Page 328 of 1354
DI−8
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
6. BASIC INSPECTION
When the Malfunction code is not confirmed in the DTC check, troubleshooting should be performed in the
order for all possible circuits to be considered as the causes of the problems.
In many cases, by carrying out the basic engine check shown in the following flow chart, the location causing
the problem can be found quickly and efficiently. Therefore, use of this check is essential in engine trouble-
shooting.
1 Is battery positive voltage 11 V or more when engine is stopped?
NO Charge or replace battery.
YES
2 Is engine cranked?
NO Proceed to STARTING and continue to trouble-
shoot.
YES
3 Does engine start?
NO Go to step 7.
YES
Page 372 of 1354
S02386
1H
1DEA1
IG1 22 IG1 IG1
E4
E4
E4
E4
E4
E4 B−R
B−Y
B−R
B−Y
BR
BRE02 E01#40 #30 #20 #10ECM
Injector 8
J/B No.1
IG Switch
8 14
7
11
7 621
202
2
2
2 B−O 31
1
1
1 No.1
No.2
No.3
No.4 B−O
B−O
B−O B−O B−O12
11
25
24
13
26
EC
BatteryFusible Link Block
MAIN
W B−R2
B
B−R
B−YB−Y
B−R
J/B No.2
AM2
FI6588
FI6538
A00064
10 V/
Division10 V/
Division(Magnification)
100 m sec./Division (idling)1 m sec./Division (Idling)
Injection durationGND GND
DI−52
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
WIRING DIAGRAM
Reference INSPECTION USING OSCILLOSCOPE
INJECTOR SIGNAL WAVEFORM
With the engine idling, measure between terminals #10, #20, #30, #40 and E01 of ECM.
HINT:
The correct waveform is as shown.
Page 397 of 1354
S02388
6
66
6 3
15
2
1J 1E21J/B No.1 From
BatteryVaper Pressure Sensor
E5
E5
E5
E4
E58 229
7 1
EA1
B−R
B−O
11Fuse Block
From
IG SwitchVSV
(for Vapor
Pressure Sensor) VSV
(for EVAP)VC
PTNK
E2
EVP
TPCE01
E01 5V ECM
E1
B−R
1P
2 1
B−R BRL−Y Y
1 2 3
R/B No.6
2
B−R
W−B2
EA 10
IGN R−W
EFI Main Relay
R−W A
A
W−B
J1 Junction
Connector B−O
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI−77
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
�If DTC P0441, P0446 or P0450 is output after DTC P0440, first troubleshoot DTC P0441, P0446 or
P0450. If no malfunction is detected, troubleshoot DTC P0440 next.
�Ask the customer whether, after the MIL came on, the customer found the fuel tank cap loose and tight-
ened it. Also ask the customer whether the fuel tank cap was loose when refuelling.
If the fuel tank cap was loose, it was the cause of the DTC. If the fuel tank cap was not loose or if the
customer was not sure if it was loose, troubleshoot according to the following procedure.
Page 418 of 1354
S02401
6
66 6 5
2 13R/B No.6
From Battery
Fuse Block
1J
1E
B−O11 1
2
From
IG SwitchECM
ISCO
ISCC E4
E4 B−L
B−Y10
9 IAC Valve
EA12
2
B−R B−R
W−B W−B
EA J1
Junction Connector
AA EFI Main Relay R−W
IGNE01
E01
J/B No.13 1
10 B−O
DI−98
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
1 Check air induction system (See page EC−5).
NG Repair or replace.
OK
2 Check A/C signal circuit (See page AC−64).
NG Repair or replace.
OK
3 Check voltage between terminals ISCO, ISCC of ECM connector and body
ground.
Page 425 of 1354
A15827
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI−105
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
DTC P1500 Starter Signal Circuit Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When the engine is cranked, the intake air flow is slow, so fuel vaporization is poor. A rich mixture is therefore
necessary in order to achieve good startability. While the engine is being cranked, the battery positive volt-
age is applied to terminal STA of the ECM. The starter signal is mainly used to increase the fuel injection
volume for the starting injection control and after−start injection control.
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
This diagnostic chart is based on the premise that the engine is cranked normally. If the engine is not
cranked, proceed to the matrix chart of problem symptoms on page DI−20.
