1995 JEEP CHEROKEE steering
[x] Cancel search: steeringPage 60 of 2198

(17) Tighten the track bar nut at the axle bracket
to 100 Nzm (74 ft. lbs.) torque.
(18) Check the front wheel alignment.
PINION SEAL REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Mark the propeller shaft yoke and pinion yoke
for installation alignment reference.
(4) Remove the propeller shaft from the yoke.
(5) Remove the pinion yoke nut and washer. Use
Remover C-452 and Wrench C-3281 to remove the
pinion yoke (Fig. 2).
(6) Mark the positions of the yoke and pinion gear
for installation alignment reference.
(7) Use Remover 7794A and slide hammer to re-
move the pinion gear seal (Fig. 3).
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light coating of gear lubricant on the
lip of pinion seal. Install seal with Installer D-163
and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 4).
(2) Align the reference marks and install yoke on
the pinion gear with Installer W-162-D.
(3) Install a new pinion nut on pinion shaft.Tighten
the nut to 217-352 Nzm (160-260 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 5).
(4) Align the installation reference marks and at-
tach the propeller shaft to the yoke.
(5) Add API grade GL 5 hypoid gear lubricant to
the differential housing, if necessary.
(6) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
(7) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
HUB BEARING AND AXLE SHAFT
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove the brake components from the axle,
refer to Group 5, Brakes.
(4) Remove the cotter pin, nut retainer and axle
hub nut (Fig. 6).
(5) Remove the hub to knuckle bolts (Fig. 6). Remove
the hub from the steering knuckle and axle shaft.
(6) Remove the disc brake rotor shield from the
bearing carrier (Fig. 6).
(7) On disconnect axles, remove vacuum shift mo-
tor housing. Refer to Vacuum Disconnect Axle in this
section.
(8) Remove the axle shaft from the housing.Avoid
damaging the axle shaft oil seals in the differen-
tial.
Fig. 2 Pinion Yoke Removal
Fig. 3 Seal Removal
Fig. 4 Pinion Seal Installation
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 25
Page 67 of 2198
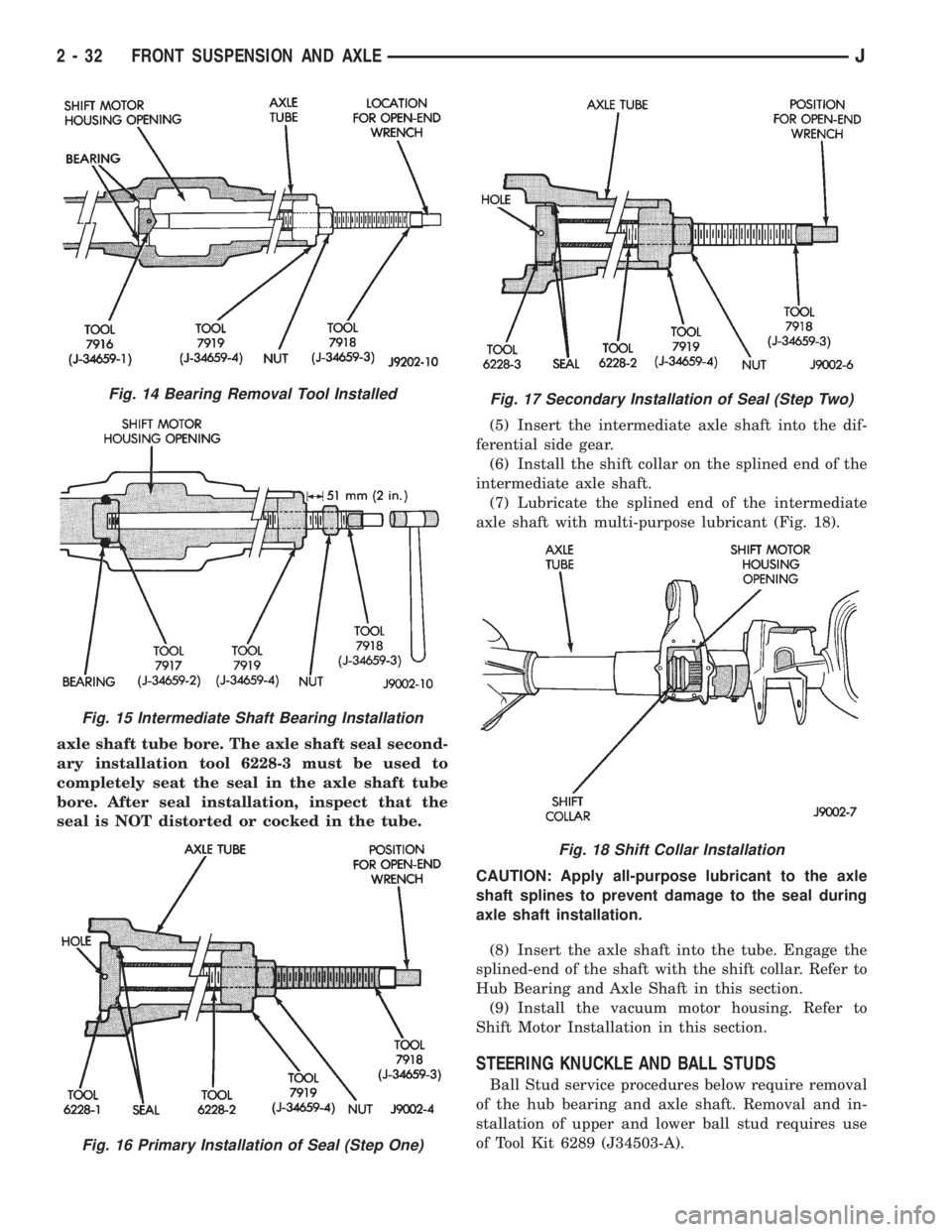
