1995 JEEP CHEROKEE Transmission adjustment
[x] Cancel search: Transmission adjustmentPage 1380 of 2198

happens when the container delivery mechanism is im-
properly calibrated. Always check the lubricant level af-
ter filling to avoid an under fill condition.
A correct lubricant level check can only be made
when the vehicle is level; use a drive-on hoist to en-
sure this. Also allow the lubricant to settle for a
minute or so before checking. These recommenda-
tions will ensure an accurate check and avoid an un-
der-or-overfill condition.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants, compo-
nent damage, incorrect clutch adjustment, or by a
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc.
Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear, shift
rail, synchro and bearing damage. If a leak goes un-
detected for an extended period, the first indications
of a problem are usually hard shifting and noise.
Incorrect or contaminated lubricants can also con-
tribute to hard shifting. The consequence of using
non-recommended lubricants is noise, excessive wear,
internal bind and hard shifting.
Improper clutch release is a frequent cause of hard
shifting. Incorrect adjustment or a worn, damaged
pressure plate or disc can cause incorrect release. If
the clutch problem is advanced, gear clash during
shifts can result.
Worn or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash
when shifting into any forward gear. In some new or re-
built transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases, this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise dur-
ing normal operation. Rotating gears generate a mild
whine that is audible but only at extreme speeds.
Severe, highly audible transmission noise is gener-
ally the result of a lubricant problem. Insufficient,
improper, or contaminated lubricant will promote
rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift rails, forks and
bearings. The overheating caused by a lubricant
problem, can also lead to gear breakage.