DI965−01
Page 429 of 1354
A00421
LOCK
BATT (+)
S02495
EFI Fuse
R/B No.2
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI−109
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
1 Check voltage between terminal BATT of ECM connector and body ground.
PREPARATION:
Remove side trim cover (See page SF−61).
CHECK:
Measure voltage between terminal BATT of ECM connector
and body ground.
OK:
Voltage: 9 − 14 V
OK Check and replace ECM (See page IN−30).
NG
2 Check EFI fuse.
PREPARATION:
Remove EFI fuse from R/B No.2.
CHECK:
Check continuity of EFI fuse.
OK:
Continuity
NG Check for short in all the harness and compo-
nents connected to EFI fuse.
OK
Check and repair harness or connector be-
tween battery and EFI fuse, EFI fuse and
ECM.
Page 431 of 1354
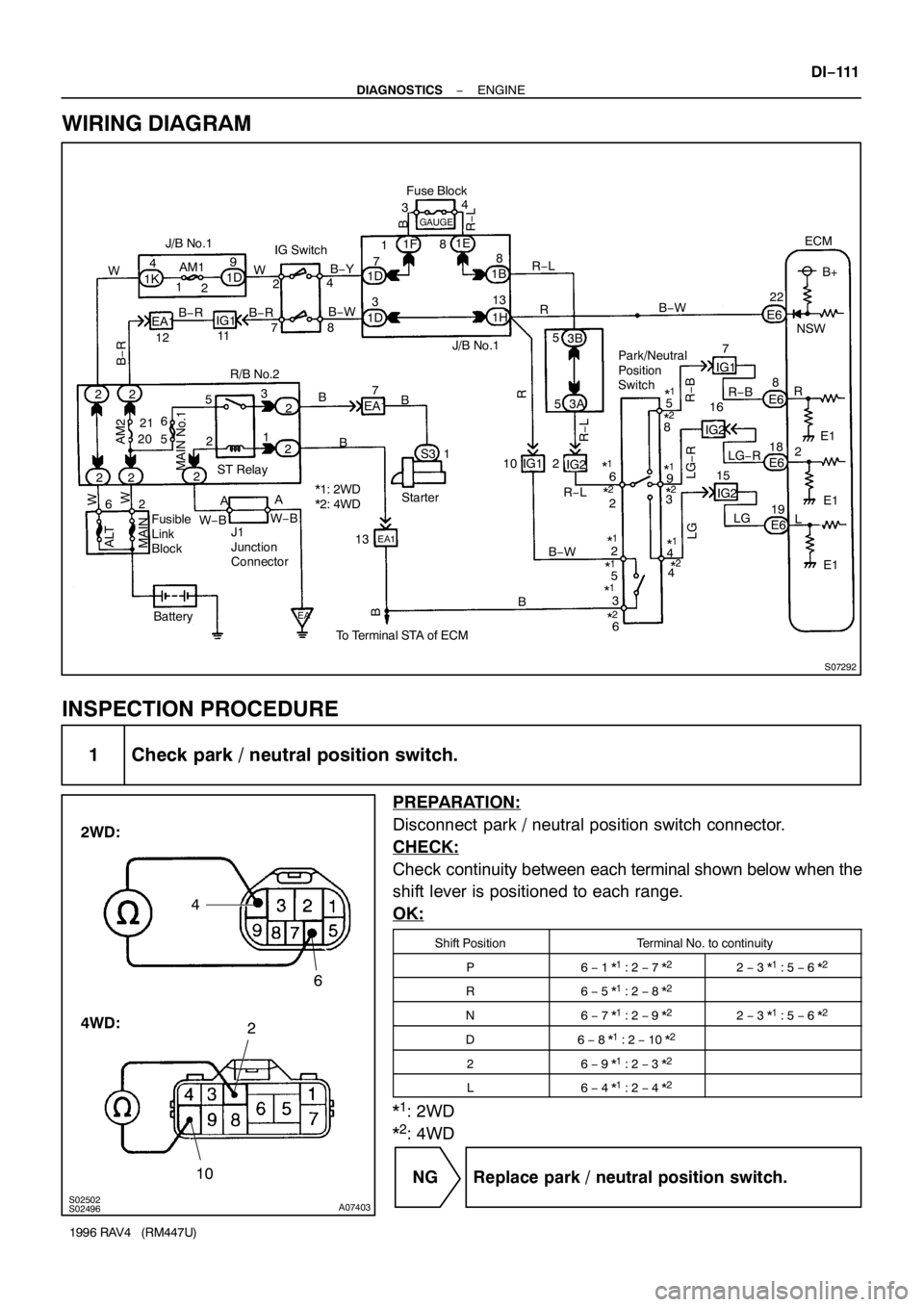
S07292
1K1D 49
EA1IG1
1211
22
2 225
23
1
22
6
5 21
20
AA
BR 1D1F1E
1B
1H
1D3718
8
13 34 Fuse Block
B
R−L
R−LECM
E6
E6
E6
E6 19 188 22
IG17
16
IG2
IG2 15 3B 5
53A
IG2 2 IG1 10 EA17
EA113S3 1 B
B
*1: 2WD
*2: 4WD
J1
Junction
Connector Fusible
Link
BlockMAIN
Battery
To Terminal STA of ECMEAB
StarterPark/Neutral
Position
Switch
R−B5 B−W W
B−R
J/B No.1
B−RB−R
724
8B−W B−Y IG Switch
W
ST Relay
ALT
AM2
MAIN No.1
B
R−L
B−W J/B No.1
LG−R
LG
LG R−B
LG−R
W−BW−BB+
R
2
LE1
E1
E1 NSW
8
9
3
4
4
6 3 5 2 6
R
AM1
1
2
GAUGE
R/B No.2
W
W2 6*
1
*2
*12 *1
*1
*2
*1
*2
*1
*2
*2
*1
R−L
S02502S02496A07403
2WD:
4WD:4
6
2
10
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI−111
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
1 Check park / neutral position switch.
PREPARATION:
Disconnect park / neutral position switch connector.
CHECK:
Check continuity between each terminal shown below when the
shift lever is positioned to each range.
OK:
Shift PositionTerminal No. to continuity
P6 − 1 *1 : 2 − 7 *22 − 3 *1 : 5 − 6 *2
R6 − 5 *1 : 2 − 8 *2
N6 − 7 *1 : 2 − 9 *22 − 3 *1 : 5 − 6 *2
D6 − 8 *1 : 2 − 10 *2
26 − 9 *1 : 2 − 3 *2
L6 − 4 *1 : 2 − 4 *2
*1: 2WD
*
2: 4WD
NG Replace park / neutral position switch.