axle shaft tube bore. The axle shaft seal second-
ary installation tool 6228-3 must be used to
completely seat the seal in the axle shaft tube
bore. After seal installation, inspect that the
seal is NOT distorted or cocked in the tube.(5) Insert the intermediate axle shaft into the dif-
ferential side gear.
(6) Install the shift collar on the splined end of the
intermediate axle shaft.
(7) Lubricate the splined end of the intermediate
axle shaft with multi-purpose lubricant (Fig. 18).
CAUTION: Apply all-purpose lubricant to the axle
shaft splines to prevent damage to the seal during
axle shaft installation.
(8) Insert the axle shaft into the tube. Engage the
splined-end of the shaft with the shift collar. Refer to
Hub Bearing and Axle Shaft in this section.
(9) Install the vacuum motor housing. Refer to
Shift Motor Installation in this section.
STEERING KNUCKLE AND BALL STUDS
Ball Stud service procedures below require removal
of the hub bearing and axle shaft. Removal and in-
stallation of upper and lower ball stud requires use
of Tool Kit 6289 (J34503-A).
Fig. 14 Bearing Removal Tool Installed
Fig. 15 Intermediate Shaft Bearing Installation
Fig. 16 Primary Installation of Seal (Step One)
Fig. 17 Secondary Installation of Seal (Step Two)
Fig. 18 Shift Collar Installation
2 - 32 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 68 of 2198

The lower ball stud has two different designs. For
this reason installer 6752 will also be needed. Check
installers for proper fit.
KNUCKLE REMOVAL
(1) Remove hub bearing and axle shaft refer to the
Removal procedure.
(2) Disconnect the tie-rod or drag link end from the
steering knuckle arm. Remove the ABS sensor wire
and bracket from knuckle.
(3) Remove the cotter pins from the upper and
lower ball studs. Remove the upper and lower ball
stud nuts.
(4) Strike the steering knuckle with a brass ham-
mer to loosen. Remove knuckle from axle tube yokes
(Fig. 19).
UPPER BALL STUD REPLACEMENT
(1) Position tools as shown to remove and install
ball stud (Fig. 20).
LOWER BALL STUD REPLACEMENT
(1) Position tools as shown to remove and install
ball stud (Fig.21). Because there are two different de-
signs for the lower ball studs try both installers for
proper fit.
