Page 372 of 1354
S02386
1H
1DEA1
IG1 22 IG1 IG1
E4
E4
E4
E4
E4
E4 B−R
B−Y
B−R
B−Y
BR
BRE02 E01#40 #30 #20 #10ECM
Injector 8
J/B No.1
IG Switch
8 14
7
11
7 621
202
2
2
2 B−O 31
1
1
1 No.1
No.2
No.3
No.4 B−O
B−O
B−O B−O B−O12
11
25
24
13
26
EC
BatteryFusible Link Block
MAIN
W B−R2
B
B−R
B−YB−Y
B−R
J/B No.2
AM2
FI6588
FI6538
A00064
10 V/
Division10 V/
Division(Magnification)
100 m sec./Division (idling)1 m sec./Division (Idling)
Injection durationGND GND
DI−52
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
WIRING DIAGRAM
Reference INSPECTION USING OSCILLOSCOPE
INJECTOR SIGNAL WAVEFORM
With the engine idling, measure between terminals #10, #20, #30, #40 and E01 of ECM.
HINT:
The correct waveform is as shown.
Page 376 of 1354
P19750
Knock Sensor 1
E1 KNKECM
10
E5 B
1 DI−56
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
DTC P0325 Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
A knock sensor is fitted to the cylinder block to detect engine knocking. This sensor contains a piezoelectric
element which generates a voltage when it becomes deformed, which occurs when the cylinder block vi-
brates due to knocking. If engine knocking occurs, ignition timing is retarded to suppress it.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0325No knock sensor 1 signal to ECM with engine speed 1,200 rpm
or more (2 trip detection logic)�Open or short in knock sensor 1 circuit
�Knock sensor 1 (looseness)
�ECM
If the ECM detects the above diagnosis conditions, it operates the fail safe function in which the corrective
retard angle value is set to the maximum value.
WIRING DIAGRAM
DI3ZP−01
Page 379 of 1354
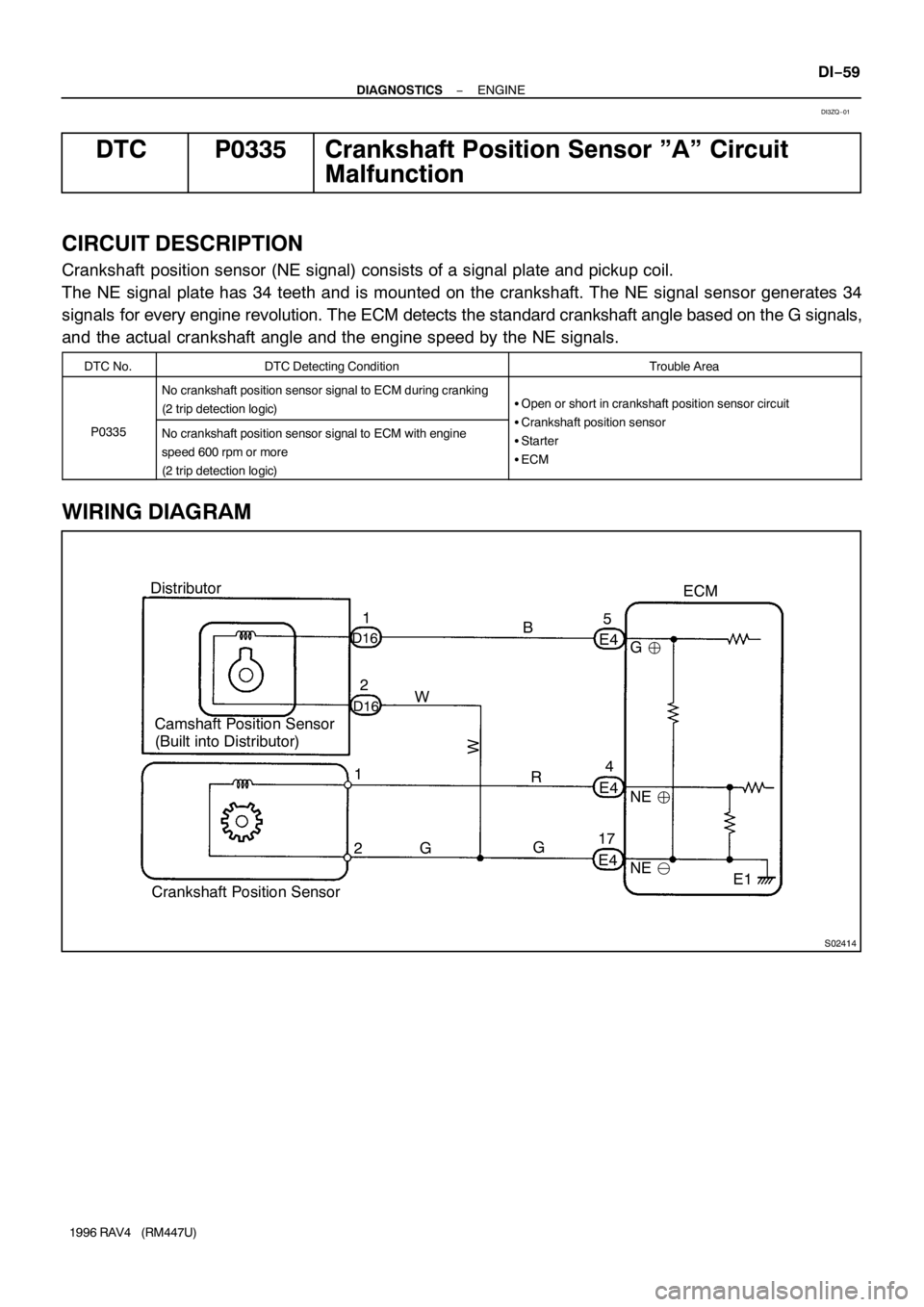
S02414
Distributor
Camshaft Position Sensor
(Built into Distributor)
D16
D16E4
E4
E4 1
B
R
W
G 1
2G4 5
17NE �
NE �
E1 ECM
Crankshaft Position Sensor2G �
W
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI−59
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
DTC P0335 Crankshaft Position Sensor ”A” Circuit
Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Crankshaft position sensor (NE signal) consists of a signal plate and pickup coil.
The NE signal plate has 34 teeth and is mounted on the crankshaft. The NE signal sensor generates 34
signals for every engine revolution. The ECM detects the standard crankshaft angle based on the G signals,
and the actual crankshaft angle and the engine speed by the NE signals.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0335
No crankshaft position sensor signal to ECM during cranking
