1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM oil type
[x] Cancel search: oil typePage 1632 of 2438

3.0L ENGINE INDEX
page page
Accessory Drive Belt Service ................ 70
Auto Lash Adjuster ....................... 75
Camshaft Service ........................ 76
Checking Engine Oil Pressure ............... 93
Crankshaft and Cylinder Block, Assembly Service . 86
Cylinder Block ........................... 89
Cylinder Head ........................... 78
Cylinder Head and Camshaft Service ......... 75
Engine Assembly ......................... 69
Engine Lubrication System ................. 91
Engine Mounts .......................... 68 Engine Specifications
..................... 95
General Information ....................... 66
Oil Filter and Bracket ..................... 94
Oil Pan ................................ 92
Oil Pump Service ........................ 92
Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly Service . . . 82
Timing Belt InspectionÐIn Vehicle ............ 72
Timing Belt Service ....................... 72
Valve Service ........................... 80
GENERAL INFORMATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER OR CODE
The engine identification number is located on the
rear of the cylinder block just below the cylinder
head (Fig. 1). BLOCK: The cylinder block is a light weight de-
sign created by reducing thickness in many parts
and a short 10 mm (3/8 inch) block skirt. High rigid-
ity is provided with ribs cast in the outer wall, a full
length water jacket, and a monoblock or beam type, main bearing cap. This single unit four bearing cap
is designed to control vibration of the cylinder block
partition walls.
CRANKSHAFT: A six throw, five weight crank-
shaft is supported by four main bearings with num-
ber three being the thrust bearing. The six separate
connecting rod throws pins reduce torque fluctua-
tions while a torsional vibration damper is used to
control torsion caused vibration of the crankshaft.
Rubber lipped seals are used at front and rear. The
front seal is retained in the oil pump case and the
rear is retained in a block-mounted housing.
3.0L ENGINE
9 - 66 3.0L ENGINE Ä
Page 1633 of 2438

PISTONS: Are aluminum alloy with a steel strut,
short height, and thin wall so as to be autothermic
and light weight. The piston head with valve re-
cesses, in combination with the cylinder head, forms
a compact spherical head with clearance for total
valve lift with pistons at top dead center. The piston
skirt, top and second ring lands are finished to a ta-
pered roughness for oil retention and high resistance
to scuffing. Piston pins, press-fitted into place, join
the pistons to the connecting rods. CYLINDER HEAD: The alloy cylinder heads fea- ture cross-flow type intake and exhaust ports. Valve
guides and inserts are hardened cast iron. Valves of
heat resistance steel are arranged i
n a V with each
camshaft on center. To improve combustion speed the
chambers are a compact spherical design with a
squish area of approximately 30 percent of the piston
top area. The cylinder heads are common to either
cylinder bank by reversing the direction of installa-
tion. CAMSHAFTS: Two overhead camshafts provide
valve actuation, one front (radiator side of cylinder
bank) and one rear. The front camshaft is provided
with a distributor drive and is longer. Both cam-
shafts are supported by four bearing journals, thrust
for the front camshaft is taken at journal two and
the rear at journal three. Front and rear camshaft
driving sprockets are interchangeable. The sprockets
and the engine water pump are driven by a single
notched timing belt. ROCKER ARM SHAFTS: The shafts are retained
by the camshaft bearing journal caps. Four shafts are
used, one for each intake and exhaust rocker arm as-
sembly on each cylinder head. The hollow shafts pro-
vide a duct for lubricating oil flow from the cylinder
head to the valve mechanisms. ROCKER ARMS: Are of light weight die-cast
with roller type follower operating against the cam
shaft. The valve actuating end of the rocker arms are
machined to retain hydraulic lash adjusters, elimi-
nating valve lash adjustment. VALVES: Are made of heat resistant steel and are
further treated to resist heat. VALVE SPRINGS: Are especially designed to be
short. The valve spring wire cross-section is oval
SPECIFICATIONS
Fig. 1 Engine Identification
Ä 3.0L ENGINE 9 - 67
Page 1634 of 2438
shaped and provides the same spring tension as
longer springs. Valve spring retainers, locks and
seals are conventional.INTAKE MANIFOLD: The aluminum alloy man-
ifold is a cross type with long runners to improve in-
ertia. The runners, attaching below at the cylinder
head, also attach above and support an air plenum.
