1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 1356 of 1938

circuit information. If the resistance is greater than 1
ohm, repair the wire harness as necessary.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
To perform a complete test of the this sensor and
its circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool and appropri-
ate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures manual. To
test the throttle position sensor only, refer to the fol-
lowing:
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) can be tested
with a digital voltmeter (DVM). The center terminal
of the sensor is the output terminal. One of the other
terminals is a 5 volt supply and the remaining ter-
minal is ground.
Connect the DVM between the center and sensor
ground terminal. Refer to Group 8W - Wiring Dia-
grams for correct pinout.
With the ignition switch in the ON position, check
the output voltage at the center terminal wire of the
connector. Check the output voltage at idle and at
Wide-Open-Throttle (WOT). At idle, TPS output volt-
age should be approximately 0.38 volts to 1.2 volts.
At wide open throttle, TPS output voltage should be
approximately 3.1 volts to 4.4 volts. The output volt-
age should gradually increase as the throttle plate
moves slowly from idle to WOT.
Check for spread terminals at the sensor and PCM
connections before replacing the TPS.
THROTTLE BODY MINIMUM AIR FLOW CHECK
PROCEDURE
(1) Warm engine in Park or Neutral until the cool-
ing fan has cycled on and off at least once.
(2) Ensure that all accessories are off.
(3) Shut off engine.
(4)3.0L Engine
(a) Hook-up the timing check device and tachom-
eter.(b) Disconnect the engine coolant temperature
sensor and set basic timing to 12É BTDC62É.
(c) Shut off engine. Reconnect coolant tempera-
ture sensor wire.
(5) Disconnect the PCV valve hose from the intake
manifold nipple (Fig. 101), (Fig. 102) or (Fig. 103).
(6) Cap the PCV valve nipple.
(7)3.3/3.8L Engines
(a) Install Air Metering Fitting 6457 (0.125 in.
orifice) to the intake manifold PCV nipple (Fig.
100).
(b) Disconnect the idle purge line from the throt-
tle body nipple.
(8)3.0/2.4L Engines
(a) Install Air Metering Fitting 6457 (0.125 in.
orifice) to the purge nipple on the throttle body.
(9)3.3/3.8L Engines
(a) Cap the 3/16 inch nipple.
(b) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
connector.
(10) Restart the engine. Allow engine to idle until
the cooling fan has cycled on and off at least one
180ÉF cycle.
(11) Using the DRB scan tool, access the Minimum
Airflow Idle Speed screen.
(12) The following will then occur:
²Idle air control motor will fully close.
²Idle spark advance will become fixed.
²DRB scan tool displays engine rpm.
(13) If idle rpm is within the range shown in the
Idle Specification chart, throttle body minimum air-
flow is set correctly.
IDLE SPECIFICATIONSÐ2.4L ENGINE
Odometer Reading Idle RPM
Below 1000 Miles.................500-875 RPM
Above 1000 Miles.................550±875 RPM
Fig. 99 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Fig. 100 Air Metering Fitting 6457
14 - 62 FUEL SYSTEMNS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1377 of 1938

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GENERAL INFORMATION
This section of the group will cover a general diag-
nosis of diesel engine fuel system components.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes:Refer to On-Board
Diagnostics in Group 25, Emission Control System
for a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) for cer-
tain fuel system components.
The PCM must be tested with the DRBIII scan
tool. The DRBIII should be the first step in any diag-
nosis of engine performance complaints. Refer to the
1997 GS 2.5L Diesel Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures manual for diagnosis and testing of the diesel
engine control system.
VISUAL INSPECTION
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected, or incor-
rectly routed wires and hoses should be made before
attempting to diagnose or service the diesel fuel
injection system. A visual check will help find these
conditions. It also saves unnecessary test and diag-
nostic time. A thorough visual inspection of the fuel
injection system includes the following checks:
(1) Be sure that the battery connections are tight
and not corroded.
