1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER clutch
[x] Cancel search: clutchPage 1412 of 1938

illuminated constantly, it usually indicates a problem
has been detected somewhere within the fuel system.
The DRBIII scan tool is the best method for commu-
nicating with the PCM to diagnose faults within the
system.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is mounted
in the center consule to a bracket located in front of
the Air Bag Module (Fig. 1).
The PCM is a pre±programmed, dual micro±proces-
sor digital computer. It will either directly operate or
partially regulate the:
²Speed Control
²Speed Control LED lamp
²Fuel Timing Solenoid
²Glow Plug Relay
²Glow Plugs
²EGR Solenoid
²Glow Plug Lamp
²Diesel PCM Relay
²Air Conditioning Operation
²Tachometer
²Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Solenoid
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet
changing operating conditions.
The PCM receives input signals from various
switches and sensors. Based on these inputs, the
PCM regulates various engine and vehicle operationsthrough different system components. These compo-
nents are referred to asPCM Outputs.The sensors
and switches that provide inputs to the PCM are con-
sideredPCM Inputs.
PCM Inputs are:
²Air Conditioning Selection
²Theft Alarm
²Clutch Switch
²Diesel PCM Relay
²ISO-Protocol
²Control Sleeve
²Fuel Temperature
²Boost Pressure Sensor
²Accelerator Pedal Sensor
²EGR
²A/C Pressure
²Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
²Low Idle Position Switch
²5 Volt Supply
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Sensor Return
²Glow Plug
²Engine Speed Sensor (rpm)
²Fuel Injector #1 Sensor
²Starter Signal
²Brake Switch
²Speed Control Switch Position
²Power Ground
²Signal Ground
²Ignition (key) Switch Sense
²Battery Voltage
²SCI Receive (DRB scan tool connection)
PCM Outputs:
After inputs are received by the PCM, certain sen-
sors, switches and components are controlled or reg-
ulated by the PCM. These are consideredPCM
Outputs.These outputs are for:
²A/C Clutch Relay (for A/C clutch operation)
²Speed Control LED
²Data Link Connectors (for DRB scan tool)
²Diesel PCM Relay
²Diesel PCM Sense
²Accelarator Pedal
²5 Volts Supply
²Glow Plug Relay
²Fan Relay
²Fuel Quantity
²Fuel Timing Solenoid
²Fuel Shut-Off Solenoid
²Engine Speed Sensor
²Glow Plug Lamp (malfunction indicator lamp)
²Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Solenoid
²Glow Plug Relay
²Tachometer
²SCI transmit (DRB scan tool connection)
Fig. 1 PCM Location
14 - 44 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1415 of 1938
AIR CONDITIONING (A/C) CONTROLSÐPCM
INPUTS
The A/C control system information applies to fac-
tory installed air conditioning units.
A/C REQUEST SIGNAL:When either the A/C or
Defrost mode has been selected and the A/C low and
high±pressure switches are closed, an input signal is
sent to the powertrain control module (PCM). The
PCM uses this input to cycle the A/C compressor
through the A/C relay.
If the A/C low or high±pressure switch opens, the
PCM will not receive an A/C request signal. The
PCM will then remove the ground from the A/C relay.
This will deactivate the A/C compressor clutch. Also,
if the engine coolant reaches a temperature outside
normal of its normal range, or it overheats, the PCM
will deactivate the A/C clutch.
BRAKE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
When the brake light switch is activated, the PCM
receives an input indicating that the brakes are
being applied. After receiving this input, the PCM is
used to control the speed control system. There is a
Primary and a Secondary brake switch. The Second-
ary brake switch is closed until the brake pedal is
pressed.