TRANSMISSION REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into first or third gear. Then
raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Support engine with adjustable jack stand. Po-
sition wood block between jack and oil pan to avoid
damaging pan.
(3) Disconnect necessary exhaust system components.
(4) Remove skid plate.
(5) Disconnect rear cushion and bracket from
transmission (Fig. 5).
(6) Remove rear crossmember.
Fig. 5 Rear Mount Components (YJ Shown)
JAX 4/5 MANUAL TRANSMISSION 21 - 3
Page 1393 of 2198
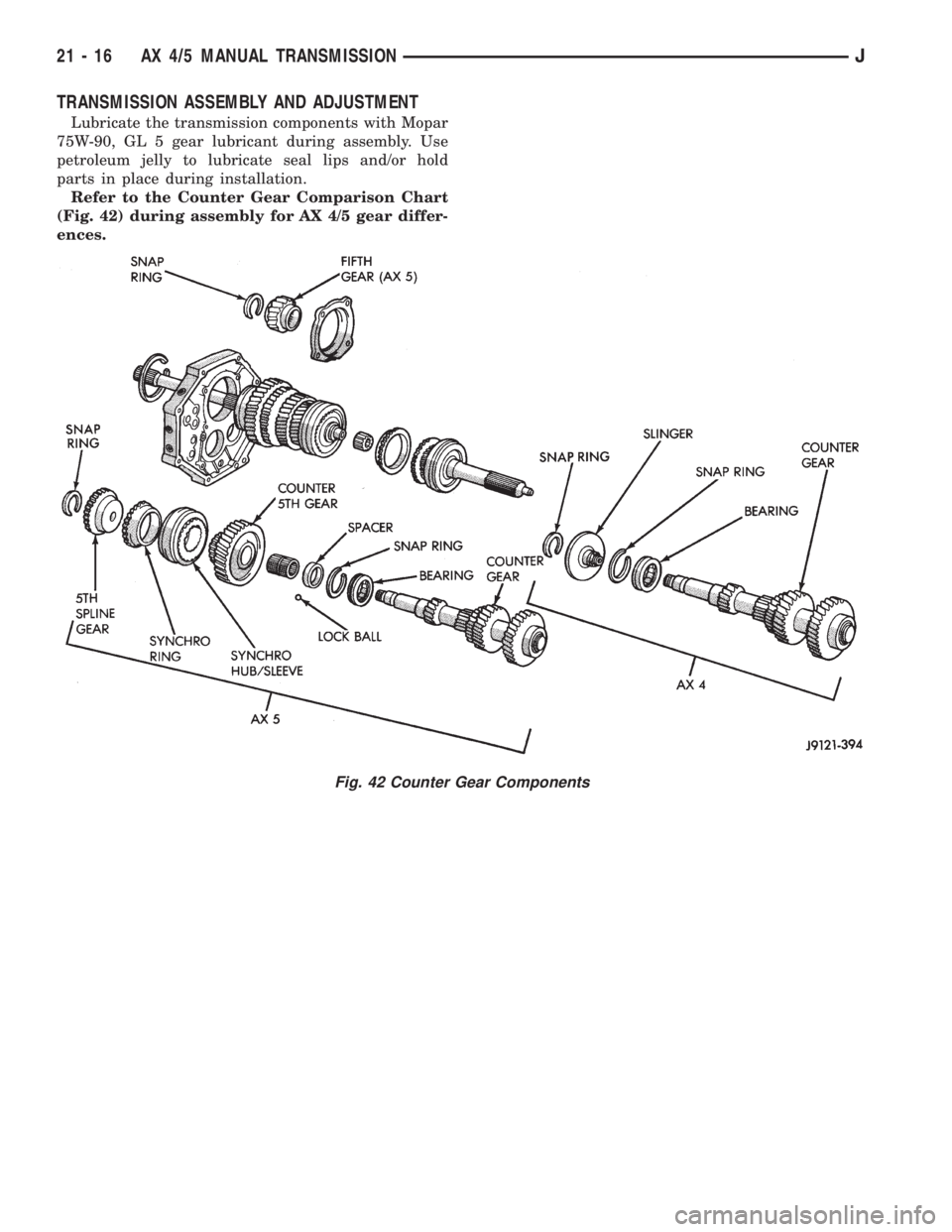
TRANSMISSION ASSEMBLY AND ADJUSTMENT
Lubricate the transmission components with Mopar
75W-90, GL 5 gear lubricant during assembly. Use
petroleum jelly to lubricate seal lips and/or hold
parts in place during installation.
Refer to the Counter Gear Comparison Chart
(Fig. 42) during assembly for AX 4/5 gear differ-
ences.
Fig. 42 Counter Gear Components
21 - 16 AX 4/5 MANUAL TRANSMISSIONJ
Page 1410 of 2198
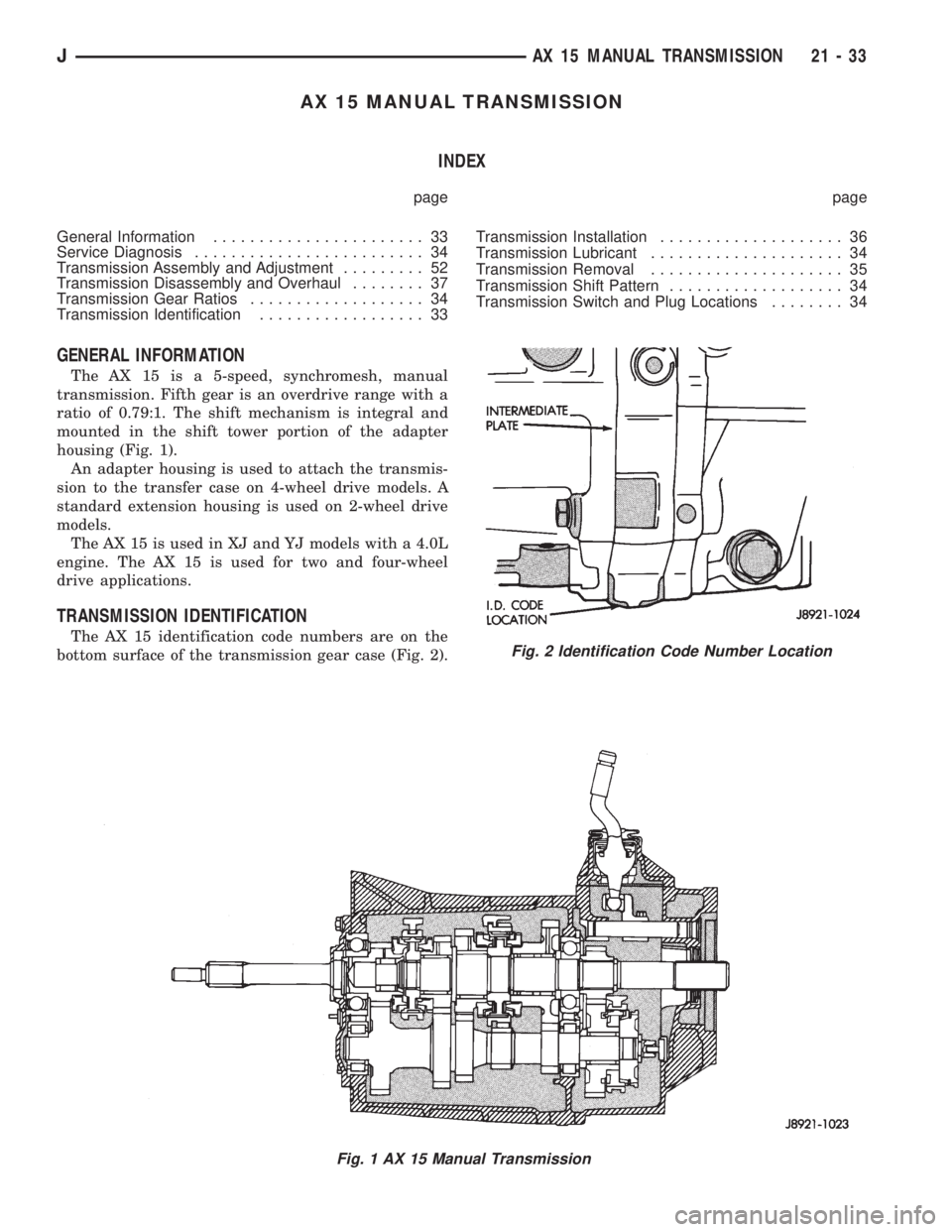
AX 15 MANUAL TRANSMISSION
INDEX
page page
General Information....................... 33
Service Diagnosis......................... 34
Transmission Assembly and Adjustment......... 52
Transmission Disassembly and Overhaul........ 37
Transmission Gear Ratios................... 34
Transmission Identification.................. 33Transmission Installation.................... 36
Transmission Lubricant..................... 34
Transmission Removal..................... 35
Transmission Shift Pattern................... 34
Transmission Switch and Plug Locations........ 34
GENERAL INFORMATION
The AX 15 is a 5-speed, synchromesh, manual
transmission. Fifth gear is an overdrive range with a
ratio of 0.79:1. The shift mechanism is integral and
mounted in the shift tower portion of the adapter
housing (Fig. 1).
An adapter housing is used to attach the transmis-
sion to the transfer case on 4-wheel drive models. A
standard extension housing is used on 2-wheel drive
models.
The AX 15 is used in XJ and YJ models with a 4.0L
engine. The AX 15 is used for two and four-wheel
