1994 JEEP CHEROKEE open hood
[x] Cancel search: open hoodPage 257 of 1784

WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUM-
BER 6094) (FIG. 26). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUM-
BER HPC-20) MAY BE USED FOR LARGER
CLAMPS. ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES
WHEN SERVICING CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only an original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Observe the previousWARNINGS.
(3) Remove pressure cap.
(4) For access to radiator draincock, remove radia-
tor grille (Fig. 29).
(5) Attach one end of a 24 inch long X 1/4 inch ID
hose to the radiator draincock. Put the other end into
a clean container. Open draincock and drain radia-
tor.
(6) If equipped, disconnect electric cooling fan elec-
trical connector (Fig. 31).
(7) Remove electric fan mounting bolts. Lift fan
straight up and out of engine compartment.
(8) Remove the mechanical (non-electrical) fan
shroud mounting bolts. Lift shroud up until align-ment tabs at the bottom are clear of slots in bracket
at bottom of radiator (Fig. 32). Place shroud over me-
chanical fan.
(9) If equipped, disconnect and plug automatic
transmission fluid cooler lines. If equipped with re-
mote cooler, remove line to cooler from bracket at
bottom of radiator.
(10) Disconnect radiator upper and lower hoses.
(11) Mark the position of the hood latch striker on
the radiator crossmember and remove hood latch
striker.
(12) Remove radiator upper crossmember bracket.
(13) Remove radiator upper crossmember.
(14) If equipped with air conditioning, separate ra-
diator from condenser by removing condenser-to-radi-
ator mounting brackets (Fig. 33).
(15) Lift radiator straight up and out of engine
compartment taking care not to damage fins.
INSTALLATION
The radiator has two alignment dowels. They are
located on the bottom tank and fit into rubber grom-
mets in the radiator lower crossmember.
(1) Lower radiator into engine compartment. Posi-
tion alignment dowels into grommets in radiator
lower crossmember (Fig. 34).
(2) If equipped with air conditioning, attach con-
denser to radiator with mounting brackets (Fig. 33).
(3) Install radiator upper crossmember.
(4) Install radiator upper crossmember bracket.
(5) Install hood latch striker.
(6) Connect radiator upper and lower hoses.
Fig. 31 Auxiliary FanÐRemove/Install
Fig. 32 Auxiliary Fan and Mechanical Fan
ShroudÐRemove/InstallÐTypical
7 - 24 COOLING SYSTEMJ
Page 275 of 1784