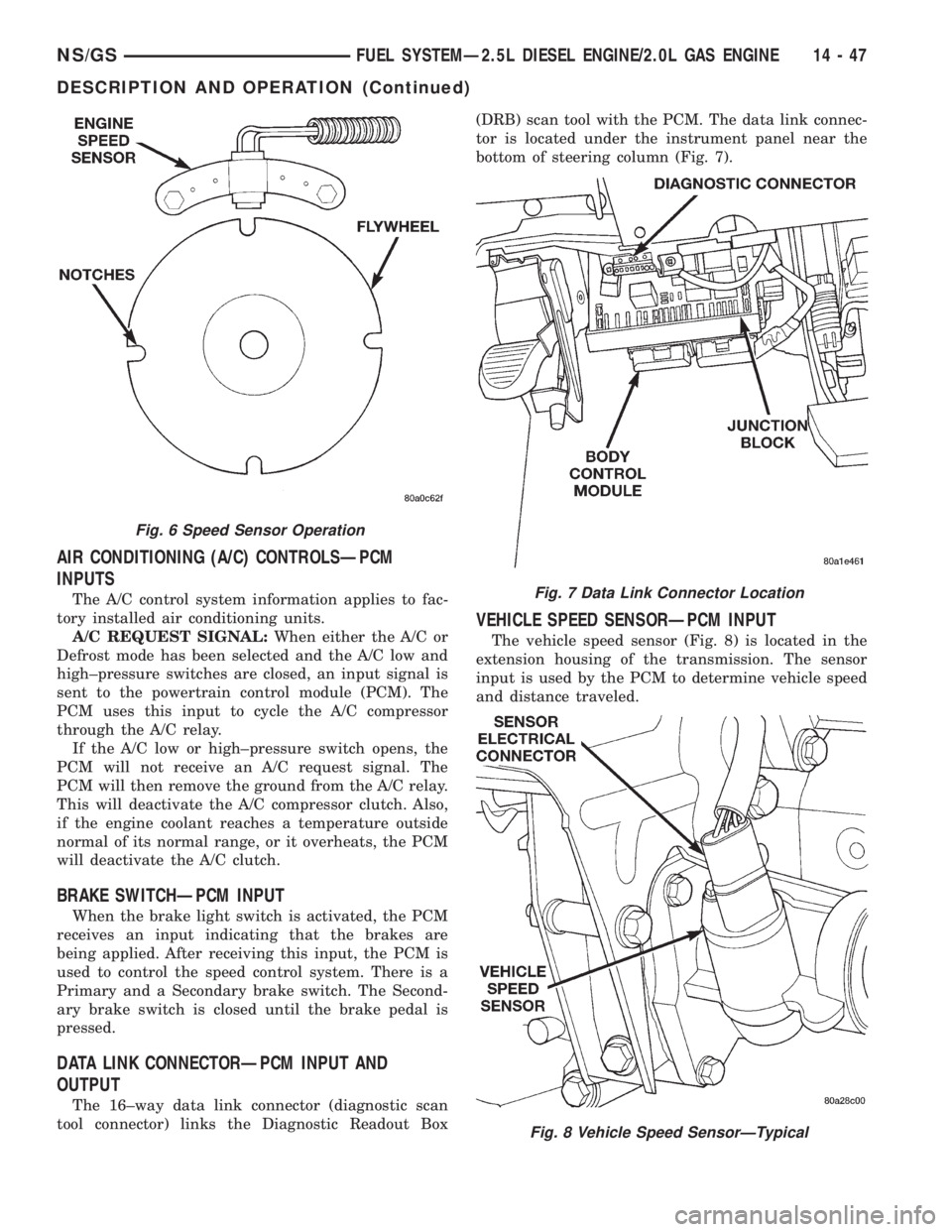
DATA LINK CONNECTORÐPCM INPUT AND
OUTPUT
The 16±way data link connector (diagnostic scan
tool connector) links the Diagnostic Readout Box(DRB) scan tool with the PCM. The data link connec-
tor is located under the instrument panel near the
bottom of steering column (Fig. 7).
VEHICLE SPEED SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The vehicle speed sensor (Fig. 8) is located in the
extension housing of the transmission. The sensor
input is used by the PCM to determine vehicle speed
and distance traveled.
