1993 FORD MONDEO change wheel
[x] Cancel search: change wheelPage 41 of 279

Chapter 2 Part A:
In-car engine repair procedures
Auxiliary drivebelt check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Camshaft oil seals - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Camshafts and hydraulic tappets - removal, inspection
and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Compression test - description and interpretation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Crankshaft oil seals - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Crankshaft pulley - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Cylinder head - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Cylinder head and valve components - cleaning and
inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2B
Cylinder head cover - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Engine oil and filter change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Engine oil level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Engine overhaul - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2B
Engine/transmission - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2B
Engine/transmission mountings - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . 22
Exhaust manifold - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . 7Flywheel/driveplate - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . 21
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Inlet manifold - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Oil cooler - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Oil level sensor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Oil pressure warning light switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . 19
Oil pump - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Repair operations possible with the engine in the vehicle . . . . . . . . 2
Spark plug renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Sump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Timing belt - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Timing belt covers - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Timing belt tensioner and toothed pulleys - removal,
inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Top Dead Centre (TDC) for No 1 piston - locating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Water pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 3
General
Engine type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Four-cylinder, in-line, double overhead camshafts
Engine code:
1.6 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . LIF
1.8 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . RKA
2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . NGA
Capacity:
1.6 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1597 cc
1.8 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1796 cc
2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1988 cc
Bore:
1.6 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76.0 mm
1.8 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80.6 mm
2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84.8 mm
Stroke - all models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88.0 mm
Compression ratio:
1.6 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.3:1
1.8 and 2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.0:1
Compression pressure - at starter motor speed, engine fully warmed-up .Not available
Firing order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3-4-2 (No 1 cylinder at timing belt end)
Direction of crankshaft rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Clockwise (seen from right-hand side of vehicle)
Cylinder head
Hydraulic tappet bore inside diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28.395 to 28.425 mm
Camshafts and hydraulic tappets
Camshaft bearing journal diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25.960 to 25.980 mm
Camshaft bearing journal-to-cylinder head running clearance . . . . . . . . 0.020 to 0.070 mm
Camshaft endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.080 to 0.220 mm
Hydraulic tappet diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28.400 mm
2A•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,suitable
for competent DIY
mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents2A
procarmanuals.com
Page 45 of 279

The cylinder head is provided with two oil
galleries, one on the inlet side and one on the
exhaust, to ensure constant oil supply to the
camshaft bearings and hydraulic tappets. A
retaining valve (inserted into the cylinder
head’s top surface, in the middle, on the inlet
side) prevents these galleries from being
drained when the engine is switched off. The
valve incorporates a ventilation hole in its
upper end, to allow air bubbles to escape
from the system when the engine is restarted.
While the crankshaft and camshaft
bearings and the hydraulic tappets receive a
pressurised supply, the camshaft lobes and
valves are lubricated by splash, as are all
other engine components.
Valve clearances - general
It is necessary for a clearance to exist
between the tip of each valve stem and the
valve operating mechanism, to allow for the
expansion of the various components as the
engine reaches normal operating
temperature.
On most older engine designs, this meant
that the valve clearances (also known as
“tappet” clearances) had to be checked and
adjusted regularly. If the clearances were
allowed to be too slack, the engine would be
very noisy, its power output would suffer, and
its fuel consumption would increase. If the
clearances were allowed to be too tight, the
engine’s power output would be reduced,
and the valves and their seats could be
severely damaged.
The engines covered in this manual,
however, employ hydraulic tappets which use
the lubricating system’s oil pressure
automatically to take up the clearance
between each camshaft lobe and its
respective valve stem. Therefore, there is no
need for regular checking and adjustment of
the valve clearances, but it is essential that
onlygood-quality oil of the recommended
viscosity and specification is used in the
engine, and that this oil is always changed at
the recommended intervals. If this advice is
not followed, the oilways and tappets may
become clogged with particles of dirt, or
deposits of burnt (inferior) engine oil, so that
the system cannot work properly; ultimately,
one or more of the tappets may fail, and
expensive repairs may be required.
On starting the engine from cold, there will
be a slight delay while full oil pressure builds
up in all parts of the engine, especially in the
tappets; the valve components, therefore,
may well “rattle” for about 10 seconds or so,
and then quieten. This is a normal state of
affairs, and is nothing to worry about,
provided that all tappets quieten quickly and
stay quiet.
After the vehicle has been standing for
several days, the valve components may
“rattle” for longer than usual, as nearly all the
oil will have drained away from the engine’s
top end components and bearing surfaces.
While this is only to be expected, care mustbe taken not to damage the engine under
these circumstances - avoid high speed
running until all the tappets are refilled with oil
and operating normally. With the vehicle
stationary, hold the engine at no more than a
fast idle speed (maximum 2000 to 2500 rpm)
for 10 to 15 seconds, or until the noise
ceases. Do not run the engine at more than
3000 rpm until the tappets are fully recharged
with oil and the noise has ceased.
If the valve components are thought to be
noisy, or if a light rattle persists from the top
end after the engine has warmed up to
normal operating temperature, take the
vehicle to a Ford dealer for expert advice.
Depending on the mileage covered and the
usage to which each vehicle has been put,
some vehicles may be noisier than others;
only a good mechanic experienced in these
engines can tell if the noise level is typical for
the vehicle’s mileage, or if a genuine fault
exists. If any tappet’s operation is faulty, it
must be renewed (Section 13).
