1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM lights
[x] Cancel search: lightsPage 58 of 2438

BRAKE RESERVOIR LEVEL INSPECTION
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW PETROLEUM OR WATER
BASE LIQUIDS TO CONTAMINATE BRAKE FLUID,
SEAL DAMAGE AND BRAKE FAILURE CAN RESULT.
RELIEVE PRESSURE IN ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYS-
TEM BEFORE ADDING BRAKE FLUID TO RESER-
VOIR. IF NOT, BRAKE FLUID COULD DISCHARGED
FROM THE RESERVOIR POSSIBLY CAUSING PER-
SONAL INJURY.
The brake reservoir level should be inspected when
other under hood service is performed. It is normal
for the reservoir level to drop as disc brake pads
wear. When fluid must be added, use Mopar, Brake
Fluid or equivalent. Use only brake fluid conforming
to DOT 3, Federal, Department of Transportation
specification. To avoid brake fluid contamination, use
fluid from a properly sealed container. On vehicles with anti-lock brakes, depressurize the
system before inspecting fluid level. Turn OFF the
ignition and remove the key. Pump the brake pedal
at least 50 times to relieve the pressure in the sys-
tem.
On all vehicles, if fluid should become low after sev-
eral thousand kilometers (miles), fill the reservoir to
level marks on the side of the reservoir (Fig. 8 or 9).
HEADLAMPS
The headlamps should be inspected for intensity
and aim whenever a problem is suspected. When lug-
gage compartment is heavily loaded, the headlamp
aim should be adjusted to compensate for vehicle
height change. For proper service procedures, refer to
Group 8L, Lamps. DRIVER SUPPLEMENTAL AIRBAG SYSTEM
If the AIRBAG indicator lamp does not light at all,
stays lit or lights momentarily or continuously while
driving, a malfunction may have occurred. Prompt service is required. Refer to Group 8M, Restraint
Systems for proper diagnostic procedures.
BODY LUBRICATION
Body mechanisms and linkages should be inspected,
cleaned and lubricated as required to maintain ease of
operation and to prevent corrosion and wear. Before a component is lubricated, oil, grease and dirt
should be wiped off. If necessary, use solvent to clean
component to be lubricated. After lubrication is com-
plete, wipe off excess grease or oil. During winter season, external lock cylinders should
be lubricated with Mopar, Lock Lubricant or equiva-
lent to ensure proper operation when exposed to water
and ice. To assure proper hood latching component operation,
use engine oil to lubricate the lock, safety catch and
hood hinges when other under hood service is per-
formed. Mopar, Multi-purpose Grease or equivalent
should be applied sparingly to all pivot and slide
contact areas.
USE ENGINE OIL ON:
² Door hingesÐHinge pin and pivot points.
² Hood hingesÐPivot points.
² Luggage compartment lid hingesÐPivot points.
USE MOPAR LUBRIPLATE OR EQUIVALENT ON:
² Door check straps.
² Hood counterbalance springs.
² Luggage compartment lid latches.
² Luggage compartment lid prop rod pivots.
² Ash tray slides.
² Fuel Fill Door latch mechanism.
² Park brake mechanism.
² Front seat tracks.
Fig. 8 Anti-lock Brake Reservoir
Fig. 9 Master Cylinder Brake ReservoirÐExcept
Anti-lock
0 - 22 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE Ä
Page 243 of 2438

DRIVE-OFF CYCLE
The DRIVE-OFF CYCLE takes place when the ve-
hicle reaches about 3 miles per hour the first time af-
ter an ignition reset. During this test, the modulator
solenoid valves are activated briefly to test their
function. The DRIVE-OFF CYCLE will be bypassed
if you drive-off with the service brake pedal de-
pressed.
LATCHING VERSUS NON-LATCHING FAULTS
Some faults detected by the (CAB) are latching.
The fault is latched and (ABS) function is disabled
until the ignition switch is reset (turned OFF/ON).