Fig. 6 Speed Sensor Operation
Fig. 7 Data Link Connector Location
Fig. 8 Vehicle Speed SensorÐTypical
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 47
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1416 of 1938

The speed sensor generates 8 pulses per sensor
revolution. These signals, in conjunction with a
closed throttle signal from the throttle position sen-
sor, indicate a closed throttle deceleration to the
PCM. When the vehicle is stopped at idle, a closed
throttle signal is received by the PCM (but a speed
sensor signal is not received).
In addition to determining distance and vehicle
speed, the output from the sensor is used to control
speed control operation.
SPEED CONTROLÐPCM INPUTS
The speed control system provides five separate
inputs to the PCM; On/Off, Set, Resume/Accel, Cancel,
and Decel.. The On/Off input informs the PCM that
the speed control system has been activated. The Set
input informs the PCM that a fixed vehicle speed has
been selected. The Resume input indicates to the PCM
that the previous fixed speed is requested.
Speed control operation will start at 50 km/h±142
km/h (35±85 mph). The upper range of operation is
not restricted by vehicle speed. Inputs that affect
speed control operation are vehicle speed sensor and
throttle position sensor.
Refer to Group 8H for further speed control infor-
mation.
DIESEL PCM RELAYÐPCM INPUT
A 12 volt signal at this input indicates to the PCM
that the Diesel relay has been activated. The Diesel
relay is located in the PDC. The PDC is located next
to the battery in the engine compartment. For the
location of the relay within the PDC, refer to label on
PDC cover.
This input is used only to sense that the Diesel
relay is energized. If the PCM does not see 12 volts +
at this input when the Diesel relay should be acti-
vated, it will set a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).
FIVE VOLT POWERÐPCM OUTPUT
This circuit supplies approximately 5 volts to
power the Accelerator Pedal Postion Sensor, Mass Air
Flow Sensor, and A/C Pressure Sensor.
ENGINE COOLANT GAUGEÐPCM OUTPUT
Refer to the Instrument Panel and Gauges group
for additional information.
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE GAUGEÐPCM OUTPUT
Refer to the Instrument Panel and Gauges group
for additional information.
GLOW PLUG LAMPÐPCM OUTPUT
The Glow Plug lamp (malfunction indicator lamp)
illuminates on the message center each time the igni-
tion (key) switch is turned on. It will stay on for
about two seconds as a bulb test.If the PCM receives an incorrect signal, or no sig-
nal from certain sensors or components, the lamp
BLINKS. This is a warning that the PCM has
recorded a system or sensor malfunction. It signals
an immediate need for service. There are only 5
HARD faults that can turn on this lamp to make it
blink.
SPEED CONTROLÐPCM OUTPUTS
These two circuits control the fuel quantity actua-
tor to regulate vehicle speed. Refer to Group 8H for
Speed Control information.
AIR CONDITIONING RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
This circuit controls a ground signal for operation
of the A/C clutch relay. Also refer to Air Conditioning
(A/C) ControlsÐPCM Input for additional informa-
tion.
The A/C relay is located in the Power Distribution
Center (PDC). The PDC is located next to the battery
in the engine compartment. For the location of the
relay within the PDC, refer to label on PDC cover.
FUEL TIMING SOLENOIDÐPCM OUTPUT
The fuel timing solenoid is located on the bottom of
the fuel injection pump (Fig. 10).
This 12+ volt, pulse width modulated (duty±cycle)
output controls the amount of fuel timing (advance)
in the fuel injection pump. The higher the duty-
Fig. 9 Glow Plug Lamp Symbol
Fig. 10 Fuel Timing Solenoid
14 - 48 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1421 of 1938

²When the PCM energizes the Diesel PCM and
other relays, terminal 87 connects to terminal 30.
This is the On position. Terminal 87 supplies voltage
to the rest of the circuit.
TESTING
The following procedure applies to the Diesel PCM
and other relays.
(1) Remove relay from connector before testing.
(2) With the relay removed from the vehicle, use
an ohmmeter to check the resistance between termi-
nals 85 and 86. The resistance should be between 75
65 ohms.
(3) Connect the ohmmeter between terminals 30
and 87A. The ohmmeter should show continuity
between terminals 30 and 87A.
