1994 JEEP CHEROKEE engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 1185 of 1784
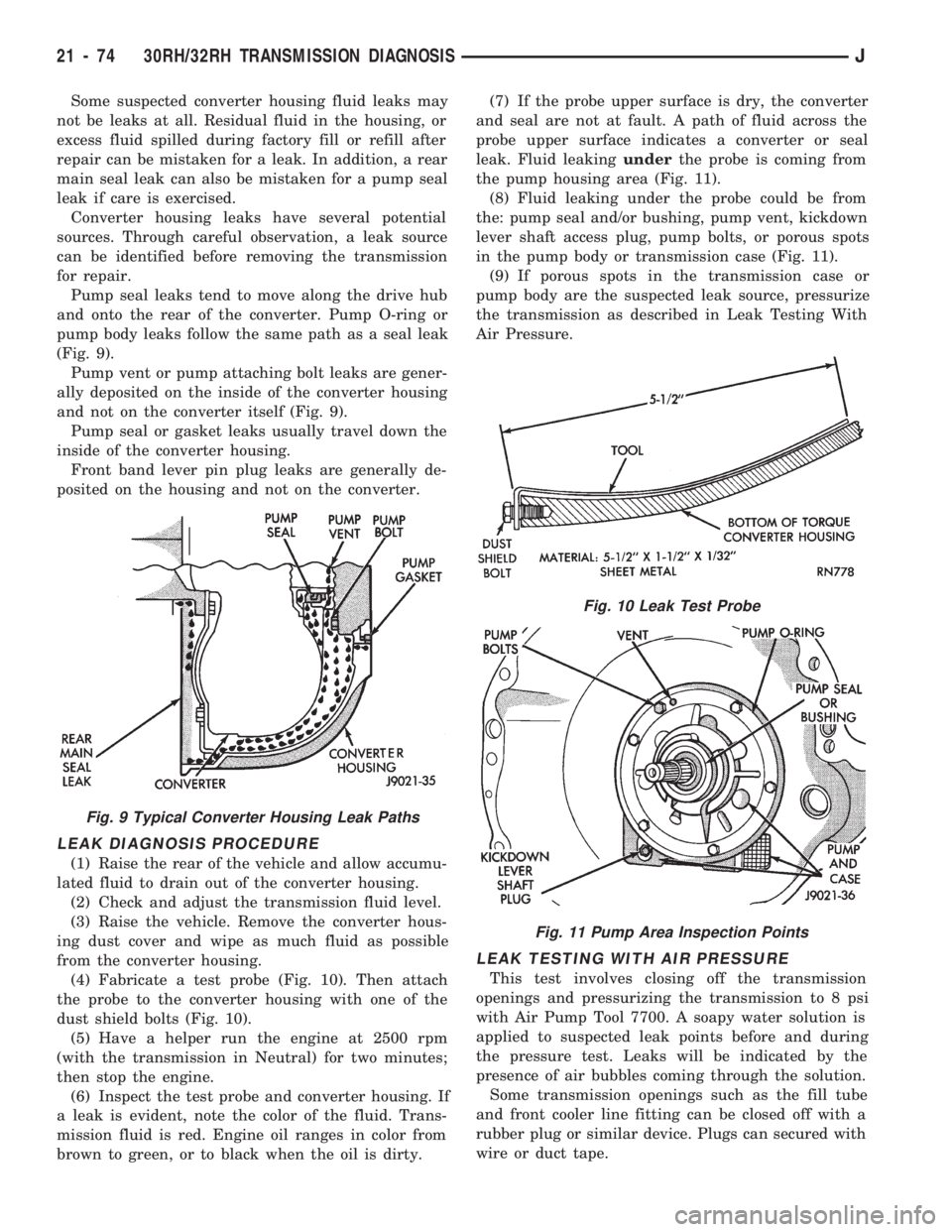
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may
not be leaks at all. Residual fluid in the housing, or
excess fluid spilled during factory fill or refill after
repair can be mistaken for a leak. In addition, a rear
main seal leak can also be mistaken for a pump seal
leak if care is exercised.
