1994 JEEP CHEROKEE battery replacement
[x] Cancel search: battery replacementPage 488 of 1784

CHIME/BUZZER WARNING SYSTEMS
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL.............................. 1
IGNITION KEY WARNING SWITCH REPLACEMENT.4OPERATION/DIAGNOSIS.................. 1
GENERAL
The buzzer or optional chime module is mounted on
the left side of the fuse block (above and to the left of
the brake/clutch pedal). The buzzer or chime sounds
an audible warning tone in any of the following con-
ditions:
²Vehicle lights are ON when the ignition has been
switched OFF and the key is removed and then the
driver's door is opened (except YJ).²The key is in the ignition and the driver's door is
open (On some vehicles, the buzzer will not sound if
the ignition switch is in the ON position).
²The ignition is switched ON and the driver's seat
belt is not buckled. Buzzer will quit after 4 to 8 sec-
onds. Besides the buzzer, a seat belt indicator lamp
turns on as a reminder to fasten seat belt.
OPERATION/DIAGNOSIS
OPERATION
Battery voltage for module operation is supplied to
two pins. Voltage is always present at pin 7. Pin 1
receives voltage when the ignition switch is in the
ON or START position.
SEAT BELT WARNING
The seat belt warning system uses both visual and
audible signals. These consist of a buzzer that is part
of a combined seat belt and key warning buzzer and
a red light on the instrument panel.
The system will always illuminate the seat belt
warning lamp for four to eight seconds when the ig-
nition switch is turned to the ON position. Also, only
if the driver does not fasten his seat belt, the buzzer
will sound during the same time interval. Passenger
belts are not connected to the system.
A timed buzzer-relay is used to operate the system
for the time period. It has a time delay mechanism
and buzzer assembly. Only the driver's seat belt
buckle has a switch that is connected to the system.
KEY-IN-IGNITION WARNING
To sound the key-in-ignition warning, the following
must occur:
²the ignition key warning switch must be closed
²the driver's door jamb switch must be closed.
These conditions ground pin 6 of the module. These
switches are closed when the key is in the ignition
and the driver's door is open.On some vehicles the chime/buzzer will not
sound if the door is open and the key is in the
ON position.
LIGHTS-ON WARNING (EXCEPT YJ)
To sound the lights-on warning, the following must
occur:
²the headlamp switch must be closed
²the driver's door jamb switch must be closed.
These conditions ground pin 6 of the module. These
switches are closed when the headlamp switch is ON
and the driver's door is open.
DIAGNOSIS
If the buzzer/chime unit does not operate as de-
scribed, check the two fuses for pins 1 and 7 (Figs. 1
and 2) and replace as required. If the fuses are not
defective, perform the following tests to determine if
the problem is in the module or in the wiring. Using
a flat head screwdriver, release the locking plastic
clip while carefully pulling out the module. Plug in a
known good module and check its operation. If the
problem is not corrected by replacing the module, re-
move the module and continue as follows:
VOLTAGE TESTS
Ignition in ON position, measure between the
following pins and vehicle ground.
²Measure voltage at buzzer/chime module connector
pin 1. Meter should read battery voltage. If not, re-
pair open to ignition switch.
Turn ignition OFF and remove the key from the ig-
nition.
