1994 JAGUAR XJ6 air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 415 of 521

General Fitting Instructions
Pressordrifttheseal in tothefull depthofthe housing ifthe housing is shouldered,orflush withthefaceofthe housing
where no shoulder is provided.
Note: Careless fitting of oil seals, which can result in damage to the seal and sealing surfaces, accounts for most
cases of failure of seals. Care in fitting is essential
if good results are to be obtained.
A3.2.7 joints And joint Faces
Remove all traces of old jointing materials prior to reassembly. Inspect joint faces for scratches or burrs and remove
with a fine file or oilstone; do not allow swarf or dirt to enter tapped holes or enclosed parts. Blow out any pipes, chan- nels or crevices with compressed air, refitting or renewing any 0-rings or seals which have been displaced by the com- pressed air.
Always use the specified gaskets. Use jointing compound only when recommended, otherwise fit joints dry. When
jointing compound is used, apply in
a thin film to metal surfaces; take great care to prevent it from entering oilways, pipes or blind tapped holes.
A3.2.8
Before removing a hose from the brake or power steering systems, thoroughly clean the end fittings and the area sur- rounding them. Obtain blanking caps beforedetaching hosefittings,sothat portscan becovered to excludedirt. Clean
the hose externally and blow through with compressed air. Examine the hose carefully for cracks, separation of plies,
security of end fittings and external damage. Reject any hose found to be faulty. When refitting the hose, ensure that
no unnecessary bends are introduced and that the hose is not twisted before or during tightening of union nuts.
Do not store hydraulic fluid in an unsealed container because it will absorb water. Fluid in this condition would be dan- gerous to use due to a lowering of its boiling point. Do not allow hydraulic fluid to be contaminated with mineral oil,
or use a container which has previously contained mineral oil.
Do not re-use fluid bled from the system. Always use clean brake fluid, or a recommended alternative, to clean the
hydraulic components. Fit a blanking cap to the hydraulic union and
a plug to its mating socket, after removal from
the vehicle, to prevent ingress of dirt. Absolute cleanliness must be observed with hydraulic components at all times.
After any work has been performed on hydraulicsystems, inspect carefully for leaks underneath the car while a second
operator applies maximum pressure to the brakes (with the engine running) and operates the steering.
Hydraulic Flexible Pipes And Hoses
A3.2.9 Metric
Bolt Identification
An IS0 metric bolt or screw, made of steel and larger than
6mm in diameter can be identified by the symbols ISOM or M embossed on top of the head (Fig. 1 ). In addition to marks
to identify the manufacturer, the head is also marked with
symbols to indicate the strength grade eg
8.8, 10.9, 12.9 or 14.9. The first figure gives the minimum strength of the bolt
material in tens of kgf / mm2. Zinc plated IS0 metric bolts
and nuts are chromate passivated and coloured greenish- khaki to gold-bronze.
A3.2.10 Metric Nut Identification
A nut with an IS0 metricthread is marked on one face (1 Fig. 2) or on one of the flats (2 Fig. 2) of the hexagon with the
strength grade symbol 8, 12 or 14. Some nuts with a
strength 4,5 or 6 are also marked and some have the metric
symbol M on the flat which is opposite to the strength grade
marking.
Aclockfacesystem is used as an alternative method of indi
- cating the strength grade (3 Fig. 2). The external chamfers
or a face of the nut is marked in a position relative to the ap-
propriate hour mark on a clock face to indicate the strength
grade. A dot is used to locate the 12 o’clock position and a dash to indicate the strength grade. If the grade is above 12,
two dots identify the 12 o’clock position. Fig.
1
I I
Fig. 2
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 4
Page 425 of 521

Body Systems & Body Repair
Sub-Section Title SRO Page
A4.4.4 ........... Underhood Labels. Location & Tvpe ................................................... 32
A4.4.5
........... Stonechip Protection Area ............................................................ 33
A4.5.1.1
.......... Glass And Body Preparation .......................................................... 34
A4.5.1.2
.......... Glazing Adhesive Application Temperature ............................................. 34
A4.5
............. Glazing ........................................................................\
... 34
A4.5.1
........... Glazing. Special Notes ............................................................... 34
A4.5.1.3
.......... Glazing Adhesive Application ......................................................... 34
A4.5.1.4
.......... Glazing Adhesive Curing ............................................................. 34
A4.6.1
........... Bumpers ........................................................................\
... 35
A4.6.1.2 .......... Bumpers. Features ................................................................... 35
A4.6.1.3
.......... BUmpeN. Service Procedures ......................................................... 37
A4.6.1.4 .......... Bumpers. Fitted Condition - Front ..................................................... 37
A4.6.2
........... BUmpeN. Cover Damage ............................................................. 39
A4.6.1.1
.......... Bumpers.