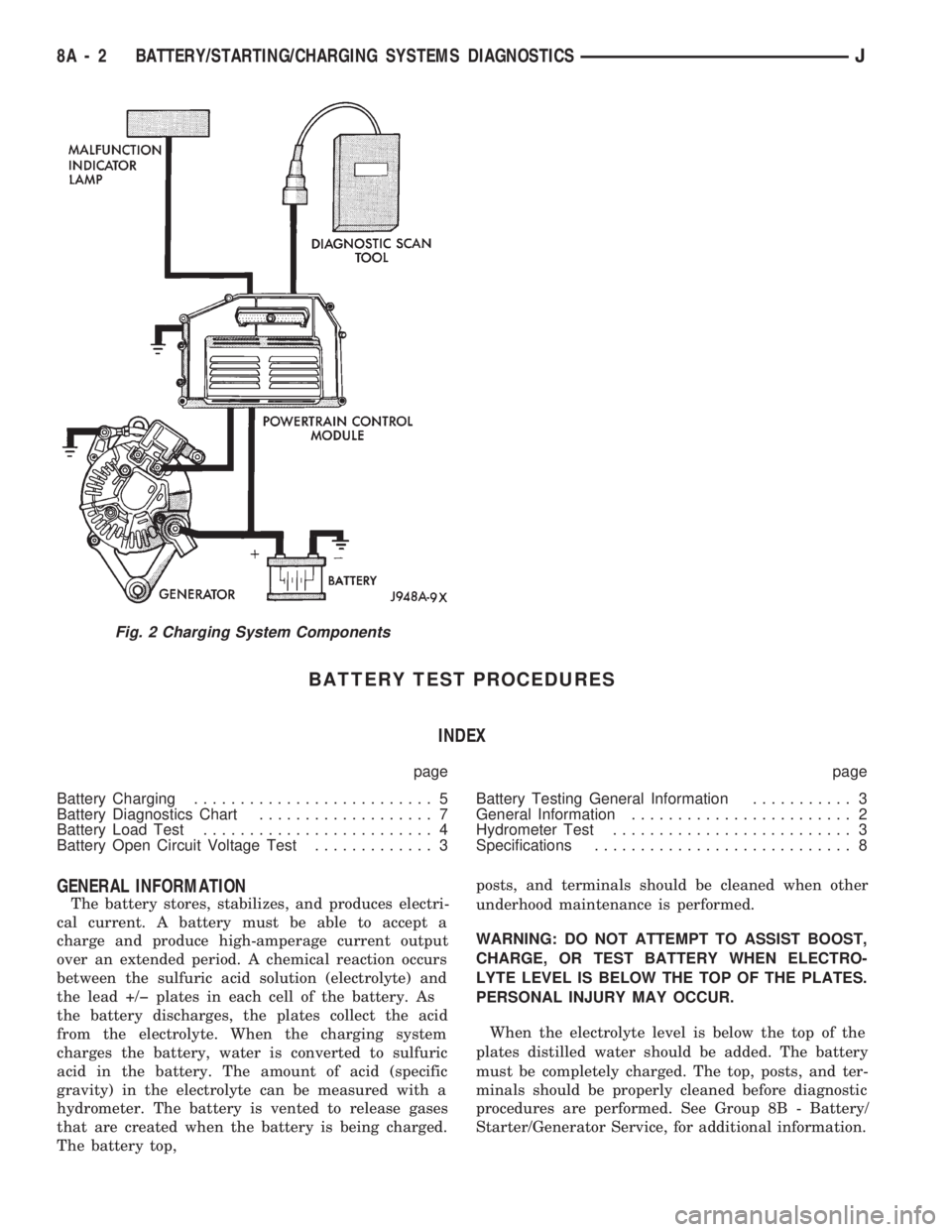
BATTERY TEST PROCEDURES
INDEX
page page
Battery Charging.......................... 5
Battery Diagnostics Chart................... 7
Battery Load Test......................... 4
Battery Open Circuit Voltage Test............. 3Battery Testing General Information........... 3
General Information........................ 2
Hydrometer Test.......................... 3
Specifications............................ 8
GENERAL INFORMATION
The battery stores, stabilizes, and produces electri-
cal current. A battery must be able to accept a
charge and produce high-amperage current output
over an extended period. A chemical reaction occurs
between the sulfuric acid solution (electrolyte) and
the lead +/þ plates in each cell of the battery. As
the battery discharges, the plates collect the acid
from the electrolyte. When the charging system
charges the battery, water is converted to sulfuric
acid in the battery. The amount of acid (specific
gravity) in the electrolyte can be measured with a
hydrometer. The battery is vented to release gases
that are created when the battery is being charged.
The battery top,posts, and terminals should be cleaned when other
underhood maintenance is performed.
WARNING: DO NOT ATTEMPT TO ASSIST BOOST,
CHARGE, OR TEST BATTERY WHEN ELECTRO-
LYTE LEVEL IS BELOW THE TOP OF THE PLATES.
PERSONAL INJURY MAY OCCUR.
When the electrolyte level is below the top of the
plates distilled water should be added. The battery
must be completely charged. The top, posts, and ter-
minals should be properly cleaned before diagnostic
procedures are performed. See Group 8B - Battery/
Starter/Generator Service, for additional information.
Fig. 2 Charging System Components
8A - 2 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICSJ
Page 281 of 1784

SPECIFICATIONS
IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD) DIAGNOSIS
GENERAL INFORMATION
Ignition off draw refers to power being drained
from the battery with the ignition switch turned off.
A normal vehicle electrical system will draw from 5
to 20 milliamps. This is with the ignition switch in
the OFF position, and all non-ignition controlled cir-
cuits in proper working order. A vehicle that has not
been operated for approximately 20 days, may dis-
charge the battery to an inadequate level. Battery
drain should not exceed approximately 20 MA (20
milliamps = 0.020 amps).
The 20 MA are needed to supply PCM memory,
digital clock memory, and ETR (electronically tuned
radio) memory.