The air plenum chamber absorbs air pulsations cre-
ated during the suction phase of each cylinder. EXHAUST MANIFOLDS: Both manifolds are a
log style made of ductile cast iron. Exhaust gasses,
collected from the front cylinder bank, leave the
front manifold through an end outlet and are fed
through an upper crossover tube to the rear mani-
fold. The collected exhaust from both manifolds are
combined, and exit to the exhaust pipe through an
articulated joint. ENGINE LUBRICATION: System is a full flow
filtration, pressure feed type. The oil pump is
mounted in the chaincase cover. The pump inner ro-
tor is driven by the crankshaft. The engine oil pan
contains a baffle plate to control oil level fluctuation
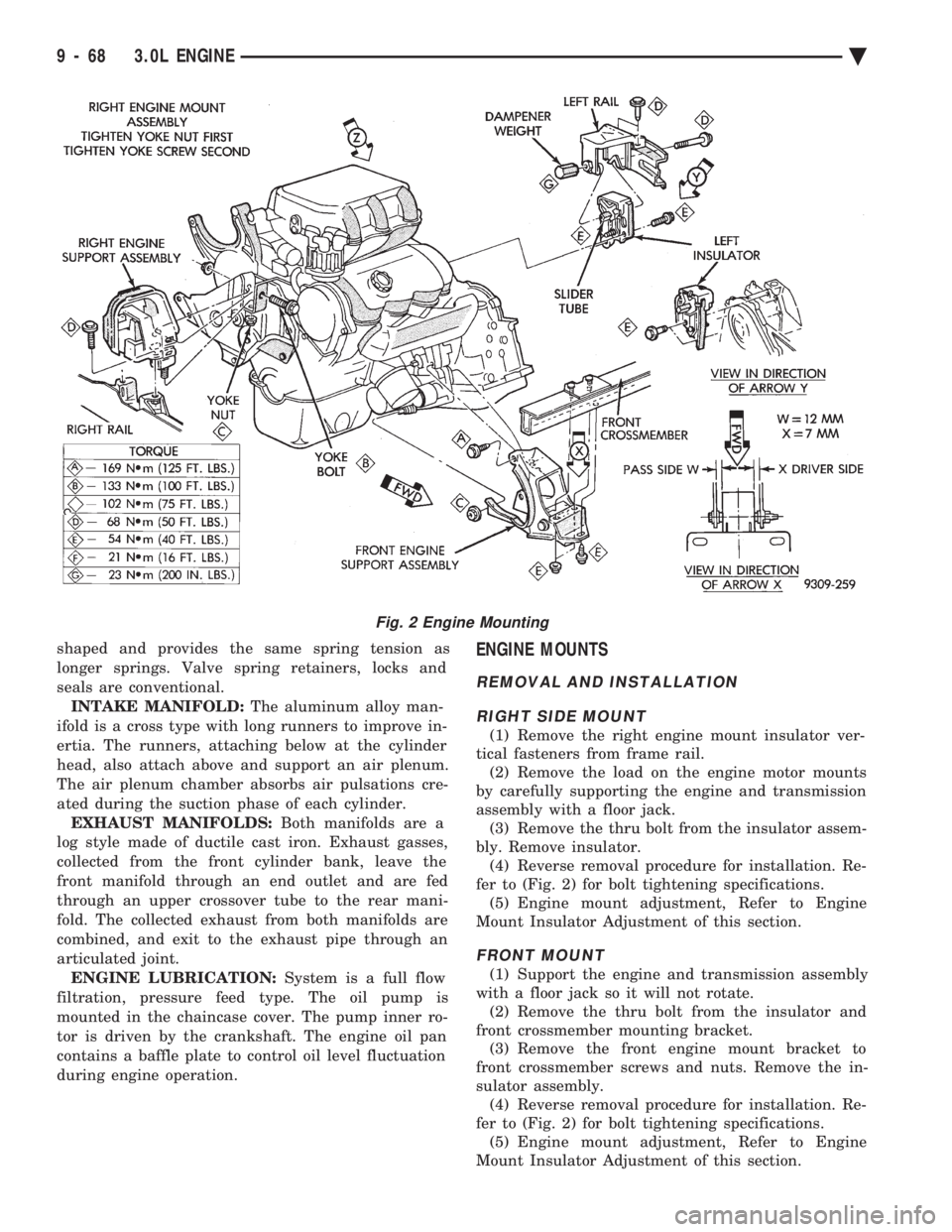
during engine operation.ENGINE MOUNTS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
RIGHT SIDE MOUNT
(1) Remove the right engine mount insulator ver-
tical fasteners from frame rail. (2) Remove the load on the engine motor mounts
by carefully supporting the engine and transmission
assembly with a floor jack. (3) Remove the thru bolt from the insulator assem-
bly. Remove insulator. (4) Reverse removal procedure for installation. Re-
fer to (Fig. 2) for bolt tightening specifications. (5) Engine mount adjustment, Refer to Engine
Mount Insulator Adjustment of this section.