Major Components ......................................................... 35
A4.6.1.5 .......... Bumpers. Fitted Condition -Rear ...................................................... 38
A4.6.2.1
.......... Bumpers. Damage Assessment ........................................................ 39
A4.6.2.2
.......... Bumpers. Repair Materials ............................................................ 39
A4.6.3 ........... Bumpers. Refinishing ................................................................ 40
A4.6.3.1
.......... Bumpers. Refinishing - Original ....................................................... 40
A4.6.3.2
.......... Bumpers. Refinishing - New .......................................................... 40
A4.6.3.3
.......... Bumpers. Refinishing - All ............................................................ 40
A4.6.4
........... Bumpers. Replacement Covers ........................................................ 40
A4.6.5
........... Recycled Materials. General Note ..................................................... 40
A4.6.6.1
.......... Body-side Moulding, Introduction ..................................................... 41
A4.6.6.2
.......... Body-side Moulding. Fitted Condition - Illustration ....................................... 41
A4.6.6.3
.......... Body-side Moulding. Fitting Process ................................................... 41
A4.6.7
........... Finisher, Door Frame - Fitted Condition ................................................ 42
A4.6.8
........... Finisher, Roof Drip Rail - Fitted Condition .............................................. 42
A4.7.1
........... Body Exterior Clearances & Alignments ................................................. 43
A4.7.1.1
.......... Body Exterior Clearances & Alignments. Introduction ..................................... 43
A4.6.6
........... Body-side
Moulding ................................................................. 41
A4.7.1.2
.......... Body Exterior Clearances & Alignments. Criteria - Clearances ............................. 43
A4.7.1.3
.......... Body Exterior Clearances & Alignments. Criteria - Alignment .............................. 43
A4.7.1.4
.......... Body Exterior Clearances & Alignments. Criteria - Exterior Fitments ........................ 43
A4.7.1.5
.......... Body Exterior Clearances & Alignments. Illustrations (Specifications) ........................ 43
A4.7.2
........... DOON ........................................................................\
..... 47
A4.7.2.1
.......... DOON. Features ..................................................................... 47
A4.7.2.2
.......... DOON. Removal .................................................................... 47
A4.7.2.3
.......... DOON. Fitting ....................................................................... \
47
A4.7.2.4
.......... DOON. Alignment ................................................................... 47
A4.7.2.5
.......... Door Seals. Table ................................................................... 48
A4.7.2.6 .......... Door Seals - Typical Sections. Illustration ............................................... 48
0
0
0
0
Issue 1 August 1994 X300 VSM ii
Page 428 of 521

0
0
0
Body Systems Body Repair
A4.1 BODY REPAIR
Introduction
This section contains information, specifications and procedures for body repair and rectification of the Jaguar sedan
range (with standard wheelbase).
All repairs, whether structural or cosmetic, must ensure the continuance of the Paint Surface and Corrosion warranty,
where applicable.
Following repair or rectification, the vehicle must be returned to the original manufactured condition with regard to
occupant safety, dimensional accuracy, finish and corrosion protection.
Similarly, repaired vehicles must be fully checked, and where appropriate reset, with regard to steering, suspension,
restraint and
braking systems.
A4.1.1 Health and Safety
(Please Read The
Fol/owing Notes Carethlly)
Where legislation governing working conditions and practises is applicable, you should observe it. Do not forget that
you have a duty, to yourself and those around you, to act in a responsible manner in the workplace.
In the United Kingdom the Health and Safety
at Work Act (1974) places a duty on employers and employees to ensure,
whenever possible, safe working conditions and practices. Wherever a potential hazard is notified to, or identified by
the operator, he must employ the correct safety procedures and equipment.
Should
a personal injury occur as a result of any workshop activity, seek medical help as soon as possible and do not
attempt self-treatment other than by the application of first aid.
With the constant introduction of new materials in the manufacture of vehicles,
it is important that potential risks are
identified and precautions made known.
WARNING: READ AND UNDERSTAND WORKING PRACTICES CLIMATE CONTROL SYSTEMS, SECTION 14, WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO
ERY
/ RECYCLE / RECHARGE EQUIPMENT.