Excessive battery drain is caused by items left
turned on, internally shorted generator, or intermit-
tent short in wiring.
If the IOD is over 20 milliamperes, the defect must
be found and corrected before replacing a battery. In
most cases the battery can be charged and returned
to service.
When a vehicle will not be used for 20 days or
more (stored), remove IOD fuse in the Power Distri-
bution Center to reduce battery discharging.
TEST PROCEDURE
Testing for higher amperage IOD must be per-
formed first to prevent damage to most milliamp
meters.
(1) Verify that all electrical accessories are OFF.
Turn off all lamps, remove ignition key, and close all
doors. If the vehicle is equipped with electronic acces-
sories (illuminated entry, high line radio), allow the
systems to automatically shut off (time out), up to 3
minutes.
(2) Determine that the underhood lamp is operat-
ing properly, then disconnect or remove bulb.
(3) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(4) Connect a typical 12-volt test lamp (low watt-
age bulb) between the negative cable clamp and the
battery negative terminal. If equipped with security
alarm, cycle the key in the door to turn off the flash-ing lights. Make sure that the doors remain closed so
that illuminated entry is not activated.
The test lamp may light brightly for up to 3 min-
utes or may not light at all (depending on the elec-
trical equipment). The term brightly being used
throughout the following tests, implies the bright-
ness of the test lamp will be the same as if it were
connected across the battery.
The test lamp must be securely clamped to the neg-
ative cable and battery terminal. If the test lamp be-
comes disconnected during any part of the IOD test,
the electronic timer function will be activated and all
tests must be repeated.
If the ammeter circuit is broken the Security
Alarm Module will turn on parking lamps.
(5) After 3 minutes, the test lamp should turn OFF
or be DIMLY lit (depending on the electrical equip-
ment). If the test lamp remains brightly lit do not
disconnect it. Remove each fuse or circuit breaker
(refer to Group 8 - Wiring Diagrams) until test lamp
is either OFF or DIMLY lit. This will eliminate the
higher amperage draw.
If test lamp is still bright after disconnecting each
fuse and circuit breaker, disconnect the wiring har-
ness from the generator. Refer to Generator Test Pro-
cedures in this group. Do not disconnect the test
lamp.
After higher amperage IOD has been corrected, low
amperage IOD may be checked.
It is now safe to install milliamp meter to check for
low amperage IOD.
(6) With test lamp still connected securely, clamp
an ammeter between battery negative terminal and
negative battery cable.
Do not open any doors or turn on any electri-
cal accessories with the test lamp disconnected
or the meter may be damaged.
(7) Disconnect test lamp. The current draw should
not exceed 0.020 amp. If it exceeds 0.020 milliamps,
isolate each circuit by removing circuit breakers and
fuses. The meter reading drops once the high current
problem is found. Repair this section of the circuit,
whether it is a wiring short or component failure.
BATTERY CLASSIFICATIONS AND RATINGSTORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
8A - 8 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICSJ
Page 428 of 1784

LAMPS
CONTENTS
page page
EXTERIOR LAMPS....................... 1
INTERIOR LAMPS...................... 19SPECIFICATIONS....................... 23
EXTERIOR LAMPS
INDEX
page page
Back-up/Rear Turn Signal/Tail Lamp Bulb
Replacement........................... 9
Center High Mounted Stop Lamp (CHMSL)ÐXJ . 10
Center High Mounted Stop Lamp (CHMSL)ÐYJ . 11
Daytime Running Lights (Canada Only)........ 16
DRL Module Replacement.................. 16
Fog Lamp Beam Adjustment................ 12
Fog Lamp Bulb/Element Replacement......... 13
Fog Lamp Replacement................... 15
Fog Lamp Service Information............... 12
Fog Lamp Switch Replacement.............. 14
Fog Lamp Trouble Diagnosis................ 12
Front Park/Turn Signal Lamp Bulb Replacement . . 8
Headlamp Beam Adjustment................. 3
Headlamp Bulb Replacement................ 3
Headlamp Delay Function Trouble DiagnosisÐXJ
Vehicles.............................. 16Headlamp Delay Module ReplacementÐXJ
Vehicles.............................. 16
Headlamp Dimmer Switch Replacement........ 6
Headlamp Switch Replacement............... 4
Headlamp Trouble DiagnosisÐXJ Vehicles...... 1
Headlamp Trouble DiagnosisÐYJ Vehicles...... 2
License Plate Lamp....................... 10
Sentinel Headlamp Delay ModuleÐXJ Vehicles . . 15
Service Information........................ 1
Side Marker Lamp Bulb Replacement.......... 7
Switch Tests............................. 2
Underhood Lamp Bulb Replacement.......... 18
Underhood Lamp Replacement.............. 18
Underhood Lamp Service Information......... 17
SERVICE INFORMATION
Exterior lamp circuits are comprised of the head-
lamp circuit, fog lamp circuit, and tail/side marker/
park lamp circuit. Battery voltage is controlled by
both the headlamp ON/OFF switch and headlamp
dimmer switch.