The following major repair operations can
be accomplished without removing the
engine from the vehicle. However, owners
should note that any operation involving the
removal of the sump requires careful
forethought, depending on the level of skill
and the tools and facilities available; refer to
the relevant text for details.
(a) Compression pressure - testing.
(b) Cylinder head cover - removal and
refitting.
(c) Timing belt covers - removal and refitting.
(d) Timing belt - renewal.
(e) Timing belt tensioner and toothed pulleys
- removal and refitting.
(f) Camshaft oil seals - renewal.
(g) Camshafts and hydraulic tappets -
removal and refitting.
(h) Cylinder head - removal, overhaul and
refitting.
(i) Cylinder head and pistons -
decarbonising.
(j) Sump - removal and refitting.
(k) Crankshaft oil seals - renewal.
(l) Oil pump - removal and refitting.
(m) Piston/connecting rod assemblies -
removal and refitting (but see note below).
(n) Flywheel/driveplate - removal and
refitting.
(o) Engine/transmission mountings - removal
and refitting.
Clean the engine compartment and the
exterior of the engine with some type of
degreaser before any work is done. It will
make the job easier, and will help to keep dirt
out of the internal areas of the engine.
Depending on the components involved, it
may be helpful to remove the bonnet, to
improve access to the engine as repairs are
performed (refer to Chapter 11 if necessary).Cover the wings to prevent damage to the
paint; special covers are available, but an old
bedspread or blanket will also work.
If vacuum, exhaust, oil or coolant leaks
develop, indicating a need for component/
gasket or seal replacement, the repairs can
generally be made with the engine in the
vehicle. The intake and exhaust manifold
gaskets, sump gasket, crankshaft oil seals
and cylinder head gasket are all accessible
with the engine in place.
Exterior components such as the intake
and exhaust manifolds, the sump, the oil
pump, the water pump, the starter motor, the
alternator and the fuel system components
can be removed for repair with the engine in
place.
Since the cylinder head can be removed
without lifting out the engine, camshaft and
valve component servicing can also be
accomplished with the engine in the vehicle,
as can renewal of the timing belt and toothed
pulleys.
In extreme cases caused by a lack of
necessary equipment, repair or renewal of
piston rings, pistons, connecting rods and
big-end bearings is possible with the engine
in the vehicle. However, this practice is not
recommended, because of the cleaning and
preparation work that must be done to the
components involved, and because of the
amount of preliminary dismantling work
required - these operations are therefore
covered in Part B of this Chapter.
1When engine performance is down, or if
misfiring occurs which cannot be attributed to
the ignition or fuel systems, a compression
test can provide diagnostic clues as to the
engine’s condition. If the test is performed
regularly, it can give warning of trouble before
any other symptoms become apparent.
2The engine must be fully warmed-up to
normal operating temperature, the oil level
must be correct, the battery must be fully
charged, and the spark plugs must be
removed. The aid of an assistant will be
required also.
3Disable the ignition system by unplugging
the ignition coil’s electrical connector, and
remove fuse 14 to disconnect the fuel pump.
4Fit a compression tester to the No 1
cylinder spark plug hole - the type of tester
which screws into the plug thread is to be
preferred.
5Have the assistant hold the throttle wide
open and crank the engine on the starter
motor; after one or two revolutions, the
compression pressure should build up to a
maximum figure, and then stabilise. Record
the highest reading obtained.
6Repeat the test on the remaining cylinders,
recording the pressure developed in each.
7At the time of writing, no compression
3 Compression test -
description and interpretation
2 Repair operations possible with
the engine in the vehicle
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•5
2A
procarmanuals.com
Page 72 of 279

inner wing panel, release the engine
wiring loom and refit the power steering
fluid reservoir.
(g) Secure the engine wiring loom neatly to
the engine/transmission so that it cannot
be damaged as the unit is removed from
the vehicle.
14Unbolt both parts of the exhaust manifold
heat shield; unclip the coolant hose to allow
the upper part to be withdrawn.
15Remove the auxiliary drivebelt (see
Chapter 1).
16Unbolt the power steering pump (see
Chapter 10); secure it as far as possible
(without disconnecting the system’s hoses)
clear of the engine/transmission.
17Raise the vehicle and support it securely
on axle stands, then remove the front
roadwheels. Drain the cooling system and (if
the engine is to be dismantled) drain the
engine oil and remove the oil filter (see
Chapter 1). Also drain the transmission as
described in the relevant Part of Chapter 7.
18Withdraw the lower part of the exhaust
manifold heat shield.
19Unscrew the nuts to disconnect the
exhaust system front downpipe from the
manifold, then unhook all the system’s rubber
mountings and withdraw the complete
exhaust system from under the vehicle (see
Chapter 4 for details).
20Where the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, mark their positions, then
disconnect the gearchange linkage and
transmission support rods from the rear of the
transmission. Unscrew the retaining nuts, and
withdraw the gear linkage heat shield from the
underbody. Unbolt the rear end of the linkage
from the underbody, swivel the linkage around
to the rear, and tie it to the underbody (see
Chapter 7, Part A, for details).
21Disconnect both anti-roll bar links from
their respective suspension strut - note the
flexible brake hose bracket attached to each
link stud - and both track rod ends from their
steering knuckles. Unfasten the clamp bolt
securing each front suspension lower arm
balljoint to its steering knuckle (see Chap-
ter 10 for details). Check that both balljoints
can be released from the knuckle assemblies
when required, but leave them in place for thetime being, secured by the clamp bolts if
necessary.