JCHIME/BUZZER WARNING SYSTEMS 8U - 1
Page 491 of 1784
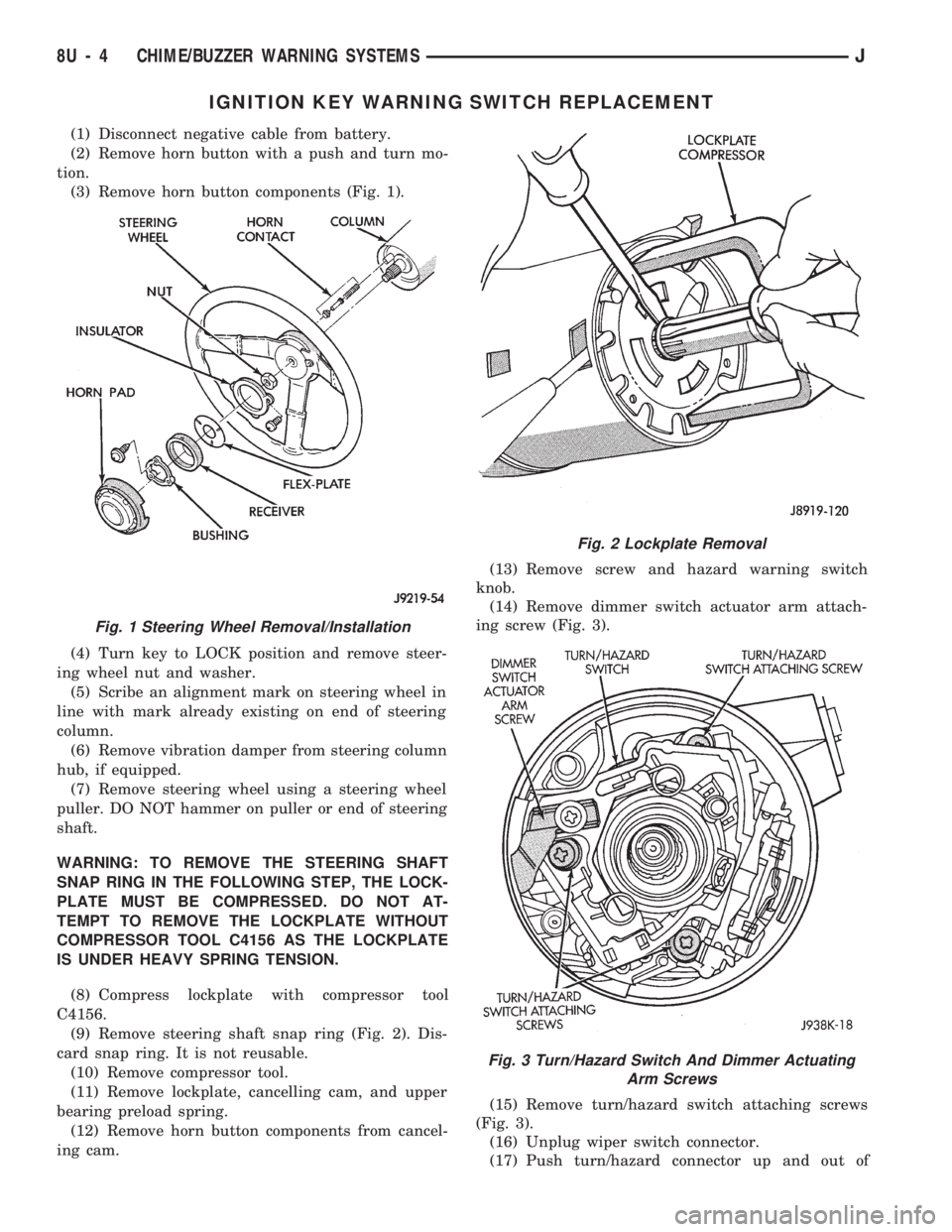
IGNITION KEY WARNING SWITCH REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove horn button with a push and turn mo-
tion.
(3) Remove horn button components (Fig. 1).
(4) Turn key to LOCK position and remove steer-
ing wheel nut and washer.
(5) Scribe an alignment mark on steering wheel in
line with mark already existing on end of steering
column.
(6) Remove vibration damper from steering column
hub, if equipped.
(7) Remove steering wheel using a steering wheel
puller. DO NOT hammer on puller or end of steering
shaft.