WEAR SUITABLE EYE AND SKIN PROTECTION.
OBSERVE ALL APPLICABLE SAFETY REQUIREMENTS.
DO
NOT VENT REFRIGERANT DIRECTLY TO ATMOSPHERE, ALWAYS USE JAGUAR APPROVED RECOV
-
Issue 1 August 1994 1 X300 VSM
Page 432 of 521

Body Systems & Body Repair
Term
ABS
ABS
/ PA
ABS
/ PC
ABS / PBT
A#. 1.6 PLASTICS - EXPLANATORY NOTES
A#. 1.6.1 Plastic component and trim materials.
This table, in conjunction with the illustrations on the following pages will enable rapid identification of the particular
material of any major plastic part.
Material Name
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
& Polyamide (nylon) blend
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
& Polycarbonate blend
Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate
& Polybutylene Terephthalate
PC
PE
PMMA
POM
PP
PPO
PUR
PVC
SMA
I PA 1 Polyamide (nylon) I
Polycarbonate
Polyethylene
Polymethyl
Methacrylate
Polyoxymethylene (acetal)
Polypropylene
Modified Polyphenylene Oxide
Polyurethane
Polyvinylchloride
Styrene Maleic Anhydride
w: Not all plastic components are nominated, only those suitable for economic reclamation.
A#. 1.6.2 Plastics - Handling Notes
w: With reference to the following conditions, consider the properties of those plastic components which may
be affected by a repair or rectification procedure.
0 As mentioned elsewhere, the exterior panel temperature of the vehicle must not exceed 95OC at any time and
may only be held at this upper limit for a maximum of 2 (two) hours.
0 Interior vehicle temperature must not exceed 86OC, the time limit being 2 (two) hours.
0 Temperatures above those specified in 1 and 2, may result in distorted or permanently damaged components. If there is any doubt whatsoever, remove those components which may be affected by the application of heat.
0 Certain items may be manufactured from 'blended' materials; these must NOT be recycled with pure materials.
For example do not mix PC/ABS (wheel trim) with ABS ('B' pillar upper trim).
0 Should plastic components become greasy, they may be cleaned with an 'SBP 3' spirit wipe, or equivalent.
A4.1.6.3 Recycled Materials
Any of the materials listed in A4.1.6.1 may be recycled provided that they are not contaminated by other incompatible
plastics or metals. For instance, the air conditioning unit case, manufactured from PP (polypropylene), must be separ- ated from the heater matrix, evaporator, control devices (electronic and mechanical) and all fixings before it can be
considered for recycling.
After disassembly, the case must be placed for disposal only
with materials of the same generic type.
w: The bumper cover assemblies have side armatures (non-eerviceable items) rivetted to them; because they
are dissimilar materials the armatures and fixings must be removed prior to recycling.
In the bumper cover intake aperture there is a cosmetic 'black-out' piece; a similar component may be found
on the fog lamp blanks (where fitted). These items should be separated from the major component for recycl- ing.
Issue 1 August 1994 5 X300 VSM
Page 436 of 521

Body Systems
A4.2.1.1 Constructional Steel Classification
Material 1 dnnlirdiam I
High strength low alloy (HLSA).
Double sided zinc plated mild steel.
1 Boron steel
1 Mild steel.
A4.2.2 BODY ALIGNMENT
The illustrations on pages 11 - Body Dimensions PLAN, and 13 -Body Dimensions SIDE VIEW, provide specifications
for damage assessment and location of replacement parts.
These dimensions must be strictly applied whether they are used for damage assessment, component location or post
repair verification.
The plan view MASTER datums are nominated on the right
-hand side of the body with the left-hand datums dimen- sioned from them. Therefore, the right-hand datums must be known to be correct before any other cross-ar dimen- sions are checked.
W: The right-hand side is always looking towards the front, from the rear of the vehicle.
All dimensions are derived from a single
(ZERO) datum point for all three axes; X for length, Z for height and V cross- car.
Issue 1 August 1994 9 X300 VSM
A4.2 BODY STRUCTURE
A4.2.1
Introduction
The Jaguar sedan range (with standard wheelbase) has a unit construction monocoque body structure with bolt-on
front fenders and welded rear fenders. The doors feature 'lift-off' hinges and welded dropglass frames.
n@#pn.s..v..
Impact prone areas, ie. seat frame and bumper mount- ings.
Exterior body panels subject to severe conditions such
as stone chipping and weather exposure (excluding
roof panel).