drive applications.
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
The AX 15 identification code numbers are on the
bottom surface of the transmission gear case (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1 AX 15 Manual Transmission
Fig. 2 Identification Code Number Location
JAX 15 MANUAL TRANSMISSION 21 - 33
Page 1412 of 2198

generally happens when the container delivery mech-
anism is improperly calibrated. Always check the lu-
bricant level after filling to avoid an under fill
condition.
A correct lubricant level check can only be made
when the vehicle is level; use a drive-on hoist to en-
sure this. Also allow the lubricant to settle for a
minute or so before checking. These recommenda-
tions will ensure an accurate check and avoid an un-
der-or-overfill condition.
HARD SHIFTING
Hard shifting is usually caused by a low lubricant
level, improper or contaminated lubricants, compo-
nent damage, incorrect clutch adjustment, or by a
damaged clutch pressure plate or disc.
Substantial lubricant leaks can result in gear, shift
rail, synchro and bearing damage. If a leak goes un-
detected for an extended period, the first indications
of a problem are usually hard shifting and noise.
Incorrect or contaminated lubricants can also con-
tribute to hard shifting. The consequence of using
non-recommended lubricants is noise, excessive wear,
internal bind and hard shifting.
Improper clutch release is a frequent cause of hard
shifting. Incorrect adjustment or a worn, damagedpressure plate or disc can cause incorrect release. If
the clutch problem is advanced, gear clash during
shifts can result.
Worn or damaged synchro rings can cause gear clash
when shifting into any forward gear. In some new or re-
built transmissions, new synchro rings may tend to
stick slightly causing hard or noisy shifts. In most
cases, this condition will decline as the rings wear-in.
TRANSMISSION NOISE
Most manual transmissions make some noise during
normal operation. Rotating gears can generate a mild
whine that may only be audible at extreme speeds.