WARNING: TO REMOVE THE STEERING SHAFT
SNAP RING IN THE FOLLOWING STEP, THE LOCK-
PLATE MUST BE COMPRESSED. DO NOT AT-
TEMPT TO REMOVE THE LOCKPLATE WITHOUT
COMPRESSOR TOOL C4156 AS THE LOCKPLATE
IS UNDER HEAVY SPRING TENSION.
(8) Compress lockplate with compressor tool
C4156.
(9) Remove steering shaft snap ring (Fig. 2). Dis-
card snap ring. It is not reusable.
(10) Remove compressor tool.
(11) Remove lockplate, cancelling cam, and upper
bearing preload spring.
(12) Remove horn button components from cancel-
ing cam.(13) Remove screw and hazard warning switch
knob.
(14) Remove dimmer switch actuator arm attach-
ing screw (Fig. 3).
(15) Remove turn/hazard switch attaching screws
(Fig. 3).
(16) Unplug wiper switch connector.
(17) Push turn/hazard connector up and out of
Fig. 1 Steering Wheel Removal/Installation
Fig. 2 Lockplate Removal
Fig. 3 Turn/Hazard Switch And Dimmer Actuating
Arm Screws
8U - 4 CHIME/BUZZER WARNING SYSTEMSJ
Page 497 of 1784

FUSIBLE LINK REPLACEMENT
CAUTION: Do not replace blown fusible links with a
standard wire. Only use fusible type wire with hypa-
lon insulation or damage to the electrical system
could occur. Also make sure correct gauge of wir-
ing is used. Refer to the wiring diagrams for proper
gauge and color.
When a fusible link blows it is important to find
out what the problem is. They are placed in the elec-
trical system for protection against shorts to ground.
This can be caused by a component failure or various
wiring failures.Do not just replace the fusible
link to correct the problem.
When diagnosing a faulty fusible link it is impor-
tant to check the wire carefully. In some instances
the link may be blown and it will not show through
the insulation, the wire should be checked over its
entire length for internal breaks.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Cut out the blown portion of the fusible link.
(3) Strip 1 inch of insulation from each end of the
existing fusible link.
(4) Place a piece of heat shrink tubing over one
side of the fusible link. Make sure the tubing will be
long enough to cover and seal the entire repair area.
(5) Cut a replacement piece of fusible link approx-
imately two inches longer than the piece removed.
(6) Remove one inch of insulation from each end of
the replacement fusible link.
(7) Spread the strands of wire apart on each of the
exposed wires (Fig. 7 example 1).
(8) Push the two ends of the wire together until
the strands of wire are close to the insulation (Fig. 7
example 2).
(9) Twist the wires together (Fig. 7 example 3).
(10) Solder the wires together using rosin core type
solder only.Do not use acid core type solder.
(11) Center the heat shrink tubing over the joint
and heat using a heat gun. Heat the joint until the
tubing is tightly sealed and sealant comes out of both
ends of the tubing.
(12) Secure the fusible link to the existing ones to
prevent chafing or damage to the insulation.
(13) Connect battery and test affected systems.
WIRING REPAIR
When replacing or repairing a wire, it is important
that the correct gauge be used as shown in the wir-
ing diagrams. The wires must also be held securely
in place to prevent damage to the insulation.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove 1 inch of insulation from each end of
the wire.
(3) Place a piece of heat shrink tubing over one
side of the wire. Make sure the tubing will be long
enough to cover and seal the entire repair area.(4) Spread the strands of the wire apart on each of
the exposed wires (Fig. 7 example 1).
(5) Push the two ends of wire together until the
strands of wire are close to the insulation (Fig. 7 ex-
ample 2).
(6) Twist the wires together (Fig. 7 example 3).
(7) Solder the connection together using rosin core
type solder only.Do not use acid core solder.
(8) Center the heat shrink tubing over the joint
and heat using a heat gun. Heat the joint until the
tubing is tightly sealed and sealant comes out of both
ends of the tubing.
(9) Secure the wire to the existing ones to prevent
chafing or damage to the insulation.