(4) Connect the ohmmeter between terminals 87
and 30. The ohmmeter should not show continuity at
this time.
(5) Connect one end of a jumper wire (16 gauge or
smaller) to relay terminal 85. Connect the other end
of the jumper wire to the ground side of a 12 volt
power source.
(6) Connect one end of another jumper wire (16
gauge or smaller) to the power side of the 12 volt
power source.Do not attach the other end of the
jumper wire to the relay at this time.
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW OHMMETER TO CON-
TACT TERMINALS 85 OR 86 DURING THIS TEST.
(7) Attach the other end of the jumper wire to
relay terminal 86. This activates the relay. The ohm-meter should now show continuity between relay ter-
minals 87 and 30. The ohmmeter should not show
continuity between relay terminals 87A and 30.
(8) Disconnect jumper wires.
(9) Replace the relay if it did not pass the continu-
ity and resistance tests. If the relay passed the tests,
it operates properly. Check the remainder of the Die-
sel PCM and other relay circuits. Refer to group 8W,
Wiring Diagrams.
BOOST PRESSURE SENSOR
If the boost pressure sensor fails, the PCM records
a DTC into memory and continues to operate the
engine in one of the three ªlimp-inº modes. When the
PCM is operating in this mode, a loss of power will
be present, as if the turbocharger was not operating.
The best method for diagnosing faults with the boost
pressure sensor is with the DRB III scan tool.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes:Refer to On-Board
Diagnostics in Group 25, Emission Control System
for a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) for cer-
tain fuel system components.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR TEST
To perform a test of the sensor and its related cir-
cuitry, refer to DRB scan tool.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes:Refer to On-Board
Diagnostics in Group 25, Emission Control System
for a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) for cer-
tain fuel system components.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's),
refer to Group 25, Emission Control System for infor-
mation. See On-Board Diagnostics.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
DIESEL PCM RELAY
The Diesel PCM relay is located in the PDC. For
the location of the relay within the PDC, refer to
label on PDC cover.
A/C CLUTCH RELAY
The A/C clutch relay is located in the PDC. For the
location of the relay within the PDC, refer to label on
PDC cover.
ENGINE SPEED SENSOR
The engine speed sensor is mounted to the trans-
mission bellhousing at the rear of the engine block
(Fig. 18).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the harness (on the sensor) from
the main electrical harness.
Fig. 17 Diesel PCM and Other Relay Terminals
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 53
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1475 of 1938

TRANSAXLE AND POWER TRANSFER UNIT
CONTENTS
page page
31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE.............. 1
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE............. 71POWER TRANSFER UNIT................. 165
31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
31TH TRANSAXLE........................ 2
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION.............. 2
SELECTION OF LUBRICANT................ 3
SPECIAL ADDITIVES...................... 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
CLUTCHES, BAND SERVOS, AND
ACCUMULATOR
...................... 3
FLOW CONTROL VALVES.................. 3
GEARSHIFT AND PARKING LOCK CONTROLS . . 4
GOVERNOR............................. 4
HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM............. 3
PRESSURE REGULATING VALVES........... 3
PRESSURE SUPPLY SYSTEM............... 3
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID
WIRING CONNECTOR................... 4
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH............. 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CLUTCH AND SERVO AIR PRESSURE TESTS . 15
FLUID LEAKAGE-TRANSAXLE TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING AREA............ 15
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TESTS............ 13
ROAD TEST............................. 4
THREE SPEED TRANSAXLE DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTS............................... 4
SERVICE PROCEDURES
ALUMINUM THREAD REPAIR.............. 18
FLUID AND FILTER CHANGE............... 16
FLUID DRAIN AND REFILL................. 18
FLUSHING COOLERS AND TUBES.......... 18
OIL PUMP VOLUME CHECK............... 19
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
FRONT PUMP OIL SEAL.................. 21