(2 trip detection logic)�Open or short in crankshaft position sensor circuit
�Crankshaft position sensor
�Starter
�ECM
No crankshaft position sensor signal to ECM with engine
speed 600 rpm or more
(2 trip detection logic)
WIRING DIAGRAM
DI3ZQ−01
Page 382 of 1354
DI−62
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
DTC P0336 Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit Range /
Performance
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Refer to Crankshaft Position Sensor ”A” Circuit Malfunction on page DI−59.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0336Engine control computer malfunction (for backup)�Distributor
�ECM
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to page DI−59.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
1 Are there any other codes (besides DTC P0336) being output?
YES Go to relevant DTC chart.
NO
Check and replace ECM
(See page IN−30).
DI3ZR−01
Page 383 of 1354

− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI−63
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
DTC P0340 Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Camshaft position sensor (G signal) consist of a signal plate an pickup coil.
The G signal plate has one tooth on its outer circumference and is built into the distributor.
When the camshaft rotate, the protrusion on the signal plate and the air gap on the pickup coil change, caus-
ing fluctuations in the magnetic field and generating an electromotive force in the pickup coil.
The NE signal plate has 34 teeth and is mounted on the crankshaft. The NE signal sensor generates 34
signals for every engine revolution. The ECM detects the standard crankshaft angle based on the G signal
and the actual crankshaft angle and the engine speed by the NE signals.
DTC No.Detection ConditionTrouble Area
P0340No camshaft position sensor signal to ECM with engine speed
600 rpm or more
�Open or short in camshaft position sensor circuit
�Camshaft position sensor
�Starter
�ECM
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to page DI−59 for the WIRING DIAGRAM.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
1 Check resistance of camshaft position sensor (signal generator) (See page
IG−14).
Reference:
INSPECTION USING OSCILLOSCOPE
Refer to page DI−59 for the OSCILLOSCOPE.
NG Replace camshaft position sensor.
OK
2 Check for open and short in harness and connector between ECM and camshaft
position sensor (See page IN−30).
NG Repair or replace harness or connector.