(10) Connect battery and test affected systems.
CONNECTOR REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect battery.
(2) Disconnect the connector to be repaired from its
mating half.
(3) Remove connector locking wedge (Fig. 8).
(4) Position the connector locking finger away from
the terminal while pulling on the wire to remove the
terminal from the connector (Fig. 9).
(5) Reset the terminal locking tang, if it has one.
(6) Insert the removed wire in the same cavity on
the repair connector.
(7) Repeat steps four through six for each wire in
the connector, being sure that all wires are inserted
into the proper cavities. For additional connector pin
out identification refer to the wiring diagrams.
(8) Insert the connector locking wedge into the re-
paired connector.
(9) Connect connector to its mating half.
Fig. 7 Wire Repair
8W - 4 WIRING DIAGRAMSJ
Page 498 of 1784

(10) Connect battery and test affected systems.
CONNECTOR AND TERMINAL ASSEMBLY
REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect Battery.
(2) Disconnect the connector being repaired from
its mating half.
(3) Cut off the existing wire connector directly be-
hind the insulator and remove six inches of tape from
the harness.
(4) Stagger cut all wires on the harness side about
1/2 inch apart (Fig. 10).
(5) Remove 1 inch of insulation from each wire on
the harness side.
(6) Stagger cut the matching wires on the repair
connector assembly in the opposite order as was done
on the harness side of the repair (allow extra length
for soldered connections). Check that the overall
length is the same as the original (Fig. 10).
(7) Remove 1 inch of insulation from each wire.(8) Place a piece of heat shrink tubing over one
side of the wire. Make sure the tubing will be long
enough to cover and seal the entire repair area.
(9) Spread the strands of the wire apart on each of
the exposed wires (Fig. 7 example 1).
(10) Push the two ends of wire together until the
strands of wire are close to the insulation (Fig. 7 ex-
ample 2).
(11) Twist the wires together (Fig. 7 example 3).
(12) Solder the connection together using rosin
core type solder only.Do not use acid core solder.
(13) Center the heat shrink tubing over the joint
and heat using a heat gun. Heat the joint until the
tubing is tightly sealed and sealant comes out of both
ends of the tubing.
(14) Repeat steps 8 through 13 for each wire.
(15) Re-tape the wire harness starting 1-1/2 inches
behind the connector and 2 inches past the repair.
(16) Reconnect the repaired connector.
(17) Connect battery and test affected systems.
TERMINAL REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect battery.
(2) Disconnect the connector being repaired from
its mating half.
(3) Remove connector locking wedge (Fig. 8).
(4) Position the connector locking finger away from
the terminal while pulling on the wire to remove the
terminal from the connector (Fig. 9).
(5) Cut the wire 6 inches from the back of the con-
nector.
(6) Remove 1 inch of insulation from the wire on
the harness side.
(7) Select a wire from the terminal repair assembly
that best matches the color wire being repaired.
(8) Cut the repair wire to the proper length and re-
move 1 inch of insulation.
(9) Place a piece of heat shrink tubing over one
side of the wire. Make sure the tubing will be long
enough to cover and seal the entire repair area.
Fig. 8 Connector Locking Wedge Tab (Typical)
Fig. 9 Connector Locking Finger and Locking
Wedge (Typical)
Fig. 10 Stagger Cutting Wires
JWIRING DIAGRAMS 8W - 5
Page 845 of 1784

CONNECTING ROD BEARING CLEARANCE
Engine connecting rod bearing clearances can be
determined by use of Plastigage, or equivalent. The
following is the recommended procedures for the use
of Plastigage:
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing cap shell (Fig. 2). Position the
Plastigage approximately 6.35 mm (1/4 inch) off cen-
ter and away from the oil holes. In addition, suspect
areas can be checked by placing the Plastigage in the
suspect area.