Converter housing leaks have several potential
sources. Through careful observation, a leak source
can be identified before removing the transmission
for repair.
Pump seal leaks tend to move along the drive hub
and onto the rear of the converter. Pump O-ring or
pump body leaks follow the same path as a seal leak
(Fig. 9).
Pump vent or pump attaching bolt leaks are gener-
ally deposited on the inside of the converter housing
and not on the converter itself (Fig. 9).
Pump seal or gasket leaks usually travel down the
inside of the converter housing.
Front band lever pin plug leaks are generally de-
posited on the housing and not on the converter.
LEAK DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURE
(1) Raise the rear of the vehicle and allow accumu-
lated fluid to drain out of the converter housing.
(2) Check and adjust the transmission fluid level.
(3) Raise the vehicle. Remove the converter hous-
ing dust cover and wipe as much fluid as possible
from the converter housing.
(4) Fabricate a test probe (Fig. 10). Then attach
the probe to the converter housing with one of the
dust shield bolts (Fig. 10).
(5) Have a helper run the engine at 2500 rpm
(with the transmission in Neutral) for two minutes;
then stop the engine.
(6) Inspect the test probe and converter housing. If
a leak is evident, note the color of the fluid. Trans-
mission fluid is red. Engine oil ranges in color from
brown to green, or to black when the oil is dirty.(7) If the probe upper surface is dry, the converter
and seal are not at fault. A path of fluid across the
probe upper surface indicates a converter or seal
leak. Fluid leakingunderthe probe is coming from
the pump housing area (Fig. 11).
(8) Fluid leaking under the probe could be from
the: pump seal and/or bushing, pump vent, kickdown
lever shaft access plug, pump bolts, or porous spots
in the pump body or transmission case (Fig. 11).
(9) If porous spots in the transmission case or
pump body are the suspected leak source, pressurize
the transmission as described in Leak Testing With
Air Pressure.
LEAK TESTING WITH AIR PRESSURE
This test involves closing off the transmission
openings and pressurizing the transmission to 8 psi
with Air Pump Tool 7700. A soapy water solution is
applied to suspected leak points before and during
the pressure test. Leaks will be indicated by the
presence of air bubbles coming through the solution.
Some transmission openings such as the fill tube
and front cooler line fitting can be closed off with a
rubber plug or similar device. Plugs can secured with
wire or duct tape.
Fig. 9 Typical Converter Housing Leak Paths
Fig. 10 Leak Test Probe
Fig. 11 Pump Area Inspection Points
21 - 74 30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSISJ
Page 1207 of 1784

30RH/32RH IN-VEHICLE SERVICE
INDEX
page page
Checking Fluid Level and Condition........... 96
Front Band Adjustment.................... 99
Gearshift Linkage Adjustment (YJ)............ 96
Governor and Park Gear Service............ 101
Oil Filter Replacement.................... 100
Park Interlock Cable Adjustment (XJ)......... 97
Park Lock Component Replacement......... 102
Park/Neutral Position Switch Service......... 103
Rear Band Adjustment.................... 99
Recommended Fluid...................... 96
Servicing Transmission Cooler Lines and Fittings. 106
Shift Cable Adjustment (XJ)................ 97
Speedometer Service.................... 103
Transmission Cooler Flow Testing........... 106
Transmission Cooler Reverse Flushing....... 105
Transmission Throttle Cable Adjustment (XJ/YJ) . 98
Valve Body Installation................... 101
Valve Body Removal..................... 100
Valve Body Service...................... 100
RECOMMENDED FLUID
The recommended and preferred fluid for 30RH/
32RH transmissions is Mopar ATF Plus, Type 7176.
Mopar Dexron II is acceptable but should only be
used when ATF Plus is not available.
Transmission fluid capacity is approximately 17
pints (7.9 liters). This is the approximate amount of
fluid required to fill the transmission and torque con-
verter after overhaul.