Thus (ABS) function is disabled even if the original
fault has disappeared during the ignition cycle in
which it occurred. Other faults are non-latching; any
warning lights that are turned on are only on as long
as the fault condition exists. As soon as the condition
goes away. The Amber Anti-Lock Warning Light is
turned off. Although a fault code will be set in most
cases. (Example:low accumulator fault will not be
stored for a time of 2 minutes after the fault is de-
tected).
BENDIX ABS SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS
The Bendix Anti-Lock 10 Brake System diagnos-
tics. Beyond the basic mechanical diagnostics, sys-
tems and components covered earlier in this section,
is accomplished by using the DRB II diagnostic
tester. See testing procedures outlined in the Bendix
Anti-Lock 10 Diagnostics Manual for the 1993 M.Y. Please reference the above mentioned manual. For
any further diagnostic service procedures that are re-
quired on the Bendix Anti-Lock 10 Brake System, re-
quiring the use of the DRB II diagnostic tester.
ON CAR HYDRAULIC ABS COMPONENT SERVICE
WARNING: FAILURE TO FULLY DE-PRESSURIZE
THE HYDRAULIC ACCUMULATOR BEFORE PER-
FORMING HYDRAULIC SYSTEM SERVICE OPERA-
TIONS. COULD RESULT IN INJURY TO SERVICE
PERSONNEL AND OR DAMAGE TO PAINTED SUR-
FACES. SEE SECTION 2 FOR ADDITIONAL WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS.
GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
The following are general precautions that should
be observed when servicing the Anti-Lock Brake Sys-
tem and/or other vehicle systems. Failure to observe
these precautions may result in Anti-Lock brake sys-
tem damage. If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle,
using an electric arc welder, the (CAB) connector
should be disconnected during the welding operation. The (CAB) or hydraulic assembly connector should
never be connected or disconnected with the ignition
switch in the ONposition.
Many components of the Anti-Lock brake system are
not serviceable and must be replaced as an assembly.
Do not attempt to disassemble any component
that is not designed to be a serviced component.
DE-PRESSURIZING HYDRAULIC ACCUMULA- TOR
The pump/motor assembly will keep the hydraulic
accumulator charged to approximately 11,032 and
13,790 kPa (1600 and 2000 psi) any time that the
ignition is in the ON position. The pump/motor assem-
bly cannot run if the ignition is off or if either battery
cable is disconnected. Unless otherwise specified, the hydraulic accumula-
tor should be de-pressurized before disassembling any
portion of the hydraulic system. The following proce-
dure should be used to relieve the pressure in the
hydraulic accumulator: (1) With ignition off, or either battery cable discon-
nected, pump the brake pedal a minimum of 40 times,
using approximately 222 N (50 lbs.) pedal force. A
noticeable change in pedal feel will occur, when the
accumulator is discharged. (2) When a definite increase in pedal effort is felt,
pump pedal a few additional times. This will insure
removal of all hydraulic pressure from the brake sys-
tem.
CHECKING BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
CAUTION: Use only brake fluid conforming to DOT 3
specifications such as Mopar Tor Equivalent. Do not
use any fluid in the brake hydraulic system, which
contains a petroleum base. Do not use a container
which has been used for petroleum based fluids or a
container that is wet with water. Petroleum based
fluids will cause swelling and distortion of rubber
parts in the hydraulic brake system and water will mix
with brake fluid, lowering the fluid boiling point. Keep
all brake fluid containers tightly capped to prevent
contamination.
The hydraulic assembly is equipped with a plastic
fluid reservoir, with a filter/strainer located in the filler
neck of each reservoir section. The Anti-Lock brake system requires that the hy-
draulic accumulator be de-pressurized when checking
the fluid level. To check the brake fluid level, the
following procedure should be used: (1) With the ignition off, de-pressurize the hydraulic
accumulator by applying the brake pedal approxi-
mately 40 times, using a pedal force of approximately
220 N (50 lbs.). A noticeable change in pedal feel will
occur when the accumulator is de-
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 93
Page 275 of 2438

MECHANICAL DIAGNOSTICS AND SERVICE
PROCEDURES
SPECIAL SERVICE TOOL
Some diagnostic procedures in this section require
the use of the DRB II diagnostics tester. The proper
application and procedures for the use of this tool are
described below.