FRONT MOUNT
(1) Support the engine and transmission assembly
with a floor jack so it will not rotate. (2) Remove the thru bolt from the insulator and
front crossmember mounting bracket. (3) Remove the front engine mount bracket to
front crossmember screws and nuts. Remove the in-
sulator assembly. (4) Reverse removal procedure for installation. Re-
fer to (Fig. 2) for bolt tightening specifications. (5) Engine mount adjustment, Refer to Engine
Mount Insulator Adjustment of this section.
Fig. 2 Engine Mounting
9 - 68 3.0L ENGINE Ä
Page 1635 of 2438

LEFT SIDE MOUNT
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist and remove left front
wheel. (2) Remove inter splash shield.
(3) Support the transmission with a transmission
jack. (4) Remove the insulator thru bolt from the mount.
(5) Remove the transmission mount fasteners and
remove mount. (6) Reverse removal procedure for installation. En-
sure that the slide tube is seated into the rail
bracket guides. Refer to (Fig. 3) for bolt tightening
specifications. (7) Engine mount adjustment, Refer to Engine
Mount Insulator Adjustment of this section.
ENGINE MOUNT RUBBER INSULATORS
Insulator location on (right side) and transmission
bracket (left side) are adjustable to allow right/left
drive train adjustment in relation to drive shaft as-
sembly length. Check and reposition right engine mount insulator
(left engine mount insulator is floating type and will
adjust automatically (Fig. 3). Adjust drive train posi-
tion, if required, for the following conditions:
² Drive shaft distress: See Driveshafts in Suspen-
sion, Group 2.
² Any front end structural damage (after repair).
² Insulator replacement.
ENGINE MOUNT INSULATOR ADJUSTMENT
(1) Remove the load on the engine motor mounts
by carefully supporting the engine and transmission
assembly with a floor jack. (2) Loosen the right engine mount insulator yoke
screw and two turns on yoke nut, then loosen the
front engine mount bracket to front crossmember
screws and nuts. Left engine mount insulator is sleeved over
shaft and long support bolt to provide lateral
movement adjustment with engine weight re-
moved or not. (3) Pry the engine right or left as required to
achieve the proper drive shaft assembly length. See
Drive Shaft in Suspension Group 2 for driveshaft
identification and related assembly length measur-
ing. (4) Tighten right engine mount insulator yoke nut
to 102 N Im (75 ft. lbs.). Then tighten front engine
mount screws and nuts to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.) and
center left engine mount insulator. (5) Recheck drive shaft length.
ENGINE ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery.
(2) Mark hood position at hinges and remove hood. (3) Drain cooling system. Refer to Cooling System
Group 7 for draining procedure. (4) Disconnect all electrical connections.
(5) Remove coolant hoses from radiator and en-
gine. (6) Remove radiator and fan assembly.
(7) See Fuel System Group 14, For procedures to
release fuel pressure, disconnect fuel lines and accel-
erator cable. (8) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(9) Hoist vehicle and drain engine oil.
(10) Remove air conditioning compressor mounting
bolts and set compressor aside. (11) Disconnect exhaust pipe at manifold.
(12) Remove transmission inspection cover and
mark flex plate to torque converter position. (13) Remove screws holding torque converter to
flex plate and attach C-clamp on bottom of converter
housing to prevent torque converter from coming out. (14) Remove power steering pump mounting bolts
and set pump aside. (15) Remove two lower transmission to block
screws. (16) Remove starter.