KNUCKLE INSTALLATION
(1) Position the steering knuckle on the ball studs.(2) Install and tighten the bottom retaining nut to
109 Nzm (80 ft. lbs.) torque. Install new cotter pin.
(3) Install and tighten the top retaining nut to 101
Nzm (75 ft. lbs.) torque. Install new cotter pin.
Fig. 19 Steering Knuckle Removal/Installation
Fig. 20 Upper Ball Stud Remove/Install
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 33
Page 69 of 2198

(4) Install the Hub Bearing and Axle Shaft accord-
ing to the installation procedure.
(5) Reconnect the tie-rod or drag link end onto the
steering knuckle arm. Install the ABS sensor wire
and bracket to the knuckle, refer to Group 5 Brakes.
AXLE BUSHING REPLACEMENT
Refer to Axle Bushing Replacement in the Front
Suspension section.
DIFFERENTIAL REMOVAL
To service the differential the axle assembly and
axle shafts must be removed. Refer to the removal
procedures in this Group.
(1) Note the installation reference letters stamped
on the bearing caps and housing machined sealing
surface (Fig. 22).
(2) Remove the differential bearing caps.
(3) Position Spreader W-129-B with the tool dowel
pins seated in the locating holes (Fig. 23). Install the
holddown clamps and tighten the tool turnbuckle fin-
ger-tight.
(4) Install a pilot stud at the left side of the differ-
ential housing. Attach Dial Indicator to housing pilot
stud. Load the indicator plunger against the opposite
side of the housing (Fig. 23) and zero the indicator.CAUTION:Do not spread over 0.38 mm (0.015 in). If
the housing is over-separated, it could be distorted
or damaged.
(5) Separate the housing enough to remove the
case from the housing. Measure the distance with the
dial indicator (Fig. 23).
(6) Remove the dial indicator.
(7) Pry the differential case loose from the housing.
To prevent damage, pivot on housing with the end of
the pry bar against spreader (Fig. 24).
Fig. 21 Lower Ball Stud Remove/Install
Fig. 22 Bearing Cap Identification
2 - 34 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 140 of 2198

ABS BRAKE DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
ABS Diagnostic Connector................... 3
ABS Warning Light Display................... 3
Antilock ECU and Hcu Diagnosis............... 3
DRB Scan Tool............................ 3General Information........................ 3
Normal Operating Conditions.................. 3
Wheel/Tire Size and Input Signals.............. 3
GENERAL INFORMATION
The DRB scan tool is required for ABS diagnosis.
The scan tool is used to identify ABS circuit faults.
Once a faulty circuit has been identified, refer to
the appropriate chassis/body diagnostic manual for
individual component testing.
ABS WARNING LIGHT DISPLAY
The amber antilock light illuminates at startup as
part of the system self check feature. The light illu-
minates for 2-3 seconds then goes off as part of the
normal check routine.
An ABS circuit fault is indicated when the amber
light remains on after startup, or illuminates during
vehicle operation.
Verify that a fault is actually related to the ABS
system before making repairs. For example, if the
red warning illuminates but the ABS light does not,
the problem is related to a service brake component
and not the ABS system. Or, if neither light illumi-
nates but a brake problem is noted, again, the prob-
lem is with a service brake component and not with
the ABS system.
ABS DIAGNOSTIC CONNECTOR
The ABS diagnostic connector is inside the vehicle.
The connector is the access point for the DRB scan tool.
On XJ models, the connector is located under the
instrument panel to the right of the steering column.
On some models, the connecter may be tucked under
the carpeting on the transmission tunnel. The con-
necter is a black, 6-way type.
On YJ models, the connector is under the instru-
ment panel by the the driver side kick panel. The
connecter is a black, 6 or 8-way type.
The DRB scan tool kit contains adapter cords for
both types of connecter. Use the appropriate cord for
test hookup.
DRB SCAN TOOL
ABS diagnosis is performed with the DRB scan tool.
