOLT 6 m m9.8 N- m (1. 0 kgf-m , 7 Ibf-ft )
Corrosio n resistan t bolt/nu t
7. Remov e th e rea r calipe r b y removin g th e mountin g
bolts.
CALIPE R BRACKE T MOUNTIN G BOL T
10 8 N- m (1 1 kgf-m , 8 0 Ibf-ft )
CALIPE R ASSEMBL Y
Corrosion resistan t bolt/nu t
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1010 of 1503
Features/Construction/Operation
Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) Description
General
In a conventional brake system, if the brake pedal is depressed excessively, the wheels can lock before the vehicle comes
to a stop. In such a case, the stability of the vehicle is reduced if the rear wheels are locked, and maneuverability of the
vehicle is reduced if the front wheels are locked, creating an extremely unstable condition.
The Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) modulates the pressure of the brake fluid applied to each caliper, thereby preventing
the locking of the wheels, whenever the wheels are likely to locked due to be excessive braking. It then restores normal
hydraulic pressure when there is no longer any possibility of wheel locking.
4-Channel Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) Features
• Increased braking stability can be achieved regardless of changing driving conditions.
• The maneuverability of the vehicle is improved as the system prevents the front wheels from locking.
• When the anti-lock brake system goes into action, kickback is felt on the brake pedal.
• The anti-lock brake system is equipped with a self-diagnosis function. When an abnormality is detected, the ABS indi-
cator light comes on. The location of the abnormality can be diagnosed from the frequency of the system indicator
light display blinks.
• This system has individual control of the front and rear wheels. Braking force is controlled on each of the four wheels
independently, resulting in optimum braking efects on the four wheels.
The system has a fail-safe function that allows normal braking if there's a problem with the anti-lock brake system.
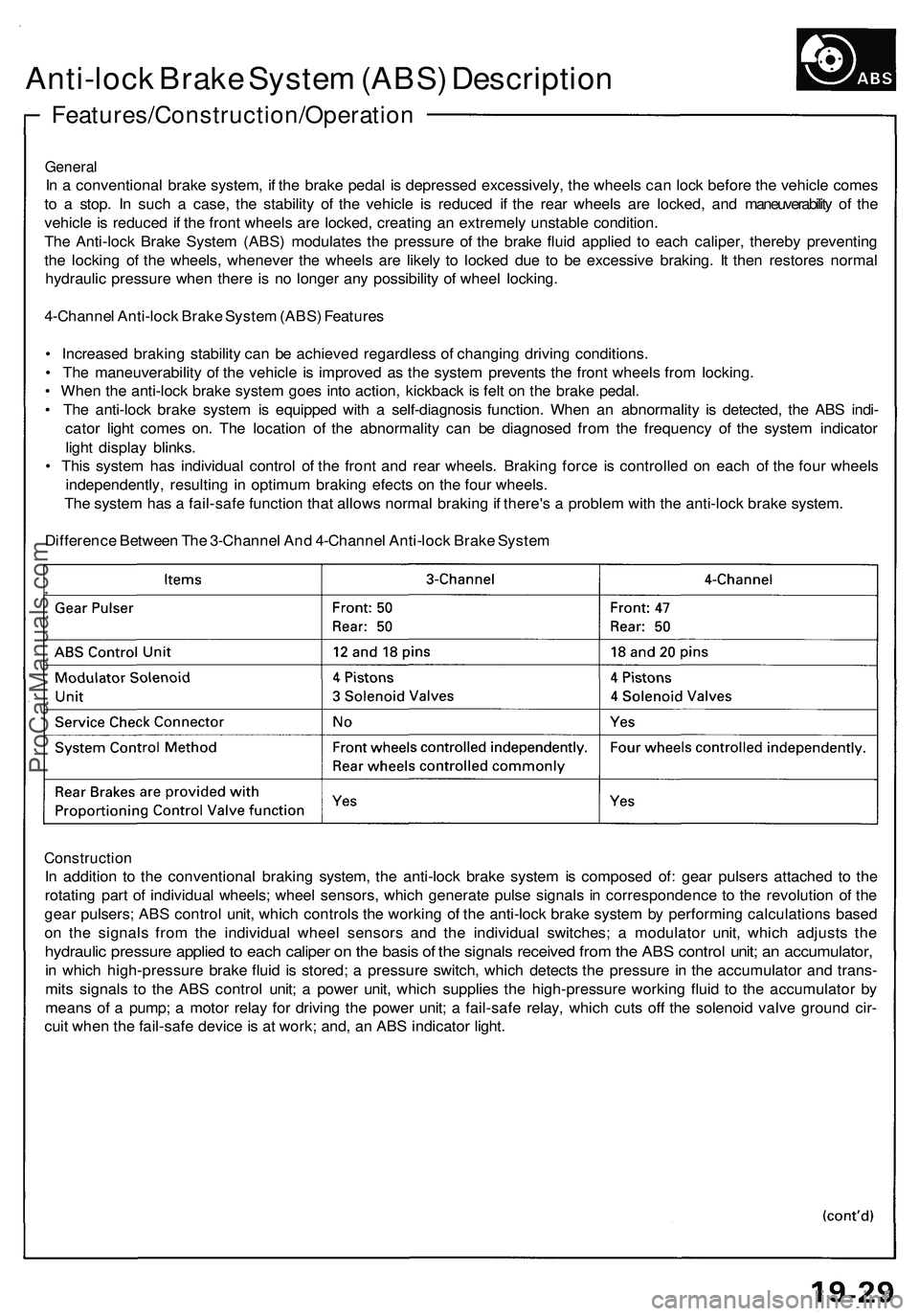