(3) The crankshaft must be turned until the con-
necting rod to be checked starts moving toward the
top of the engine. Only then should the rod cap with
Plastigage in place be assembled. Tighten the rod
cap nut to 45 Nzm (33 ft. lbs.) torque.DO NOT ro-
tate the crankshaft or the Plastigage may be
smeared, giving inaccurate results.
(4) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage with the scale provided on
the package (Fig. 3). Plastigage generally comes in 2
scales (one scale is in inches and the other is a met-
ric scale). Locate the band closest to the same width.
This band shows the amount of clearance. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken
(refer to Engine Specifications).
(5) Plastigage is available in a variety of clearance
ranges. The 0.025-0.076 mm (0.001-0.003 inch) range
is usually the most appropriate for checking engine
bearing clearances.
REPAIR DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole.
This brings the hole back to its original thread size.
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
SERVICE ENGINE ASSEMBLY (SHORT BLOCK)
A service replacement engine assembly (short
block) may be installed whenever the original cylin-
der block is defective or damaged beyond repair. It
consists of the cylinder block, crankshaft, piston and
rod assemblies. If needed, the camshaft must be pro-
cured separately and installed before the engine is
installed in the vehicle.
A short block is identified with the letter ``S'' stamped
on the same machined surface where the build date
code is stamped for complete engine assemblies.
Installation includes the transfer of components
from the defective or damaged original engine. Fol-
low the appropriate procedures for cleaning, inspec-
tion and torque tightening.
HYDROSTATIC LOCK
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(refer to Group 14, Fuel System).
(2) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and in-
take manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure in
the cylinder head. Remove the plugs from the engine.
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (i.e. coolant,
fuel, oil, etc.).
(7) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt engine oil into the cylinders to lubricate
the walls. This will prevent damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 37 Nzm (27 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
Nzm (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil (refer to Group 0, Lubrica-
tion and Maintenance).
(15) Connect the negative cable to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
Fig. 3 Clearance Measurement
9 - 4 ENGINESJ
Page 859 of 1784

(14) Install the remaining flywheel housing bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 38 Nzm (28 ft. lbs.) torque.
(15) Install the starter motor and connect the ca-
ble. Tighten the bolts to 45 Nzm (33 ft. lbs.) torque.
(16) Install the oil filter.
(17) Lower the vehicle.
(18) Connect the coolant hoses and tighten the
clamps.
(19) If equipped with power steering:
(a) Remove the protective caps
(b) Connect the hoses to the fittings at the steer-
ing gear. Tighten the nut to 52 Nzm (38 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(c) Fill the pump reservoir with fluid.
(20) Remove the pulley-to-water pump flange
alignment capscrew and install the fan and spacer or
Tempatrol fan assembly.
(21) Tighten the serpentine drive belt according to
the specifications listed in Group 7, Cooling System.
(22) Install the fan shroud and radiator.
(23) Connect the radiator hoses.
(24) Connect the heater hoses.
(25) Connect the throttle valve rod and retainer.
(26) Connect the throttle cable and install the rod.
(27) Install the throttle valve rod spring.
(28) Connect the speed control cable, if equipped.
(29) Connect the oxygen sensor wire connector.
(30) Install the vacuum hose and check valve on
the brake booster.
(31) Connect the coolant temperature sensor wire
connector.
(32) Connect the idle speed actuator wire connec-
tor.
(33) Connect the fuel inlet and return hoses at the
fuel rail. Verify that the quick-connect fitting assem-
bly fits securely over the fuel lines by giving the fuel
lines a firm tug.
(34) Install the fuel line bracket to the intake
manifold.
(35) Connect all fuel injection wire connections.
(36) Install the engine ground strap.
(37) Connect the ignition coil wire connector.
(38) Remove the coolant temperature sending unit
to permit air to escape from the block. Fill the cool-
ing system with coolant. Install the coolant tempera-
ture sending unit when the system is filled.
(39) Install the battery and connect the battery ca-
bles.
