1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM Ignition coil
[x] Cancel search: Ignition coilPage 232 of 2438

The primary functions of the (CAB) are:
² (1) Detect wheel locking tendencies.
² (2) Control fluid modulation to the brakes while in
Anti-Lock mode.
² (3) Monitor the system for proper operation.
² (4) Provide communication to the DRB II while in
diagnostic mode. The (CAB) continuously monitors the speed of each
wheel, through the signals generated at the Wheel
Speed Sensors, to determine if any wheel is begin-
ning to lock. When a wheel locking tendency is de-
tected, the (CAB) will isolate the master cylinder
from the wheel brakes. This is done by activating the
Isolation Valves. The (CAB) then commands the ap-
propriate Build or Decay valves to modulate brake
fluid pressure in some or all of the hydraulic circuits.
The fluid used for modulation comes from the booster
servo circuit. The (CAB) continues to control pres-
sure in individual hydraulic circuits until a locking
tendency is no longer present. The (ABS) system is constantly monitored by the
(CAB) for proper operation. If the (CAB) detects a
fault, it can disable the Anti-Lock braking function.
Depending on the fault, the (CAB) will light one or
both of the brake warning lamps. The (CAB) contains a System Diagnostic Program
which triggers the brake system warning lamps
when a system fault is detected. Faults are stored in
a diagnostic program memory. There are 19 fault
codes that may be stored in the (CAB) and displayed
through the DRB II. These fault codes will remain in
the (CAB) memory even after the ignition has been
turned off. These fault codes will remain in memory
until they are cleared with the DRB II, or automati-
cally erased from the memory after (50) ignition
switch on/off cycles.
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (INPUTS)
² Four wheel speed sensors.
² Boost pressure transducer.
² Primary pressure transducer.
² Low fluid level switch.
² Differential pressure switch.
² Parking brake switch.
² Dual function pressure switch (warning pressure
only)
² Stop lamp switch.
² Ignition switch.
² System relay voltage.
² Ground.
² Low Accumulator
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (OUTPUTS)
²Ten modulator valves-3 decay, 3 build and 4 isola-
tion.
² Red Brake warning lamp.
² Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp.
² System relay actuation. ²
Diagnostic communication.
ABS SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC CONNECTOR
The Bendix Anti-Lock system diagnostic connector
is located under the lower dash panel or in the area
of the fuse box (Fig. 8). The fuse box is located be-
hind the access panel that is on the bottom portion of
the dash panel, left of the steering column. The diag-
nostics connector is a blue 6 way connector.
ANTI-LOCK SYSTEM RELAYS AND WARNING
LAMPS
PUMP/MOTOR RELAY
Pump/Motor power is supplied by the Pump/Motor
Relay. The Pump/Motor relay is located inside the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). The relay coil is
energized by a ground from the Dual Function Pres-
sure Switch. See (Fig. 9) for the location of the pump/
motor relay in the (PDC).
SYSTEM RELAY
The (ABS) Modulator Valves and Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp Relay are controlled through a System Re-
lay. The System relay is located on the top left inner
fender behind the headlight (Fig. 10). The system re-
lay provides power to the (CAB) for modulator valve
operation (pins 47 and 50) after the start-up cycle
when the ignition is turned on.