22Where the vehicle is fitted with air
conditioning, unbolt the accumulator/
dehydrator from the subframe; secure it as far
as possible (without disconnecting the
system’s hoses) clear of the engine/
transmission.
Warning: Do not disconnect the
refrigerant hoses.
23Unbolt the steering gear from the
subframe; if the bolts are not accessible from
above, a Ford service tool will be required to
reach them from underneath the vehicle (see
Chapter 10 for details).
24Unscrew the two bolts securing the power
steering system pipes to the right-hand side
of the subframe.
25Hold the radiator in its raised position, by
inserting split pins through the holes in the
rear of the engine compartment front
crossmember and into the radiator’s upper
mounting extensions. Unbolt the radiator
mounting brackets from the subframe; note
that they are handed, and are marked to
ensure correct refitting (see illustrations).
Collect and store the bottom mounting
rubbers for safekeeping, noting which way up
they are fitted.
26Unbolt the engine/transmission rear
mounting from the subframe - where the
vehicle is fitted with automatic transmission, a
separate damper may be fitted beneath the
subframe, which must be unbolted to reach
the mounting’s fasteners. Where the vehicle is
fitted with manual transmission, also unscrew
the mounting centre bolt, and unbolt the
mounting bracket from the transmission.
27Unscrew the engine/transmission front
mounting centre bolt, and unbolt the
mounting from the subframe, noting the
location of the wiring connector bracket.
28Use white paint or similar (do not use a
sharp-pointed scriber, which might break the
underbody protective coating and cause
rusting) to mark the exact relationship of the
subframe to the underbody. Unscrew the four
mounting bolts from the subframe (note their
different-sized washers - see also illus-tration 4.47A) and allow the subframe to hang
down on the suspension lower arm balljoints.
Disconnect the balljoints one at a time from
the steering knuckle assemblies (see Chap-
ter 10) and lower the subframe to the ground;
withdraw the subframe from under the
vehicle.
29Marking or labelling all components as
they are disconnected (see paragraph 5
above) and catching as much as possible of
the escaping coolant in the drain tray,
disconnect the cooling system hoses and
pipes as follows - refer to Chapter 3 for further
details, if required:
(a) Remove the radiator top hose.
(b) Remove the (heater) hose running from
the thermostat to the engine
compartment bulkhead union.
(c) Disconnect from the thermostat the hose
running to the expansion tank - secure the
hose clear of the working area.
(d) Disconnect from the thermostat the
coolant hose/pipe which runs to the
radiator bottom hose.
(e) Disconnect the radiator bottom hose from
the radiator union, from the (sump) heater
coolant pipe and from the water pump
union - secure the hose clear of the
working area.
(f) Unbolt the (heater) coolant pipe from the
sump, trace the pipe/hose round to the
engine compartment bulkhead union,
disconnecting (where fitted) the oil cooler
hoses from the cooler unions, then
remove it.
(g) Unless the vehicle has air conditioning
fitted, secure the radiator as far forwards
as possible while it is in its raised position;
if air conditioning is fitted, remove the
radiator completely (see Chapter 3).
30Where the vehicle is fitted with air
conditioning, unplug the compressor’s
electrical connector, and unbolt the
compressor from the engine (see
illustration). Secure it as far as possible
(without disconnecting the system’s hoses)
clear of the engine/transmission.
Warning: Do not disconnect the
refrigerant hoses.
2B•6 Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures
4.25A Use split pins as shown to secure
radiator in its raised position . . .
4.25B . . . while you unbolt the bottom
mountings (arrowed) - note that the
mountings are handed, and do not lose the
mounting rubbers
4.30 Unscrew bolts (arrowed) to release
air conditioning compressor from engine
procarmanuals.com
Page 75 of 279
gear linkage heat shield. Reconnect the
gearchange linkage and transmission support
rods to the transmission, adjusting the linkage
using the marks made on removal (see
Chapter 7, Part A, for details).
56Re-install the remaining components and
fasteners in the reverse order of removal.
57Add coolant, engine oil and transmission
fluids as needed (see Chapter 1).
58Run the engine, and check for proper
operation and the absence of leaks. Shut off
the engine, and recheck the fluid levels.
59Remember that, since the front suspension
subframe and steering gear have been
disturbed, the wheel alignment and steering
angles must be checked fully and carefully as
soon as possible, with any necessary
adjustments being made. This operation is best
carried out by an experienced mechanic, using
proper checking equipment; the vehicle should
therefore be taken to a Ford dealer or similarly-
qualified person for attention.
1It is much easier to dismantle and work on
the engine if it is mounted on a portable engine
stand. These stands can often be hired from a
tool hire shop. Before the engine is mounted
on a stand, the flywheel/driveplate should be
removed (Part A of this Chapter, Section 21)
so that the stand bolts can be tightened into
the end of the cylinder block/crankcase.
2If a stand is not available, it is possible to
dismantle the engine with it mounted on
blocks, on a sturdy workbench or on the floor.
Be extra-careful not to tip or drop the engine
when working without a stand.
3If you are going to obtain a reconditioned
engine, all external components must be
removed first, to be transferred to the
replacement engine (just as they will if you are
doing a complete engine overhaul yourself).
Note:When removing the external
components from the engine, pay close
attention to details that may be helpful or
important during refitting. Note the fitted
position of gaskets, seals, spacers, pins,
washers, bolts and other small items.These
external components include the following:
(a) Alternator and brackets (Chapter 5).
(b) HT leads and spark plugs (Chapter 1).
(c) Thermostat and housing (Chapter 3).
(d) Dipstick tube.