CHECKING FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
(1) Position vehicle on flat, level surface. This is
important in obtaining an accurate fluid level check.
(2) To avoid false readings, which could produce
under or over fill condition, do not check level until
fluid is at normal operating temperature.
(3) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Operate engine at curb idle speed.
WARNING: WHEN PERFORMING UNDERHOOD OP-
ERATIONS WITH THE ENGINE RUNNING, KEEP
YOUR HANDS WELL AWAY FROM HOT OR ROTAT-
ING ENGINE COMPONENTS. DO NOT WEAR
LOOSE ARTICLES OF CLOTHING WHICH COULD
BECOME ENTANGLED IN ENGINE COMPONENTS
OR ACCESSORIES.
(6) Shift transmission through all gear ranges and
back to Neutral (leave engine running).
(7) Clean exterior of dipstick cap and fill tube be-
fore removing transmission dipstick.
(8) Remove dipstick and inspect fluid level.
²Correct level is to FULL mark
²Acceptable level is between ADD and FULL marks
(9) Check fluid condition. Fluid should be dark to
light red in color and free of dirt or debris.
(10) If fluid is discolored or smells burned but
transmission operation was OK, check cooler flow,
flush cooler and lines and change fluid and filter.
Then road test again to confirm proper operation.(11) If fluid is black or dark brown, burned/turned
to sludge, contains large quantities of metal or fric-
tion material particles, transmission will need over-
haul. Especially if problems were evident during
road test and preliminary diagnosis. Fluid cooler
should also be flow tested and flushed if necessary.
GEARSHIFT LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT (YJ)
(1) Check linkage adjustment by starting engine in
Park and Neutral.
(2) Adjustment is OK if engine starts only in park
and Neutral. Adjustment is incorrect if engine starts
in one but not both positions.
(3) If engine starts in any position other than Park
or Neutral, or if engine will not start at all, park/
neutral position switch may be faulty.
(4) Shift transmission into Park.
(5) Raise vehicle.
(6) Check condition of shift rods, bellcrank, bell-
crank brackets and linkage bushings/grommets (Fig.
1). Tighten, repair, replace worn, damaged parts. Do
not attempt adjustment if linkage components are
worn or damaged.
(7) Loosen shift rod trunnion lock bolt or nut. Be
sure upper shift rod slides freely in trunnion (Fig. 1).
Also be sure shift rods and bellcrank rotate freely
and do not bind at any point.
(8) Verify that manual lever is in Park detent
(Fig. 1). Move lever all the way rearward to be sure
it is in Park.
(9) Check for positive engagement of park lock by
attempting to rotate propeller shaft. Shaft will not
turn when park pawl is engaged.
(10) Adjust shift rod trunnion to a obtain free pin
fit in bellcrank arm and tighten trunnion lock bolt or
nut. Prevent shift rod from turning while tightening
bolt or nut. Gearshift linkage lash must be elimi-
nated to obtain proper adjustment. Eliminate lash by
pulling downward on shift rod and pressing upward
on bellcrank.
21 - 96 30RH/32RH IN-VEHICLE SERVICEJ
Page 1210 of 1784

THROTTLE CABLE ADJUSTMENT
PROCEDURE
Cable adjustment is performed entirely in the
engine compartment. It is not necessary to raise
the vehicle for access to any other components.
(1) Shift transmission into Park and shut engine
off.
(2) Press cable release button (Fig. 5).
(3) Push cable conduit back into cable adjuster
body as far as possible (Fig. 6).
(4) Rotate throttle body lever to wide open throttle
position. Cable will ratchet to correct adjustment
point as lever is rotated (Fig. 6).
FRONT BAND ADJUSTMENT
The front band adjusting screw is located on the
left side of the transmission case above the manual
valve and throttle valve levers.
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Loosen band adjusting screw locknut. Then
back locknut off 4-5 turns.
(3) Clean adjusting screw threads with Mopar rust
penetrant if necessary. Then lubricate threads withMopar spray lube or petroleum jelly. Be sure screw
turns freely in case. This is necessary for accurate
adjustment.