ANTI-LOCK WARNING LAMP RELAY
The Anti-Lock Warning Lamp is controlled by the
Yellow Light Relay. See (Fig. 10) for location behind
the left headlight. With the relay de-energized, the
lamp is lit. When the system relay is energized by
Fig. 8 A.B.S. Diagnostic Connector Location
5 - 82 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 270 of 2438
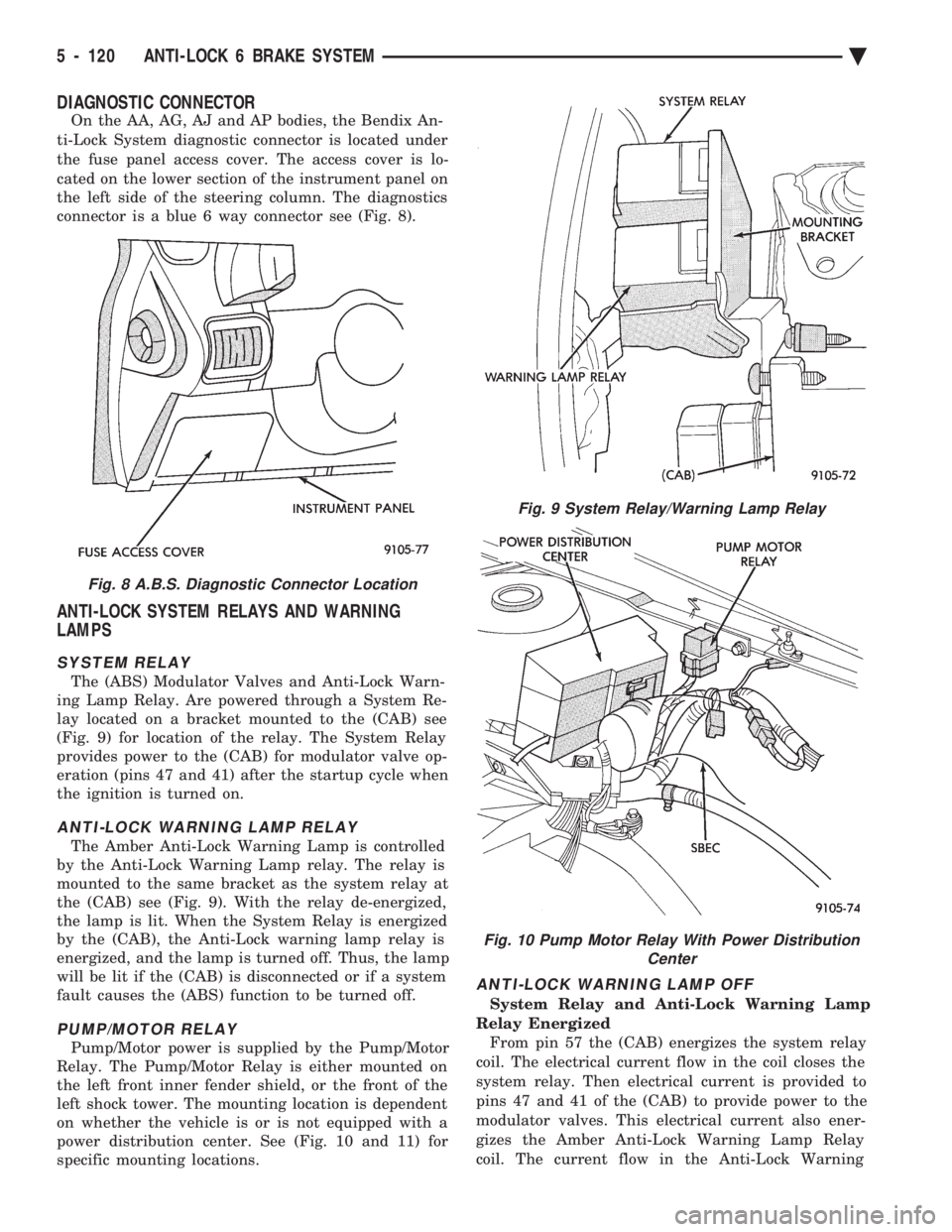
DIAGNOSTIC CONNECTOR
On the AA, AG, AJ and AP bodies, the Bendix An-
ti-Lock System diagnostic connector is located under
the fuse panel access cover. The access cover is lo-
cated on the lower section of the instrument panel on
the left side of the steering column. The diagnostics
connector is a blue 6 way connector see (Fig. 8).
ANTI-LOCK SYSTEM RELAYS AND WARNING
LAMPS
SYSTEM RELAY
The (ABS) Modulator Valves and Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp Relay. Are powered through a System Re-
lay located on a bracket mounted to the (CAB) see
(Fig. 9) for location of the relay. The System Relay
provides power to the (CAB) for modulator valve op-
eration (pins 47 and 41) after the startup cycle when
the ignition is turned on.
ANTI-LOCK WARNING LAMP RELAY
The Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp is controlled
by the Anti-Lock Warning Lamp relay. The relay is
mounted to the same bracket as the system relay at
the (CAB) see (Fig. 9). With the relay de-energized,
the lamp is lit. When the System Relay is energized
by the (CAB), the Anti-Lock warning lamp relay is
energized, and the lamp is turned off. Thus, the lamp
will be lit if the (CAB) is disconnected or if a system
fault causes the (ABS) function to be turned off.
PUMP/MOTOR RELAY
Pump/Motor power is supplied by the Pump/Motor
Relay. The Pump/Motor Relay is either mounted on
the left front inner fender shield, or the front of the
left shock tower. The mounting location is dependent
on whether the vehicle is or is not equipped with a
power distribution center. See (Fig. 10 and 11) for
specific mounting locations.
