1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM low oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: low oil pressurePage 290 of 2438

² Left rear wheel
² Right front wheel
(1) Pump brake pedal three or four times, then
hold a constant moderate to heavy foot pressure on
the brake pedal.
CAUTION: Just cracking the bleeder screw often re-
stricts fluid flow, and a slow, weak fluid discharge
will NOT get all the air out.
(2) Open bleeder screw (Fig. 7) at least 1 full turn.
When bleeder screw opens, brake pedal will drop to
the floor. (3) Close bleeder screw. Release brake pedal off
floor only afterbleeder screw is completely closed.
(4) Repeat steps 1 through 3, four or five times, at
each bleeder screw. This should pass a sufficient
amount of brake hydraulic fluid to expel all trapped
air. Be sure to monitor brake fluid level in master
cylinder fluid reservoir. It must stay at a level that
will not allow air to re-enter the hydraulic system
through the master cylinder. After 4 to 8 ounces of hydraulic fluid has been bled
from the bleeder screw at this wheel, and an air-free
flow has been maintained, a good bleed is indicated. Repeat above procedure at all other remaining
bleeder screws, while checking brake pedal for travel. If brake pedal travel is still excessive or has
not improved, enough brake fluid has not passed
through the hydraulic system to expel all trapped
air. Be sure to monitor brake fluid level in the mas-
ter cylinder brake fluid reservoir. It must stay at the
proper level so air will not be allowed to re-enter the
brake system through the master cylinder. Test drive vehicle to be sure brakes are operating
correctly and that pedal is not spongy.
TESTING FOR FLUID CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts. Swollen rubber parts indicate the presence of petro-
leum in the brake fluid. To test for contamination, put small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If fluid sepa-
rates into layers, there is mineral oil contamination. If contaminated, drain and thoroughly flush sys-
tem. Replace master cylinder, proportioning valve,
caliper seals, wheel cylinder seals and all hoses.
Fig. 6 Proper Method for Purging Air From Brake System
Fig. 7 Open Bleeder Screw at Least One Full Turn(Typical)
5 - 4 BRAKES Ä
Page 306 of 2438

ANTILOCK WARNING LAMP DIODE
The Warning Lamp Relay on the Bendix Antilock
4 Brake System has been replaced with a diode. The
diode is used to control the function of the warning
lamp and is located inside the CAB module wiring
harness. The diode is a replaceable component of the
wiring harness, and will not require replacement of
the entire wiring harness if only the diode is diag-
nosed to have failed. When the system relay is de-energized, the Anti-
lock warning lamp will be lit. This will occur because
a ground path exists for the Antilock warning lamp
through the Antilock warning lamp diode and the
system relay armature. When the system relay is en-
ergized by the CAB, the system relay armature will
no longer provide a ground and the lamp will turn
off. Thus, the lamp will be lit if either the CAB is
disconnected or a system fault causes the Antilock to
be turned off.
PUMP/MOTOR RELAY
Pump/Motor power is supplied by the Pump/Motor
Relay. The Pump/Motor Relay is either mounted on
the left front inner fender shield, or the front of the
left shock tower. The mounting location is dependent
on whether the vehicle is or is not equipped with a
power distribution center. See (Fig. 11 and 12) for
specific mounting locations.
ANTILOCK WARNING LAMP OFF
System Relay Energized
From pin 57, the CAB energizes the Antilock sys-
tem relay coil, thus the electrical current flow in the
coil closes the system relay. Then electrical current
is provided to pins 47 and 41 of the CAB to provide
power to the modulator valves. The CAB turns off the Amber Antilock Warning
Lamp by breaking the ground path through pin 15 of
the CAB.
ANTILOCK WARNING LAMP ON
System Relay De-Energized.
When the Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is on,
there is no electrical current flow from the CAB at
pin 57 and the System Relay coil is NOT energized.
No electrical current flows to pin 47 and 41 (modula-
tor valve power), or to the Antilock Warning Lamp
diode. Thus, the Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is
not energized. The Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is
now grounded through the Antilock Warning Lamp
diode and pin 15 of the CAB turning on the Amber
Antilock Warning Lamp.
HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS AND VALVE OPERATION
Through the following operation descriptions and
diagrams. The function of the various hydraulic con-
trol valves in the ABS system will be described. The
fluid control valves mentioned below, control the flow
of pressurized brake fluid to the wheel brakes during
the different modes of Antilock braking. For explanation purposes we will assume all speed
sensors are sending the same wheel speed informa-
tion, requiring the same hydraulic fluid modulation
at the same rate.
NORMAL BRAKING
BUILD/DECAY VALVES
Closed (Fig. 1)
The brake pedal is applied. The travel of the brake
pedal closes primary and secondary circuits from the
master cylinder fluid supply. Brake fluid from the
master cylinder primary and secondary circuits flows
through the build/decay valves to the wheel brakes.
ABS BRAKING-BUILD PRESSURE
BUILD/DECAY VALVES
Open (Fig. 2)
Fig. 11 Pump Motor Relay Location On AA Body W/O Power Distribution Center
Fig. 12 Pump Motor Relay Location On AJ BodyWith Power Distribution Center
5 - 20 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 311 of 2438

LATCHING VERSUS NON-LATCHING ABS FAULTS
Some faults detected by the CAB are latching; the
fault is latched and ABS is disabled until the igni-
tion switch is reset. Thus ABS is disabled even if the
original fault has disappeared. Other faults are non-
latching; any warning lights that are turned on, are
only turned on as long as the fault condition exists.
As soon as the condition goes away, the Antilock
Warning Light is turned off. Although a fault code
will be set in most cases.
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTICS
Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System Diagnostics, be-
yond basic mechanical diagnostics, covered earlier in
this section, are accomplished by using the DRB scan
tool. See testing procedures outlined in the 1994 Ben-
dix Antilock 4 Diagnostics Manual. Please refer to the above mentioned manual for
any further electronic diagnostics and service proce-
dures that are required on the Bendix Antilock 4
Brake System.
ON-CAR ABS BRAKE SYSTEM SERVICE
GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
The following are general cautions which should be
observed when servicing the Bendix Antilock 4
Brake System and other vehicle electronic systems.
Failure to observe these precautions may result in
Antilock Brake System component damage. If welding work is to be performed on a vehicle us-
ing an electric arc welder, disconnect the 60 way wir-
ing harness connector from the CAB, prior to
performing the welding operation. The wiring harness connector should never be con-
nected or disconnected from the CAB with the igni-
tion key in the ON or Run position. (3) Most components making up the assemblies of
the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System can not be ser-
viced separately from those assemblies. This will re-
quire replacement of the complete assembly for the
servicing of these components. Do not disassemble
any component from an assembly which is desig-
nated as non-serviceable.
CHECKING BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
CAUTION: Only use brake fluid conforming to DOT
3 specifications, such as Mopar or Equivalent. Do
not use any fluid which contains a petroleum base.
Do not use a container which has been used for pe-
troleum based fluids or a container which is wet
with water. Petroleum based fluids will cause swell-
ing and distortion of rubber parts in the hydraulic
brake system. Water will mix with brake fluid, low-
ering the boiling point of the brake fluid, possibly causing brake fluid to boil resulting in brake fade.
Keep all brake fluid containers capped to prevent
contamination. Remove the front cap of the master
cylinder reservoir and fill to the bottom of the split
ring.
For the specific procedure for the inspection of
brake fluid level and adding of brake to the reser-
voir. Refer to the Service Adjustments Section in this
group of the service manual.
BLEEDING BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM
The base brakes and Antilock Brake System must
be bled anytime air is permitted to enter the hydrau-
lic system, due to disconnection of brake lines, hoses
or components. If the Antilock Modulator Assembly is removed
from the vehicle, both the Base Brake System and
the Antilock Brake System must be bled using the
appropriate procedure. It is important to note that
excessive air in the brake system will cause a soft or
spongy feeling brake pedal. During brake bleeding operations, ensure that
brake fluid level remains close to the FULL level in
the reservoir. Check brake fluid level periodically
during bleeding procedure, adding DOT 3 brake fluid
as required.
CAUTION: The base brake and Antilock brake hy-
draulic systems, on the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake
System, can NOT be bled using any type of brake
pressure bleeding equipment. This type of bleeding
equipment does not develop the pressure required
in the brake hydraulic system, to adequately bleed
all trapped air. The only approved method for bleed-
ing air out of the hydraulic system on vehicles
equipped with the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System,
is the manual procedure of pressurizing the hydrau-
lic system using constant, moderate to heavy foot
pressure on the brake pedal.
The Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System must be bled
as two independent brake systems. The non ABS por-
tion of the brake system is to be bled the same as
any non ABS system. Refer to the Service Adjust-
ments section in this manual for the proper bleeding
procedure to be used. The Bendix Antilock 4 Brake
System can only be bled using a manual method of
pressurizing the brakes hydraulic system. The Antilock portion of brake system MUST be
bled separately. This bleeding procedure requires the
use of the DRB Diagnostic tester and the bleeding se-
quence procedure outlined below.
Ä ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 25
Page 333 of 2438

MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH
CONTENTS
page page
CLEANING PRECAUTIONS ................. 6
CLUTCH CABLE MECHANISM .............. 1
CLUTCH CABLE REPLACEMENT ............ 2
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS ........... 1
CLUTCH DISC REPLACEMENT ............. 5
CLUTCH PEDAL NOISE/POP ............... 2 CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
......... 4
EXCESSIVE CLUTCH SPIN TIME/CLASH INTO REVERSE COMPLAINTS ............ 1
GENERAL INFORMATION .................. 1
RELEASE BEARING AND FORK ............. 6
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the breakdown of these designations
is included in the Introduction Section at the front of
this service manual. The clutch used in all models are a single, dry disc
type with no adjustment for wear being provided in
the clutch itself. The clutch pedal is connected to the release shaft
through a cable and lever. The upper end of the clutch pedal pivots in the
pedal bracket on two nylon bushings. These bushings
do not require periodic lubrication.
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS
For all clutch chatter complaints, do the following:
(1) Check for loose, misaligned, or broken engine
and transmission mounts. If present, they should be
corrected at this time. Test vehicle for chatter. If
chatter is gone, there is no need to go any further. If
chatter persists: (2) Check to see if clutch cable routing is correct
and operates smoothly. (3) Check for loose connections in drive train. Cor-
rect any problems and determine if clutch chatter
complaints has been satisfied. If not, (4) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle, for procedure. (5) Check to see if the release bearing is sticky or
binding. Replace bearing, if needed. (6) Check linkage for excessive wear on bushings.
Replace all worn parts. A small amount of bearing
grease between the release shaft bushings and the
shaft is beneficial, but not required. (7) Check flywheel and clutch pressure plate for
contamination (dirt, oil) or scored. Replace flywheel
and/or pressure plate, if required. (8) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged. Replace with new disc. (9) Check input shaft splines for damage. Replace
if necessary. (10) Check for uneven wear on clutch fingers.
EXCESSIVE CLUTCH SPIN TIME/CLASH INTO
REVERSE COMPLAINTS
For all excessive clutch spin time/clash into reverse
complaints, do the following: (1) Depress clutch pedal to floor and hold. After
three seconds, shift to reverse. If clash is present,
clutch has excessive spin time. (2) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle, for procedure. (3) Check the input shaft spline, clutch disc splines
and release bearing for dry rust. If present, clean
rust off and apply a light coat of bearing grease to
the input shaft splines. Apply grease on the input
shaft splines only where the clutch disc slides. (4) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged, replace with new disc if required. (5) Check the input shaft for damaged splines. Re-
place as necessary. (6) Check for excessive clutch disc runout or
warpage. (7) Install clutch assembly and transaxle.
CLUTCH CABLE MECHANISM
The manual transaxle clutch release system has a
unique self-adjusting mechanism to compensate for
clutch disc wear. This adjuster mechanism is located
within the clutch pedal. The preload spring main-
tains tension on the cable. This tension keeps the
clutch release bearing continuously loaded against
the fingers of the clutch cover assembly. When the pedal is depressed, teeth on the adjuster
and the positioner engage and pull the release cable.
A spring located behind the adjuster ensures proper
tooth engagement. When the pedal is released, the adjuster contacts
the bumper. This separates the adjuster and posi-
tioner teeth, allowing the preload spring to function.
Ä MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH 6 - 1
Page 338 of 2438

(3) Clean the flywheel face with medium sandpa-
per (80-160 grade), then wipe the surface with min-
eral spirits. If the surface is severely scored, heat
checked, or warped, replace the flywheel.