(4) Tighten band adjusting screw to 8 Nzm (72 in.
lbs.) torque with inch-pound torque wrench.If
Adapter Extension C-3705 is needed in order to
reach adjusting screw, tighten screw to only 5-6
Nzm (47-50 in. lbs.) torque (Fig. 7).
(5) Back off front band adjusting screw as follows:
²On 30RH (2.5L), back adjusting screw off
2-1/2 turns
²On 32RH (4.0L), back adjusting screw off
2-1/4 turns
(6) Hold adjuster screw in position and tighten
locknut to 41 Nzm (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Lower vehicle.
REAR BAND ADJUSTMENT
The transmission oil pan must be removed for ac-
cess to the rear (low-reverse) band adjusting screw.
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Remove transmission oil pan and drain fluid.
(3) Loosen band adjusting screw locknut 5-6 turns.
Be sure adjusting screw turns freely in lever.
(4) Tighten adjusting screw as follows: On 32Rh
transmission, tighten screw to 8 Nzm (72 in. lbs.)
torque. On 30RH transmission, tighten adjusting
screw to 5 Nzm (41 in. lbs.) torque (Fig. 8).
(5) Back off rear band adjusting screw as follows:
²On 30RH (2.5L), back adjusting screw off 7
turns
²On 32RH (4.0L), back adjusting screw off 4
turns
(6) Hold adjusting screw in place and tighten lock-
nut to 34 Nzm (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Position new gasket on oil pan and install pan
on transmission. Tighten pan bolts to 17 Nzm (150 in.
lbs.) torque.
(8) Lower vehicle and refill transmission with rec-
ommended fluid.
Fig. 5 Throttle Valve Cable Components
Fig. 6 Throttle Valve Cable Adjustment
Fig. 7 Front Band Adjustment
J30RH/32RH IN-VEHICLE SERVICE 21 - 99
Page 1217 of 1784

condenser. The auxiliary cooler is a serviceable com-
ponent and can be repaired if necessary.
The main and auxiliary coolers should be thor-
oughly reverse flushed if a transmission failure
contaminates the fluid. Reverse flushing the cooler
and lines will prevent sludge and particles from
flowing back into the transmission after repair.
The same flushing procedure is used for main and
auxiliary coolers. Pressure equipment is preferred for
reverse flushing. However, reverse flushing can be
performed using hand operated equipment as de-
scribed in the following procedure.
REVERSE FLUSHING PROCEDURE
(1) Disconnect cooler lines at transmission. Refer
to Figure 21 for cooler line fitting identification.
Front fitting is outlet to cooler and rear fitting is in-
let from cooler.
(2) Position drain pan under cooler outlet line to
material flushed through cooler and lines.
(3) Reverse flush cooler using hand operated suc-
tion gun filled with mineral spirits. Insert gun nozzle
(or hose) into cooler inlet (return) line. Then force
mineral spirits through Line and cooler.
(4) Continue reverse flushing until fluid exiting in-
let (pressure) line is clear and free of debris/residue.
Replace radiator if fluid cannot be pumped
through cooler.
(5) Clear flushing materials from cooler and lines
with short pulses of compressed air. Insert air gun
nozzle into cooler inlet (return) line and continue
short pulses of air until all fluid is cleared from
cooler and lines.
(6) Pump one quart of fresh automatic transmis-
sion fluid through cooler and lines before reconnect-
ing cooler lines.
TRANSMISSION COOLER FLOW TESTING
The transmission main and auxiliary coolers
should be flow tested whenever a fluid overheat con-
dition is suspected. An overheat condition is indi-
cated when the fluid changes from the normal red, to
a dark orange, or brown color.
The same method of flow testing is used for both
coolers.Cooler flow is checked by measuring the amount of
fluid flow through the cooler in a 20 second time pe-
riod. The test is performed with the engine running
and transmission in neutral. Fluid is then pumped
through the cooler by the transmission oil pump.