Severe, obviously audible transmission noise is
generally the result of a lubricant problem. Insuffi-
cient, improper, or contaminated lubricant can pro-
mote rapid wear of gears, synchros, shift rails, forks
and bearings. The overheating caused by a lubricant
problem, can also lead to gear breakage.
TRANSMISSION REMOVAL
(1) Shift transmission into first or third gear.
(2) Raise vehicle on a hoist.
(3) Disconnect necessary exhaust system components.
(4) Support transmission with adjustable jack stand.
(5) Disconnect rear cushion and mounting bracket
from transmission, or transfer case (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Rear Mount Components (YJ Shown)
JAX 15 MANUAL TRANSMISSION 21 - 35
Page 1429 of 2198

GEAR AND SYNCHRO INSPECTION
Install the synchro rings on their respective gears.
Rotate each ring on the gear and note synchro action.
Replace any synchro ring that exhibits a lack of
braking action or binds on the gear. Also replace any
ring that is worn or has chipped or broken teeth.
Measure end clearance between the synchro ring
and the gear with a feeler gauge (Fig. 66). Clearance
should be 0.06 mm to 1.6 mm (0.024 to 0.063 in.).
Install the needle bearings in the first, second and
third gears. Then install the gears on the output
shaft and check shaft-to-gear clearance with a dial
indicator (Fig. 67).
Maximum allowable clearance is 0.16 mm (0.0063
in.). If any gear exhibits excessive clearance, replace
the gear and needle bearing.
Check clearance between the shift forks and syn-
chro sleeves with a feeler gauge (Fig. 68). Clearance
should not exceed 1.0 mm (0.039 in.). Replace the
synchro sleeve (and matching hub) if clearance ex-
ceeds the stated limit.
Check condition of the reverse idler gear bushing
(Fig. 69). Replace the gear if the bushing is scored or
worn.
Gear Case, Housing And Intermediate Plate
Clean the case, housing and plate with solvent and
dry with compressed air. Replace any component that
is cracked, warped or damaged in any way.
Inspect the threads in the case, housing and plate.
Minor thread damage can be repaired with steel
thread inserts if necessary. However, do not attempt
to repair if the cracks are evident around any
threaded hole.
Inspect the reverse pin in the adapter/extensionhousing. Replace the pin if worn or damaged. Refer
to the replacement procedure in the Transmission As-
sembly section.
TRANSMISSION ASSEMBLY AND ADJUSTMENT
Lubricate the transmission components with gear
lubricant during assembly. Use petroleum jelly to lu-
bricate seal lips and/or hold parts in place during in-
stallation.
Fig. 66 Checking Synchro Ring End Clearance
Fig. 67 Checking Gear-To-Shaft Clearance
Fig. 68 Checking Shift Fork-To-Sleeve Clearance
21 - 52 AX 15 MANUAL TRANSMISSIONJ
Page 1447 of 2198

30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Air Pressure Test......................... 74
Analyzing the Road Test.................... 71
Converter Housing Leak Diagnosis............ 75
Converter Stall Test........................ 74
Diagnosis Guides and Charts................ 77
Effects of Incorrect Fluid Level............... 71
Fluid Level Check......................... 70Gearshift Cable/Linkage Adjustment........... 71
General Information....................... 70
Hydraulic Pressure Test.................... 72
Preliminary Diagnosis...................... 70
Road Test............................... 71
Transmission Throttle Valve Cable Adjustment.... 71
GENERAL INFORMATION
Automatic transmission problems are generally a
result of:
²poor engine performance
²incorrect fluid level
²incorrect throttle valve cable adjustment
²incorrect band adjustment
²incorrect hydraulic control pressure adjustments
²hydraulic component malfunctions
²mechanical component malfunctions.
Begin diagnosis by checking the easily accessible
items such as fluid level, fluid condition and control
linkage adjustment. A road test will determine if fur-
ther diagnosis is necessary.
Procedures outlined in this section should be per-
formed in the following sequence to realize the most
accurate results:
²Preliminary diagnosis
²Check fluid level and condition
²Check control linkage Adjustment
²Road test
²Stall test
²Hydraulic pressure test
²Air pressure tests
²Leak test
²Analyze test results and consult diagnosis charts
PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSIS
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are driveable and an alternate pro-
cedure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or move
forward).