(40) Install the air cleaner bonnet to the throttle
body.
(41) Install the air cleaner.
(42) Lower the hood and secure in place.
(43) Start the engine and inspect for leaks.
(44) Stop the engine and check the fluid levels.
Add fluid, as required.ENGINE CYLINDER HEAD COVER
A cured gasket is part of the engine cylinder head
cover.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Disconnect the Crankcase Ventilation (CCV)
vacuum hose from engine cylinder head cover (Fig.
1).
(3) Disconnect the fresh air inlet hose from the en-
gine cylinder head cover (Fig. 1).
(4) Remove the engine cylinder head cover mount-
ing bolts.
(5) Remove the engine cylinder head cover.
CLEANING
Remove any original sealer from the cover sealing
surface of the engine cylinder head and clean the
surface using a fabric cleaner.
Remove all residue from the sealing surface using
a clean, dry cloth.
INSPECTION
Inspect the engine cylinder head cover for cracks.
Replace the cover, if cracked.
The original grey gasket material should NOT be
removed. If sections of the gasket material are miss-
ing or are compressed, replace the engine cylinder
head cover. However, sections with minor damage
such as small cracks, cuts or chips may be repaired
with a hand held applicator. The new material must
be smoothed over to maintain gasket height. Allow
the gasket material to cure prior to engine cylinder
head cover installation.
INSTALLATION
(1) If a replacement cover is installed, transfer the
CCV valve grommet the oil filler cap from the origi-
nal cover to the replacement cover.
(2) Install engine cylinder head cover. Tighten the
mounting bolts to 10 Nzm (85 in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 1 Engine Cylinder Head Cover
9 - 18 2.5L ENGINEJ
Page 867 of 1784

least 1 600 km (1,000 miles). The oil supplement
need not be drained until the next scheduled oil
change.
(7) Install the engine cylinder head cover.
VALVE TIMING
Disconnect the spark plug wires and remove the
spark plugs.
Remove the engine cylinder head cover.
Remove the capscrews, bridge and pivot assembly,
and rocker arms from above the No.1 cylinder.
Alternately loosen each capscrew, one turn at a
time, to avoid damaging the bridge.
Rotate the crankshaft until the No.4 piston is at
top dead center (TDC) on the compression stroke.
Rotate the crankshaft counterclockwise (viewed
from the front of the engine) 90É.
Install a dial indicator on the end of the No.1 cyl-
inder intake valve push rod. Use rubber tubing to se-
cure the indicator stem on the push rod.
Set the dial indicator pointer at zero.
Rotate the crankshaft clockwise (viewed from the
front of the engine) until the dial indicator pointer
indicates 0.305 mm (0.012 inch) travel distance (lift).
The timing notch index on the vibration damper
should be aligned with the TDC mark on the timing
degree scale.
If the timing notch is more than 13 mm (1/2 inch)
away from the TDC mark in either direction, the
valve timing is incorrect.
If the valve timing is incorrect, the cause may be a
broken camshaft pin. It is not necessary to replace
the camshaft because of pin failure. A spring pin is
available for service replacement.
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the serpentine drive belt and fan
shroud.
(3) Remove the vibration damper retaining bolt
and washer.
(4) Use Vibration Damper Removal Tool 8068 to
remove the damper from the crankshaft (Fig. 1).
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant
to the keyway in the crankshaft and insert the key.
With the key in position, align the keyway on the vi-
bration damper hub with the crankshaft key and tap
the damper onto the crankshaft.
(2) Install the vibration damper retaining bolt and
washer.
(3) Tighten the damper retaining bolt to 108 Nzm
(80 ft. lbs.) torque.(4) Install the serpentine drive belt and tighten to
the specified tension (refer to Group 7, Cooling Sys-
tems for the proper specifications and procedures).
(5) Connect negative cable to battery.