(1) Disconnect cooler inlet line at transmission fitting.
(2) Securely attach hose to end of inlet line and po-
sition line in a one quart test container.
(3) Add extra quart of fluid to transmission.
(4) Use stopwatch to check flow test time.
(5) Shift transmission into neutral and set parking
brake.
(6) Start and run engine at curb idle speed and im-
mediately note cooler flow. Approximately one quart of
fluid should flow into test container in 20 second period.
(7) If cooler flow is intermittent, flows less than
one quart in 20 seconds, or does not flow at all,
cooler is faulty and must be replaced.
SERVICING TRANSMISSION COOLER LINES AND
FITTINGS
Fitting Types
The transmission cooler lines are attached with
quick disconnect fittings.
A flange on the cooler line serves as the sealing
mechanism. The wire retainer clip (Fig. 22), secures
the cooler line in the fitting by this flange. The clip
fits behind the flange to hold the line in place.
Three different fitting styles may be used. Type 1
fittings have the retainer clip exposed (Fig. 22). Type
2 fittings have the retainer clip and fitting body en-
cased in a shrink wrap material (Fig. 23). Type 3 fit-
tings have the retainer clip encased in a metal sleeve
crimped onto the fitting body (Fig. 24).
Fitting Release Tool
A release tool isrequiredto disconnect each of the
fitting types. A plastic tool is clipped directly to one
of the cooler lines on models with the type 2 and 3
fittings. This tool can also be used to disconnect type
1 fittings. The tool is needed to spread the wire re-
tainer clip in each fitting. The clip must be opened in
order to release the cooler line from the fitting.
Fig. 21 Identifying Transmission Cooler Lines
Fig. 22 Type 1 Quick Disconnect Fitting
21 - 106 30RH/32RH IN-VEHICLE SERVICEJ
Page 1219 of 1784

30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
INDEX
page page
ConverterÐPump SealÐDrive Plate Service . . . 109
Transmission and Converter Installation....... 109Transmission and Converter Removal........ 108
TRANSMISSION AND CONVERTER REMOVAL
(1) Remove fan shroud attaching bolts.
(2) Disconnect transmission fill tube at upper
bracket.
(3) Raise vehicle.
(4) Remove inspection cover from converter hous-
ing and remove skid plate for access, if necessary.
(5) Remove transmission fill tube and fill tube
O-ring.
(6) Remove starter motor.
(7) Mark propeller shafts and axle yokes for align-
ment reference.
(8) Disconnect propeller shafts at yokes. Secure
shafts to frame rails with wire.
(9) Disconnect exhaust pipes at exhaust manifolds,
if necessary.
(10) Drain transfer case lubricant.
(11) Disconnect vehicle speed sensor wires.
(12) Disconnect transfer case shift linkage.
(13) Disconnect gearshift linkage and throttle ca-
ble at transmission levers.
(14) Disconnect park/neutral position switch wires.
(15) Disconnect and remove crankshaft position
sensor. Retain sensor bolt for reinstallation.
CAUTION: The crankshaft position sensor can be
damaged during transmission removal (or installa-
tion) if the sensor is still bolted to the engine block.
To avoid damage, remove the sensor before remov-
ing the transmission.
(16) Remove converter housing access cover and
mark drive plate and converter for alignment refer-
ence.
(17) Remove bolts attaching converter to drive
plate.
(18) Support engine with support stand.
(19) Support transmission-transfer case assembly
with transmission jack. Secure transmission to jack
with safety chain.
(20) Remove bolts/nuts attaching cushion and
torque arm bracket to skid plate (Fig. 1).
(21) Remove skid plate, or rear crossmember, if
equipped.
(22) Lower transmission slightly and disconnect
cooler lines at transmission.Refer to In-Vehicle
Service section for procedures.(23) Remove bolts attaching transmission to en-
gine.
(24) Move transmission and converter rearward
until clear of crankshaft.
(25) Hold converter in position and lower transmis-
sion until converter housing clears engine.