(e) Fuel injection system components
(Chapter 4).
(f) All electrical switches and sensors - refer
to the appropriate Chapter.
(g) Inlet and exhaust manifolds (Part A of this
Chapter).
(h) Oil filter (Chapter 1).
(i) Engine/transmission mounting brackets
(Part A of this Chapter, Section 22).
(j) Flywheel/driveplate (Part A of this
Chapter, Section 21).
4If you are obtaining a “short” engine (whichconsists of the engine cylinder
block/crankcase, crankshaft, pistons and
connecting rods all assembled), then the
cylinder head, sump, oil pump, and timing belt
will have to be removed also.
5If you are planning a complete overhaul, the
engine can be dismantled and the internal
components removed in the following order.
(a) Inlet and exhaust manifolds (Part A of this
Chapter).
(b) Timing belt, toothed pulleys and
tensioner, and timing belt inner cover
(Part A of this Chapter).
(c) Cylinder head (Part A of this Chapter,
Section 14).
(d) Flywheel/driveplate (Part A of this
Chapter, Section 21).
(e) Sump (Part A of this Chapter, Section 15).
(f) Oil pump (Part A of this Chapter, Sec-
tion 16).
(g) Piston/connecting rod assemblies
(Section 9).
(h) Crankshaft (Section 10).
6Before beginning the dismantling andoverhaul procedures, make sure that you have
all of the correct tools necessary. Refer to the
introductory pages at the beginning of this
manual for further information.
Note:New and reconditioned cylinder heads
are available from the manufacturers, and
from engine overhaul specialists. Due to the
fact that some specialist tools are required for
the dismantling and inspection procedures,
and new components may not be readily
available (refer to Section 1 of this Part), it may
be more practical and economical for the
home mechanic to purchase a reconditioned
head, rather than to dismantle, inspect and
recondition the original head.
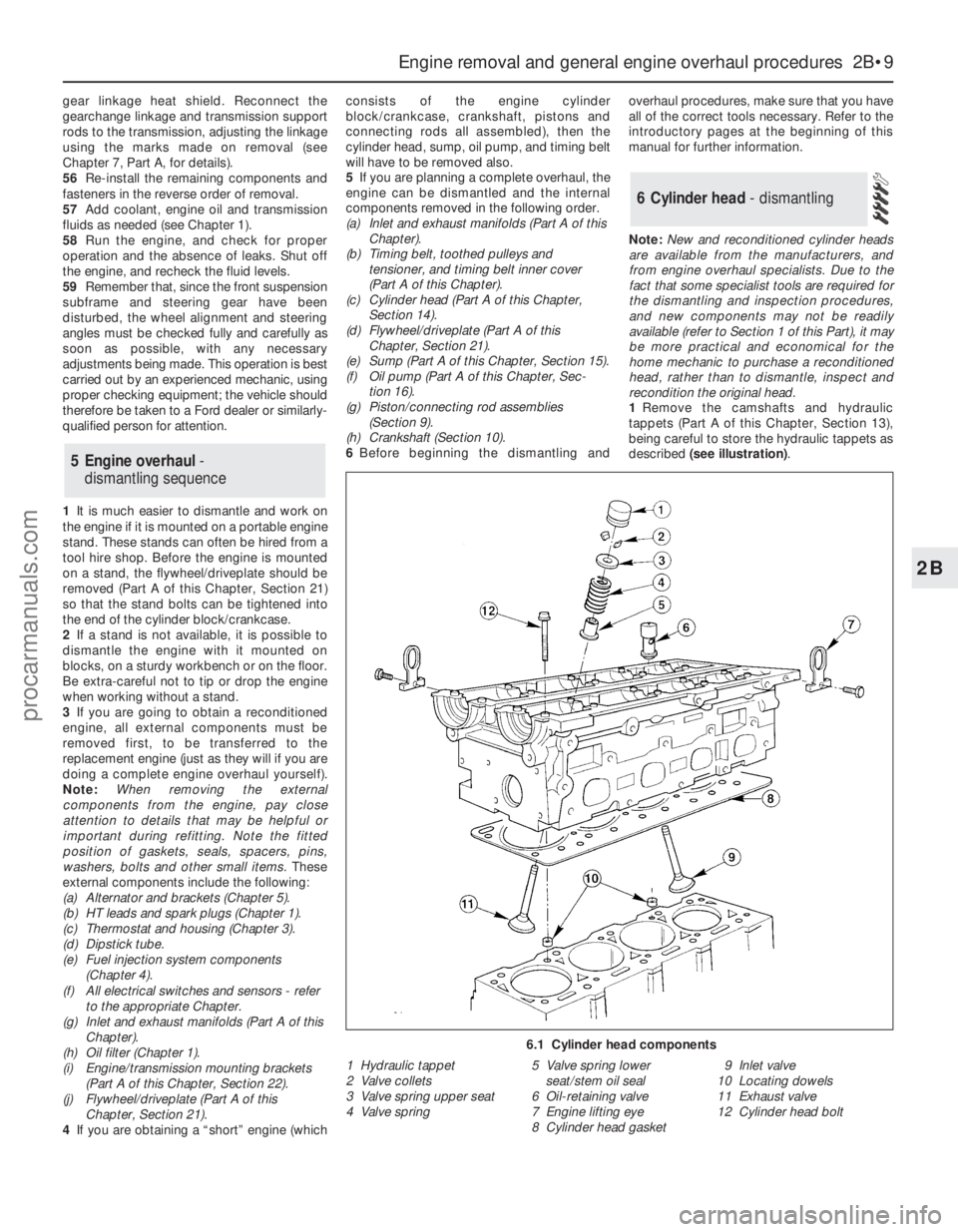
1Remove the camshafts and hydraulic
tappets (Part A of this Chapter, Section 13),
being careful to store the hydraulic tappets as
described (see illustration).