CAUTION: Do not flat-machine the flywheel face.
The surface profile is tapered.
(4) The heavy side of the flywheel is indicated by a
daub of white paint near the outside diameter. To
minimize the effects of flywheel unbalance, perform
the following installation procedure: (a) Loose assemble the flywheel to the crank-
shaft. Use new flywheel attaching bolts which have
sealant on the threads. If new bolts are not avail-
able, apply Loctite sealant to the threads of the
original bolts. This sealant is required to prevent
engine oil leakage. (b) Rotate the flywheel and crankshaft until the
daub of white paint (heavy side) is at the 12 o'clock
position. (c) Torque flywheel attaching bolts to 95 N Im(70
ft. lbs.). Use a crisscross pattern when tightening
bolts.
(5) The disc assembly should be handled without
touching the facings. Replace disc if the facings show
evidence of grease or oil soakage, or wear to within
less than .38 mm (.015 inch) of the rivet heads. The
splines on the disc hub and transaxle input shaft
should be a snug fit without signs of excessive wear.
Metallic portions of disc assembly should be dry and
clean, and not been discolored from excessive heat.
Each of the arched springs between the facings
should not be broken and all rivets should be tight. (6) Wipe the friction surface of the pressure plate
with mineral spirits. (7) Using a straight edge, check clutch cover (pres-
sure plate) for flatness. The clutch cover (pressure
plate) friction area should be slightly concave, with
the inner diameter 0.02 mm to 0.1 mm (.0008 in. to
.0039 in.) below the outer diameter. It should also be
free from discoloration, burned areas, cracks,
grooves, or ridges. (8) Using a surface plate, test cover for flatness.
All sections around attaching bolt holes should be in
contact with surface plate within .015 inch. (9) The cover should be a snug fit on flywheel dow-
els. If the clutch assembly does not meet these re-
quirements, it should be replaced.
INSTALLATION
(1) Mount clutch assembly on flywheel,being care-
ful to properly align dowels and the alignment marks
made before removal. The flywheel side of the clutch
disc is marked for proper installation. If new clutch
or flywheel is installed, align cover balance spot as
close as possible to flywheel balance orange spot. Ap-
ply pressure to the alignment tool. Center the tip of the tool into the crankshaft and the sliding cone into
the clutch fingers. Tighten the clutch attaching bolts
sufficiently to hold the disc in position. (2) To avoid distortion of the clutch cover, bolts
should be tightened a few turns at a time, in a criss-
cross pattern, until they are all seated. Tighten bolts
to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.) following a crisscross pattern
sequence. Remove clutch disc alignment tool. (3) Install transaxle. See group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle, for procedures.
RELEASE BEARING AND FORK
Remove the transaxle from the vehicle. See group
21 for removal and installation procedures.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
(1) Remove clutch release shaft E-clip.
(2) Remove the clutch release shaft and then slide
the fork and bearing assembly off the bearing pilot. (3) Remove the fork from the bearing thrust plate.
(4) Examine the condition of the bearing. It is pre-
lubricated and sealed and should not be im-
mersed in oil or solvent. (5) The bearing should turn smoothly when held in
the hand under a light thrust load. A light drag
caused by the lubricant fill is normal. If the bearing
is noisy, rough, or dry, replace the complete bearing
assembly with a new bearing. (6) The bearing has a plastic sleeve pre-lubricated
at assembly. Wipe out the old grease. Refill the
sleeve cavities and coat the inner surface with mul-
tipurpose grease. If the liner is cracked or worn, re-
place the bearing assembly. (7) Check the condition of the spring clips. If the
clips are broken or distorted, replace the bearing as-
sembly. (8) Before assembling the fork, lubricate the
rounded thrust pads and the spring clip cavities with
multipurpose grease. (9) Assemble the fork to the bearing by sliding the
thrust pads under the spring clips. Be careful to
avoid distorting the spring clips. These clips prevent
the bearing thrust plate from rotating with the bear-
ing. (10) Slide the bearing and fork assembly onto the
input shaft bearing retainer. (11) Position the release shaft bushings in the
housing and install the release shaft. A small
amount of bearing grease between the release shaft
bushing and the shaft is beneficial but not required.