The dimmer switch functions as a fog lamp switch.
Voltage is applied to the fog lamp switch only when
the dimmer switch is in the low beam position.
HEADLAMP TROUBLE DIAGNOSISÐXJ VEHICLES
LOW AND HIGH BEAM INOPERATIVE BOTH
HEADLAMPS
(1) Place the headlamp switch in the ON position.
(2) Test the 40 amp fuse for continuity. If bad, re-
place fuse.
(3) Insert the test probe into terminal 5 of the
front lamp wire harness connector. Measure the re-
sistance from terminal 5 to body ground. The ohm-
meter should indicate zero ohms. If not OK, repair
the open circuit in the harness to body ground.(4) Disconnect the front lamp wire connector. Mea-
sure resistance between connector terminals 5 and 2.
Next measure between terminal 5 and 7. The ohm-
meter should indicate zero ohms for both measure-
ments. If not OK, replace the headlamp bulbs.
(5) Measure the voltage between the dimmer
switch wire connector terminal 2 and body ground.
The voltmeter should indicate battery voltage. If not
OK, continue with the next step.
The dimmer switch is integral with the turn
signal and is located on the steering column.
The dimmer switch switches the headlamp beam
when the turn signal lever is pulled rearward.
(6) Disconnect the dimmer switch wire connector
and place the headlamp switch in the OFF position.
Measure the resistance from terminal 2 to vehicle
body ground. The ohmmeter should indicate infinite
resistance. If OK, replace the headlamp switch and
continue with the next step. If not OK, repair the
short circuit in the wire harness that leads to termi-
nal 2.
JLAMPS 8L - 1
Page 444 of 1784
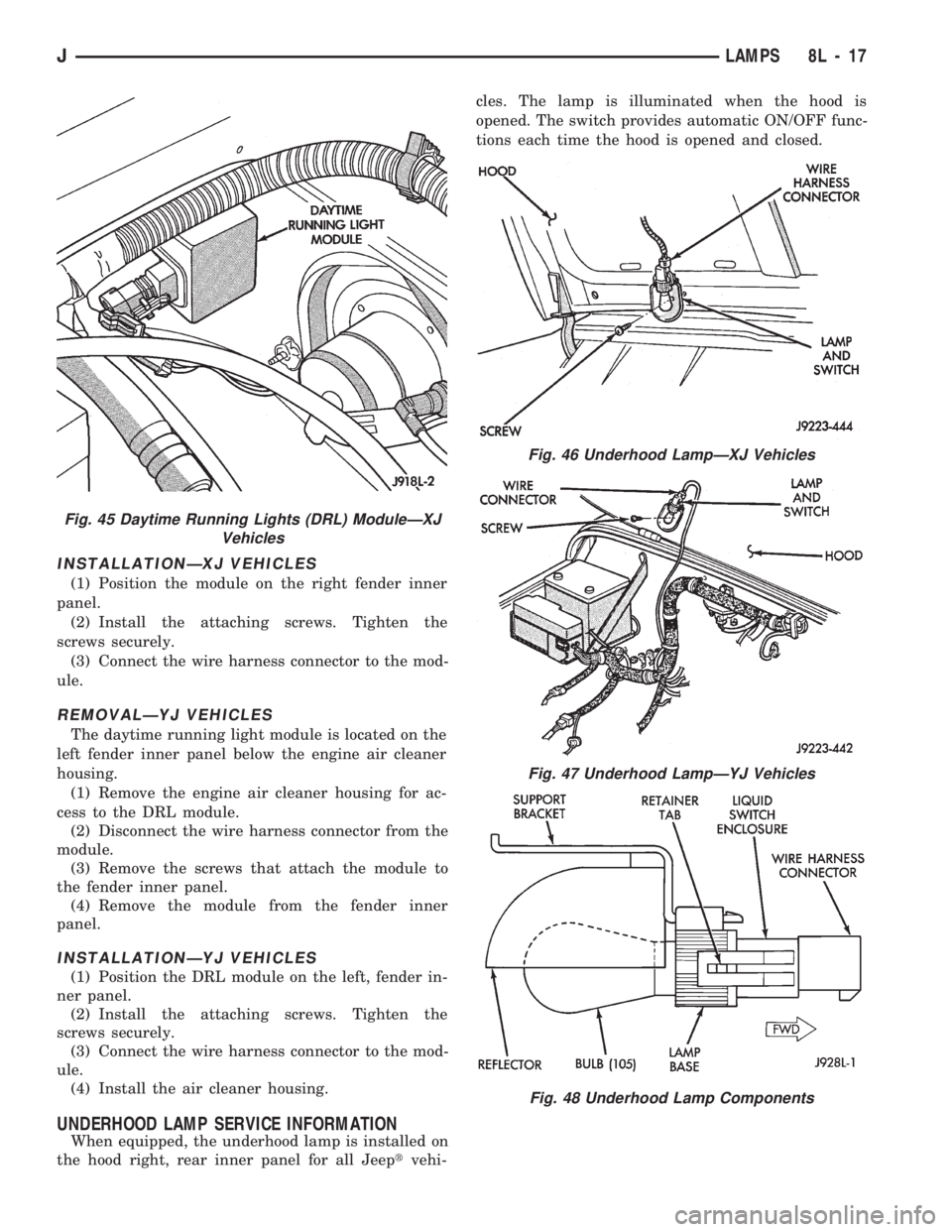
INSTALLATIONÐXJ VEHICLES
(1) Position the module on the right fender inner
panel.
(2) Install the attaching screws. Tighten the
screws securely.
(3) Connect the wire harness connector to the mod-
ule.
REMOVALÐYJ VEHICLES