ANTI-LOCK WARNING LAMP OFF
System Relay and Anti-Lock Warning Lamp
Relay Energized From pin 57 the (CAB) energizes the system relay
coil. The electrical current flow in the coil closes the
system relay. Then electrical current is provided to
pins 47 and 41 of the (CAB) to provide power to the
modulator valves. This electrical current also ener-
gizes the Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp Relay
coil. The current flow in the Anti-Lock Warning
Fig. 8 A.B.S. Diagnostic Connector Location
Fig. 9 System Relay/Warning Lamp Relay
Fig. 10 Pump Motor Relay With Power Distribution Center
5 - 120 ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 336 of 2438

CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
The clutch pedal position switch functions as a
safety interlock device. It prevents possible engine
cranking with the clutch engaged. The clutch pedal position switch is wired in series
between the starter relay coil and the ignition
switch. The clutch pedal position switch is mounted to a
bracket located next to the clutch pedal. The switch
is held in place by four plastic wing tabs. The clutch pedal position switch has an adjustable
striker plate. The striker plate is located on the left
side of the clutch pedal (Fig. 3).
DIAGNOSIS
Disconnect clutch pedal position switch harness
from instrument panel wiring harness. Using a ohm
meter, check for continuity between the two termi-
nals in the connector on the switch harness. There
should be no continuity between the terminals when
the switch is in its neutral (fully extended) position.
When the switch is depressed more than 1.25 mm
(0.050) the ohm meter should show continuity. If all ohm meter readings are correct and the
switch does not operate correctly, adjustment is re-
quired. Refer to Switch Adjustment Procedure to ad-
just switch.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical harness to switch connec-
tor. (2) Depress wing tabs on switch and push switch out
of mounting bracket. Then slide wires through slot in
bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Slide switch wires through slot in switch bracket.
(2) Line up switch tab with slot in switch bracket
and push switch into position. Do not pull on the switch
wires to seat switch into bracket, switch damage may
occur. (3) After installation, the switch must be adjusted
and checked for proper operation. Refer to Switch
Adjustment Procedure.
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
When performing switch adjustment, the floor mat
should be removed before beginning adjustment proce-
dures. (1) Set the park brake.
(2) Disconnect clutch cable at the transaxle end of
the cable. (3) Depress clutch pedal, loosen adjusting nut and
slide the striker plate forward to fully compress the
clutch pedal position switch plunger. (4) Tighten adjusting nut to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.).
(5) Reconnect clutch cable.
The clutch pedal position switch is now ad-
justed. A final check is required to insure that the
switch is ``made'' below the clutch release point. (1) With the park brake set and the vehicle IN
NEUTRAL turn the key to the start position. The
vehicle should not crank. If the vehicle cranks do
not continue with this test. Recheck the switch and
switch adjustment to determine the cause. If the ve-
hicle does not crank proceed to step 2. (2) With the park brake set and the vehicle IN
GEAR turn the key to the start position.
WARNING: BEFORE PERFORMING STEP THREE BE
SURE THAT THE AREA IN FRONT OF THE VEHICLE
IS CLEAR OF OBSTRUCTIONS AND PEOPLE. VE-
HICLE MAY MOVE WHEN PERFORMING THIS TEST.
(3) Slowly depress the clutch pedal and feel for any
vehicle motion when the starter is energized. If there is
no motion the switch is properly adjusted. If motion is
felt, repeat the adjustment procedure.
Fig. 3 Clutch Pedal Position Switch and Components
6 - 4 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH Ä
Page 383 of 2438

STARTER TEST PROCEDURES ON VEHICLE INDEX
page page
Diagnostic Preparation ..................... 11
General Information ....................... 11 Starter Control Circuit Tests
................ 15
Starter Feed Circuit Tests .................. 11
GENERAL INFORMATION
The starting system (Fig. 1) has:
² Ignition switch
² Starter relay (Fig. 2)
² Neutral starting and back-up switch with auto-
matic transmissions
² Clutch pedal mounted starter interlock switch
with manual transmissions
² Wiring harness
² Battery
² Starter motor with an integral solenoid
These components form two separate circuits. A
high amperage circuit that feeds the starter motor up
to 300+ amps, and a control circuit that operates on
less than 20 amps.
DIAGNOSTIC PREPARATION
Before going on with starting system diagnostics,
verify: (1) The battery top, posts, and terminals are clean.
(2) The generator drive belt tension and condition
is correct. (3) The battery state-of-charge is correct.