(2) Be sure that the 68 way connector is fully
engaged with the PCM (Fig. 12).
(3) Verify that the electrical connections for the
Diesel PCM relay are clean and free of corrosion.
This relay is located in the PDC. For the location ofthe relay within the PDC, refer to label on PDC
cover.
(4) Verify that the electrical connections for the
fuel heater relay are clean and free of corrosion. This
relay is located in the PDC. For the location of the
relay within the PDC, refer to label on PDC cover.
(5) Be sure the electrical connectors at the ends of
the glow plugs (Fig. 13) are tight and free of corro-
sion.
(6) Be sure that the electrical connections at the
glow plug relay are tight and not corroded. The glow
plug relay is located in the engine compartment on
the left±inner fender (Fig. 14).
Fig. 12 PCM LocationÐTypical
Fig. 13 Glow Plug Connector
Fig. 14 Glow Plug Relay Location
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 9
Page 1378 of 1938

(7) Inspect the starter motor and starter solenoid
connections for tightness and corrosion.
(8) Verify that the electrical connector is firmly
connected to the fuel shutdown solenoid. Inspect the
connector for corrosion or damaged wires. The sole-
noid is mounted to the rear of the injection pump
(Fig. 15).
(9) Verify that the fuel heater electrical connector
is firmly attached to the filter bowl at the bottom of
the fuel filter/water separator. Inspect the connector
for corrosion or damaged wires.
(10) Verify that the electrical pigtail connector
(sensor connector) (Fig. 16) for the fuel injector sen-
sor is firmly connected to the engine wiring harness.
Inspect the connector for corrosion or damaged wires.
This sensor is used on the #1 cylinder injector only.
(11) Verify that the electrical pigtail connector
(sensor connector) (Fig. 17) for the fuel timing sole-
noid is firmly connected to the engine wiring har-
ness. Inspect the connector for corrosion or damaged
wires. The fuel timing solenoid is located on the bot-
tom of the fuel injection pump (Fig. 17).
(12) Inspect for exhaust system restrictions such
as pinched exhaust pipes or a collapsed or plugged
muffler.
(13) Verify that the harness connector is firmly
connected to the vehicle speed sensor (Fig. 18).
(14) Verify turbocharger wastegate operation.
Refer to Group 11, Exhaust System and Intake Man-
ifold Group for information.
(15) Verify that the harness connector is firmly
connected to the engine coolant temperature sensor.The sensor is located on the side of cylinder head
near the rear of fuel injection pump (Fig. 19).
(16) Check for air in the fuel system. Refer to the
Air Bleed Procedure.
(17) Inspect all fuel supply and return lines for
signs of leakage.
(18) Be sure that the ground connections are tight
and free of corrosion. Refer to Group 8, Wiring for
locations of ground connections.
(19) Inspect the air cleaner element (filter) for
restrictions.
(20) Be sure that the turbocharger output hose is
properly connected to the charge air cooler (inter-
cooler) inlet tube. Verify that the charge air cooler
output hose is properly connected to the cooler and
Fig. 15 Fuel Shutdown Solenoid Location
Fig. 16 Fuel Injector Sensor
Fig. 17 Fuel Timing Solenoid
14 - 10 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1379 of 1938

the intake manifold. Refer to Group 11, Exhaust Sys-
tem and Intake Manifold for information.
(21) Be sure that the vacuum hoses to the vacuum
pump are connected and not leaking. The pump is
located on the front of engine (internal) and is driven
from the crankshaft gear and chain (Fig. 20). Discon-
nect the hose and check for minimum vacuum from
the pump. Refer to Group 5, Brake System for spec-
ifications and procedures.(22) Be sure that the accessory drive belt is not
damaged or slipping.
(23) Verify there is a good connection at the engine
speed sensor. Refer to the Fuel Injection System in
this section for location of the engine speed sensor
location.
(24) Verify there is a good connection at the Mass
Air Flow Sensor, which is a part of the air intake
assembly.