Vehicle Is Driveable
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Adjust throttle cable and gearshift linkage if
complaint was based on delayed, erratic, or harsh
shifts.
(3) Road test vehicle and note transmission operat-
ing characteristics.(4) Perform stall test if complaint is based on slug-
gish, low speed acceleration or abnormal throttle
opening needed to maintain normal speeds with
properly tuned engine.
(5) Perform hydraulic pressure tests.
(6) Perform air pressure test to check clutch-band
operation.
Vehicle Is Disabled
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Check for broken, disconnected throttle linkage.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose,
missing pressure port plugs.
(4) Raise vehicle, start engine, shift transmission
into gear and note following:
(a) If propeller shafts turn but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shafts do not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged drive plate, converter,
oil pump or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shafts do not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic pressure test to
determine if problem is a hydraulic or mechanical.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
Transmission fluid level should be checked monthly
under normal operation. If the vehicle is used for
trailer towing or similar heavy load hauling, check
fluid level and condition weekly.
Fluid level is checked with the engine running at
curb idle speed, the transmission in Neutral and the
transmission fluid at normal operating temperature.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK PROCEDURE
(1) Transmission fluid must be at normal operating
temperature for accurate fluid level check. Drive ve-
hicle if necessary to bring fluid temperature up to
normal hot operating temperature of 82ÉC (180ÉF).
(2) Position vehicle on level surface. This is ex-
tremely important for accurate fluid level check.
(3) Start and run engine at curb idle speed.
21 - 70 30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSISJ
Page 1448 of 2198

(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Shift transmission momentarily into all gear
ranges. Then shift transmission back to Neutral.
(6) Clean top of filler tube and dipstick to keep dirt
from entering tube.
(7) Remove dipstick and check fluid level as fol-
lows:
(a) Dipstick has three fluid level indicator levels
(Fig. 1) which are: a MIN dot, an OK crosshatch
area, and a MAX fill arrow.
(b) Correct maximum level is to MAX arrow
mark. Correct acceptable level is to OK mark in
crosshatch area.
(c) Incorrect level is at or below MIN dot.
(d) If fluid is low, add only enough Mopar ATF
Plus to restore correct level. Do not overfill.
CAUTION: Do not overfill the transmission. Overfill-
ing may cause leakage out the pump vent which
can be mistaken for a pump seal leak. Overfilling
will also cause fluid aeration and foaming as the ex-
cess fluid is picked up and churned by the gear
train. This will significantly reduce fluid life.
EFFECTS OF INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn
the fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid causing the
same conditions that occur with a low level.
In either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating,
oxidation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve, clutch and servo operation. Foaming also
causes fluid expansion which can result in fluid over-
flow from the transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid
overflow can easily be mistaken for a leak if inspec-
tion is not careful.
TRANSMISSION THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
ADJUSTMENT
Throttle cable adjustment is important to proper
operation. This adjustment positions the throttle
valve which controls shift speed, quality and part
throttle downshift sensitivity.
If cable adjustment setting is too short, early shifts
and slippage between shifts may occur. If the setting
is too long, shifts may be delayed and part throttle
downshifts may be very sensitive. Refer to the In-Ve-
hicle Service section for adjustment procedure.
GEARSHIFT CABLE/LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
Gearshift cable/linkage adjustment is important be-
cause it positions the valve body manual valve. Incor-
rect adjustment will cause creeping in Neutral,
premature clutch wear, delayed engagement in any
gear, or a no-start in Park or Neutral position.Proper operation of the neutral start switch will
provide a quick check on adjustment. Refer to the In-
Vehicle Service section for adjustment procedure.
ROAD TEST
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and all
cable/linkage adjustments have been checked and ad-
justed if necessary.
Observe engine performance during the road test. A
poorly tuned engine will not allow an accurate anal-
ysis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for slippage and shift variations. Note whether the
shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed, early, or if part
throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Watch closely for slippage or engine flare which
usually indicates clutch, band or overrunning clutch
problems. If the condition is advanced, an overhaul
may be necessary to restore normal operation.
A slipping clutch or band can often be determined
by comparing which internal units are applied in the
various gear ranges. The Clutch and Band Applica-
tion chart (Fig. 3) provides a basis for analyzing road
test results.