(26) Remove converter from transmission.
(27) Remove transfer case from transmission.
(28) If necessary, following components can now be
serviced:
²torque converter
²torque converter drive plate
²oil pump seal
²engine rear core hole plugs
²engine rear oil galley plugs
Fig. 1 Transmission Rear Mount
21 - 108 30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION REMOVAL AND INSTALLATIONJ
Page 1220 of 1784
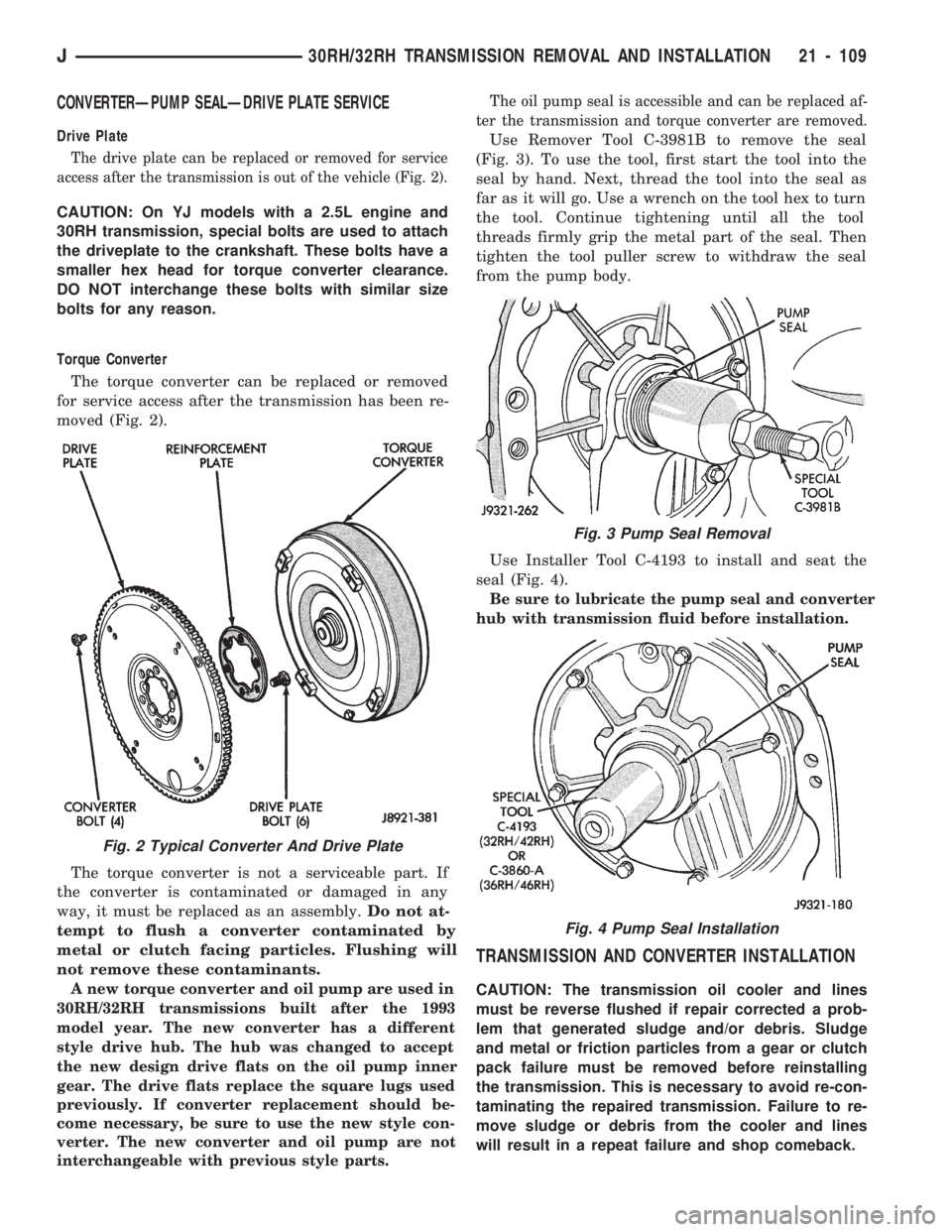
CONVERTERÐPUMP SEALÐDRIVE PLATE SERVICE
Drive Plate
The drive plate can be replaced or removed for service
access after the transmission is out of the vehicle (Fig. 2).