Refer to the DRB scan tool manual for test hookup and
procedures. Diagnosis information is provided in the ap-
propriate chassis/body diagnostic manual.
WHEEL/TIRE SIZE AND INPUT SIGNALS
Antilock system operation is dependant on accurate
signals from the wheel speed sensors. Ideally, the ve-
hicle wheels and tires should all be the same size
and type. However, the Jeep ABS system is designed
to operate with a compact spare tire installed.
NORMAL OPERATING CONDITIONS
Sound Levels
The hydraulic control unit pump and solenoid valves
may produce some sound as they cycle on and off. This
is a normal condition and should not be mistaken for
faulty operation. Under most conditions, pump and so-
lenoid valve operating sounds will not be audible.
Vehicle Response In Antilock Mode
During antilock braking, the hydraulic control unit
solenoid valves cycle rapidly in response to antilock
electronic control unit signals.
The driver will experience a pulsing sensation
within the vehicle as the solenoids decrease, hold, or
increase pressure as needed. Brake pedal pulsing will
also be noted and is anormal condition.
Steering Response
A modest amount of steering input is required dur-
ing extremely high deceleration braking, or when
braking on differing traction surfaces. An example of
differing traction surfaces would be when the left
side wheels are on ice and the right side wheels are
on dry pavement.
Owner Induced Faults
Driving away with the parking brakes still applied
will cause warning light illumination. Pumping the
brake pedal will also generate a system fault and in-
terfere with ABS system operation.
ANTILOCK ECU AND HCU DIAGNOSIS
An ECU or HCU fault can only be determined
through testing with the DRB scan tool. Do not re-
place either component unless a fault is actually in-
dicated.
JABS BRAKE DIAGNOSIS 5 - 3
Page 141 of 2198

SERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Brake Drag............................... 6
Brake Fade.............................. 6
Brake Fluid Contamination................... 7
Brake Noise.............................. 7
Brake Pull............................... 6
Brake Warning Light Operation................ 5
Brakes Do Not Hold After Driving Through Deep
Water Puddles........................... 7
Component Inspection...................... 5
Contaminated Brakelining.................... 7
Diagnosing Parking Brake Malfunctions.......... 8
Diagnosis Procedures....................... 4
General Information........................ 4Hard Pedal or High Pedal Effort............... 6
Low Pedal............................... 5
Master Cylinder/Power Booster Test............ 8
Pedal Falls Away.......................... 5
Pedal Pulsation (Non-ABS Brakes Only)......... 6
Power Booster Check Valve Test............... 9
Power Booster Vacuum Test.................. 9
Preliminary Brake Check..................... 4
Rear Brake Grab.......................... 7
Road Testing............................. 5
Spongy Pedal............................. 5
Wheel and Tire Problems.................... 7
GENERAL INFORMATION
The diagnosis information in this section covers
service brake components which include:
²disc brake calipers
²disc brakeshoes
²drum brake wheel cylinders
²drum brakeshoes and brake drums
²drum brake support plates
²parking brake mechanism
²master cylinder/combination valve
²vacuum power brake booster
²brake pedal and brakelight switch
²brake warning light
DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURES
Service brake diagnosis involves determining if a
problem is related to a mechanical, hydraulic or vac-
uum operated component. A preliminary brake check,
followed by road testing and component inspection
are needed to determine a problem cause.
Road testing will either verify proper brake opera-
tion or confirm the existence of a problem. Compo-
nent inspection will, in most cases, identify the
actual part responsible for a problem.
The first diagnosis step is the preliminary brake
check. This involves inspecting fluid level, parking
brake action, wheel and tire condition, checking for
obvious leaks or component damage and testing
brake pedal response. A road test will confirm or
deny the existence of a problem. The final diagnosis
procedure involves road test analysis and a visual in-
spection of brake components.
PRELIMINARY BRAKE CHECK
(1) If amber ABS light is illuminated, refer to ABS
Brake System Diagnosis. If red warning light is illu-
minated, or if neither warning light is illuminated,
continue with brake check.(2) Inspect condition of tires and wheels. Damaged
wheels and worn, damaged, or underinflated tires
can cause pull, shudder, tramp and a condition simi-
lar to grab.