AIR IN FUEL SYSTEM
Air will enter the fuel system whenever the fuel
supply lines, fuel filter/water separator, fuel filter
bowl, injection pump, high±pressure lines or injectors
are removed or disconnected. Air will also enter the
fuel system whenever the fuel tank has been run
empty.
Air trapped in the fuel system can result in hard
starting, a rough running engine, engine misfire, low
power, excessive smoke and fuel knock. After service
is performed, air must be bled from the system
before starting the engine.
Inspect the fuel system from the fuel tank to the
injectors for loose connections. Leaking fuel is an
indicator of loose connections or defective seals. Air
can also enter the fuel system between the fuel tank
and the injection pump. Inspect the fuel tank and
fuel lines for damage that might allow air into the
system.
For air bleeding, refer to Air Bleed Procedure in
the Service Procedures section of this group.
Fig. 18 Vehicle Speed SensorÐTypical
Fig. 19 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Location
Fig. 20 Vacuum Pump at Front of Engine
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1380 of 1938

FUEL HEATER RELAY TEST
The fuel heater relay is located in the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC). Refer to RelaysÐOperation/
Testing in Fuel Ingection System section of this
group for test procedures.
FUEL INJECTOR TEST
The fuel injection nozzels, located on the engine
cylinder head, spray fuel under high pressure into
the individual combustion chambers. Pressurized
fuel, delivered by the fuel injection pump, unseats a
spring-loaded needle valve inside the injector, and
the fuel is atomized as it escapes through the injector
opening into the engine's combustion chamber. If the
fuel injector does not operate properly, the engine
may misfire, or cause other driveability problems.
A leak in the injection pump±to±injector high±pres-
sure fuel line can cause many of the same symptoms
as a malfunctioning injector. Inspect for a leak in the
high±pressure lines before checking for a malfunc-
tioning fuel injector.
WARNING: THE INJECTION PUMP SUPPLIES HIGH-
±PRESSURE FUEL OF UP TO APPROXIMATELY
45,000 KPA (6526 PSI) TO EACH INDIVIDUAL INJEC-
TOR THROUGH THE HIGH±PRESSURE LINES. FUEL
UNDER THIS AMOUNT OF PRESSURE CAN PENE-
TRATE THE SKIN AND CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY.
WEAR SAFETY GOGGLES AND ADEQUATE PRO-
TECTIVE CLOTHING. AVOID CONTACT WITH FUEL
SPRAY WHEN BLEEDING HIGH±PRESSURE FUEL
LINES.
WARNING: DO NOT BLEED AIR FROM THE FUEL
SYSTEM OF A HOT ENGINE. DO NOT ALLOW FUEL
TO SPRAY ONTO THE EXHAUST MANIFOLD WHEN
BLEEDING AIR FROM THE FUEL SYSTEM.
To determine which fuel injector is malfunctioning,
run the engine and loosen the high±pressure fuel line
nut at the injector (Fig. 21). Listen for a change in
engine speed. If engine speed drops, the injector was
operating normally. If engine speed remains the
same, the injector may be malfunctioning. After test-
ing, tighten the line nut to 30 N´m (22 ft. lbs.)
torque. Test all injectors in the same manner one at
a time.
Once an injector has been found to be malfunction-
ing, remove it from the engine and test it. Refer to
the Removal/Installation section of this group for pro-
cedures.
After the injector has been removed, install it to a
bench±mount injector tester. Refer to operating
instructions supplied with tester for procedures.
The opening pressure or ªpopº pressure should be
15,000±15,800 kPa (2175±2291 psi). If the fuel injec-tor needle valve is opening (ªpoppingº) to early or to
late, replace the injector.
FUEL INJECTOR SENSOR TEST
The fuel injector sensor is used only on the fuel
injector for the number±1 cylinder (Fig. 22). It is not
used on the injectors for cylinders number 2, 3, or 4.