(17) Lower vehicles and disconnect vacuum lines
and ground strap. (18) Install transmission holding fixture.
(19) Attach engine lifting hoist and support en-
gine. (20) Remove upper transmission case to block
bolts. (21) See Engine Mounting in (Fig. 2) and separate
mount/insulators as follows: (a) Mark RIGHT insulator on right yoke and en-
gine plate supports. Remove insulator to rails
screws. (b) Remove FRONT engine mount through bolt
and nut.
Fig. 3 Left Insulator Movement
Ä 3.0L ENGINE 9 - 69
Page 1657 of 2438
(clearance between piston O.D. and cylinder) minus
0.02 mm which is the boring margin. (3) Bore all cylinders to calculated boring finish di-
mension. Then bore the final finish dimension (piston
O.D. plus cylinder clearance). (4) Check clearance between piston and cylinder,
clearance should be 0.03 to 0.05 mm (.0012 to .002
inch).
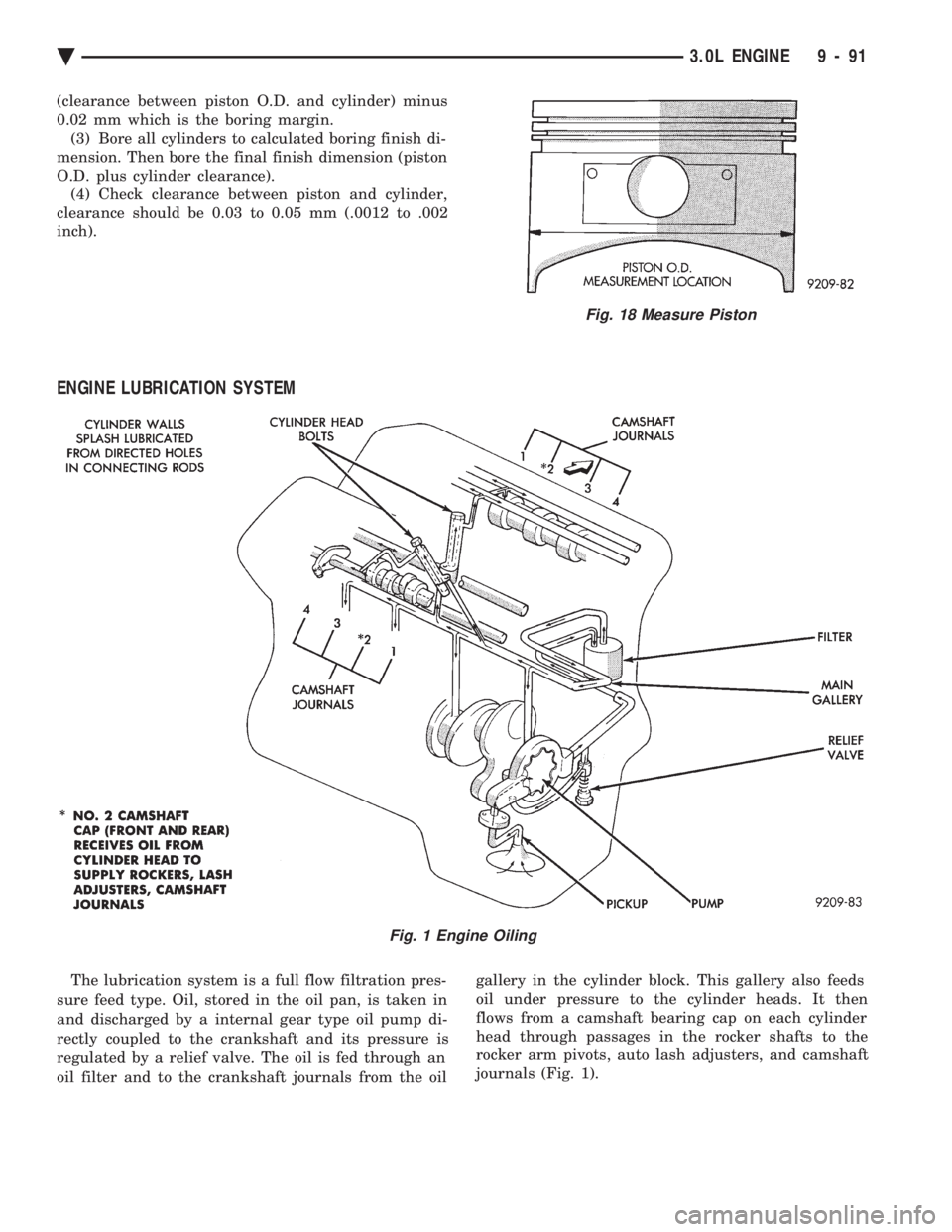
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM
The lubrication system is a full flow filtration pres-
sure feed type. Oil, stored in the oil pan, is taken in
and discharged by a internal gear type oil pump di-
rectly coupled to the crankshaft and its pressure is
regulated by a relief valve. The oil is fed through an
oil filter and to the crankshaft journals from the oil gallery in the cylinder block. This gallery also feeds
oil under pressure to the cylinder heads. It then
flows from a camshaft bearing cap on each cylinder
head through passages in the rocker shafts to the
rocker arm pivots, auto lash adjusters, and camshaft
journals (Fig. 1).