DRB II DIAGNOSTIC TESTER Some of the diagnostic procedures that are ex-
plained in this section require the use of the DRB II
Diagnostics Tester to insure that proper diagnostics
are performed. Refer to those sections for proper test-
ing procedures and the DRB II operators manual for
its proper operational information.
INTERMITTENT FAULTS
As with virtually any electronic system, intermit-
tent faults in the ABS system may be difficult to ac-
curately diagnose. Most intermittent faults are caused by faulty elec-
trical connections or wiring. When an intermittent
fault is encountered, check suspect circuits for: (1) Poor mating of connector halves or terminals
not fully seated in the connector body. (2) Improperly formed or damaged terminals. All
connector terminals in a suspect circuit should be
carefully reformed to increase contact tension. (3) Poor terminal to wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body to in-
spect. (4) Pin presence in the connector assembly
If a visual check does not find the cause of the
problem, operate the car in an attempt to duplicate
the condition and record the Fault code. Most failures of the ABS system will disable Anti-
Lock function for the entire ignition cycle even if the
fault clears before key-off. There are some failure
conditions, however, which will allow ABS operation
to resume during the ignition cycle in which a fail-
ure occurred. If the failure conditions are no longer
present. The following conditions may result in inter-
mittent illumination of the Amber Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp. All other failures will cause the lamp to
remain on until the ignition switch is turned off. Cir-
cuits involving these inputs to the (CAB) should be
investigated if a complaint of intermittent warning
system operation is encountered. (1) Low system voltage. If Low System Voltage is
detected by the (CAB), the (CAB) will turn on the
Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp until normal sys-
tem voltage is achieved. Once normal voltage is seen
at the (CAB), normal operation resumes. (2) Anti-Lock relay. If the relay fails to make the
ground circuit connection or is an intermittent
ground. The (CAB) will turn on the Amber Anti-Lock
Warning Light. (3) Excess decay, an extended pressure decay pe-
riod, will turn on the Amber Anti-Lock Warning
Light until the vehicle comes to a complete stop. Additionally, any condition which results in inter-
ruption of electrical current to the (CAB) or modula-
tor assembly. May cause the Amber Anti-Lock
Warning Lamp to turn on intermittently.
ABS BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES
ABS SYSTEM SELF DIAGNOSIS
The ABS system is equipped with a self diagnostic
capability which may be used to assist in isolation of
ABS faults. The features of the self diagnostics sys-
tem are described below.
START-UP CYCLE
The self diagnostic ABS start up cycle begins when
the ignition switch is turned to the on position. An
electrical check is completed on the ABS components.
Such as Wheel Speed Sensor Continuity and System
and other Relay continuity. During this check the
Amber Anti-Lock Light is turned on for approxi-
mately 1- 2 seconds. Further Functional testing is accomplished once
the vehicle is set in motion.
² The solenoid valves and the pump/motor are acti-
vated briefly to verify function.
² The voltage output from the wheel speed sensors is
verified to be within the correct operating range. If the vehicle is not set in motion within 3 minutes
from the time the ignition switch is set in the on po-
sition. The solenoid test is bypassed but the pump/
motor is activated briefly to verify that it is
operating correctly.
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB)
Fault codes are kept in a Non-Volatile memory un-
til either erased by the technician using the DRB II
or erased automatically after 50 ignition cycles (key
ON-OFF cycles). The only fault that will not be
erased after 50 (KEY CYCLES) is the (CAB) fault. A
(CAB) fault can only be erased by the technician us-
ing the DRB II diagnostic tester. More than one fault
can be stored at a time. The number of key cycles
since the most recent fault was stored is also dis-
played. Most functions of the (CAB) and ABS system
can be accessed by the technician for testing and di-
agnostic purposes by using the DRB II.