ANALYZING THE ROAD TEST
Refer to the Clutch and Band Application chart
(Fig. 3) and note which elements are in use in the
various gear ranges.
The rear clutch is applied in all forward ranges (D,
2, 1). The overrunning clutch is applied in first gear
(D and 2 range only). The rear band is applied in 1
and R range only.
For example: If slippage occurs in first gear in D
and 2 range but not in 1 range, the overrunning
Fig. 3 Clutch And Band Application Chart
J30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 71
Page 1476 of 2198

30RH/32RH IN-VEHICLE SERVICE
INDEX
page page
Converter Drainback Check Valve Service...... 113
Fluid and Filter Replacement................. 99
Fluid Level Check......................... 99
Front Band Adjustment.................... 102
Governor and Park Gear Service............. 105
Oil Filter Replacement..................... 103
Park Interlock Cable Adjustment (XJ).......... 101
Park Lock Component Replacement.......... 108
Park/Neutral Position Switch Service.......... 109
Rear Band Adjustment.................... 103
Recommended Fluid....................... 99Refilling After Overhaul or Fluid/Filter Change . . . 100
Shift Cable Adjustment (XJ)................. 100
Shift Linkage Adjustment (YJ)............... 100
Speedometer Service..................... 109
Throttle Valve Cable Adjustment (XJ/YJ)....... 101
Transmission Cooler Flow Testing............ 113
Transmission Cooler Line and Fitting Service.... 111
Transmission Cooler Reverse Flushing......... 114
Valve Body Installation.................... 104
Valve Body Removal...................... 104
Valve Body Service....................... 104
RECOMMENDED FLUID
Recommended (and preferred) fluid for 30RH/32RH
transmissions is Mopar ATF Plus, type 7176.
Dexron II is not really recommended and should
only be used when ATF Plus is not available.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
Transmission fluid level should be checked monthly
under normal operation. If the vehicle is used for
trailer towing or similar heavy load hauling, check
fluid level and condition weekly.
Fluid level is checked with the engine running at
curb idle speed, the transmission in Neutral and the
transmission fluid at normal operating temperature.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK PROCEDURE
(1) Transmission fluid must be at normal operating
temperature for accurate fluid level check. Drive ve-
hicle if necessary to bring fluid temperature up to
normal hot operating temperature of 82ÉC (180ÉF).
(2) Position vehicle on level surface. This is ex-
tremely important for accurate fluid level check.
(3) Start and run engine at curb idle speed.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Shift transmission momentarily into all gear
ranges. Then shift transmission back to Neutral.
(6) Clean top of filler tube and dipstick to keep dirt
from entering tube.
(7) Remove dipstick and check fluid level as fol-
lows:
(a) Dipstick has three fluid level indicator levels
(Fig. 1) which are a MIN dot, an OK crosshatch
area, and a MAX fill arrow.
(b) Correct maximum level is to MAX arrow
mark. Correct acceptable level is to OK mark in
crosshatch area.
(c) Incorrect level is at or below MIN dot.
(d) If fluid is low, add only enough Mopar ATF
Plus restore correct level. Do not overfill.CAUTION: Do not overfill the transmission. Overfill-
ing may cause leakage out the pump vent which
can be mistaken for a pump seal leak. Overfilling
will also cause fluid aeration and foaming as the ex-
cess fluid is picked up and churned by the gear
train. This will reduce fluid life significantly.
FLUID AND FILTER REPLACEMENT
NORMAL CHANGE INTERVAL
The fluid and filter should be changed (and the
bands adjusted) at recommended maintenance inter-
vals, or whenever the transmission has been disas-
sembled for any reason.
Refer to the Driveline section in Group O, Lubrica-
tion and Maintenance for recommended change inter-
vals. Refer to the fluid/filter replacement and band
adjustment procedures in this section.
SEVERE USAGE CHANGE INTERVAL
Under severe usage, the fluid and filter should be
changed and the bands adjusted at 12,000 mile (19
000 Km) intervals.
Severe usage is defined as:
(a) More than half of vehicle operation occurs in
heavy city traffic during hot weather (above 90É F).
(b) Vehicle is used for taxi, police, limousine, or
similar commercial operation.
Fig. 1 Fluid Level Marks On Transmission Dipstick
J30RH/32RH IN-VEHICLE SERVICE 21 - 99