Install the retainer clip in the shaft groove near the
large bushing. (12) Install the release lever and retaining clip on
the outer end of the release shaft.
CLEANING PRECAUTIONS
Condensation from steam vapors tend to accumu-
late on the internal clutch mechanism when the ve-
6 - 6 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH Ä
Page 343 of 2438

COOLING SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS ............... 24
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER ................. 28
GENERAL INFORMATION .................. 1 SERVICE PROCEDURES
.................. 10
SPECIFICATIONS ....................... 29
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the breakdown of these designations
is included in the Introduction Section at the front of
this service manual.
COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system consists of an engine cooling
module, thermostat, coolant, a water pump to circu-
late the coolant. The engine cooling module may con-
sist of a radiator, electric fan motor, shroud, radiator
pressure cap, coolant reserve system, transmission oil
cooler, hoses, clamps, air condition condenser, trans-
mission oil lines and charge air cooler.
² When Engine is cold: Thermostat is closed, cooling
system has no flow through the radiator. The coolant
bypass flows through the engine only. ²
When Engine is warm: Thermostat is open, cooling
system has bypass flow and coolant flow through ra-
diator. Its primary purpose is to maintain engine temper-
ature in a range that will provide satisfactory engine
performance and emission levels under all expected
driving conditions. It also provides hot water (cool-
ant) for heater performance and cooling for auto-
matic transmission oil. It does this by transferring
heat from engine metal to coolant, moving this
heated coolant to the radiator, and then transferring
this heat to the ambient air. Coolant flow circuits for 2.2L and 2.5L engine
equipped vehicles are shown in (Fig 1). Turbocharged
equipped engines coolant routing and plumbing are
shown in (Fig 2). The 3.0L engine coolant routing is
shown in (Fig 3). The 3.3L and 3.8L engine coolant
routing is shown in (Fig 5).
Fig. 1 Cooling System OperationÐ2.2/2.5L Engines
Ä COOLING SYSTEM 7 - 1
Page 352 of 2438
SERVICE PROCEDURES INDEX
page page
Automatic Transmission Oil Coolers .......... 23
Coolant ................................ 14
Coolant Recovery System (CRS) ............. 17
