1994 JEEP CHEROKEE check oil
[x] Cancel search: check oilPage 1265 of 1784

(2) Attach dial indicator to converter housing. Po-
sition indicator plunger against input shaft and zero
indicator.
(3) Move input shaft in and out and record read-
ing. End play should be 0.56 - 2.31 mm (0.022 - 0.091
in.).
(4) If end play is incorrect, transmission is incor-
rectly assembled, or output shaft thrust washer
and/or thrust plate are worn and need to be changed.
VALVE BODY INSTALLATION
(1) Install new manual lever shaft seal in case.
Use 15/16 deep well socket to install seal.
(2) Make sure neutral switch hasnotbeen in-
stalled in case. Remove switch if necessary as it will
interfere with valve body installation.
(3) Install new seal rings on accumulator piston
(Fig. 155). Lubricate accumulator piston, seals and
accumulator bore with transmission fluid.(4) Install accumulator piston and spring (Fig. 155)
in case.
(5) Place valve body manual lever in low to move
park lock rod rearward.
(6) Position valve body on case. Work park rod past
sprag and install valve body-to-case bolts finger
tight.
(7) Install park/neutral position switch in case.
Tighten switch to 34 Nzm (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Align valve body on case (Fig. 156).
(9) Install and tighten valve body-to-case bolts al-
ternately and evenly to 12 Nzm (105 in. lbs.) torque.
Start at center and work outward when tightening
bolts.Do not overtighten valve body bolts. This
could result in distortion and cross leakage af-
ter installation..
(10) Connect converter clutch solenoid wire to case
connector (Fig. 156).
(11) Install new filter on valve body (Fig. 157).
Tighten filter screws to 4 Nzm (35 in. lbs.).
BAND ADJUSTMENT AND OIL PAN
INSTALLATION
(1) Adjustfront bandas follows:
(a) Loosen locknut.
(b) Tighten adjusting screw to 72 in. lbs. torque.
Fig. 153 Installing Oil Pump And Reaction Shaft
Support
Fig. 154 Checking Input Shaft End Play
Fig. 155 Installing Accumulator Piston And Spring
Fig. 156 Valve Body Installation
21 - 154 30RH/32RH TRANSMISSION OVERHAULJ
Page 1271 of 1784

The Component Function Chart (Fig. 7) describes
basic function of various geartrain elements. The
Component Application Chart (Fig. 8) indicates
which elements (including valve body solenoids), are
applied in the various gear ranges.
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
The basic hydraulic system consists of the oil
pump, valve body and solenoids and four hydraulic
accumulators. The oil pump provides the necessary
system lubrication and operating pressure.
The valve body controls application of the clutches,
brakes, second coast band and the torque converter
clutch. The valve body solenoids control sequencing
of the 1-2, 2-3 and 3-4 shift valves within the valve
body. The solenoids are activated by signals from the
transmission control module.
The accumulators are used in the clutch and brake
feed circuits to control initial apply pressure. Spring
loaded accumulator pistons modulate the initial
surge of apply pressure for smooth engagement.
OIL PUMP
A gear-type oil pump is used. The pump gears are
mounted in the pump body. The pump drive gear is
operated by the torque converter hub. Drive tangs on
the hub engage in drive slots in the drive gear.
TRANSMISSION VALVE BODY COMPONENTS
Transmission operating pressure is supplied to the
clutch and brake apply circuits through the transmis-
sion valve body. The valve body consists of an upper
body, lower body, separator plate and upper andlower gaskets (Fig. 9). The various spool valves,
sleeves, plugs and springs are located within the two
body sections.
The manual valve, 1-2 shift valve, primary regula-
tor valve, accumulator control valve, check balls, so-
lenoids and oil strainers are located in the lower
body section (Fig. 10). The remaining control and
shift valves plus check balls and one additional oil
strainer are located in the upper body section (Fig.
11).