LATCHING VERSUS NON-LATCHING ABS FAULTS
Some faults detected by the (CAB) are latching; the
fault is latched and (ABS) is disabled until the igni-
tion switch is reset. Thus ABS is disabled even if the
original fault has disappeared. Other faults are non-
latching; any warning lights that are turned on, are
only turned on as long as the fault condition exists.
Ä ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 125
Page 311 of 2438

LATCHING VERSUS NON-LATCHING ABS FAULTS
Some faults detected by the CAB are latching; the
fault is latched and ABS is disabled until the igni-
tion switch is reset. Thus ABS is disabled even if the
original fault has disappeared. Other faults are non-
latching; any warning lights that are turned on, are
only turned on as long as the fault condition exists.
As soon as the condition goes away, the Antilock
Warning Light is turned off. Although a fault code
will be set in most cases.
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTICS
Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System Diagnostics, be-
yond basic mechanical diagnostics, covered earlier in
this section, are accomplished by using the DRB scan
tool. See testing procedures outlined in the 1994 Ben-
dix Antilock 4 Diagnostics Manual. Please refer to the above mentioned manual for
any further electronic diagnostics and service proce-
dures that are required on the Bendix Antilock 4
Brake System.
ON-CAR ABS BRAKE SYSTEM SERVICE
GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
The following are general cautions which should be
observed when servicing the Bendix Antilock 4
Brake System and other vehicle electronic systems.
Failure to observe these precautions may result in
Antilock Brake System component damage. If welding work is to be performed on a vehicle us-
ing an electric arc welder, disconnect the 60 way wir-
ing harness connector from the CAB, prior to
performing the welding operation. The wiring harness connector should never be con-
nected or disconnected from the CAB with the igni-
tion key in the ON or Run position. (3) Most components making up the assemblies of
the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System can not be ser-
viced separately from those assemblies. This will re-
quire replacement of the complete assembly for the
servicing of these components. Do not disassemble
any component from an assembly which is desig-
nated as non-serviceable.
CHECKING BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
CAUTION: Only use brake fluid conforming to DOT
3 specifications, such as Mopar or Equivalent. Do
not use any fluid which contains a petroleum base.
Do not use a container which has been used for pe-
troleum based fluids or a container which is wet
with water. Petroleum based fluids will cause swell-
ing and distortion of rubber parts in the hydraulic
brake system. Water will mix with brake fluid, low-
ering the boiling point of the brake fluid, possibly causing brake fluid to boil resulting in brake fade.
Keep all brake fluid containers capped to prevent
contamination. Remove the front cap of the master
cylinder reservoir and fill to the bottom of the split
ring.
For the specific procedure for the inspection of
brake fluid level and adding of brake to the reser-
voir. Refer to the Service Adjustments Section in this
group of the service manual.
BLEEDING BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM
The base brakes and Antilock Brake System must
be bled anytime air is permitted to enter the hydrau-
lic system, due to disconnection of brake lines, hoses
or components. If the Antilock Modulator Assembly is removed
from the vehicle, both the Base Brake System and
the Antilock Brake System must be bled using the
appropriate procedure. It is important to note that
excessive air in the brake system will cause a soft or
spongy feeling brake pedal. During brake bleeding operations, ensure that
brake fluid level remains close to the FULL level in
the reservoir. Check brake fluid level periodically
during bleeding procedure, adding DOT 3 brake fluid
as required.
CAUTION: The base brake and Antilock brake hy-
draulic systems, on the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake
System, can NOT be bled using any type of brake
pressure bleeding equipment. This type of bleeding
equipment does not develop the pressure required
in the brake hydraulic system, to adequately bleed
all trapped air. The only approved method for bleed-
ing air out of the hydraulic system on vehicles
equipped with the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System,
is the manual procedure of pressurizing the hydrau-
lic system using constant, moderate to heavy foot
pressure on the brake pedal.
The Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System must be bled
as two independent brake systems. The non ABS por-
tion of the brake system is to be bled the same as
any non ABS system. Refer to the Service Adjust-
ments section in this manual for the proper bleeding
procedure to be used. The Bendix Antilock 4 Brake
System can only be bled using a manual method of
pressurizing the brakes hydraulic system. The Antilock portion of brake system MUST be
bled separately. This bleeding procedure requires the
use of the DRB Diagnostic tester and the bleeding se-
quence procedure outlined below.
Ä ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 25
Page 376 of 2438

It is important when using the Test Indicator that
the battery be level and have a clean top to see the
correct indications. A light may be required to view
the Indicator.
WARNING: DO NOT USE OPEN FLAME NEAR BAT-
TERY BECAUSE OF EXPLOSIVE GASES AT FORM
ABOVE BATTERY.
STATE OF CHARGE TESTS
USING TEST INDICATOR
The built in test hydrometer (Figs. 3, 4 and 5) mea-
sures the specific gravity of the electrolyte. Specific
Gravity (SG) of the electrolyte will show state of
charge voltage. The test indicator WILL NOT show
cranking capacity of the battery. Refer to Battery
Load. Look into the sight glass (Figs. 4 and 5) and
note the color of the indicator (Fig. 5). Refer to the
following description of colors:
² GREEN = 75 to 100 degree state of charge
The battery is adequately charged for further test-
ing and may be returned to use. If the vehicle will
not crank for a maximum 15 seconds, refer to Bat-
tery Load Test in this Group for more information.
² BLACK OR DAR K=0to75degree state of
charge The battery is INADEQUATELY charged and
must be charged until green dot is visible, (12.4 volts
or greater) before the battery is tested or returned to
use. Refer to Causes of Battery Discharging.
² YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR = Battery must
be replace
WARNING: DO NOT CHARGE, ASSIST BOOST,
LOAD TEST, OR ADD WATER TO THE BATTERY
WHEN YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR DOT IS VISI-
BLE. PERSONAL INJURY MAY OCCUR.
A yellow or bright color dot shows electrolyte level
in battery is below the test indicator (Fig. 5). Water
cannot be added to a maintenance free battery. The
battery must be replaced. A low electrolyte level may
be caused by an over charging condition. Refer to
Generator Test Procedures on Vehicle.
CAUSES OF BATTERY DISCHARGING
It is normal to have a small 5 to 30 milliamperes
continuous electrical draw from the battery. This
draw will take place with the ignition in the OFF po-
sition, and the courtesy, dome, storage compart-
ments, and engine compartment lights OFF. The
continuous draw is due to various electronic features
or accessories that require electrical current with the
ignition OFF to function properly. When a vehicle is
not used over an extended period approximately 20
days the Main Fusible Link Connector (Fig. 6)
should be disconnected. This is located near the bat- tery on the engine wiring harness. Disconnection of
this connector will help prevent battery discharging.
Refer to Fig. 7 for Battery Diagnostics.
ABNORMAL BATTERY DISCHARGING
(1) Corroded battery posts, cables or terminals.
(2) Loose or worn generator drive belt.
(3) Electrical loads that exceed the output of the
charging system due to equipment or accessories in-
stalled after delivery. (4) Slow driving speeds in heavy traffic conditions
or prolonged idling with high-amperage electrical
systems in use. (5) Defective electrical circuit or component caus-
ing excess Ignition Off Draw (IOD). Refer to Ignition
OFF Draw (IOD). (6) Defective charging system.
(7) Defective battery.
BATTERY OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TEST
An open circuit voltage, no load test will show the
state of charge in a battery. Also, if it will pass a
load test of 50 percent of the battery cold crank rat-
ing. Refer to Battery Load Test. If a battery has an
open circuit voltage reading of 12.4 volts or greater,
and will not pass a load test, it is defective and re-
placement would be required. To test open circuit
voltage, perform the following operation: (1) Remove both battery cables, negative first. If
the battery has been boosted, charged, or loaded just
prior to this operation, allow the battery a few min-
utes to stabilize. (2) Using a voltmeter connected to the battery
posts and measure the open circuit voltage (Fig. 8).