To test the sensor, unplug the sensor connector
(Fig. 22) from the engine wiring harness. Check
resistance across terminals. Resistance should be 110
ohms610 ohms at 20ÉC (68ÉF). Replace sensor if
specification cannot be met.
FUEL INJECTION PUMP TEST
The injection pump is not to be serviced or
the warranty may be voided. If the injection
pump requires service, the complete assembly
must be replaced.
Incorrect injection pump timing (mechanical or
electrical) can cause poor performance, excessive
smoke and emissions and poor fuel economy.
Fig. 21 Typical Inspection of Fuel Injector
Fig. 22 Fuel Injector Sensor Location
14 - 12 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1382 of 1938

START positions, fuel supply is allowed at the injec-
tion pump.
(1) Disconnect the electrical pigtail connector (test
connector) (Fig. 23) from the main engine wiring har-
ness. Do not disconnect wiring directly at solenoid.
(2) Connect the leads of a voltmeter between a
good ground and the disconnected engine wiring har-
ness.
(3) Turn the key to the ON position. Do not
attempt to start engine.
(4) 12V+ should be observed at wiring harness. If
not, refer to Group 8, Wiring for wiring schematics
and repair as necessary.
(5) T
urn the key to the START position. 12V+ should
be observed at wiring harness. If not, refer to Group 8,
Wiring for wiring schematics and repair as necessary.
The fault may be in the ignition (key) switch.
12V+ must be observed in both the ON and START
positions. If 12V+ was observed, proceed to the next
step.
(6) With key still in the ON position, connect and
disconnect the wiring harness to the solenoid. As this
is done, a clicking noise should be heard coming from
the solenoid. If not, replace solenoid. Refer to Fuel
Shutdown Solenoid in the Removal/Installation sec-
tion of this group for procedures.
HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINE LEAK TEST
High±pressure fuel line leaks can cause starting
problems and poor engine performance.
WARNING: DUE TO EXTREME FUEL PRESSURES
OF UP TO 45,000 KPA (6526 PSI), USE EXTREME
CAUTION WHEN INSPECTING FOR HIGH±PRESSURE
FUEL LEAKS. DO NOT GET YOUR HAND, OR ANY
PART OF YOUR BODY NEAR A SUSPECTED LEAK.
INSPECT FOR HIGH±PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS WITH
A SHEET OF CARDBOARD. HIGH FUEL INJECTION
PRESSURE CAN CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY IF
CONTACT IS MADE WITH THE SKIN.
Start the engine. Move the cardboard over the
high±pressure fuel lines and check for fuel spray onto
the cardboard (Fig. 24). If a high±pressure line con-
nection is leaking, bleed the system and tighten the
connection. Refer to the Air Bleed Procedure in this
group for procedures. Replace damaged, restricted or
leaking high±pressure fuel lines with the correct
replacement line.
CAUTION: The high±pressure fuel lines must be
clamped securely in place in the holders. The lines
cannot contact each other or other components. Do
not attempt to weld high±pressure fuel lines or to
repair lines that are damaged. Only use the recom-
mended lines when replacement of high±pressure
fuel line is necessary.
WASTEGATE (TURBOCHARGER)
Refer to Group 11, Exhaust System and Intake
Manifold for information.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
AIR BLEED PROCEDURES
AIR BLEEDING AT FUEL FILTER
A certain amount of air may become trapped in the
fuel system when fuel system components are ser-
viced or replaced. Bleed the system as needed after
fuel system service according to the following proce-
dures.
WARNING: DO NOT BLEED AIR FROM THE FUEL
SYSTEM OF A HOT ENGINE. DO NOT ALLOW FUEL
TO SPRAY ONTO THE EXHAUST MANIFOLD WHEN
BLEEDING AIR FROM THE FUEL SYSTEM.
Some air enters the fuel system when the fuel fil-
ter or injection pump supply line is changed. This
small amount of air is vented automatically from the
injection pump through the fuel drain manifold tubes
if the filter was changed according to instructions.