6 Cylinder head - dismantling
5 Engine overhaul-
dismantling sequence
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures 2B•9
2B
6.1 Cylinder head components
1 Hydraulic tappet
2 Valve collets
3 Valve spring upper seat
4 Valve spring5 Valve spring lower
seat/stem oil seal
6 Oil-retaining valve
7 Engine lifting eye
8 Cylinder head gasket9 Inlet valve
10 Locating dowels
11 Exhaust valve
12 Cylinder head bolt
procarmanuals.com
Page 144 of 279

Ignition timing and base idle
speed check
Note:The following procedure is a check only,
essentially of the ECU. Both the ignition timing
and the base idle speed are controlled by the
ECU. The ignition timing is not adjustable at
all; the base idle speed is set in production,
and should not be altered.
38If the fault code read-out (with any checks
resulting from it) has not eliminated the fault,
the next step is to check the ECU’s control of
the ignition timing and the base idle speed.
This task requires the use of a Ford STAR
tester (a proprietary fault code reader can be
used only if it is capable of inducing the ECU
to enter its “Service Adjustment Programme”),
coupled with an accurate tachometer and a
good-quality timing light. Without this
equipment, the task is not possible; the
vehicle must be taken to a Ford dealer for
attention.
39To make the check, apply the handbrake,
switch off the air conditioning (where fitted)
and any other electrical loads (lights, heated
rear window, etc), then select neutral (manual
transmission) or the “P” position (automatic
transmission). Start the engine, and warm it
up to normal operating temperature. The
radiator electric cooling fan must be running
continuously while the check is made; this
should be activated by the ECU, when
prompted by the tester. Switch off the engine,
and connect the test equipment as directed
by the manufacturer - refer to paragraph 26
above for details of STAR tester connection.
40Raise and support the front of the vehicle
securely, and remove the auxiliary drivebelt
cover (see Chapter 1). Emphasise the two
pairs of notches in the inner and outer rims of
the crankshaft pulley, using white paint. Note
that an ignition timing reference mark is not
provided on the pulley - in the normal
direction of crankshaft rotation (clockwise,
seen from the right-hand side of the vehicle)
the first pair of notches are irrelevant to the
vehicles covered in this manual, while the
second pair indicate Top Dead Centre (TDC)
when aligned with the rear edge of the raised
mark on the sump; when checking the ignition
timing, therefore, the (rear edge of the) sumpmark should appear just before the TDC
notches (see Part A of Chapter 2, Section 4,
for further information if required).
41Start the engine and allow it to idle. Work
through the engine-running test procedure
until the ECU enters its “Service Adjustment
Programme” - see paragraph 35 above.
42Use the timing light to check that the
timing marks appear approximately as
outlined above at idle speed. Do not spend
too much time on this check; if the timing
appears to be incorrect, the system may have
a fault, and a full system test must be carried
out (see below) to establish its cause.
43Using the tachometer, check that the
base idle speed is as given in the
Specifications Section of Chapter 4.
44If the recorded speed differs significantly
from the specified value, check for air leaks,
as described in the preliminary checks
(paragraphs 15 to 18 above), or any other
faults which might cause the discrepancy.
45The base idle speed is set in production
by means of an air bypass screw (located in
the front right-hand corner of the throttle
housing) which controls the amount of air that
is allowed to pass through a bypass passage,
past the throttle valve when it is fully closed in
the idle position; the screw is then sealed with
a white tamperproof plug (see illustration). In
service, the idle speed is controlled by the
ECU, which has the ability to compensate for
engine wear, build-up of dirt in the throttle
housing, and other factors which might
require changes in idle speed. The air bypass
screw setting should not, therefore, be
altered. If any alterations are made, a blue
tamperproof plug must be fitted, and the
engine should be allowed to idle for at least
five minutes on completion, so that the ECU
can re-learn its idle values.
46When both checks have been made and
the “Service Adjustment Programme” is
completed, follow the tester instructions to
return to the fault code read-out, and
establish whether the fault has been cured or
not.
Basic check of ignition system
47If the checks so far have not eliminated
the fault, the next step is to carry out a basic
check of the ignition system components,
using an engine analyser with an oscilloscope
- without such equipment, the only tests
possible are to remove and check each spark
plug in turn, to check the spark plug (HT) lead
connections and resistances, and to check
the connections and resistances of the
ignition coil. Refer to the relevant Sections of
Chapters 1 and 5.
Basic check of fuel system
48If the checks so far have not eliminated
the fault, the next step is to carry out a basic
check of the fuel system components.
49Assuming that the preliminary checks
have established that the fuel pump is
operating correctly, that the fuel filter isunlikely to be blocked, and also that there are
no leaks in the system, the next step is to
check the fuel pressure (see Chapter 4). If this
is correct, check the injectors (see Chapter 4)
and the Positive Crankcase Ventilation system
(see Chapter 1).
System test
50The final element of the Ford testing
procedure is to carry out a system test, using
a break-out box - this is a device that is
connected between the ECU and its electrical
connector, so that the individual circuits
indicated by the fault code read-out can be
tested while connected to the system, if
necessary with the engine running. In the case
of many of the system’s components, this
enables their output voltages to be measured
- a more accurate means of testing.