Door intrusion beams
Internal brackets, fillets and strengtheners.
I
Page 444 of 521

Body Systems & Body Repair
A4.2.5.2 PANELS, ALIGN AND WELD
. Observe all appropriate safety procedures.
. Apply appropriate sealer or joint preparation.
. Align the replacement panel with associated panels and clamp in position; with certain panels it may be necessary
. Recheck alignment and panel contours and readjust as necessary.
= Select the correct 'arms' for resistance spot welding and ensure that tips are correctly trimmed.
w:
0 SRO 77.10.05 di77.10.06
to MIG tack weld (A Fig. 1) or use 'PK screws.
It is recommended that 'arms' of not more than 300 mm (12 in.) long are used and test the equipment for satis-
factory operation by producing test coupons (B Fig. 1). In the absence of test equipment, a satisfactory weld
can be verified by pulling the test coupons apart and viewing the welded condition.
Resistance spot weld where required (C Fig. 1).
. Note the presence of zinc coated panels and treat as detailed in the previous sections.
. Dress back all MIG tack welds.
. MIG seam weld the butt joints (D Fig. 1).
. As required, dress all welds.
. Final braze and fill as necessary prior to paint preparation.
//
C
Fig. 1
B
D
Issue 1 August 1994 X300 VSM 17
Page 461 of 521

Body Systems & Body Repair
Optimum temperature 6OoC - 7OoC
Minimum temperature 35%
Maximum Temperature 7 5oc
A4.5 GLAZING
A4.5.1 Special notes
In order that the design condition of the vehicle is preserved when direct glazing repairs are carried out, it is essential
that both the applied materials and processes are as stipulated.
Application time - including
positioning
4 minutes
Will not bond
A4.5.1.1 Glass and Body Preparation
The preparation methods and materials, as used with the Betaseal HV3 system on previous Jaguar vehicles, are fully
compatible with the current sedan range.
Ease of working and extended process time may be gained by ensuring that the vehicle body and replacement glass
are 'soaked
at room temperature, a minimum of 2OoC, prior to adhesive application and fitting.
Should damage occur to the body flange finish, rectify as appropriate with the full paint refinishing process as de
- scribed in the 'Paint Refinishing Manual' see section 4.4.1.1.
A4.5.1.2 Adhesive Application Temperature
The specified adhesive has a high viscosity and is not easily applied at 'room temperature' using conventional
methods. When the adhesive is applied it chills rapidly on contact with the body and reverts to the hard condition, thus
providing full retention (not full strength) within minutes.
Raising the temperature of the adhesive lowers the viscosity and speeds up the flow.
It is recommended therefore that
the adhesive is pre-warmed in a heated cabinet for a minimum of 20 (twenty) minutes and the extrusion gun has inte- gral heating elements, see Preliminary pages for details.
A4.5.1.3 Adhesive Application
CAUTION: The glass will not bond to the body if the time
taken to apply the adhesive AND position the glass. exceeds the stated limit.
It is recommended that the bead of adhesive conforms tothe shape and dimensions as shown in Fig. 1 and is positioned
along the edge of the rubber.
m: The depth of the glass and thus the thickness of the
adhesive, is controlled by the screen rubber 'bot- toming' on the body flange.
A4.5.1.4 Adhesive Curing
The specified polyurethane adhesive cures by exposure to
moisture and NOT by heat. Cure times may vary consider- ablyand are dependant upon ambient humidity levels, how- everthe initial 'chill off will occur within l to4 minutes, after
which the screen may not be moved (this is entirely depend- ant upon the application temperature and rate of cooling). 1
12nnrl6mnr
J76-1031
1.