Fig. 8 Component Application Chart
Fig. 9 Two-Section Transmission Valve Body
21 - 160 AW-4 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONJ
Page 1280 of 1784

PRESSURE TEST ANALYSIS
If pressures in D and Reverse are higher than
specified, check for the following:
²throttle cable loose, worn, binding or out of adjust-
ment
²throttle valve, downshift plug, throttle cam, or pri-
mary regulator valve are sticking, worn or damaged
If pressures in D and Reverse are lower than spec-
ified, check for following:
²throttle cable loose, worn, binding or out of adjust-
ment
²throttle valve, downshift plug, throttle cam stick-
ing, worn or damaged
²primary regulator valve sticking, worn, or dam-
aged
²oil pump gears or housing worn or damaged
²overdrive clutch worn or damaged
If pressures are low in D range only, check for fol-
lowing:
²forward clutch worn or damaged
²fluid leakage in D range circuit (component seal
and O-rings)
If pressures are low in Reverse only, check for fol-
lowing:
²shift cable and manual valve out of adjustment
²fluid leakage in reverse circuit (component seal
and O-rings)
²direct clutch worn or damaged
²first/reverse brake worn or damaged
TORQUE CONVERTER STALL TEST
Stall testing checks the holding ability of the trans-
mission clutches and brakes and of the torque con-
verter stator overrunning clutch.
(1) Be sure transmission fluid is at normal operat-
ing temperature.
(2) Connect tachometer to engine. Position tachom-
eter so it can be viewed from drivers seat.
(3) Apply parking brakes and block wheels.
(4) Apply and hold service brakes.
(5) Shift transfer case into 2H position. On models
with NP249 transfer case, leave transfer case in 4H
position.
(6) Start engine.
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW ANYONE TO STAND AT
THE FRONT OR REAR OF THE VEHICLE DURING
THE TEST.
(7) Shift transmission into D range.
(8) Press accelerator pedal to wide open throttle
position and note maximum engine rpm. Stall speed
should be 2100 to 2400 rpm in D range.
CAUTION: Do not maintain wide open throttle for
more than 3-4 seconds at a time.(9) Release throttle and shift transmission into
Neutral. Allow transmission fluid to cool for 15-20
seconds.
(10) Shift transmission into Reverse.
(11) Press accelerator down to wide open throttle
position and note maximum engine rpm. Stall speed
should be 2100-to-2400 rpm in Reverse.
STALL SPEED TEST ANALYSIS
If engine rpm is lower than specified in D and Re-
verse, check for the following:
²engine output/performance insufficient
²stator overrunning clutch in torque converter not
holding if engine speed was 1500 rpm or less.
If stall speed in D range is higher than specified,
check for the following:
²line pressure low
²forward clutch slipping
²No. 2 one-way clutch not holding
²overdrive one-way clutch not holding
If stall speed in Reverse was higher than specified,
check for the following:
²line pressure low
²direct clutch slipping
²first/ reverse brake slipping
²overdrive one-way clutch not holding
If stall speeds were higher than specified in both D
and Reverse, check for the following:
²low fluid level
²line pressure low
²overdrive one-way clutch not holding
TIME LAG TEST
This test checks general condition of the overdrive
clutch, forward clutch, rear clutch and first/reverse
brake. Condition is indicated by the amount of time
required for clutch/brake engagement with the en-
gine at curb idle speed. Engagement time is mea-
sured for D and Reverse positions. A stop watch is
recommended for test accuracy.
TEST PROCEDURE
(1) Check and adjust transmission fluid level if
necessary.
(2) Bring transmission to normal operating tem-
perature.
(3) Apply parking brakes and turn off air condi-
tioning unit.
(4) Shift transfer case into 2H range. On models
with NP249 transfer case, leave transfer case in 4H
range.
(5) Start engine and check curb idle speed. Adjust
speed if necessary. Curb idle must be correct to en-
sure accurate test results.
(6) Shift transmission into Neutral and set stop
watch.