OK
DI3ZS−01
Page 385 of 1354

P25430
Throttle Body
Exhaust GasEGR Valve
Diagram ECM
VSV
Throttle
Valve
Intake Air
Chamber
EGR
Vacuum
Modulator
S02387
From
Battery6
1J2
1
1E J/B No.1EFI Main Relay
Fuse Block
11
10E423
EA12 R/B No.6ECM
J1
Junction Connector
AA
W−B B−W VSV (for EGR)
2
1
B−O
IGNEGR
E01
EAFrom
IG Switch
B−O 666 3
125
R−W
B−RB−R
W−B
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI−65
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
DTC P0401 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient
Detected
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The EGR system recirculates exhaust gas, which is controlled to the proper quantity to suit the driving condi-
tions, into the intake air mixture to slow down combustion, reduce the combustion temperature and reduce
NOx emissions. The amount of EGR is regulated by the EGR vacuum modulator according to the engine
load.
If even one the following conditions is fulfilled, the VSV is turned
ON by a signal from ECM. This results in atmospheric air acting
on the EGR valve, closing the EGR valve and shutting off the
exhaust gas (EGR cut−off).
�Before the engine is warmed up
�During deceleration (throttle valve closed) .
�Light engine load (amount of intake air very small).
�Engine idling.
�Engine speed over 4,400 rpm.
�High engine load (amount of intake air very large)
.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0401
After the engine is warmed up, the intake manifold absolute
pressure is lager than the valve calculated by the ECM while
the EGR system is ON
(2 trip detected logic)
�EGR valve stuck closed
�Open or short in VSV circuit for EGR
�Vacuum or EGR hose disconnected
�Manifold absolute pressure sensor
�EGR VSV open or close malfunction
�ECM
WIRING DIAGRAM
DI3ZT−01
Page 391 of 1354
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI−71
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
DTC P0402 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Excessive
Detected
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Refer to Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected on page DI−65.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0402
After the engine is warmed up, conditions (a) and (b) continue
(a) The intake manifold absolute pressure is larger than the
value calculated by the ECM while the EGR system is ON.
(b) Misfiring is detected during idling
(2 trip detection logic)�EGR valve stuck open
�Vacuum or EGR hose is connected to wrong post
�Manifold absolute pressure sensor
�ECM
See DTC P0140 for System Check Driving Pattern and Wiring Diagram.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
�If DTC ”P0105” and / or ”P0106” and ”P0402” are output simultaneously, perform troubleshooting of
DTC ”P0105” first.
�If DTC ”P0401” and ”P0402” are output simultaneously, perform troubleshooting of DTC ”P0402” first.
1 Check the connection of the vacuum hose, EGR hose (See page EC−5).
NG Repair or replace.
OK
2 Check EGR valve (See page EC−8).
NG Repair or replace.
OK
3 Check the VSV for EGR * .
* If you have TOYOTA hand−held tester, see page DI−65, step 2.
If you have no TOYOTA hand−held tester, see page DI−65, step 2.
OK Go to step 5.
NG
DI3ZU−01
Page 397 of 1354
S02388
6
66
6 3
15
2
1J 1E21J/B No.1 From
BatteryVaper Pressure Sensor
E5
E5
E5
E4
E58 229
7 1
EA1
B−R
B−O
11Fuse Block
From
IG SwitchVSV
(for Vapor
Pressure Sensor) VSV
(for EVAP)VC
PTNK
E2
EVP
TPCE01
E01 5V ECM
E1
B−R
1P
2 1
B−R BRL−Y Y
1 2 3
R/B No.6
2
B−R
W−B2
EA 10
IGN R−W
EFI Main Relay
R−W A
A
W−B
J1 Junction
Connector B−O
− DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI−77
1996 RAV4 (RM447U)
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
�If DTC P0441, P0446 or P0450 is output after DTC P0440, first troubleshoot DTC P0441, P0446 or
P0450. If no malfunction is detected, troubleshoot DTC P0440 next.
�Ask the customer whether, after the MIL came on, the customer found the fuel tank cap loose and tight-
ened it. Also ask the customer whether the fuel tank cap was loose when refuelling.
If the fuel tank cap was loose, it was the cause of the DTC. If the fuel tank cap was not loose or if the
customer was not sure if it was loose, troubleshoot according to the following procedure.