Fig. 18 Measure Piston
Fig. 1 Engine Oiling
Ä 3.0L ENGINE 9 - 91
Page 1664 of 2438

3.3/3.8L ENGINE INDEX
page page
Camshaft .............................. 112
Camshaft BearingsÐEngine Removed From Vehicle .............................. 113
Checking Engine Oil Pressure .............. 125
Connecting Rods ........................ 118
Crankshaft Oil Seals Service ............... 121
Crankshaft Service ...................... 118
Cylinder Block, Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly Service ...................... 114
Cylinder Heads ......................... 102
Engine Assembly ........................ 101
Engine Core Oil and Cam Plugs ............ 113
Engine Lubrication System ................ 122 Engine Mounts
.......................... 99
Engine Specifications ..................... 126
General Information ....................... 98
Hydraulic Tappets ....................... 108
Installing Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly . 117
Intake Manifold Sealing ................... 104
Oil Filter .............................. 125
Oil Pan Service ......................... 122
Oil Pump Service ....................... 123
Rocker Arms and Shaft Assembly ........... 102
Timing Chain Cover, Oil Seal and Chain ...... 109
Valve Service .......................... 104
Valve Timing ........................... 109
GENERAL INFORMATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER OR CODE
The engine identification number is located on the
rear of the cylinder block just below the cylinder
head (Fig. 2). ENGINE: The 3.3L (201 Cubic. Inches.) and 3.8L
(231 Cubic. Inches.) displacement engines are 60É V
type six cylinder power plant with cast iron cylinder
block and aluminum cylinder heads (Fig. 1). Firing
order for these engines is 1-2-3-4-5-6. High turbu-
lence cylinder heads allow a 8.9-1 compression ratio. CRANKSHAFT: The nodular iron crankshaft is
supported by four main bearings, with number two being the thrust bearing. Crankshaft end sealing is
provided by front and rear rubber seal. PISTONS: The pistons are cast aluminum alloy.
Three rings are used. Piston pins, press fitted into
place, join the pistons to forged steel connecting rods. CAMSHAFT: The nodular iron camshaft is
mounted in four steel backed babbitt bearings. A
thrust plate located in front of the first bearing, and
bolted to the block, controls end play. Silent timing
chain drives the camshaft. This chain is enclosed by
a cast aluminum cover which also carries a front
crankshaft seal, provides front oil pan closure, water
pump mounting.
SPECIFICATIONS
9 - 98 3.3/3.8L ENGINE Ä
Page 1688 of 2438

ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM
The lubrication system is a full flow filtration pres-
sure feed type. Oil from the oil pan is pumped by a
internal gear type oil pump directly coupled to the
crankshaft. Its pressure is regulated by a relief valve
located in the Chain Case Cover. The oil is pumped
through an oil filter and feeds a main oil galley.This
oil gallery feeds oil under pressure to the main and
rod bearings, camshaft bearings. Passages in the cyl-
inder block feed oil to the hydraulic lifters and
rocker shaft brackets which feeds the rocker arm piv-
ots (Fig. 1).
OIL PAN SERVICE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable, remove en-
gine oil dipstick. (2) Raise vehicle. Drain engine oil.