Fitted condition
2. Bead application
Fig. 1
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 34
Page 465 of 521
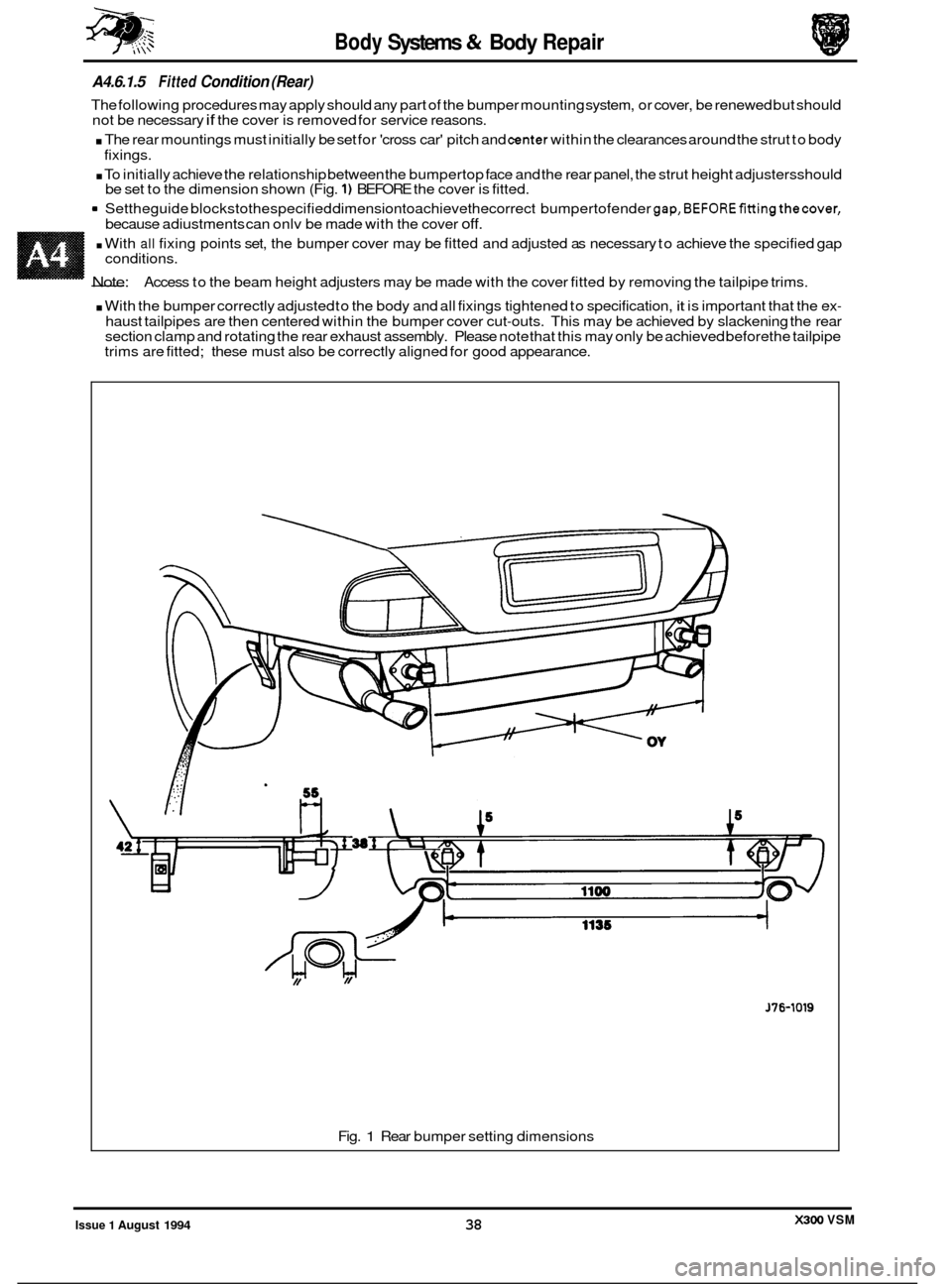
Body Systems & Body Repair
A4.6.1.5 Fitted Condition (Rear)
The following procedures may apply should any part of the bumper mounting system, or cover, be renewed but should
not be necessary if the cover is removed for service reasons.
. The rear mountings must initially be set for 'cross car' pitch and center within the clearances around the strut to body
. To initially achieve the relationship between the bumpertop face and the rear panel, the strut height adjustersshould
9 Settheguide blockstothespecified dimensiontoachievethecorrect bumpertofender gap,BEFOREfittingthecover,
fixings.
be set to the dimension shown (Fig.
1) BEFORE the cover is fitted.
because adiustments can onlv be made with the cover
off.
. With all fixing points set, the bumper cover may be fitted and adjusted as necessary to achieve the specified gap
- Note:
conditions.
Access to the beam height adjusters may be made with the cover fitted by removing the tailpipe trims.
. With the bumper correctly adjusted to the body and all fixings tightened to specification, it is important that the ex-
haust tailpipes are then centered within the bumper cover cut-outs. This may be achieved by slackening the rear
section clamp and rotating the rear exhaust assembly. Please note that this may only be achieved before the tailpipe
trims are fitted; these must also be correctly aligned for good appearance.
J76-1019
Fig. 1 Rear bumper setting dimensions
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 38