Fig. 6 Main Fusible Link Connector
8A - 4 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS Ä
Page 381 of 2438

IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD)
GENERAL INFORMATION
A normal electrical system will draw from 5 to 30
milliamperes from the battery. This is with the ignition
in the OFF position, and all non-ignition controlled cir-
cuits in proper working order. The amount of IOD will
depend on body model and electrical components. A ve-
hicle that has not been operated for an extended period
of approximately 20 days may discharge the battery to
an inadequate level. In this case, the Main Fusible Link
Connector should be disconnected. The Main Fusible
Link connector is located rearward of the battery on the
engine wiring harness (Fig. 19).
If the IOD is over 30 milliamperes, the defect must
be found and corrected before condemning the bat-
tery. Usually, the battery can be charged and re-
turned to service (Fig. 16).
IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD) TESTS
VEHICLES WITHOUT ELECTRONIC AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION/LOAD LEVELINGSUSPENSION OR ALARM SYSTEMS
Testing for HIGHER AMPERAGE IOD must be
performed first to prevent damage to most milliamp
meters. A standard 12 volt test light and a milliamp meter
that is equipped with two leads will be used for the
following tests. The milliamp meter should be able to
handle up to two amps.
(1) Verify that all electrical accessories are OFF.
Turn off all lights, close trunk lid, close glove box door,
turn off sun visor vanity lights, close all doors and re- move ignition key. Allow the Illuminated Entry System
if equipped to time out in approximately 30 seconds.
(2) Verify the engine compartment lamp bulb is
working by opening/closing hood. Remove the lamp. (3) Disconnect negative battery cable (Fig. 15).
(4) Connect a typical 12 volt test light between the
negative cable clamp and the negative battery post (Fig.
19). The test light may be brightly lit for up to three
minutes or may not be lit at all. This depending on the
body model or electronic components on the vehicle. (a) The term brightly used throughout the follow-
ing tests. This implies the brightness of the test light
will be the same as if it were connected across the
battery posts. This would be with a fully charged bat-
tery.
(b) The test light or the milliamp meter MUST
be positively connected to the battery post and the
battery cable during all IOD testing. (c) Do not allow the test light or the milliamp
meter to become disconnected during any of the
IOD tests. If this happens, the electronic timer
functions will be started and all IOD tests must be
repeated from the beginning. Clamp the test light
at both ends to prevent accidental disconnection.
(d) After three minutes time has elapsed, the test
light should turn OFF or be dimly lit depending on
the electronic components on the vehicle. If the test
light remains BRIGHTLY lit, do not disconnect test
light. Disconnect each fuse or circuit breaker until
test light is either OFF or DIMLY lit. Refer to the
Front Wheel Drive Car Wiring Diagrams Service
Manual. This will eliminate higher amperage IOD. It
is now safe to install the milliamp meter without
damage to the meter to check for low amperage IOD.
(e) Possible sources of high IOD are usually ve-
hicle lamps trunk lamp, glove compartment, lug-
gage compartment, etc.. (f) If test light is still brightly lit after discon-
necting each fuse and circuit breaker, disconnect
the wiring harness from the generator. Refer to
Generator Testing. Do not disconnect test light.
CAUTION: This last test has higher amperage IOD and
must be performed before going on with low amper-
age IOD tests. The higher amperage IOD must be elim-
inated before hooking up milliamp meter to check for
low amperage IOD. If higher amperage IOD has not
been eliminated, milliamp meter may be damaged.
Most milliamp meters will not handle over one or two
amps. Do not hook up meter if test light is glowing
brightly. Refer to maximum amperage specifications
and instructions supplied with milliamp meter.