(7) During following test steps, start stop watch as
soon as shift lever reaches D and Reverse ranges.
JAW-4 TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSIS 21 - 169
Page 1284 of 1784

AW-4 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE
INDEX
page page
Accumulator Pistons and Springs........... 179
Adapter Housing Seal Replacement.......... 182
Checking Fluid Level and Condition.......... 173
Manual Valve Shaft Seal Replacement....... 178
Park Interlock Cable Adjustment............ 186
Park Rod and Pawl Service................ 181
Park/Neutral Position Switch............... 173
Second Coast Brake Servo................ 181
Shift Cable Adjustment................... 186
Speed Sensor.......................... 182Speed Sensor RotorÐSpeedometer Drive Gear . 183
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Service....... 184
Transmission Control Module (TCM) Service . . . 173
Transmission Cooler Line Fittings........... 187
Transmission Cooler Service............... 187
Transmission Throttle Cable Adjustment....... 185
Transmission Throttle Cable Replacement..... 184
Transmission Valve Body Installation......... 177
Transmission Valve Body Removal.......... 176
Transmission Valve Body Solenoids.......... 175
CHECKING FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
Recommended fluid for AW-4 transmissions is Mo-
par Dexron IIE/Mercon. Mopar Dexron II may be
used if Mercon fluid is not readily available.
CHECKING FLUID LEVEL
(1) Be sure transmission fluid is at normal operat-
ing temperature. Normal operating temperature is
reached after approximately 15 miles (25 km) of op-
eration.
(2) Position vehicle on level surface. This is impor-
tant for an accurate fluid level check.
(3) Shift transmission through all gear ranges and
back to Park.
(4) Apply parking brakes.
(5) Verify that transmission is in Park.
(6) Wipe off dipstick handle to prevent dirt from
entering fill tube. Then remove dipstick and check
fluid level and condition.
(7) Correct fluid level isto FULL mark on dip-
stick when fluid is at normal operating temper-
ature(Fig. 1).
(8) If fluid level is low, top off level with Mopar
Dexron IIE/Mercon. Mopar Dexron II may also be
used if Mercon is not available.Do not overfill
transmission. Add only enough fluid to bring
level to Full mark.
CHECKING FLUID CONDITION
Inspect the appearance of the fluid during the fluid
level check. The fluid should be clear and free of for-eign material or particles. If the fluid is dark brown
or black in color and smells burnt, the fluid has been
overheated and should be replaced.
Transmission operation should also be checked if
the fluid is severely discolored and contains quanti-
ties of foreign material, metal particles, or clutch disc
friction material.
A small quantity of friction material or metal
particles in the oil pan is normal. The particles
are usually generated during the break-in pe-
riod and indicate normal seating of the various
transmission components.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
SERVICE
Use the DRB II scan tool to diagnose transmission
control module function whenever a fault is sus-
pected. Replace the module only when actually faulty.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE
REPLACEMENT
The transmission control module is mounted under
the instrument panel. On left hand drive models, it is
at the driver side of the lower finish panel (Fig. 2).
On right hand drive models, it is at the passenger
side of the lower finish panel (Fig. 3).
To remove the module, disconnect the wire harness,
remove the mounting screws and remove the module
from the finish panel. Tighten the module mounting
screws securely after installation. Also be sure the
wire harness is not twisted, kinked or touching any
body panels.
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH
SWITCH TESTING
Test switch continuity with an ohmmeter. Discon-
nect the switch and check continuity at the connector
terminal positions and in the gear ranges indicated
in Figure 3. Switch continuity should be as follows:Fig. 1 Transmission Fluid Level
JAW-4 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE 21 - 173
Page 1286 of 1784
(8) Tighten switch adjusting bolt to 13 Nzm(9ft.
lbs.) torque.
(9) Bend at least two washer lock tabs over switch
attaching nut to secure it.
(10) Connect shift linkage rod to shift lever on left
side of case.