PARK/NEUTRAL STARTING AND BACK-UP
LAMP SWITCH........................ 19
TRANSAXLE AND TORQUE CONVERTER
REMOVAL............................ 20
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR PINION GEAR..... 19DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
ACCUMULATOR-RECONDITION............ 36
DIFFERENTIAL REPAIR................... 46
FRONT CLUTCH-RECONDITION............ 32
FRONT PLANETARY & ANNULUS GEAR-
RECONDITION........................ 35
KICKDOWN SERVO (CONTROLLED LOAD)-
RECONDITION........................ 37
LOW/REVERSE (REAR)
SERVO-RECONDITION.................. 36
OIL PUMP-RECONDITION................. 31
OUTPUT SHAFT REPAIR.................. 43
PARKING PAWL......................... 42
REAR CLUTCH-RECONDITION............. 33
TRANSAXLE........................... 21
TRANSFER SHAFT REPAIR................ 38
VALVE BODY RECONDITION............... 27
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
VALVE BODY........................... 50
ADJUSTMENTS
BAND ADJUSTMENT..................... 51
BEARING ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES...... 52
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING................. 53
GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT.......... 51
HYDRAULIC CONTROL PRESSURE
ADJUSTMENTS....................... 52
OUTPUT SHAFT BEARING................ 52
THROTTLE PRESSURE LINKAGE
ADJUSTMENT......................... 51
TRANSFER SHAFT BEARING.............. 54
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
31TH TRANSAXLE HYDRAULIC SCHEMATIC . . 56
SPECIFICATIONS
31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE............. 64
31TH TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS........... 65
SPECIAL TOOLS
31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE............. 66
NSTRANSAXLE AND POWER TRANSFER UNIT 21 - 1
Page 1476 of 1938

GENERAL INFORMATION
31TH TRANSAXLE
NOTE: Safety goggles should be worn at all times
when working on these transaxles.
This transaxle combines torque converter, three
speed transmission, final drive gearing, and differen-
tial into a front wheel drive system. The identifica-
tion markings and usage of the transaxle are charted
in Diagnosis and Tests.
NOTE: Transaxle operation requirements are differ-
ent for each vehicle and engine combination. Some
internal parts will be different to provide for this.
Therefore, when replacing parts, refer to the seven
digit part number stamped on rear of the transaxle
oil pan flange.
Within this transaxle, there are three primary
areas:
(1) Main center line plus valve body.
(2) Transfer shaft center line (includes governor
and parking sprag).
(3) Differential center line.
(4) Center distances between the main rotating
parts in these three areas are held precise to main-
tain a low noise level.
(5) The torque converter, transaxle area, and dif-
ferential are housed in an integral aluminum die
casting.The differential oil sump is common
with the transaxle sump. Separate filling of the
differential is NOT necessary.
(6) The torque converter is attached to the crank-
shaft through a flexible driving plate. Cooling of the
converter is accomplished by circulating the tran-
saxle fluid through a remote cooler. There are two
types of coolers used. An oil-to-water type cooler
located in the radiator side tank and/or an oil-to air
heat exchanger. The torque converter assembly is a
sealed unit that cannot be disassembled.
(7) The transaxle fluid is filtered by an internal fil-
ter attached to the lower side of the valve body
assembly.
(8) Engine torque is transmitted to the torque con-
verter then, through the input shaft to multiple-disc
clutches in the transaxle. The power flow depends on
the application of the clutches and bands. Refer to
Elements in Use Chart in Diagnosis and Tests sec-
tion.
(9) The transaxle consists of:
²Two multiple-disc clutches
²An overrunning clutch
²Two servos
²A hydraulic accumulator
²Two bands²Two planetary gear sets
This provides three forward ratios and a reverse
ratio. The common sun gear of the planetary gear
sets is connected to the front clutch by a driving
shell. The drive shell is splined to the sun gear and
front clutch retainer. The hydraulic system consists
of an oil pump, and a single valve body which con-
tains all of the valves except the governor valves.
The transaxle sump and differential sump are both
vented through the dipstick. Output torque from the
main center line is delivered through helical gears to
the transfer shaft. This gear set is a factor of the
final drive (axle) ratio. The shaft also carries the gov-
ernor and parking sprag. An integral helical gear on
the transfer shaft drives the differential ring gear.