After higher amperage IOD has been corrected, low
amperage IOD may be checked. The MAXIMUM IOD=
30 MILLIAMPERES.
Fig. 19 IOD Test
Ä BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 9
Page 385 of 2438
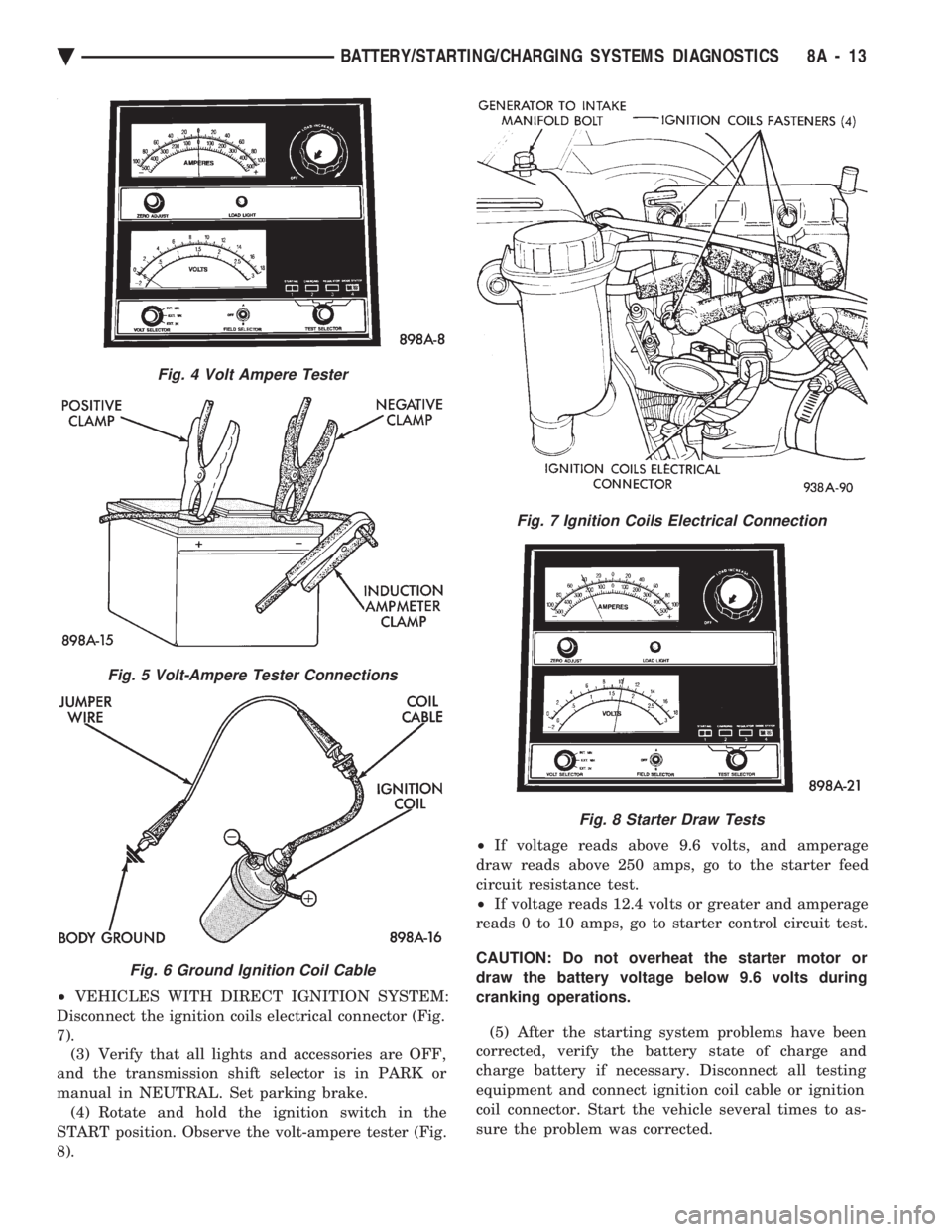
² VEHICLES WITH DIRECT IGNITION SYSTEM:
Disconnect the ignition coils electrical connector (Fig.
7). (3) Verify that all lights and accessories are OFF,
and the transmission shift selector is in PARK or
manual in NEUTRAL. Set parking brake. (4) Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. Observe the volt-ampere tester (Fig.