(11) Connect switch wires to harness and lower ve-
hicle.
(12) Check switch operation. Engine should start
in Park and Neutral only.
TRANSMISSION VALVE BODY SOLENOIDS
SOLENOID REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission oil pan drain plug and
drain fluid.
(2) Remove pan bolts and remove oil pan.
(3) Remove oil screen bolts and remove screen (Fig.
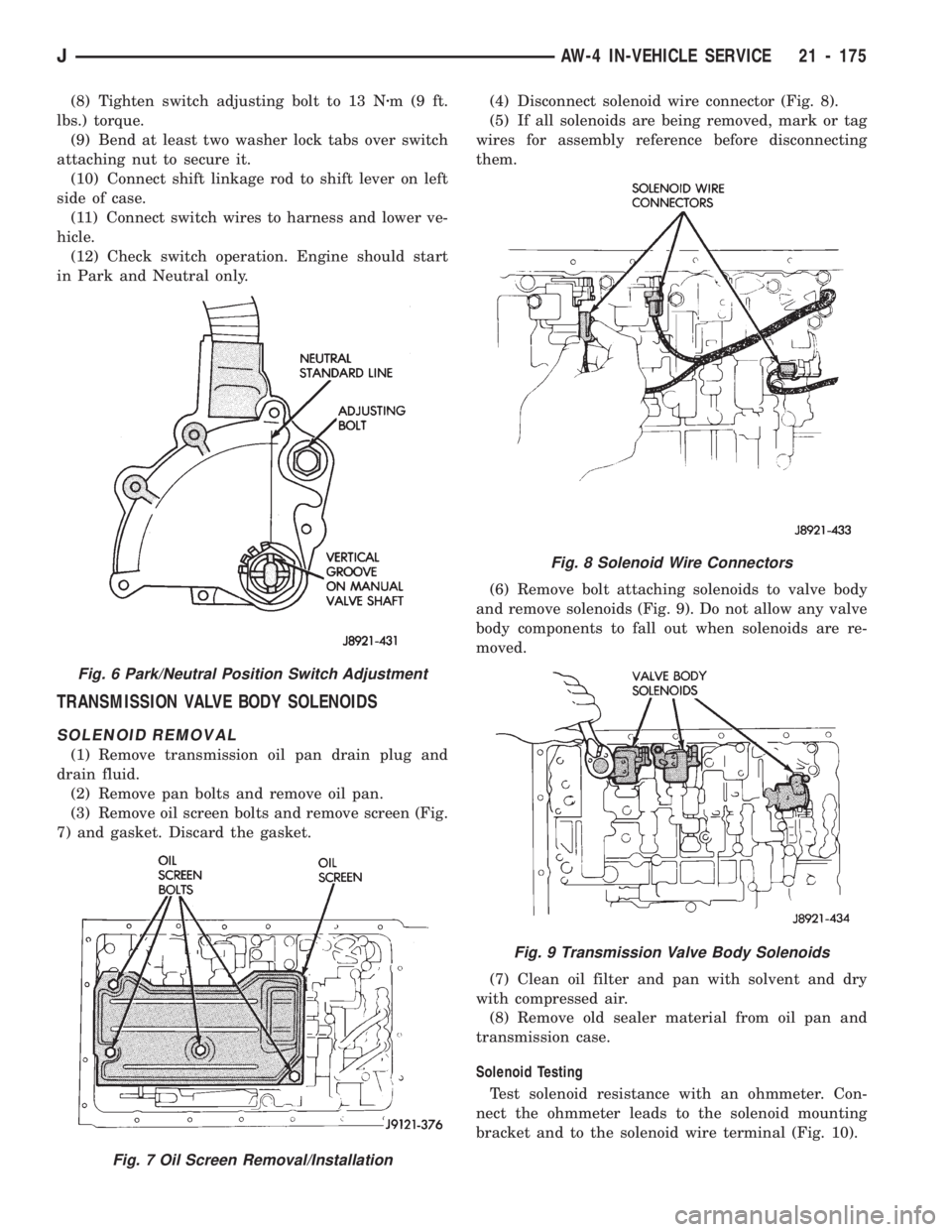
7) and gasket. Discard the gasket.(4) Disconnect solenoid wire connector (Fig. 8).