Difference Between The 3-Channel And 4-Channel Anti-lock Brake System
Construction
In addition to the conventional braking system, the anti-lock brake system is composed of: gear pulsers attached to the
rotating part of individual wheels; wheel sensors, which generate pulse signals in correspondence to the revolution of the
gear pulsers; ABS control unit, which controls the working of the anti-lock brake system by performing calculations based
on the signals from the individual wheel sensors and the individual switches; a modulator unit, which adjusts the
hydraulic pressure applied to each caliper on the basis of the signals received from the ABS control unit; an accumulator,
in which high-pressure brake fluid is stored; a pressure switch, which detects the pressure in the accumulator and trans-
mits signals to the ABS control unit; a power unit, which supplies the high-pressure working fluid to the accumulator by
means of a pump; a motor relay for driving the power unit; a fail-safe relay, which cuts off the solenoid valve ground cir-
cuit when the fail-safe device is at work; and, an ABS indicator light.ProCarManuals.com
Page 1013 of 1503
Wheel Sensor
The wheel sensor is a contactless type, and it detects the rotating speeds of a wheel. It is composed of a permanent
magnet and coil. When the gear pulsers attached to the rotating parts of each wheel (rear wheel: outboard joint of the
driveshaft, front: hub bearing unit) turn, the magnetic flux around the coil in the wheel sensor alternates, generating volt-
ages with frequency in proportion to wheel rotating speed. These pulses are inputted into the ABS control unit, and the
ABS control unit identifies the wheel speeds.
Features/Construction/Operation (cont'd)
Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) DescriptionProCarManuals.com
Page 1014 of 1503
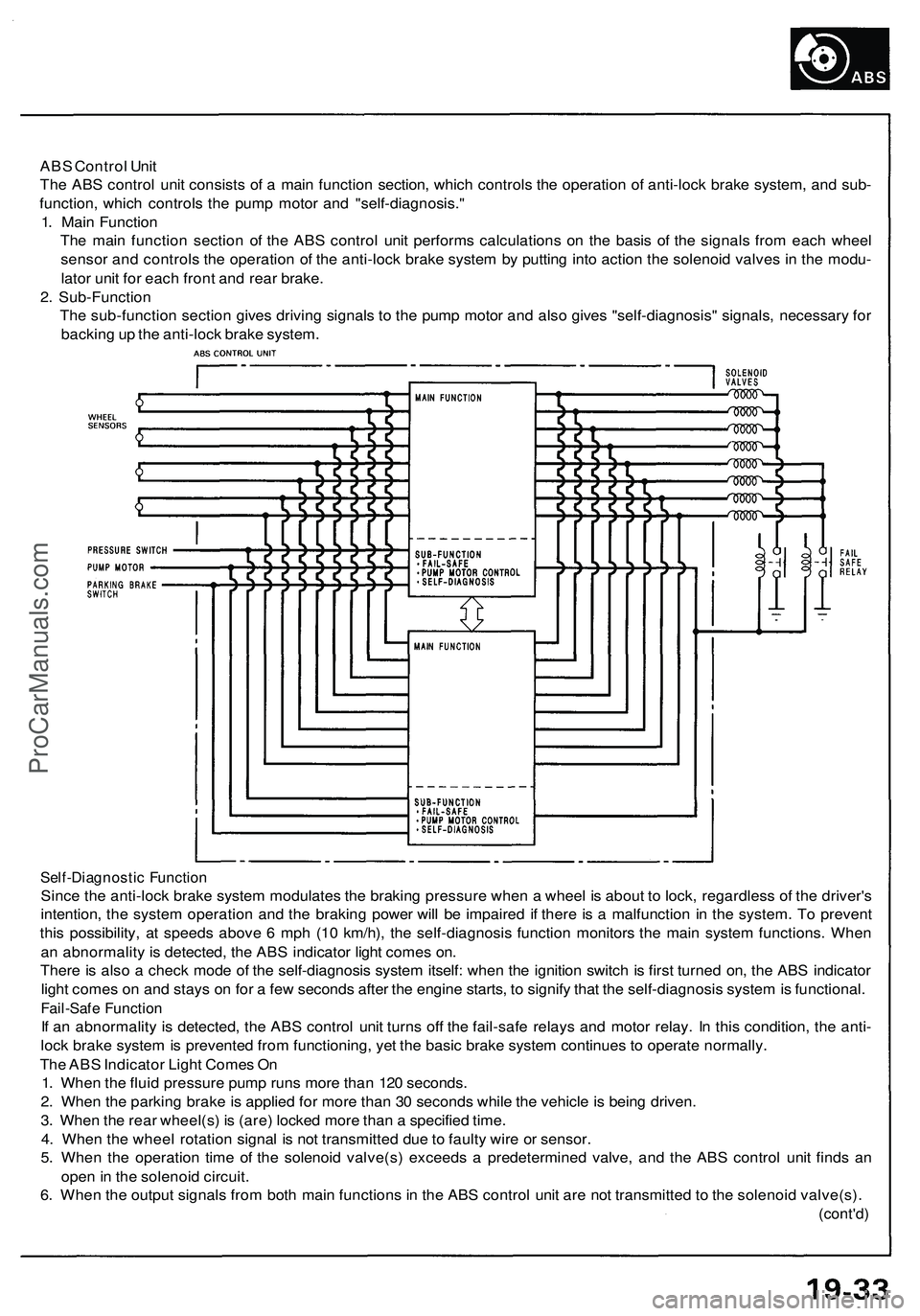
ABS Control Unit
The ABS control unit consists of a main function section, which controls the operation of anti-lock brake system, and sub-
function, which controls the pump motor and "self-diagnosis."