Ensure the bowl of the fuel filter/water separator is
full of fuel
It may be necessary to manually bleed the system
if:
²The bowl of the fuel filter/water separator is not
partially filled before installation of a new filter
²The injection pump is replaced
Fig. 24 Typical Test for Leaks with Cardboard
14 - 14 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1384 of 1938
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
CAUTION: Be careful not to damage or kink the
cable core wire (within the cable sheathing) while
servicing the accelerator pedal or throttle cable.
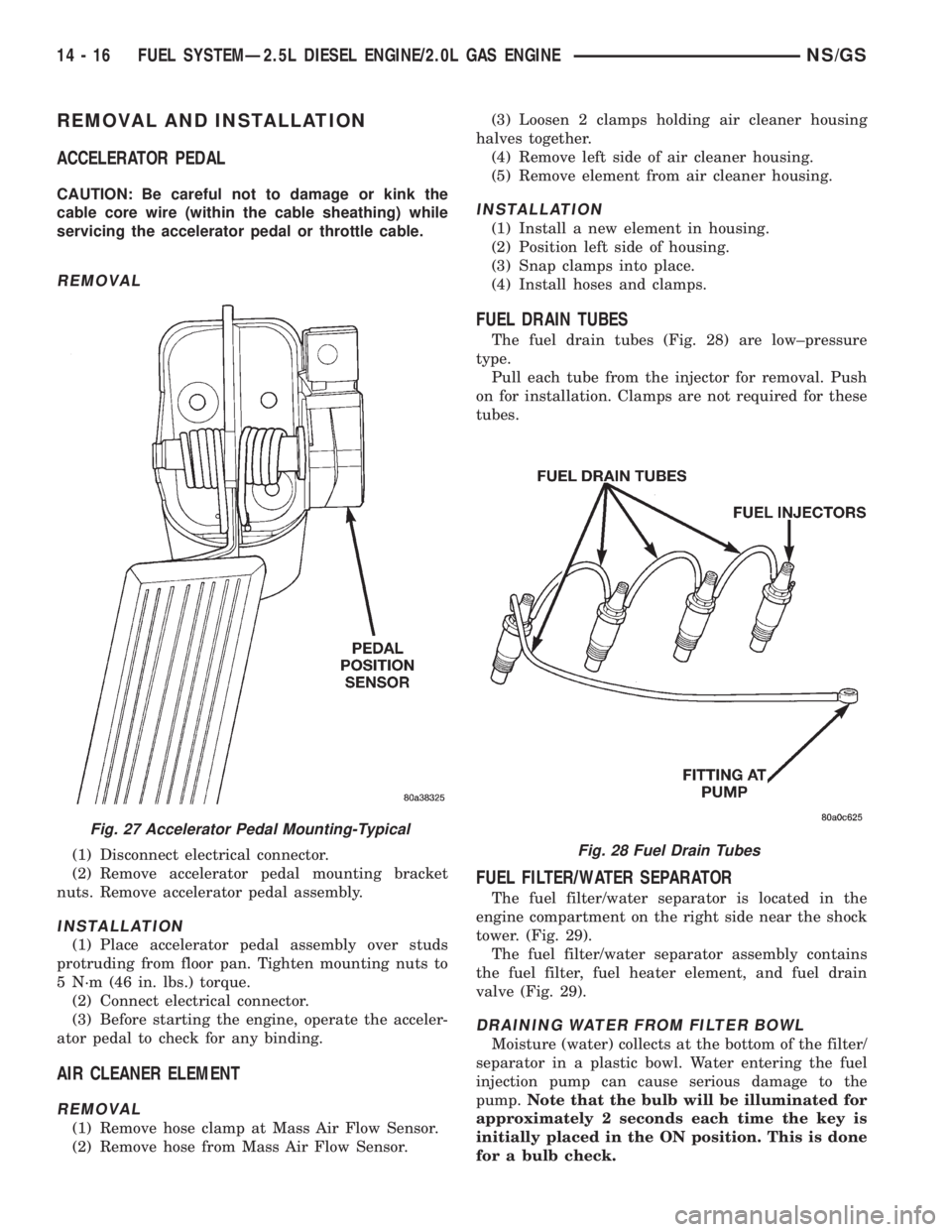
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector.