51In addition to the break-out box and the
adaptors required to connect it, several items
of specialist equipment are needed to
complete these tests. This puts them quite
beyond the scope of many smaller dealers, let
alone the DIY owner; the vehicle should be
taken to a Ford dealer for attention.
Note:This Section is concerned principally
with the sensors which give the ECU the
information it needs to control the various
engine management sub-systems - for further
details of those systems and their other
components, refer to the relevant Chapter of
this manual.
General
ECU (Electronic Control Unit)
1This component is the heart of the entire
engine management system, controlling the
fuel injection, ignition and emissions control
systems. It also controls sub-systems such as
the radiator cooling fan, air conditioning and
automatic transmission, where appropriate.
Refer to Section 2 of this Chapter for an
illustration of how it works.
Air mass meter
2This uses a “hot-wire” system, sending the
ECU a constantly-varying (analogue) voltage
signal corresponding to the mass of air
passing into the engine. Since air mass varies
with temperature (cold air being denser than
warm), measuring air mass provides the ECU
with a very accurate means of determining the
correct amount of fuel required to achieve the
ideal air/fuel mixture ratio.
Crankshaft speed/position sensor
3This is an inductive pulse generator bolted
(in a separate bracket) to the cylinder
block/crankcase, to scan the ridges between
36 holes machined in the inboard (right-hand)
face of the flywheel/driveplate. As each ridge
4 Information sensors -
general information, testing,
removal and refitting
6•10 Emissions control systems
3.45 Throttle housing air bypass screw is
sealed on production with a white
tamperproof plug (arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 174 of 279

15Locate the steering column shaft on the
flexible coupling, swivel the clamp plate
round, then insert the bolt and tighten to the
specified torque.
16Refit the driver’s side lower trim panel.
17Refit the steering column upper and lower
shrouds.
18Reconnect the battery negative lead.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5, Section 1).
2Turn the steering wheel so that the front
wheels are in the straight-ahead position.
Remove the ignition key, then turn the
steering wheel slightly as necessary until the
steering lock engages.
3Unscrew the clamp plate bolt securing the
steering column shaft to the flexible coupling.
Swivel the clamp plate around, and disengage
it from the flexible coupling stub.
4Carefully prise the rubber boot from the
bulkhead, and withdraw it into the passenger
compartment. Take care not to damage the
sealing lip of the boot.
5Using an Allen key, unscrew the clamp bolt
securing the flexible coupling to the pinion
shaft on the steering gear, and withdraw the
coupling from inside the vehicle.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure, but tighten the clamp bolts to the
specified torque. Make sure that the rubber
boot engages correctly in the bulkhead and
on the flexible coupling.
Removal
1Remove the steering column flexible
coupling as described in Section 29.
2Apply the handbrake, then jack up the frontof the vehicle and support it on axle stands.
Remove both front wheels.
3Working beneath the vehicle, unbolt the
rear engine mounting from the transmission
and underbody.
4Extract the split pins from the track rod end
balljoint nuts, then unscrew the nuts, and
detach the rods from the arms on the steering
knuckles using a conventional balljoint
removal tool. Take care not to damage the
balljoint seals.
5Position a suitable container beneath the
steering gear, then unscrew the union nuts
securing the power steering fluid supply,
return, and cooler lines to the steering gear.
Identify the lines for position, then unbolt the
clamps, disconnect the lines, and allow the
fluid to drain into the container. Cover the
apertures in the steering gear and also the
ends of the fluid pipes, to prevent the ingress
of dust and dirt into the hydraulic circuit.
6Unscrew and remove the steering gear
mounting bolts. The bolts are located on top
of the steering gear, and are difficult to reach.
Ideally, the special U-shaped Ford spanner
should be used, but it is just possible to reach
them with a normal spanner (see illustration).
7Withdraw the steering gear through the
wheel arch.
Refitting
8If the steering gear is being replaced with a
new one, the new unit will be supplied
together with union nuts already fitted. The
new nuts must only be used with new feed
and return lines - otherwise, they must be
removed and discarded. If the original lines
and union nuts are being used, the Teflon
rings on the union nuts must be renewed. To
do this, the rings must be expanded
individually onto a fitting adaptor (see
illustration), then located in the grooves of
the union nuts.
9Locate the steering gear on the subframe,
and insert the two mounting bolts. Tighten the
bolts to the specified torque (see illustration).
Note that, if the special Ford tool is being
used, the bottom of the tool must be turned
anti-clockwise in order to tighten the
mounting bolts.10Remove the covers from the apertures on
the steering gear, then reconnect the fluid
lines and tighten the union nuts to the
specified torque. Refit the clamps and tighten
the bolts.
11Refit the track rod end balljoints to the
steering knuckles, and tighten the nuts to the
specified torque. Check that the split pin
holes are aligned; if necessary, turn the nuts
to the nearest alignment, making sure that the
torque wrench setting is still within the
specified range. Insert new split pins, and
bend them back to secure.
12Refit the rear engine mounting to the
transmission and underbody, and tighten the
bolts to the specified torque.
13Refit the front wheels, and lower the
vehicle to the ground.
14Refit the steering column flexible coupling
with reference to Section 29.
15Bleed the power steering hydraulic
system as described in Section 33.
16Have the front wheel alignment checked,
and if necessary adjusted, at the earliest
opportunity (refer to Section 36).Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5, Section 1).
2Working inside the vehicle, unscrew the
clamp plate bolt securing the steering column
shaft to the flexible coupling. Swivel the clamp
plate around, and disengage it from the
flexible coupling stub.
3Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle and support it on axle stands.
Remove both wheels.
4On manual transmission models,
disconnect the gearchange linkage and
support rods from the transmission, as
described in Chapter 7, Part A.
5Remove the exhaust downpipe complete,
as described in Chapter 4.
6Remove the cover from under the radiator
by unscrewing the screws and releasing the
clips.
31 Power steering gear
(left-hand-drive models with
ABS) - removal and refitting
30 Power steering gear (all except
left-hand-drive models with
ABS) - removal and refitting
29 Steering column flexible
coupling - removal and refitting
10•20 Suspension and steering systems
30.6 U-shaped Ford spanner for
unscrewing the steering gear mounting
bolts
30.8 Using an adaptor to fit the Teflon
rings to the union nuts
1 Adaptor 2 Teflon ring 3 Union nut
4 Groove location for the Teflon ring
30.9 Tightening the steering gear
mounting bolts using the U-shaped
spanner (arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 175 of 279

7Support the radiator in its raised position,
by inserting split pins through the small holes
in the radiator mounting extensions which
protrude through the upper mountings (see
illustration).
8Unbolt and remove the radiator lower
mounting brackets.
9Where applicable, unscrew the bolts
securing the air conditioning accumulator to
the subframe.
10Working beneath the vehicle, unbolt the
engine rear mounting from the transmission
and underbody.
11Unscrew the front engine mounting-to-
cylinder block bolts, and also the through-
bolt.
12Extract the split pins from the track rod
end balljoint nuts, then unscrew the nuts, and
detach the rods from the arms on the steering
knuckles using a conventional balljoint
removal tool. Take care not to damage the
balljoint seals.
13Working on each side in turn, unscrew the
mounting nuts, and remove the anti-roll bar
links from the front suspension struts. Note
that, on models fitted with ABS, the ABS
sensor wiring support brackets are located
beneath the nuts.
14Working on each side in turn, note which
way round the front suspension lower arm
balljoint clamp bolt is fitted, then unscrew and
remove it from the knuckle assembly. Lever
the balljoint down from the knuckle - if it is
tight, prise the joint open carefully using a
large flat-bladed tool. Take care not to
damage the balljoint seal during the
separation procedure.
15Support the weight of the front subframe
assembly on two trolley jacks (or two scissor
jacks).
16Unscrew and remove the subframe
mounting bolts, then lower the subframe
sufficiently to gain access to the power
steering fluid pipes on top of the steering
gear. Note that the front subframe mountingbolts are gold in colour - the rear ones are
silver.
17Position a suitable container beneath the
steering gear, then unscrew the union nuts
securing the power steering fluid supply,
return, and cooler lines to the steering gear.
Identify the lines for position, then unbolt the
clamps, disconnect the lines, and allow the
fluid to drain into the container. Cover the
apertures in the steering gear and also the
ends of the fluid pipes, to prevent the ingress
of dust and dirt into the hydraulic circuit.
18Lower the subframe, together with the
power steering gear, to the ground.
19Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove
the power steering gear from the subframe.
20Using a suitable Allen key, unscrew the
clamp bolt securing the flexible coupling to
the pinion shaft on the steering gear, and
withdraw the coupling.
21Refer to Section 30, paragraph 8 for
details of renewing the Teflon rings.Refitting
22Refit the flexible coupling to the pinion
shaft on the steering gear, then insert and
tighten the clamp bolt using an Allen key.
23Locate the power steering gear on the
subframe, then insert the mounting bolts and
tighten to the specified torque.
24Raise the subframe until it is possible to
refit the fluid lines. Tighten the union nuts and
clamps.
25Raise the subframe, making sure that the
alignment holes are in line with the holes in
the underbody. At the same time, make sure
that the flexible coupling locates correctly on
the steering column. Ford technicians use a
special tool to ensure that the subframe is
correctly aligned - refer to Chapter 2 for more
details of the alignment procedure. With the
subframe aligned, insert and tighten the
mounting bolts to the specified torque. Note
that the front mounting bolts are gold in
colour - the rear bolts are silver.
26Working on each side in turn, refit the
front suspension lower arm balljoint to the
knuckle assembly, and insert the clamp bolt
with its head facing forwards. Refit the nut
and tighten to the specified torque.
27Working on each side in turn, refit the
anti-roll bar links and tighten the mounting
nuts to the specified torque. On models fitted
with ABS, don’t forget to locate the wheel
sensor wiring support brackets beneath the
nuts.
28Refit the track rod end balljoints to the
steering knuckles, and tighten the nuts to the
specified torque. Check if the split pin holes
are aligned, and if necessary turn the nuts to
the nearest alignment, making sure that the
torque wrench setting is still within the
specified range. Insert new split pins, and
bend them back to secure.
29Refit and tighten the engine front
mounting bolts.
30Refit the engine rear mounting and tighten
the bolts.31Where applicable, insert and tighten the
air conditioning accumulator bolts.
32Refit the radiator lower mounting brackets
and tighten the bolts.
33Remove the split pins supporting the
radiator in its raised position.
34Refit the cover under the radiator.
35Refit the exhaust downpipe as described
in Chapter 4.
36On manual transmission models,
reconnect the gearchange linkage and
support rods.
37Refit the front wheels, and lower the
vehicle to the ground.
38Working inside the vehicle, reconnect the
steering column clamp plate, then insert the
bolt and tighten to the specified torque.
39Reconnect the battery negative lead.