Page 449 of 1354

FI3605
013 sec. ON
OFF
− DIAGNOSTICSAUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (A241E)
DI−129
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
(5) See page DI−138 to confirm the details of the
DTCs.
NOTICE:
When simulating symptoms with an OBD II scan tool (ex-
cluding TOYOTA hand−held tester) to check the DTCs, use
the normal mode. For codes on the DTC chart subject to ”2
trip detection logic”, turn the ignition switch off after the
symptoms have been simulated for the first time. Then re-
peat the simulation process again. When the program has
been simulated twice, the MIL lights up and the DTCs are
recorded in the ECM.
3. Check Mode:
INSPECT DIAGNOSIS
HINT:
TOYOTA hand−held tester only:
Compared to the normal mode, the check mode has high sens-
ing ability to detect malfunctions.
Furthermore, the same diagnostic items which are detected in
the normal mode can also be detected in the check mode.
(a) Check the DTC.
(1) Initial conditions.
�Battery positive voltage 11 V or more
�Throttle valve fully closed
�Transaxle in the PARK position
�Air conditioning switched off
(2) Prepare the TOYOTA hand−held tester.
(3) Connect the TOYOTA hand−held tester to the
DLC3.
(4) Turn the ignition switch ON and switch the TOYOTA
hand−held tester ON.
(5) Switch the TOYOTA hand−held tester from the nor-
mal mode to the check mode (Check that the MIL
flashes.).
(6) Start the engine (The MIL goes off after the engine
start.).
(7) Simulate the conditions of the malfunction de-
scribed by the customer.
NOTICE:
Leave the ignition switch ON until you have checked the
DTCs, etc.
(8) After simulating the malfunction conditions, use the
TOYOTA hand−held tester diagnosis selector to
check the DTCs and freezed frame data, etc.
HINT:
Take care not to turn the ignition switch OFF.
Turning the ignition switch off switches the diagnosis system
from check mode to normal mode, so all DTCs, etc. are erased.
(9) After checking the DTC, inspect the applicable cir-
cuit.