TIMING CASE COVER OIL SEAL REPLACEMENT
This procedure is done with the timing case cover
installed.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the serpentine drive belt.
(3) Remove the vibration damper.
(4) Remove the radiator shroud.
(5) Carefully remove the oil seal (Fig. 2). Make
sure seal bore is clean.
(6) Position the replacement oil seal on Timing
Case Cover Alignment and Seal Installation Tool
6139 with seal open end facing inward. Apply a light
film of Perfect Seal, or equivalent, on the outside di-
ameter of the seal. Lightly coat the crankshaft with
engine oil.
(7) Position the tool and seal over the end of the
crankshaft and insert a draw screw tool into Seal In-
stallation Tool 6139 (Fig. 3). Tighten the nut against
the tool until it contacts the cover.
Fig. 1 Vibration Damper Removal Tool 8068
Fig. 2 Timing Case Cover Oil Seal Removal
9 - 26 2.5L ENGINEJ
Page 872 of 1784

CAMSHAFT PIN REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
WARNING: DO NOT LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAIN COCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND PRES-
SURIZED BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOL-
ANT CAN OCCUR.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Drain the radiator. DO NOT waste reusable
coolant. Drain the coolant into a clean container.
(3) Remove the fan and shroud.
(4) Disconnect the radiator overflow tube, radiator
hoses, automatic transmission fluid cooler pipes (if
equipped).
(5) Remove the radiator.
(6) If equipped with air conditioning:
CAUTION: DO NOT loosen or disconnect any air
conditioner system fittings. Move the condenser
and receiver/drier aside as a complete assembly.
(a) Remove the A/C compressor serpentine drive
belt idler pulley.
(b) Disconnect and remove the generator.
(c) Remove the A/C condenser attaching bolts
and move the condenser and receiver/drier assem-
bly up and out of the way.
(7) Remove the serpentine drive belt.
(8) Remove the crankshaft vibration damper.
(9) Remove the timing case cover. Clean the gas-
ket material from the cover.
(10) Rotate crankshaft until the crankshaft
sprocket timing mark is closest to and on the center
line with the camshaft sprocket timing mark (Fig.
15).
(11) Remove camshaft sprocket retaining bolt.
(12) Remove the crankshaft oil slinger.
(13) Remove the sprockets and chain as an assem-
bly (Fig. 16).CAUTION: The following procedural step must be
accomplished to prevent the camshaft from damag-
ing the rear camshaft plug during pin installation.
(14) Inspect the damaged camshaft pin.
(15) If the pin is a spring-type pin, remove the bro-
ken pin by inserting a self-tapping screw into the pin
and carefully pulling the pin from the camshaft.
(16) If the pin is a dowel-type pin, center-punch it.
Ensure the exact center is located when center-
punching the pin.
CAUTION: Cover the opened oil pan area to prevent
metal chips from entering the pan.
(17) Drill into the pin center witha4mm(5/32
inch) drill bit.
(18) Insert a self-tapping screw into the drilled pin
and carefully pull the pin from the camshaft.
CAMSHAFT BEARINGS
The camshaft rotates within four steel-shelled, bab-
bitt-lined bearings that are pressed into the cylinder
block and then line reamed. The camshaft bearing
bores and bearing diameters are not the same size.
They are stepped down in 0.254 mm (0.010 inch) in-
crements from the front bearing (largest) to the rear
bearing (smallest). This permits easier removal and
installation of the camshaft. The camshaft bearings
are pressure lubricated.
It is not advisable to attempt to replace cam-
shaft bearings unless special removal and instal-
lation tools are available.
Camshaft end play is maintained by the load
placed on the camshaft by the oil pump and distrib-
utor drive gear. The helical cut of the gear holds the
camshaft sprocket thrust face against the cylinder
block face.
Fig. 15 Timing Chain Alignment
Fig. 16 Camshaft and Crankshaft Sprocket and
Chain
J2.5L ENGINE 9 - 31