(5) If all solenoids are being removed, mark or tag
wires for assembly reference before disconnecting
them.
(6) Remove bolt attaching solenoids to valve body
and remove solenoids (Fig. 9). Do not allow any valve
body components to fall out when solenoids are re-
moved.
(7) Clean oil filter and pan with solvent and dry
with compressed air.
(8) Remove old sealer material from oil pan and
transmission case.
Solenoid Testing
Test solenoid resistance with an ohmmeter. Con-
nect the ohmmeter leads to the solenoid mounting
bracket and to the solenoid wire terminal (Fig. 10).
Fig. 8 Solenoid Wire Connectors
Fig. 9 Transmission Valve Body Solenoids
Fig. 6 Park/Neutral Position Switch Adjustment
Fig. 7 Oil Screen Removal/Installation
JAW-4 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE 21 - 175
Page 1288 of 1784

(5) Disconnect throttle cable from throttle cam
(Fig. 13).
(6) Remove valve body bolts. Bolt locations are out-
lined in Figure 14.
(7) Lower valve body and remove overdrive clutch
accumulator springs, direct clutch accumulator
springs and second brake accumulator spring (Fig.
15)
(8) Remove valve body and check ball and spring
(Fig. 16).
TRANSMISSION VALVE BODY INSTALLATION
(1) Connect cable to throttle cam (Fig. 13).
(2) Install check ball and spring (Fig. 16).
(3) Position accumulator springs and spacers on
valve body.(4) Align valve body manual valve with shift sector
(Fig. 17) and carefully position valve body on case.
(5) Install valve body bolts (Fig. 14). Tighten bolts
evenly to 10 Nzm (7 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Install valve body oil tubes. Be sure tube ends
(L) and (M) are installed as shown in Figure 18.
(7) Remove old sealer material from oil pan and
transmission case.
(8) Clean oil screen and oil pan with solvent (if not
done previously). Dry both components with com-
pressed air only. Do not use shop towels.
(9) Install new gaskets on oil screen and install
screen on case. Tighten screen attaching bolts to 10
Nzm (7 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 13 Removing/Installing Throttle Cable
Fig. 14 Transmission Valve Body Bolt Locations
Fig. 15 Accumulator Springs
Fig. 16 Removing/Installing Check Ball And Spring
JAW-4 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE 21 - 177
Page 1298 of 1784

TRANSMISSION COOLER SERVICE
Main Cooler
The transmission main cooler is located in the ra-
diator. The main cooler can be flushed when neces-
sary, however, the cooler is not a repairable
component. If the cooler is damaged, plugged, or
leaking, the radiator will have to be replaced.
Auxiliary Cooler
The auxiliary cooler is mounted in front of the ra-
diator at the driver side of the vehicle (Fig. 48). The
cooler can be flushed when necessary, while mounted
in the vehicle. The cooler can also be removed for ac-
cess, repair, or replacement as needed.
The main and auxiliary coolers should both be
flushed whenever a transmission or converter clutch
malfunction generates sludge, debris, or particles of
clutch friction material.
Cooler Service
The main cooler (and radiator) and the auxiliary
cooler can be removed for service or access to other
components. Auxiliary cooler removal requires that
the front bumper and radiator support be removed
for access to the cooler lines and attaching bracket.
REVERSE FLUSHING MAIN AND AUXILIARY
COOLERS AND COOLER LINES
Reverse flushing the cooler and lines will prevent
sludge and particles from flowing back into the
transmission after repair. The flushing procedure ap-
plies to standard (in-radiator) coolers and auxiliary
coolers equally.