(4) The battery will pass load test.
(5) The battery cable connections at the starter
and engine block are clean and free from corrosion. (6) The wiring harness connectors and terminals
are clean and free from corrosion. (7) Proper circuit grounding.
(8) Refer to Starter System Diagnostics (Fig. 3).
STARTER FEED CIRCUIT TESTS
The following procedure will require a suitable
volt/ampere tester (Fig. 4).
CAUTION: Ignition system also must be disabled to
prevent engine start while performing the following
tests.
(1) Connect a volt-ampere tester (Fig. 4) to the bat-
tery terminals (Fig. 5). Refer to the operating in-
structions provided with the tester being used. (2) Disable ignition system as follows:
² VEHICLES WITH CONVENTIONAL DISTRIBU-
TORS: Disconnect the ignition coil cable from the
distributor cap. Connect a suitable jumper wire be-
tween the coil cable end-terminal and a good body
ground (Fig. 6).
Fig. 1 Starting Components/Wiring
Fig. 2 Starter Relay
Ä BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 11
Page 385 of 2438
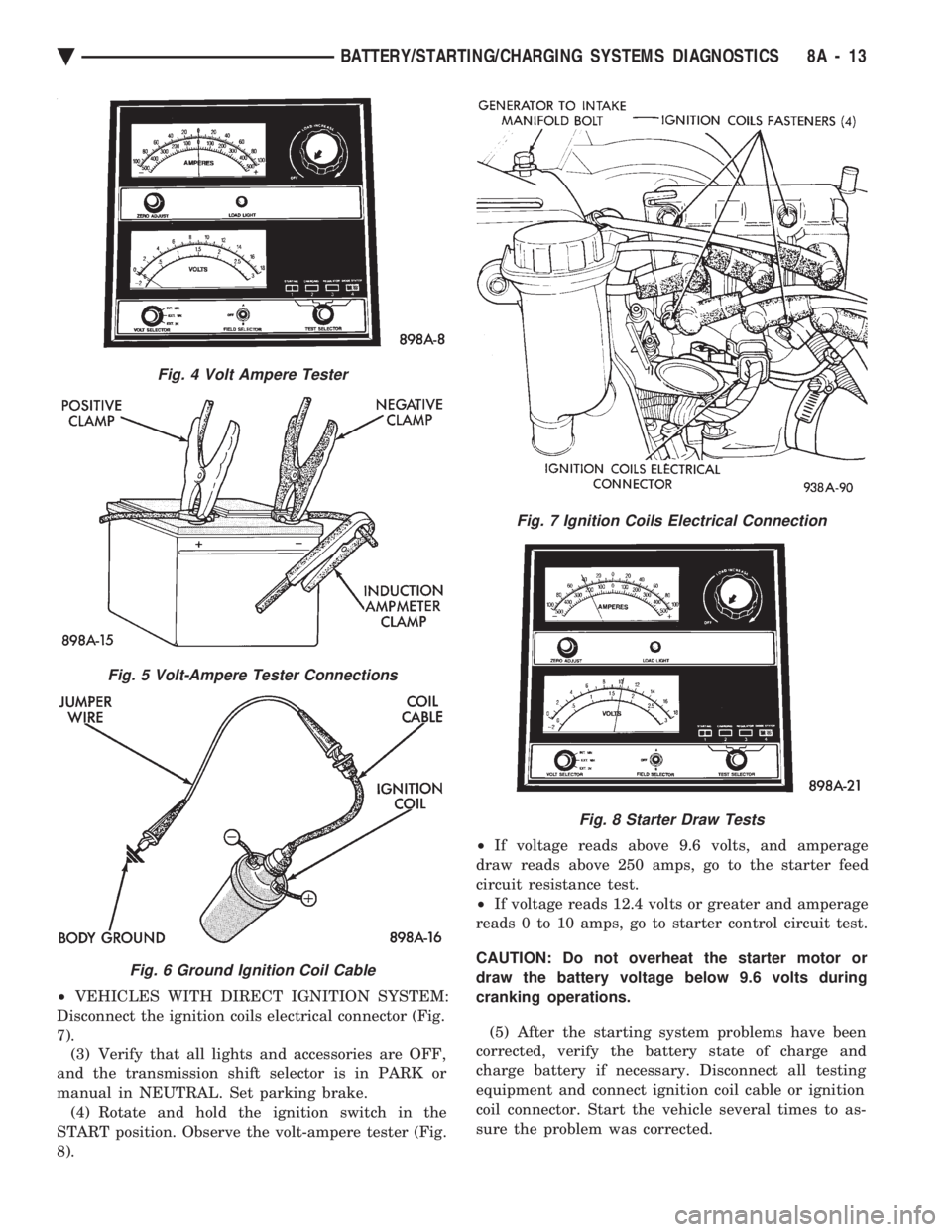
² VEHICLES WITH DIRECT IGNITION SYSTEM:
Disconnect the ignition coils electrical connector (Fig.