The daytime running light module is located on the
left fender inner panel below the engine air cleaner
housing.
(1) Remove the engine air cleaner housing for ac-
cess to the DRL module.
(2) Disconnect the wire harness connector from the
module.
(3) Remove the screws that attach the module to
the fender inner panel.
(4) Remove the module from the fender inner
panel.
INSTALLATIONÐYJ VEHICLES
(1) Position the DRL module on the left, fender in-
ner panel.
(2) Install the attaching screws. Tighten the
screws securely.
(3) Connect the wire harness connector to the mod-
ule.
(4) Install the air cleaner housing.
UNDERHOOD LAMP SERVICE INFORMATION
When equipped, the underhood lamp is installed on
the hood right, rear inner panel for all Jeeptvehi-cles. The lamp is illuminated when the hood is
opened. The switch provides automatic ON/OFF func-
tions each time the hood is opened and closed.
Fig. 45 Daytime Running Lights (DRL) ModuleÐXJ
Vehicles
Fig. 46 Underhood LampÐXJ Vehicles
Fig. 47 Underhood LampÐYJ Vehicles
Fig. 48 Underhood Lamp Components
JLAMPS 8L - 17
Page 843 of 1784

can easily be wiped off. Components should be
torqued in place within 15 minutes. The use of a lo-
cating dowel is recommended during assembly to pre-
vent smearing the material off location.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE
To provide best vehicle performance and lowest ve-
hicle emissions, it is most important that the tune-up
be done accurately. Use the specifications listed on
the Vehicle Emission Control Information label
found on the engine compartment hood.
(1) Test battery specific gravity. Add water, if nec-
essary. Clean and tighten battery connections.
(2) Test cranking amperage draw (refer to Group
8B, Battery/Starter Service for the proper proce-
dures).
(3) Tighten the intake manifold bolts (refer to
Group 11, Exhaust System and Intake Manifold for
the proper specifications).