(3) If complaint was based on noise when braking,
check suspension components. Jounce front and rear
of vehicle and listen for noise that might be caused
by loose, worn, or damaged suspension or steering
components.
(4) Inspect brake fluid level:
(a) If vehicle has one-piece master cylinder, fluid
level should be within 6 mm (1/4 in.) of reservoir
rim.
(b) If vehicle has nylon reservoir with single
filler cap, correct level is to FULL mark on side of
reservoir. Acceptable level is between FULL and
ADD marks.
(c) Remember that fluid level in the reservoir
compartments will decrease in proportion to nor-
mal lining wear. However, if fluid level is abnor-
mally low, look for leaks at calipers, wheel
cylinders, brakelines and master cylinder.
(5) Inspect brake fluid condition:
(a) Fluid should be free of foreign material.Note
that brake fluid tends to darken over time.
This is normal and should not be mistaken for
contamination. If fluid is clear of foreign ma-
terial, it is OK.
(b) If fluid is highly discolored, or appears to con-
tain foreign material, drain out a sample with a
clean suction gun. Pour sample in a glass container
and note condition described in step (c).
(c) If fluid separates into layers, obviously con-
tains oil, or a substance other than brake fluid,
system seals and cups will have to be replaced and
hydraulic system flushed.
(6) Check parking brake operation. Verify free
movement and full release of cables and foot pedal or
5 - 4 SERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSISJ
Page 144 of 2198

fied. This causes pull to switch direction in favor of
the brake unit that is functioning normally.
When diagnosing a change in pull condition, re-
member that pull will return to the original direction
if the dragging brake unit is allowed to cool down
(and is not seriously damaged).
REAR BRAKE GRAB
Rear grab (or pull) is usually caused by contami-
nated lining, bent or binding shoes and support
plates, or improperly assembled components. This is
particularly true when only one rear wheel is in-
volved. However, when both rear wheels are affected,
the master cylinder could be at fault.
BRAKES DO NOT HOLD AFTER DRIVING THROUGH
DEEP WATER PUDDLES
This condition is caused by water soaked lining. If
the lining is only wet, it can be dried by driving with
the brakes lightly applied for a mile or two. However,
if the lining is both wet and dirty, disassembly and
cleaning will be necessary.
CONTAMINATED BRAKELINING
Brakelining contaminated by water is salvageable.
The lining can either be air dried or dried using heat.
In cases where brakelining is contaminated by oil,
grease, or brake fluid, the lining should be replaced.
Replacement is especially necessary when fluids/lu-
bricants have actually soaked into the lining mate-
rial. However, grease or dirt that gets onto the lining
surface (from handling) during brake repairs, can be
cleaned off. Spray the lining surface clean with Mo-
par brake cleaner.
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION
There are two basic causes of brake fluid contami-
nation. The first involves allowing dirt, debris, or
other materials to enter the cylinder reservoirs when
the cover is off. The second involves adding non-rec-
ommended fluids to the cylinder reservoirs.
Brake fluid contaminated with only dirt, or debris
usually retains a normal appearance. In some cases,
the foreign material will remain suspended in the
fluid and be visible. The fluid and foreign material
can be removed from the reservoir with a suction gun
but only if the brakes have not been applied. If the
brakes are applied after contamination, system flush-
ing will be required. The master cylinder may also
have to be disassembled, cleaned and the piston seals
replaced. Foreign material lodged in the reservoir
compensator/return ports can cause brake drag by re-
stricting fluid return after brake application.
Brake fluid contaminated by a non-recommended
fluid may appear discolored, milky, oily looking, or
foamy. However, remember that brake fluid will
darken in time and occasionally be cloudy in appear-ance. These are normal conditions and should not be
mistaken for contamination.
If some type of oil has been added to the system,
the fluid will separate into distinct layers. To verify
this, drain off a sample with a clean suction gun.