CAUTION: On YJ models with a 2.5L engine and
30RH transmission, special bolts are used to attach
the driveplate to the crankshaft. These bolts have a
smaller hex head for torque converter clearance.
DO NOT interchange these bolts with similar size
bolts for any reason.
Torque Converter
The torque converter can be replaced or removed
for service access after the transmission has been re-
moved (Fig. 2).
The torque converter is not a serviceable part. If
the converter is contaminated or damaged in any
way, it must be replaced as an assembly.Do not at-
tempt to flush a converter contaminated by
metal or clutch facing particles. Flushing will
not remove these contaminants.
A new torque converter and oil pump are used in
30RH/32RH transmissions built after the 1993
model year. The new converter has a different
style drive hub. The hub was changed to accept
the new design drive flats on the oil pump inner
gear. The drive flats replace the square lugs used
previously. If converter replacement should be-
come necessary, be sure to use the new style con-
verter. The new converter and oil pump are not
interchangeable with previous style parts.The oil pump seal is accessible and can be replaced af-
ter the transmission and torque converter are removed.
Use Remover Tool C-3981B to remove the seal
(Fig. 3). To use the tool, first start the tool into the
seal by hand. Next, thread the tool into the seal as
far as it will go. Use a wrench on the tool hex to turn
the tool. Continue tightening until all the tool
threads firmly grip the metal part of the seal. Then
tighten the tool puller screw to withdraw the seal
from the pump body.
Use Installer Tool C-4193 to install and seat the
seal (Fig. 4).
Be sure to lubricate the pump seal and converter
hub with transmission fluid before installation.
TRANSMISSION AND CONVERTER INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The transmission oil cooler and lines
must be reverse flushed if repair corrected a prob-
lem that generated sludge and/or debris. Sludge
and metal or friction particles from a gear or clutch
pack failure must be removed before reinstalling
the transmission. This is necessary to avoid re-con-
taminating the repaired transmission. Failure to re-
move sludge or debris from the cooler and lines
will result in a repeat failure and shop comeback.
Fig. 2 Typical Converter And Drive Plate
Fig. 3 Pump Seal Removal
Fig. 4 Pump Seal Installation
J30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION 21 - 109
Page 1267 of 1784

AW-4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
CONTENTS
page page
AW-4 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE............. 173
AW-4 TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS........ 167
AW-4 TRANSMISSION OVERHAUL........ 192
AW-4 TRANSMISSION REMOVAL AND
INSTALLATION....................... 189GENERAL INFORMATION................ 156
TRANSMISSION/TRANSFER CASE
SPECIFICATIONS..................... 320
GENERAL INFORMATION
INDEX
page page
Components and Operation................ 157
Description............................ 156
FirstÐThirdÐReverse Gear Components...... 159
Fourth Gear Overdrive Components......... 158
Geartrain Operation and Application Charts.... 159Hydraulic System........................ 160
Torque Converter........................ 158
Transmission Identification................. 157
Transmission Ranges and Shift Lever Positions . 157
DESCRIPTION
The AW-4 is a 4-speed, electronically controlled au-
tomatic transmission (Fig. 1). Running gear consists
of a torque converter, oil pump, three planetary gear
sets, clutch and brake units, hydraulic accumulators,
a valve body with electrical solenoids and a transmis-sion control module (TCM). The AW-4 is used in XJ
models with a 4.0L engine.
Cables are used for shifting and transmission
throttle pressure control. A park/neutral position
switch permits engine starting in Park and Neutral
range only.