The final drive gearing is completed with one of two
gear ratios of 2.98 or 3.19 depending on model and
application.
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
NOTE: The transmission and differential sump have
a common oil sump with a communicating opening
between the two.
The torque converter fills in both the P Park and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in P Park
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate.The
engine should be running at idle speed for at
least one minute, with the vehicle on level
ground. This will assure complete oil level sta-
bilization between differential and transmis-
sion.The fluid should be at normal operating
temperature (approximately 82 C. or 180 F.). The
fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT region (cross-
hatched area) on the dipstick.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, the air bubbles can cause overheat-
ing, fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can inter-
fere with normal valve, clutch, and servo operation.
Foaming can also result in fluid escaping from the
transaxle dipstick where it may be mistaken for a
leak.
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle overhaul is needed.
Be sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick closely.
21 - 2 TRANSAXLE AND POWER TRANSFER UNITNS
Page 1477 of 1938

If there is any doubt about its condition, drain out a
sample for a double check.
SELECTION OF LUBRICANT
It is important that the proper lubricant be used in
these transmissions. Mopar ATF PLUS 3 (Automatic
Transmission Fluid- type 7176) should be used to aid
in ensuring optimum transmission performance. It is
important that the transmission fluid be maintained
at the prescribed level using the recommended fluids.
SPECIAL ADDITIVES
Chrysler Corporation does not recommend the
addition of any fluids to the transmission, other than
fluid listed above. An exception to this policy is the
use of special dyes to aid in detecting fluid leaks. The
use of transmission sealers should be avoided, since
they may adversely affect seals.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH
A torque converter clutch is standard on all vehi-
cles. The torque converter clutch is activated only in
direct drive and is controlled by the engine electron-
ics. A solenoid on the valve body, is powered by the
powertrain control module to activate torque con-
verter clutch.
HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The hydraulic control system makes the transaxle
fully automatic, and has four important functions to
perform. The components of any automatic control
system may be grouped into the following basic
groups:
The pressure supply system, the pressure regulat-
ing valves, the flow control valves, the clutches, and
band servos.
Taking each of these basic groups or systems in
turn, the control system may be described as follows:
PRESSURE SUPPLY SYSTEM
The pressure supply system consists of an oil pump
driven by the engine through the torque converter.
The single pump furnishes pressure for all the
hydraulic and lubrication requirements.Oil pump
housing assemblies are available with prese-
lected pump gears.
PRESSURE REGULATING VALVES
The pressure regulating valve controls line pres-
sure dependent on throttle opening. The governor
valve transmits regulated pressure to the valve body
(in conjunction with vehicle speed) to control upshift
and downshift.The throttle valve transmits regulated pressure to
the transaxle (dependent on throttle position) to con-
trol upshift and downshift.
FLOW CONTROL VALVES
The manual valve provides the different transaxle
drive ranges as selected by the vehicle operator.
The 1-2 shift valve automatically shifts the tran-
saxle from first to second or from second to first,
depending on the vehicle operation.
The 2-3 shift valve automatically shifts the tran-
saxle from second to third or from third to second
depending on the vehicle operation.
The kickdown valve makes possible a forced down-
shift from third to second, second to first, or third to
first (depending on vehicle speed). This can be done
by depressing the accelerator pedal past the detent
feel near wide open throttle.
The shuttle valve has two separate functions and
performs each independently of the other. The first is
providing fast release of the kickdown band, and
smooth front clutch engagement when a lift-foot
upshift from second to third is made. The second
function is to regulate the application of the kick-
down servo and band when making third to second
kickdown.
The by-pass valve provides for smooth application
of the kickdown band on 1-2 upshifts.
The torque converter clutch solenoid allows for the
electronic control of the torque converter clutch. It
also disengages the torque converter at closed throt-
tle. This is done during engine warm-up, and part-
throttle acceleration.
The switch valve directs oil to apply the torque
converter clutch in one position. The switch valve
releases the torque converter clutch in the other posi-
tion.