(4) Perform cylinder compression test:
(a) Check engine oil level and add oil, if neces-
sary.
(b) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature.
(c) Select a route free from traffic and other
forms of congestion, observe all traffic laws and
briskly accelerate through the gears several times.
The higher engine speed may help clean out valve
seat deposits which can prevent accurate compres-
sion readings.
CAUTION: DO NOT overspeed the engine.
(d) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As
spark plugs are being removed, check electrodes for
abnormal firing indicators - fouled, hot, oily, etc.
Record cylinder number of spark plug for future
reference.
(e) Disconnect coil wire from distributor and se-
cure to good ground to prevent a spark from start-
ing a fire.
(f) Be sure throttle blades are fully open during
the compression check.
(g) Insert compression gage adaptor into the
No.1 spark plug hole. Crank engine until maxi-
mum pressure is reached on gauge. Record this
pressure as No.1 cylinder pressure.
(h) Repeat Step 4g for all remaining cylinders.
(i) Compression should not be less than 689 kPa
(100 psi) and not vary more than 172 kPa (25 psi)
from cylinder to cylinder.
(j) If cylinder(s) have abnormally low compres-
sion pressures, repeat steps 4a through 4h.
(k) If the same cylinder(s) repeat an abnormally
low reading, it could indicate the existence of a
problem in the cylinder.
The recommended compression pressures are
to be used only as a guide to diagnosing engineproblems. An engine should NOT be disassem-
bled to determine the cause of low compression
unless some malfunction is present.
(5) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary. Ad-
just gap (refer to Group 8D, Ignition System for gap
adjustment and torque).
(6) Test resistance of spark plug cables (refer to
Group 8D, Ignition System).
(7) Inspect the primary wire. Test coil output volt-
age, primary and secondary resistance. Replace parts
as necessary (refer to Group 8D, Ignition System and
make necessary adjustment).
(8) Set ignition timing to specifications (refer to
Specification Label on engine compartment hood).
(9) Perform a combustion analysis.
(10) Test fuel pump for pressure and vacuum (refer
to Group 14, Fuel System for the proper specifica-
tions).
(11) Inspect air filter element (refer to Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance for the proper proce-
dure).
(12) Inspect crankcase ventilation system (refer to
Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for the proper
procedure).
(13) For emission controls refer to Group 25, Emis-
sion Controls System for service procedures.
(14) Inspect and adjust accessory belt drives (refer
to Group 7, Cooling System for the proper adjust-
ments).
(15) Road test vehicle as a final test.
HONING CYLINDER BORES
Before honing, stuff plenty of clean shop towels un-
der the bores and over the crankshaft to keep abra-
sive materials from entering the crankshaft area.
(1) Used carefully, the Cylinder Bore Sizing Hone
C-823 equipped with 220 grit stones, is the best tool
for this job. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce
taper and out-of-round as well as removing light
scuffing, scoring or scratches. Usually a few strokes
will clean up a bore and maintain the required lim-
its.
CAUTION: DO NOT use rigid type hones to remove
cylinder wall glaze.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done if
the cylinder bore is straight and round. Use a cylin-
der surfacing hone, Honing Tool C-3501, equipped
with 280 grit stones (C-3501-3810). 20-60 strokes, de-
pending on the bore condition, will be sufficient to
provide a satisfactory surface. Using honing oil
C-3501-3880 or a light honing oil available from ma-
jor oil distributors.
CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits or kerosene.
9 - 2 ENGINESJ
Page 1180 of 1784

30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Air Pressure Test........................ 73
Analyzing the Road Test................... 70
Converter Housing Leak Diagnosis........... 73
Converter Stall Test...................... 72
Diagnosis Guides and Charts............... 76
Fluid Level and Condition.................. 69Gearshift Linkage........................ 70
General Information....................... 69
Hydraulic Pressure Test................... 71
Preliminary Diagnosis..................... 69
Road Test.............................. 70
Transmission Throttle Valve Cable Adjustment . . 70
GENERAL INFORMATION
Automatic transmission problems are generally the
result of:
²poor engine performance
²incorrect fluid level
²incorrect cable/linkage adjustment
²incorrect band adjustment
²incorrect hydraulic control pressure adjustments
²hydraulic component malfunctions
²mechanical component malfunctions.