1. Main Function
The main function section of the ABS control unit performs calculations on the basis of the signals from each wheel
sensor and controls the operation of the anti-lock brake system by putting into action the solenoid valves in the modu-
lator unit for each front and rear brake.
2. Sub-Function
The sub-function section gives driving signals to the pump motor and also gives "self-diagnosis" signals, necessary for
backing up the anti-lock brake system.
Self-Diagnostic Function
Since the anti-lock brake system modulates the braking pressure when a wheel is about to lock, regardless of the driver's
intention, the system operation and the braking power will be impaired if there is a malfunction in the system. To prevent
this possibility, at speeds above 6 mph (10 km/h), the self-diagnosis function monitors the main system functions. When
an abnormality is detected, the ABS indicator light comes on.
There is also a check mode of the self-diagnosis system itself: when the ignition switch is first turned on, the ABS indicator
light comes on and stays on for a few seconds after the engine starts, to signify that the self-diagnosis system is functional.
Fail-Safe Function
If an abnormality is detected, the ABS control unit turns off the fail-safe relays and motor relay. In this condition, the anti-
lock brake system is prevented from functioning, yet the basic brake system continues to operate normally.
The ABS Indicator Light Comes On
1. When the fluid pressure pump runs more than 120 seconds.
2. When the parking brake is applied for more than 30 seconds while the vehicle is being driven.
3. When the rear wheel(s) is (are) locked more than a specified time.
4. When the wheel rotation signal is not transmitted due to faulty wire or sensor.
5. When the operation time of the solenoid valve(s) exceeds a predetermined valve, and the ABS control unit finds an
open in the solenoid circuit.
6. When the output signals from both main functions in the ABS control unit are not transmitted to the solenoid valve(s).
(cont'd)ProCarManuals.com