8). ²
If voltage reads above 9.6 volts, and amperage
draw reads above 250 amps, go to the starter feed
circuit resistance test.
² If voltage reads 12.4 volts or greater and amperage
reads 0 to 10 amps, go to starter control circuit test.
CAUTION: Do not overheat the starter motor or
draw the battery voltage below 9.6 volts during
cranking operations.
(5) After the starting system problems have been
corrected, verify the battery state of charge and
charge battery if necessary. Disconnect all testing
equipment and connect ignition coil cable or ignition
coil connector. Start the vehicle several times to as-
sure the problem was corrected.
Fig. 4 Volt Ampere Tester
Fig. 5 Volt-Ampere Tester Connections
Fig. 6 Ground Ignition Coil Cable
Fig. 7 Ignition Coils Electrical Connection
Fig. 8 Starter Draw Tests
Ä BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 13
Page 420 of 2438

VARIANCE SETTING PROCEDURE
There are two methods for setting variance while
in variance set mode. If the CAL symbol is on proce-
dure 2 must be used.
PROCEDURE 1
(1) Turn ignition switch to the on position.
(2) Press and hold the Comp/Temp button till the
display is turned OFF. (3) While continuing to hold Comp/Temp button
depress and hold US/Metric button until the VAR
symbol lights in approximately 5 seconds. (4) Release buttons.
(5) To determine the zone number which, corre-
sponds with your geographic area refer to Fig. 4.
(6) Press the US/Metric button until the zone num-
ber matches the display. (7) Press the Comp/Temp button to finish setting
of variation. (8) Variation is complete.
PROCEDURE 2 (1) Move away from any large metal objects like
buildings, or bridges. With the engine running and
the doors closed point vehicle true north. (2) Press and hold Comp/Temp button. The display
will go blank. (3) While continuing to hold Comp/Temp button
depress and hold the US/Metric button until the
VAR symbol lights in approximately 5 seconds. (4) Release buttons.
(5) Press the Comp/Temp button to finish setting
of variation. (6) Variation is complete.
DEMAGNETIZING PROCEDURE
Do not attach magnetic devices, such as magnetic
CB antennas to the vehicle roof, as they can cause
the compass to give false readings. Every vehicle has its own magnetic field. This
magnetic field is created by the various processes a
steel roof goes through when the vehicle is built. A
magnetic field also can be created if the roof is sub-
jected to A magnet, example:
² Magnetic c.b. antenna
² Magnetic tipped screwdriver and etc.
If the roof becomes magnetized use a demagnetiz-
ing Tool 6029 to demagnetize the roof. In this demagnetizing procedure you will use the
demagnetizing tool to demagnetize the roof and
mounting screws in the overhead console. It is impor-
tant that you follow the instructions below exactly.
The mounting screws and the mounting brackets
around the compass area are steel, and therefore aid
in the degaussing of the roof panel. (1) Be sure the ignition switch is in the OFF posi-
tion before you begin the demagnetizing procedure. (2) Open the sun glass compartment to gain access
to the overhead console mounting screws. (3) Plug the demagnetizing tool into a standard
110/115 volt AC outlet, keeping the demagnetizing
tool at least 12 inches away from the compass area
when plugging it in. (4) Slowly approach the console mounting screw
with the plastic coated tip of the tool for at least 2
seconds. (5) With the demagnetizing tool still energized,
slowly back it away from the screw until the tip is at
least 12 inches from the screw head. (6) After you have pulled at least 12 inches from
the last screw, remove the demagnetizing tool from
inside of the vehicle and disconnect it from the elec-
trical outlet. (7) Place an 8 1/2 in. X 11 in. piece of paper
lengthwise on the roof of vehicle directly above com-
pass. The purpose of the paper is to protect the roof
panel from scratches and define the area to be de-
magnetized.
Fig. 4 Variance Settings
8C - 4 OVERHEAD CONSOLE Ä