40Bleed the power steering hydraulic
system as described in Section 33.
41Have the front wheel alignment checked,
and if necessary adjusted, at the earliest
opportunity (refer to Section 36).
1Remove the track rod end and its locknut
from the track rod, as described in Section 35.
Make sure that a note is made of the exact
position of the track rod end on the track rod,
in order to retain the front wheel alignment
setting on refitting.
2Release the outer retaining clip and inner
plastic clamp band, and disconnect the gaiter
from the steering gear housing.
3Disconnect the breather from the gaiter,
then slide the gaiter off the track rod.
4Scrape off all grease from the old gaiter,
and apply to the track rod inner joint. Wipe
clean the seating areas on the steering gear
housing and track rod.
5Slide the new gaiter onto the track rod and
steering gear housing, and reconnect the
breather.
6Fit a new inner plastic clamp band and
outer retaining clip.
7Refit the track rod end as described in
Section 35.
8Have the front wheel alignment checked,
and if necessary adjusted, at the earliest
opportunity (refer to Section 36).
1Following any operation in which the power
steering fluid lines have been disconnected,
the power steering system must be bled, to
remove any trapped air.
2With the front wheels in the straight-ahead
position, check the power steering fluid level
in the reservoir and, if low, add fresh fluid until
it reaches the “MAX” or “MAX COLD” mark.
Pour the fluid slowly, to prevent air bubbles
forming, and use only the specified fluid (refer
to Chapter 1 Specifications).
33 Power steering hydraulic
system - bleeding
32 Power steering gear rubber
gaiters - renewal
Suspension and steering systems 10•21
10
31.7 Method of supporting the radiator in
its raised position
1 Radiator upper mounting extension
2 Small hole
3 Pin or split pin inserted through hole
procarmanuals.com
Page 223 of 279

1A compact disc (CD) player is available as
an optional extra on most models. On some
models, an autochanger version is available,
which can hold a number of discs at a time.
Removal
2The battery negative (earth) lead should be
disconnected before commencing work.
CD player, or autochanger control
unit
3The procedure is identical to that for the
radio/cassette player described in Section 23.
CD player autochanger
4The CD player autochanger unit is mounted
on the right-hand side of the luggage
compartment. The wiring loom passes up the
“C” pillar, across to the left-hand side “A”
pillar, then to the centre console area.
5Remove the trim cover from the
autochanger unit.
6Unscrew the mounting screws, and remove
the autochanger unit from its mounting
bracket.
7Disconnect the multi-plug and remove the
unit from inside the vehicle.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Removal
1Remove the door trim panel as described in
Chapter 11.
2Unscrew the cross-head screws, and
withdraw the speaker from the door inner
panel.
3Disconnect the wiring and remove the
speaker.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Removal
1Prise out the trim cover from the headlining
immediately below the base of the aerial.
2Unscrew the cross-head screw from the
base of the aerial, and remove the aerial mast.
Refitting
3Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Warning: Handle the air bag unit
with extreme care, as a
precaution against personal
injury, and always hold it with the
cover facing away from the body. If in
doubt concerning any proposed work
involving the air bag unit or its control
circuitry, consult a Ford dealer or other
qualified specialist.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5, Section 1).
Warning: Before proceeding, wait
a minimum of 15 minutes, as a
precaution against accidental
firing of the air bag unit. This
period ensures that any stored energy in
the back-up capacitor is dissipated.
2Rotate the steering wheel so that one of the
mounting bolt holes is visible above the
steering column upper shroud.
3Unscrew and remove the first mounting
bolt, then turn the steering wheel as
necessary and remove the remaining
mounting bolts (see illustration).
4Carefully withdraw the air bag unit from the
steering wheel far enough to disconnect the
wiring multi-plug, then remove it from inside
the vehicle (see illustration). Warning: Stand the unit with the
cover uppermost, and do not
expose it to heat sources in
excess of 100ºC.
Warning: Do not attempt to open
or repair the air bag unit, or apply
any electrical current to it. Do not
use any air bag unit which is visibly
damaged or which has been tampered
with.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5, Section 1).
Warning: Before proceeding, wait
a minimum of 15 minutes, as a
precaution against accidental
firing of the air bag unit. This
period ensures that any stored energy in
the back-up capacitor is dissipated.
2Remove the facia panel as described in
Chapter 11.
3Disconnect the multi-plug from the module,
by pressing the locking tab upwards and
swivelling the retaining strap.
4Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove
the module from the vehicle.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
Removal
1Remove the air bag unit as described in
Section 28.
2Disconnect the horn switch multi-plug.
3If fitted, disconnect the multi-plugs for the
cruise control.
4Remove the steering wheel and shrouds.
5Using a small screwdriver, release the
retaining tabs, then remove the clock spring
from the steering column.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure, but make sure that the steering
wheel is centralised. The clock spring must be
fitted in its central position, with the special
alignment marks aligned and the TOP mark
uppermost. To check for this position, turn the
clock spring housing anti-clockwise until it is
tight, then turn in the opposite direction by
two-and-three-quarter turns.
30 Air bag clock spring-
removal and refitting
29 Air bag control module -
removal and refitting
28 Air bag unit (driver’s side) -
removal and refitting
27 Radio aerial -
removal and refitting
26 Speakers -
removal and refitting
25 Compact disc player -
removal and refitting
12•22 Body electrical system
28.3 Unscrewing an air bag mounting bolt28.4 Disconnecting the air bag wiring
multi-plug (arrowed)
procarmanuals.com