Then pour the sample into a glass container and ob-
serve fluid action. If the fluid separates into distinct
layers, it is definitely contaminated.
The only real correction for contamination by non-
recommended fluid is to flush the entire hydraulic
system and replace all the seals.
BRAKE NOISE
Squeak/Squeal
Factory installed brakelining is made from as-
bestos free materials. These materials have dif-
ferent operating characteristics than previous
lining material. Under certain conditions, as-
bestos free lining may generate some squeak,
groan or chirp noise. This noise is considered
normal and does not indicate a problem. The
only time inspection is necessary, is when noise
becomes constant or when grinding, scraping
noises occur.
Constant brake squeak or squeal may be due to lin-
ings that are wet or contaminated with brake fluid,
grease, or oil. Glazed linings, rotors/drums with hard
spots, and dirt/foreign material embedded in the
brake lining also cause squeak. Loud squeak, squeal,
scraping, or grinding sounds are a sign of severely
worn brake lining. If the lining has worn completely
through in spots, metal-to-metal contact occurs.
Thump/Clunk
Thumping or clunk noises during braking are fre-
quentlynotcaused by brake components. In many
cases, such noises are caused by loose or damaged
steering, suspension, or engine components. However,
calipers that bind on the slide surfaces can generate
a thump or clunk noise. In addition, worn out, im-
properly adjusted, or improperly assembled rear
brakeshoes can also produce a thump noise.
Chatter/Shudder
Brake chatter, or shudder is usually caused by
loose or worn components, or glazed/burnt lining. Ro-
tors with hard spots can also contribute to chatter.
Additional causes of chatter are out of tolerance ro-
tors, brake lining not securely attached to the shoes,
loose wheel bearings and contaminated brake lining.
WHEEL AND TIRE PROBLEMS
Some conditions attributed to brake components
may actually be caused by a wheel or tire problem.
A damaged wheel can cause shudder, vibration and
pull. A worn or damaged tire can also cause pull.
Severely worn tires with very little tread left can
JSERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSIS 5 - 7
Page 168 of 2198

(5) Connect vacuum hose to brake booster check
valve.
(6) Install master cylinder and combination valve.
(7) Bleed brakes. Then tighten brakeline fittings to
15-18 Nzm (130-160 in. lbs.) at master cylinder and
18-24 Nzm (160-210 in. lbs.) at combination valve.
BRAKE PEDAL REMOVAL
(1) Remove lower trim panel and A/C duct if nec-
essary.
(2) Remove steering column lower trim panel and
bezel.(3) Remove necessary dash panel-to-instrument
panel brace rods.
(4) Disconnect and remove brakelight switch.
(5) Remove retainer clip securing booster push rod
to pedal (Fig. 16).
(6) Remove nut securing pedal shaft in support
bracket.
(7) Slide pedal shaft outward for clearance and re-
move brake pedal (Figs. 28 and 29).
(8) Remove pedal bushings if they are to be re-
placed.
BRAKE PEDAL INSTALLATION
(1) Install new bushings in pedal. Lubricate bush-
ings and pivot pin with Mopar multi mileage grease.
(2) Position pedal, sleeve and spacer(s) in bracket
and install pivot pin.
(3) Install new nut on pivot pin.Pivot pin nut is
specially formed and should not be reused. Be
sure to install new nut to secure pin.
(4) ) Tighten new pivot pin nut to 27 Nzm (20 ft.
lbs.) on models with manual transmission. Tighten
nut to 35 Nzm (26 ft. lbs.) on models with automatic
transmission.
(5) Install booster push rod on pedal pin (Fig. 16).
Secure push rod with original, or new retainer clip if
necessary.
(6) Install and connect brakelight switch.
(7) Install dash brace rod, if equipped.
(8) Install instrument panel and steering column
trim covers.
Fig. 28 Brake Pedal And Support Bracket (YJ)
Fig. 29 Brake Pedal And Support Bracket (XJ)
JPOWER BRAKE BOOSTERÐBRAKE PEDALÐBRAKELIGHT SWITCH 5 - 31