Pressure equipment is preferred for reverse flush-
ing. However, reverse flushing can be performed us-
ing hand operated equipment as described in the
following procedure.
(1) Disconnect cooler lines at transmission and at
auxiliary cooler (Figs. 48 and 49).
(2) Position drain pan under cooler line to catch
material flushed through coolers and lines.
(3) Reverse flush each cooler using hand operated
suction gun filled with mineral spirits. Insert gun
nozzle (or hose) into cooler inlet (return) line. Then
force mineral spirits through into line and through
cooler.(4) Continue reverse flushing until fluid exiting in-
let (pressure) line is clear and free of debris/residue.
(5) Replace radiator if fluid cannot be pumped
through main cooler. Replace auxiliary cooler if leaks
are evident, or if fluid cannot be pumped through it.
(6) Clear flushing materials from coolers and lines
with short pulses of compressed air. Insert air gun
nozzle into cooler inlet (return) line and continue
short pulses of air until all fluid is cleared from
cooler and lines.
(7) Pump one quart of fresh automatic transmis-
sion fluid through cooler and lines before reconnect-
ing cooler lines.
FLOW TESTING TRANSMISSION MAIN
COOLER
Cooler flow is checked by measuring the amount of
fluid flow through the cooler in a 20 second time pe-
riod. The test is performed with the engine running
and transmission in neutral. Fluid is then pumped
through the cooler by the transmission oil pump.
(1) Disconnect cooler inlet line at transmission fit-
ting.
(2) Securely attach hose to end of inlet line and po-
sition line in a one quart test container.
(3) Add extra quart of fluid to transmission.
(4) Use stopwatch to check flow test time.
(5) Shift transmission into neutral and set parking
brake.
(6) Start and run engine at curb idle speed and im-
mediately note cooler flow. Approximately one quart
of fluid should flow into test container in 20 second
period.
(7) If cooler flow is intermittent, flows less than
one quart in 20 seconds, or does not flow at all,
cooler is faulty and must be replaced.
TRANSMISSION COOLER LINE FITTINGS
Quick disconnect fittings are used at the transmis-
sion cooler line connections. The fitting seals and
guides are serviceable.
Replace the seals and guides whenever the fittings
exhibit leakage, or will not properly snap into place.
JAW-4 IN-VEHICLE SERVICE 21 - 187
Page 1301 of 1784

(5) Align and install converter in oil pump.
TRANSMISSION AND TORQUE CONVERTER
INSTALLATION
(1) Mount transmission on transmission jack. Then
secure transmission to jack with safety chains.
(2) Lubricate converter drive hub and oil pump
seal lip with Mopar Mercon transmission fluid. Then
install converter. Be sure converter is fully seated in
oil pump gears before proceeding. Hold converter in
place with C-clamp or strap attached to converter
housing.
(3) Align and position transmission and converter
on engine.
(4) Remove clamp or strap used to hold torque con-
verter in place.
(5) Move transmission forward seat and it on en-
gine. Be sure torque converter hub is fully seated.
(6)
Install converter housing-to-engine bolts (Fig.
53).
(7) Install converter-to-drive plate bolts.
(8) Install and connect starter motor.
(9) Install and connect crankshaft position sensor.
(10) Install transfer case on transmission. Tighten
transfer case attaching nuts to 41 Nzm (30 ft. lbs.)
torque
(11) Connect transfer case shift linkage and vac-
uum hoses.
(12) Connect exhaust components.
(13) Install rear crossmember and remove jack
used to support transmission assembly.
(14) Connect speed sensor wire harness to sensor.
(15) Connect wire harness to park/neutral position
switch.
(16) Align and connect front and rear propeller
shafts.
Fig. 51 Checking Operation Of Torque Converter
Stator One-Way Clutch
Fig. 52 Installing Oil Pump Seal
21 - 190 AW-4 TRANSMISSION REMOVAL AND INSTALLATIONJ