(3) Remove oil pan screws and remove oil pan.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
(1) Clean oil pan in solvent and wipe dry with a
clean cloth. Clean all gasket material from mounting
surfaces of pan and block. (2) Inspect oil drain plug and plug hole for stripped
or damaged threads and repair as necessary. Install
a new drain plug gasket. Tighten to 27 N Im (20 ft.
lb.). (3) Inspect oil pan mounting flange for bends or
distortion. Straighten flange if necessary. (4) Clean oil screen and pipe in clean solvent. In-
spect condition of screen.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install oil pick-up tube into Chain Case Cover
tighten screw to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.) (Fig. 2).
(2) Apply a 1/8 inch bead of Mopar Silicone Rubber
Adhesive Sealant or equivalent, at the parting line of
the chain case cover and the rear seal retainer (Fig. 3). (3) Use a new pan gasket (Fig. 4).
(4) Install pan and tighten screws to 23 N Im (200 in.
lb.).
(5) Lower vehicle and install oil dipstick.
(6) Connect negative battery cable.
(7) Fill crankcase with oil to proper level.
Fig. 1 Engine Oiling System
Fig. 2 Oil Pump Pick-up Tube Service
9 - 122 3.3/3.8L ENGINE Ä
Page 1709 of 2438

(13) Disconnect articulated exhaust pipe joint from
turbocharger housing. (14) Remove turbocharger coolant inlet line assem-
bly from engine (Fig. 11). (15) Lift turbocharger off manifold mounting studs
and lower assembly down and out of vehicle.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
REMOVAL
Remove 9 exhaust manifold retaining fasteners and
remove exhaust manifold (Fig. 14).
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
(1) Discard gasket and clean all gasket surfaces of
manifolds and cylinder head. (2) Test manifold gasket surfaces for flatness with
straight edge. Surface must be flat within 0.15 mm
per 300 mm (.006 in. per foot) of manifold length. (3) Inspect manifolds for cracks or distortion. Re-
place manifold if necessary.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
INSTALLATION
(1) Install new manifold gasket. DO NOT APPLY
SEALER . (2) Set exhaust manifold in place. Tighten retain-
ing nuts and bolt, starting at center and progressing
outward in both directions to 23 N Im (200 in. lbs.)
torque. Repeat this procedure until all fasteners are
at specified torque (Fig. 14).
TURBOCHARGER
INSTALLATION
(1) Position turbocharger on exhaust manifold. Ap-
ply antiseize compound to threads and install the
lower (passenger side) retaining nut (Fig. 12).
Tighten nut to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Apply thread sealant to lower (inlet) coolant
line fitting and install fitting into turbocharger hous-
ing (Fig. 11). (3) Install lower coolant line assembly to engine
(Fig. 11). (4) Install oil drain back tube and fitting (with
new gasket) to turbocharger housing (Fig. 13). (5) Install turbocharger to block support bracket
and install screws finger tight (Fig. 13). Tighten
block screw FIRST to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.) torque,
then tighten screw to turbocharger housing to 27
N Im (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Reposition exhaust pipe. Tighten articulated
joint shoulder bolts to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.) torque.
(7) See Suspension, Group 2, and install right
driveshaft and wheel and tire assembly. Install air
deflector on crossmember. (8) From Above: Install three turbocharger to
manifold retaining nuts. Tighten to 54 N Im (40 ft.
lbs.) torque (Fig. 12). (9) Reconnect Heated Oxygen sensor electrical con-
nection and vacuum lines. (10) Attach oil feed line to turbocharger bearing
housing. Tighten fitting to 14 N Im (125 in. lbs.)
torque (Fig. 12). (11) Install coolant line and tighten fittings to 41
N Im (30 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig. 11).
(12) Install air cleaner support (Fig. 1).
(13) Align front engine mount in crossmember
bracket. Install through bolt and tighten to 54 N Im
(40 ft. lbs.) torque. (14) Install air cleaner assembly (Fig. 1).
(15) Fill cooling system. Refer to Cooling System,
Group 7 for procedure.
INTAKE/EXHAUST MANIFOLD SERVICEÐ3.0L
ENGINE
The intake system has a large air intake plenum of
aluminum alloy and a cross type intake manifold
(Fig. 2).
Fig. 13 Oil Return Tube and Support Bracket
Fig. 14 Exhaust ManifoldÐTurbo III Engine
Ä EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11 - 13