7). (3) Verify that all lights and accessories are OFF,
and the transmission shift selector is in PARK or
manual in NEUTRAL. Set parking brake. (4) Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. Observe the volt-ampere tester (Fig.
8). ²
If voltage reads above 9.6 volts, and amperage
draw reads above 250 amps, go to the starter feed
circuit resistance test.
² If voltage reads 12.4 volts or greater and amperage
reads 0 to 10 amps, go to starter control circuit test.
CAUTION: Do not overheat the starter motor or
draw the battery voltage below 9.6 volts during
cranking operations.
(5) After the starting system problems have been
corrected, verify the battery state of charge and
charge battery if necessary. Disconnect all testing
equipment and connect ignition coil cable or ignition
coil connector. Start the vehicle several times to as-
sure the problem was corrected.
Fig. 4 Volt Ampere Tester
Fig. 5 Volt-Ampere Tester Connections
Fig. 6 Ground Ignition Coil Cable
Fig. 7 Ignition Coils Electrical Connection
Fig. 8 Starter Draw Tests
Ä BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 13
Page 386 of 2438

STARTER FEED CIRCUIT RESISTANCE TEST
Before going on with this operation, review Diag-
nostic Preparation and Starter Feed Circuit Tests.
The following operation will require a voltmeter, ac-
curate to 1/10 of a volt.
CAUTION: Ignition system also must be disabled to
prevent engine start while performing the following
tests.
(1) Disable ignition system as follows:
² VEHICLES WITH CONVENTIONAL DISTRIBU-
TORS: Disconnect the ignition coil cable from the
distributor cap. Connect a suitable jumper wire be-
tween the coil cable end-terminal and a good body
ground (Fig. 6).
² VEHICLES WITH DIRECT IGNITION SYSTEM:
Disconnect the ignition coils electrical connector (Fig.
7). (2) With all wiring harnesses and components
properly connected, perform the following: (a) Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to
the negative battery post, and positive lead to the
negative battery cable clamp (Fig. 9). Rotate and
hold the ignition switch in the START position.
Observe the voltmeter. If voltage is detected, cor-
rect poor contact between cable clamp and post. (b) Connect positive lead of the voltmeter to the
positive battery post, and negative lead to the pos-
itive battery cable clamp. Rotate and hold the igni-
tion switch key in the START position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor con-
tact between the cable clamp and post.
(c) Connect negative lead of voltmeter to nega-
tive battery terminal, and positive lead to engine
block near the battery cable attaching point (Fig.
10). Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt,
correct poor contact at ground cable attaching point. If voltage reading is still above 0.2 volt after
correcting poor contacts, replace ground cable.
(3) Remove starter heat shield. Refer to Starter re-
placement to gain access to the starter motor and so-
lenoid connections. Perform the following steps: (a) Connect positive voltmeter lead to the starter
motor housing and the negative lead to the nega-
tive battery terminal (Fig. 11). Hold the ignition
switch key in the START position. If voltage reads
above 0.2 volt, correct poor starter to engine
ground.
(b) Connect the positive voltmeter lead to the
positive battery terminal, and negative lead to bat-
tery cable terminal on starter solenoid (Fig. 12).
Rotate and hold the ignition switch key in the
START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt,
correct poor contact at battery cable to solenoid
connection. If reading is still above 0.2 volt after
correcting poor contacts, replace positive battery
cable. (c) If resistance tests do not detect feed circuit
failures, remove the starter motor and go to Bench
Testing Starter Solenoid.
Fig. 9 Test Battery Connection Resistance
Fig. 10 Test Ground Circuit Resistance
Fig. 11 Test Starter Motor Ground
8A - 14 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS Ä
Page 387 of 2438

STARTER CONTROL CIRCUIT TESTS
The starter control circuit has:
² Starter solenoid
² Starter relay (Fig. 2)
² Neutral starting and back-up switch with auto-
matic transmissions
² Clutch pedal mounted starter interlock switch
with manual transmissions
² Ignition switch
² Battery
² All related wiring and connections
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition system must be disabled.
² VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH A CONVEN-
TIONAL DISTRIBUTOR: Disconnect coil wire from
distributor cap center tower. Secure wire to a good
ground to prevent engine from starting (Fig. 6).
² VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH DIRECT IGNI-
TION SYSTEM: Unplug the coils electrical connector
(Fig. 7).
STARTER SOLENOID TEST
WARNING: CHECK TO ENSURE THAT THE TRANS-
MISSION IS IN PARK OR NEUTRAL WITH THE
PARKING BRAKE APPLIED
(1) Verify battery condition. Battery must be in
good condition with a full charge before performing
any starter tests. Refer to Battery Tests. (2) Perform this starter solenoid test BEFORE per-
forming the starter relay test. (3) Raise the vehicle.
(4) Perform a visual inspection of the starter/
starter solenoid for corrosion, loose connections or
faulty wiring. (5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Locate the starter relay as follows:
² On AC, AG, AJ and AY Bodies the relay is located
in the Power Distribution Center. This Center is mounted near the front of the left front strut tower
(Fig. 13). The position of the starter relay within this
Center will be shown on the Center cover.
² On AA/AP Bodies the relay is located on the front
of the left front strut tower (Fig. 14).
(7) Remove the starter relay from the connector.
(8) Connect a remote starter switch or a jumper
wire between the battery positive post and terminal
87 on the starter relay connector. To decide the
starter relay terminal numbers, refer to the Starter
Relay Tests.
² If engine now cranks, starter/starter solenoid is
good. Go to the starter relay test.
² If engine does not crank with this test, or solenoid
chatters, check wiring and connectors from starter
Fig. 12 Test Positive Battery Cable Resistance
Fig. 13 Starter Relay LocationÐAC, AG, AJ, and AY Bodies
Fig. 14 Starter Relay LocationÐAA/AP Body
Ä BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 15
Page 388 of 2438

relay to starter solenoid for loose or corroded connec-
tions. Particularly at starter terminals.
² Repeat test. If engine still fails to crank properly,
trouble is within starter or starter mounted solenoid,
and it must be removed for repairs. Refer to Group
8B, Battery/Starter/Generator Service, Starter re-
placement.
STARTER RELAY TEST
WARNING: CHECK TO ENSURE THAT THE TRANS-
MISSION IS IN PARK OR NEUTRAL WITH THE
PARKING BRAKE APPLIED
(1) Verify battery condition. Battery must be in
good condition with a full charge before performing
any starter tests. Refer to Battery Tests. (2) Perform the preceding starter solenoid tests
BEFORE performing starter relay tests. Refer to
Starter Solenoid Test. (3) Locate and remove the starter relay. For
starter relay locations, refer to Starter Solenoid Test
(Fig. 13 or 14). (4) After the starter relay has been located and re-
moved, refer to Starter Relay Tests (Fig. 15).
NEUTRAL STARTING AND BACK-UP SWITCH
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION ONLY
For electrical diagnostics, when checking starter
circuits, refer to Starter Relay Tests (Fig. 15). For replacement of switch, refer to Group 21, Tran-
saxle, Neutral Starting and Switch Replacement.
STARTER INTERLOCK SWITCHÐCLUTCH PEDAL MOUNTED
MANUAL TRANSMISSION ONLY
For electrical diagnostics, refer to the Starter Relay
Tests. For replacement and/or adjustment of the switch,
refer to Group 6, Manual Transaxle Clutch, Manual
Transaxle Starter Interlock Switch.
IGNITION SWITCH TEST
After testing the starter solenoid and relay, test ig-
nition switch and wiring. Refer to Group 8D, Ignition
Systems, or the Front Wheel Drive Car Wiring Dia-
grams Service Manual. Check all wiring for opens or
shorts, and all connectors for being loose or corroded.
BENCH TESTING STARTER SOLENOID
(1) Disconnect field coil wire from field coil termi-
nal (Fig. 16 or 17). (2) Check for continuity between solenoid terminal
and field coil terminal with a continuity tester. Con-
tinuity should be detected (Fig. 18 or 19). (3) Check for continuity between solenoid terminal
and solenoid housing (Fig. 20 or 21). Continuity
should be detected. If continuity is detected, solenoid
is good. (4) If continuity is not detected in either test, sole-
noid has an open circuit and is defective. If equipped
with:
² BOSCH STARTER: Replace the solenoid.
² NIPPONDENSO STARTER: Replace the starter
assembly.
8A - 16 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS Ä