(2) Remove accelerator pedal mounting bracket
nuts. Remove accelerator pedal assembly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place accelerator pedal assembly over studs
protruding from floor pan. Tighten mounting nuts to
5 N´m (46 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect electrical connector.
(3) Before starting the engine, operate the acceler-
ator pedal to check for any binding.
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Remove hose clamp at Mass Air Flow Sensor.
(2) Remove hose from Mass Air Flow Sensor.(3) Loosen 2 clamps holding air cleaner housing
halves together.
(4) Remove left side of air cleaner housing.
(5) Remove element from air cleaner housing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install a new element in housing.
(2) Position left side of housing.
(3) Snap clamps into place.
(4) Install hoses and clamps.
FUEL DRAIN TUBES
The fuel drain tubes (Fig. 28) are low±pressure
type.
Pull each tube from the injector for removal. Push
on for installation. Clamps are not required for these
tubes.
FUEL FILTER/WATER SEPARATOR
The fuel filter/water separator is located in the
engine compartment on the right side near the shock
tower. (Fig. 29).
The fuel filter/water separator assembly contains
the fuel filter, fuel heater element, and fuel drain
valve (Fig. 29).
DRAINING WATER FROM FILTER BOWL
Moisture (water) collects at the bottom of the filter/
separator in a plastic bowl. Water entering the fuel
injection pump can cause serious damage to the
pump.Note that the bulb will be illuminated for
approximately 2 seconds each time the key is
initially placed in the ON position. This is done
for a bulb check.
Fig. 27 Accelerator Pedal Mounting-Typical
Fig. 28 Fuel Drain Tubes
14 - 16 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
Page 1389 of 1938
three injection pump mounting flanges while
gear is being removed.
(d) Install the drive bolt into the gear puller
(Fig. 43). Tighten the drive bolt to press (remove)
the drive gear from injection pump shaft while
driving injection pump rearward from timing gear
cover mounting studs.
(14) Remove pump from engine.Do not rotate
engine while gear puller is installed. Engine
damage will occur.
INSTALLATION/ADJUSTING PUMP TIMING
(1) Clean the mating surfaces of injection pump
and timing gear cover.
(2) Install a new injection pump±to±timing gear
cover gasket.(3) Remove the gear removing bolt (drive bolt)
from gear puller.CAUTION: Do not remove the
special gear puller or timing cover adapter
tools from timing cover at this time. Gear mis-
alignment will result.
(4) P
lace the key way on the pump shaft to the 11
o'clock position as viewed from the front of pump.
Install the pump into the rear of timing gear cover
while aligning key way on pump shaft into pump gear.
(5) Install and snug the 3 injection pump mount-
ing nuts. This is not the final tightening sequence.
(6) Remove the special gear puller and adapter
tools from timing gear cover.
(7) Install the injection pump drive gear nut and
washer. Tighten nut to 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.) torque.