CLUTCHES, BAND SERVOS, AND ACCUMULATOR
The front and rear clutch pistons, and both servo
pistons are moved hydraulically to engage the
clutches and apply the bands. The pistons are
released by spring tension when hydraulic pressure
is released. On the 2-3 upshift, the kickdown servo
piston is released by spring tension and hydraulic
pressure.
The accumulator controls the hydraulic pressure
on the apply side of the kickdown servo during the
1-2 upshift; thereby, cushioning the kickdown band
application at any throttle position.
NSTRANSAXLE AND POWER TRANSFER UNIT 21 - 3
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1478 of 1938

GEARSHIFT AND PARKING LOCK CONTROLS
The transaxle is controlled by a lever type gear-
shift incorporated within the steering column. The
control has six selector lever positions: P (park), R
(reverse), N (neutral), and D (drive), 2 (second), and
1 (first). The parking lock is applied by moving the
selector lever past a gate to the P position.Do not
apply the parking lock until the vehicle has
stopped; otherwise, a severe ratchet noise will
occur.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID WIRING
CONNECTOR
If wiring connector is unplugged, the torque con-
verter will not engage (Fig. 1) .
GOVERNOR
The governor may be serviced by removing the
transaxle oil pan and valve body assembly. The gov-
ernor may be unbolted from the governor support
and removed from the transaxle for reconditioning or
replacement.
When cleaning or assembling the governor, make
sure the governor valves move freely in the bores of
the governor body.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
THREE SPEED TRANSAXLE DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTS
Automatic transaxle malfunctions may be caused
by four general conditions:
(1) Poor engine performance
(2) Improper adjustments
(3) Hydraulic malfunctions
(4) Mechanical malfunctionsDiagnosis of these problems should always begin
by checking the easily accessible variables; fluid level
and condition, gearshift cable adjustment, and throt-
tle pressure cable adjustment. Then perform a road
test to determine if the problem has been corrected
or that more diagnosis is necessary. If the problem
exists after the preliminary tests and corrections are
completed, hydraulic pressure tests should be per-
formed
31TH HYDRAULIC TROUBLE CODE CHARTS
The following charts should be used to help diag-
nose hydraulic or mechanical faults in the transaxle .
ROAD TEST
Prior to performing a road test, check the fluid
level, and control cable adjustments.
During the road test, the transaxle should be oper-
ated in each position to check for slipping and any
variation in shifting.
If vehicle operates at high speeds, but has poor
acceleration, the converter's overrunning clutch may
be slipping. If acceleration is normal, but high throt-
tle opening is needed for high speeds, the stator
clutch may have seized.
Observe closely for slipping or engine speed flare-
up. Slipping or flare-up in any gear usually indicates
clutch, band, or overrunning clutch problems. If the
condition is far advanced, an overhaul will probably
be necessary to restore normal operation.
In most cases, the clutch or band that is slipping
can be determined by noting the transaxle operation
in all selector positions. Then comparing which inter-
nal units are applied in those positions. The Ele-
ments in Use Chart provides a basis for road test
analysis .
The rear clutch is applied in both the D first gear
and 1 first gear positions. Also the overrunning
clutch is applied in D first gear and the low/reverse
band is applied in 1 first gear position. If the tran-
saxle slips in D range first gear, but does not slip in
1 first gear, the overrunning clutch is slipping. Simi-
larly, if the transaxle slips in any two forward gears,
the rear clutch is slipping.
Using the same procedure, the rear clutch and
front clutch are applied in D third gear. If the tran-
saxle slips in third gear, either the front clutch or the
rear clutch is slipping. By selecting another gear
which does not use one of those units, the unit which
is slipping can be determined. If the transaxle also
slips in reverse, the front clutch is slipping. If the
transaxle does not slip in reverse, the rear clutch is
slipping.
The process of eliminating can be used to detect
any unit which slips and to confirm proper operation
of good units. Road testing can usually diagnose slip-
ping units. Although the actual cause of the problem
Fig. 1 Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Wiring
Connector
21 - 4 TRANSAXLE AND POWER TRANSFER UNITNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)