Fig. 1 AW-4 Automatic Transmission
21 - 156 TRANSMISSION AND TRANSFER CASEJ
Page 1280 of 1784

PRESSURE TEST ANALYSIS
If pressures in D and Reverse are higher than
specified, check for the following:
²throttle cable loose, worn, binding or out of adjust-
ment
²throttle valve, downshift plug, throttle cam, or pri-
mary regulator valve are sticking, worn or damaged
If pressures in D and Reverse are lower than spec-
ified, check for following:
²throttle cable loose, worn, binding or out of adjust-
ment
²throttle valve, downshift plug, throttle cam stick-
ing, worn or damaged
²primary regulator valve sticking, worn, or dam-
aged
²oil pump gears or housing worn or damaged
²overdrive clutch worn or damaged
If pressures are low in D range only, check for fol-
lowing:
²forward clutch worn or damaged
²fluid leakage in D range circuit (component seal
and O-rings)
If pressures are low in Reverse only, check for fol-
lowing:
²shift cable and manual valve out of adjustment
²fluid leakage in reverse circuit (component seal
and O-rings)
²direct clutch worn or damaged
²first/reverse brake worn or damaged
TORQUE CONVERTER STALL TEST
Stall testing checks the holding ability of the trans-
mission clutches and brakes and of the torque con-
verter stator overrunning clutch.
(1) Be sure transmission fluid is at normal operat-
ing temperature.
(2) Connect tachometer to engine. Position tachom-
eter so it can be viewed from drivers seat.
(3) Apply parking brakes and block wheels.
(4) Apply and hold service brakes.
(5) Shift transfer case into 2H position. On models
with NP249 transfer case, leave transfer case in 4H
position.
(6) Start engine.
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW ANYONE TO STAND AT
THE FRONT OR REAR OF THE VEHICLE DURING
THE TEST.
(7) Shift transmission into D range.
(8) Press accelerator pedal to wide open throttle
position and note maximum engine rpm. Stall speed
should be 2100 to 2400 rpm in D range.
CAUTION: Do not maintain wide open throttle for
more than 3-4 seconds at a time.(9) Release throttle and shift transmission into
Neutral. Allow transmission fluid to cool for 15-20
seconds.
(10) Shift transmission into Reverse.
(11) Press accelerator down to wide open throttle
position and note maximum engine rpm. Stall speed
should be 2100-to-2400 rpm in Reverse.
STALL SPEED TEST ANALYSIS
If engine rpm is lower than specified in D and Re-
verse, check for the following:
²engine output/performance insufficient
²stator overrunning clutch in torque converter not
holding if engine speed was 1500 rpm or less.
If stall speed in D range is higher than specified,
check for the following:
²line pressure low
²forward clutch slipping
²No. 2 one-way clutch not holding
²overdrive one-way clutch not holding
If stall speed in Reverse was higher than specified,
check for the following:
²line pressure low
²direct clutch slipping
²first/ reverse brake slipping
²overdrive one-way clutch not holding
If stall speeds were higher than specified in both D
and Reverse, check for the following:
²low fluid level
²line pressure low
²overdrive one-way clutch not holding
TIME LAG TEST
This test checks general condition of the overdrive
clutch, forward clutch, rear clutch and first/reverse
brake. Condition is indicated by the amount of time
required for clutch/brake engagement with the en-
gine at curb idle speed. Engagement time is mea-
sured for D and Reverse positions. A stop watch is
recommended for test accuracy.
TEST PROCEDURE
(1) Check and adjust transmission fluid level if
necessary.
(2) Bring transmission to normal operating tem-
perature.
(3) Apply parking brakes and turn off air condi-
tioning unit.
(4) Shift transfer case into 2H range. On models
with NP249 transfer case, leave transfer case in 4H
range.
(5) Start engine and check curb idle speed. Adjust
speed if necessary. Curb idle must be correct to en-
sure accurate test results.
(6) Shift transmission into Neutral and set stop
watch.
(7) During following test steps, start stop watch as
soon as shift lever reaches D and Reverse ranges.
JAW-4 TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 169