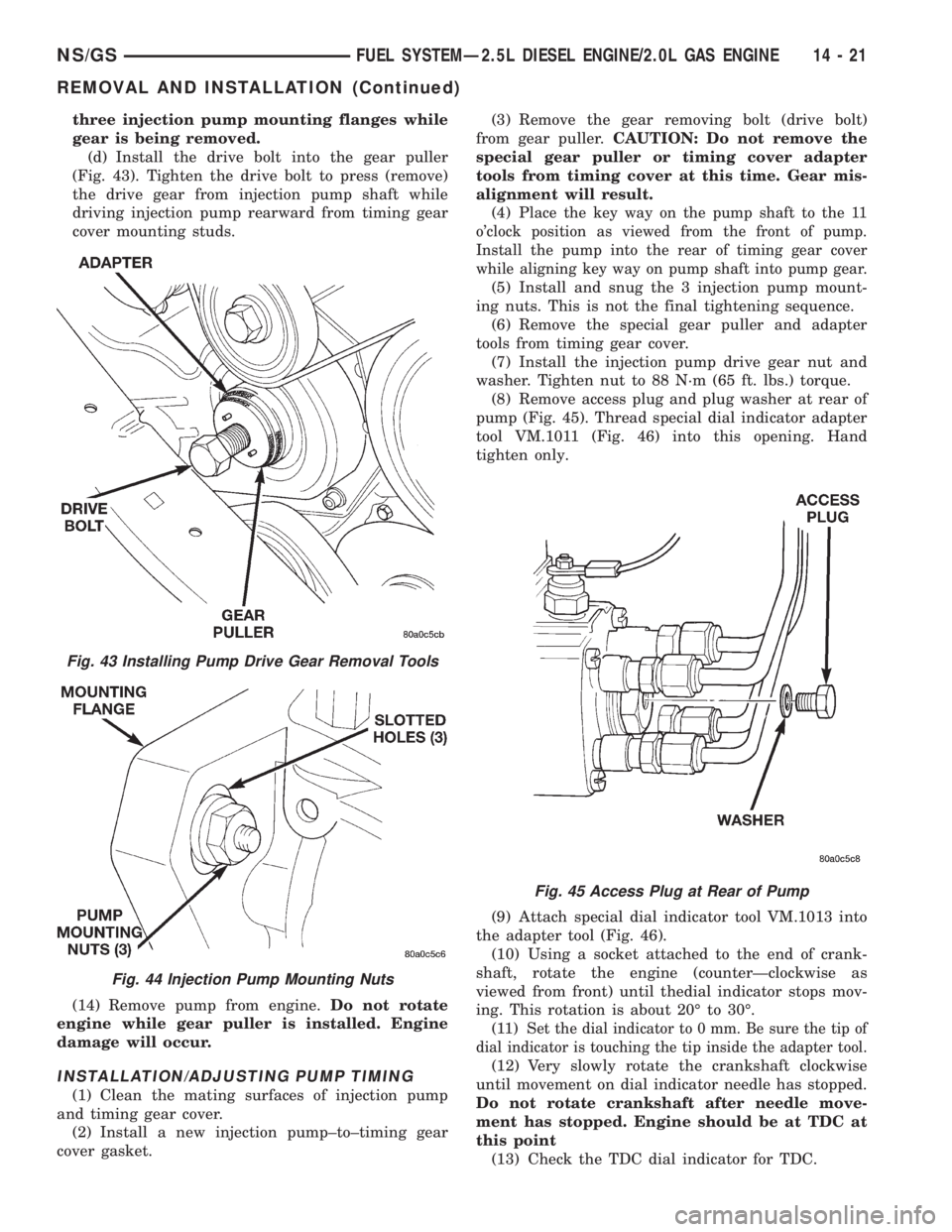
(8) Remove access plug and plug washer at rear of
pump (Fig. 45). Thread special dial indicator adapter
tool VM.1011 (Fig. 46) into this opening. Hand
tighten only.
(9) Attach special dial indicator tool VM.1013 into
the adapter tool (Fig. 46).
(10) Using a socket attached to the end of crank-
shaft, rotate the engine (counterÐclockwise as
viewed from front) until thedial indicator stops mov-
ing. This rotation is about 20É to 30É.
(11) S
et the dial indicator to 0 mm. Be sure the tip of
dial indicator is touching the tip inside the adapter tool.
(12) Very slowly rotate the crankshaft clockwise
until movement on dial indicator needle has stopped.
Do not rotate crankshaft after needle move-
ment has stopped. Engine should be at TDC at
this point
(13) Check the TDC dial indicator for TDC.
Fig. 43 Installing Pump Drive Gear Removal Tools
Fig. 44 Injection Pump Mounting Nuts
Fig. 45 Access Plug at Rear of Pump
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 21
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)