Begin diagnosis by checking the easily accessible
items such as fluid level, fluid condition and control
linkage adjustment. A road test will determine if fur-
ther diagnosis is necessary.
Procedures outlined in this section should be per-
formed in the following sequence to realize the most
accurate results:
²Preliminary diagnosis
²Check fluid Level and condition
²Check control linkage Adjustment
²Road test
²Stall test
²Hydraulic pressure test
²Air pressure tests
²Leak Tests
²Analyze test results and consult diagnosis charts
PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSIS
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are driveable and an alternate pro-
cedure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or
move forward).
Vehicle Is Driveable
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Adjust throttle cable and gearshift linkage if
complaint was based on delayed, erratic, or harsh
shifts.
(3) Road test vehicle and note transmission operat-
ing characteristics.
(4) Perform stall test if complaint is based on slug-
gish, low speed acceleration or abnormal throttle
opening needed to maintain normal speeds with
properly tuned engine.
(5) Perform hydraulic pressure tests.(6) Perform air pressure test to check clutch-band
operation.
Vehicle Is Disabled
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Check for broken, disconnected throttle link-
age.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or
loose, missing pressure port plugs.
(4) Raise vehicle, start engine, shift transmission
into gear and note following:
(a) If propeller shafts turn but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shafts do not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged drive plate, converter,
oil pump or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shafts do not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic pressure test to
determine if problem is a hydraulic or mechanical.
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
(1) Position vehicle on level surface. This is impor-
tant in obtaining an accurate fluid level check.
(2) To avoid false readings, which could produce
under or over fill condition, do not check level until
fluid is at normal operating temperature.
(3) Shift transmission into Neutral.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Operate engine at curb idle speed.
WARNING: WHEN PERFORMING UNDERHOOD OP-
ERATIONS WITH THE ENGINE RUNNING, KEEP
YOUR HANDS WELL AWAY FROM HOT OR ROTAT-
ING ENGINE COMPONENTS. DO NOT WEAR
LOOSE ARTICLES OF CLOTHING WHICH COULD
BECOME ENTANGLED IN ENGINE COMPONENTS
OR ACCESSORIES.
(6) Clean dipstick filler cap and tube before remov-
ing dipstick.
(7) Remove dipstick and inspect fluid level.
²Correct level is to FULL mark
²Acceptable level is between ADD and FULL marks
J30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 69
Page 1296 of 1784

(5) Remove cable bracket bolt and remove cable
and bracket from case (Fig. 43).
(6) Remove and discard cable seal.
THROTTLE CABLE INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate and install new seal on cable.
(2) Insert cable in transmission case.
(3) Attach cable to throttle cam (Fig. 42).
(4) Install cable bracket on case and tighten at-
taching bolt to 10 Nzm (7 ft-lbs) torque (Fig. 43).
(5) Remove old sealer material from oil pan and
transmission case. Clean oil pan with solvent and dry
it with compressed air.(6) Apply bead of Mopar or Loctite 599 sealer to oil
pan sealing surface. Sealer bead should be at least 3
mm (1/8 in.) wide. Then install pan and tighten pan
bolts to 7 Nzm (65 in. lbs.) torque.
(7) Install new gasket on oil pan drain plug. Install
and tighten plug to 20 Nzm (15 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Connect cable to engine bracket and throttle
linkage.
(9) Fill transmission with Mopar Mercon.
(10) Adjust the cable as described in cable adjust-
ment procedure.
TRANSMISSION THROTTLE CABLE ADJUSTMENT
(1) Shift transmission into Park, shut engine off
and raise hood.
(2) Press cable release button (Fig. 44).
(3) Push cable conduit back into cable sheath as
far as possible (Fig. 45).
(4) Rotate lever on throttle body to wide open
throttle position. Cable will ratchet to correct adjust-
ment point as lever is rotated (Fig. 45).
Fig. 42 Removing/Installing Transmission Throttle
Cable
Fig. 43 Removing/Installing Transmission Throttle
Cable And Bracket
Fig. 44 Throttle Cable Components
Fig. 45 Throttle Cable Adjustment
JAW-4 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE 21 - 185