Cooling System Drain, Clean, Flush and Refill . . 15
Electric Fan Motor ........................ 22
Engine Thermostats ....................... 13
Fan Shroud ............................. 23 Fans
.................................. 21
Radiator Hoses .......................... 21
Radiator Pressure Cap .................... 18
Radiators ............................... 18
Testing System for Leaks .................. 17
Water Pumps ........................... 10
WATER PUMPS
A quick test to tell whether or not the pump is
working is to see if the heater warms properly. A
defective pump will not be able to circulate heated
coolant through the long heater hose. The water pump on all models can be replaced
without discharging the air conditioning system.
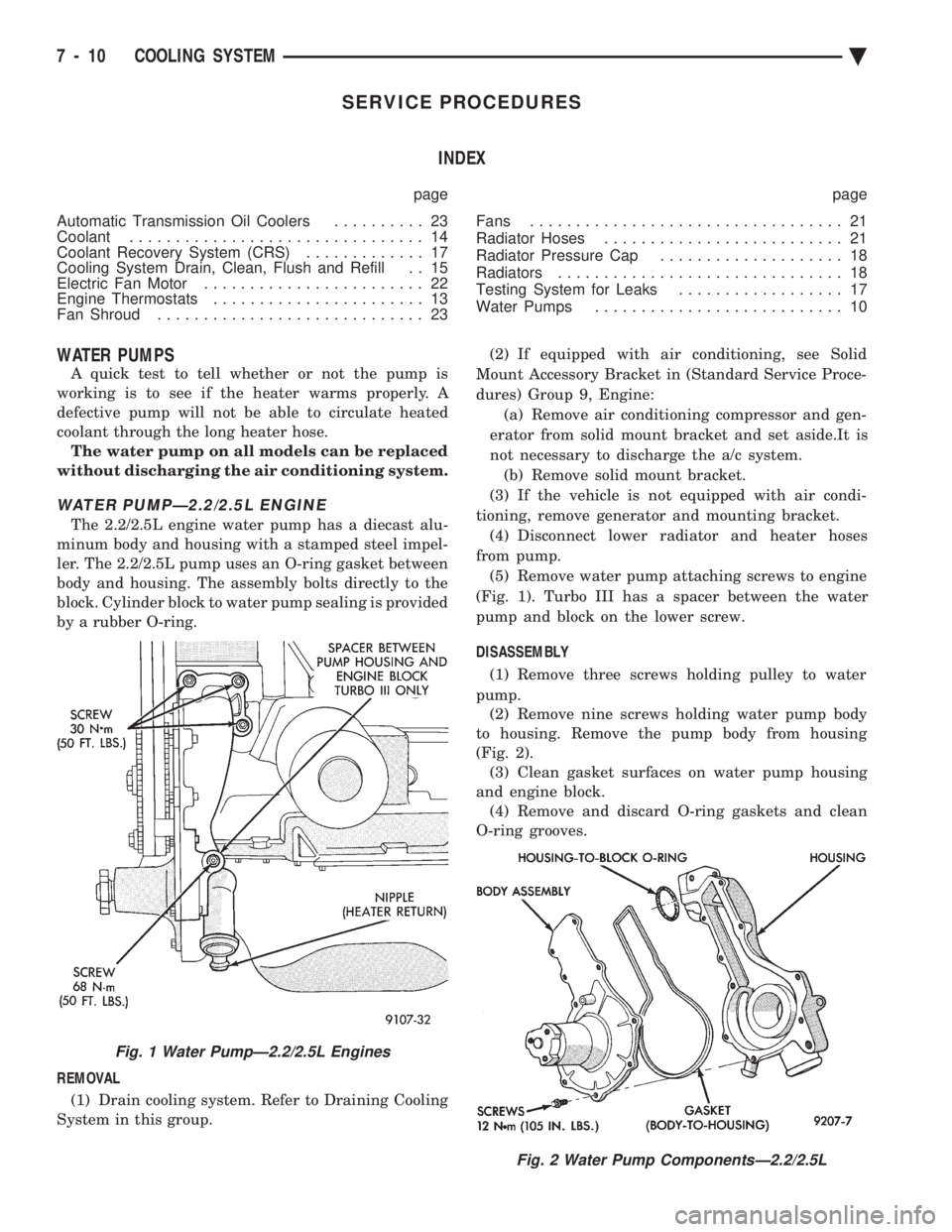
WATER PUMPÐ2.2/2.5L ENGINE
The 2.2/2.5L engine water pump has a diecast alu-
minum body and housing with a stamped steel impel-
ler. The 2.2/2.5L pump uses an O-ring gasket between
body and housing. The assembly bolts directly to the
block. Cylinder block to water pump sealing is provided
by a rubber O-ring.
REMOVAL (1) Drain cooling system. Refer to Draining Cooling
System in this group. (2) If equipped with air conditioning, see Solid
Mount Accessory Bracket in (Standard Service Proce-
dures) Group 9, Engine: (a) Remove air conditioning compressor and gen-
erator from solid mount bracket and set aside.It is
not necessary to discharge the a/c system. (b) Remove solid mount bracket.
(3) If the vehicle is not equipped with air condi-
tioning, remove generator and mounting bracket. (4) Disconnect lower radiator and heater hoses
from pump. (5) Remove water pump attaching screws to engine
(Fig. 1). Turbo III has a spacer between the water
pump and block on the lower screw.
DISASSEMBLY (1) Remove three screws holding pulley to water
pump. (2) Remove nine screws holding water pump body
to housing. Remove the pump body from housing
(Fig. 2). (3) Clean gasket surfaces on water pump housing
and engine block. (4) Remove and discard O-ring gaskets and clean
O-ring grooves.
Fig. 2 Water Pump ComponentsÐ2.2/2.5L
Fig. 1 Water PumpÐ2.2/2.5L Engines
7 - 10 COOLING SYSTEM Ä
Page 356 of 2438

INSTALLATIONÐ3.3L AND 3.8L ENGINE
Place a new gasket (dipped in water) on the water
box surface, center thermostat into opening in the in-
take manifold. Place housing over gasket and ther-
mostat, making sure thermostat is in recess provided
(Fig. 13). Bolt housing to intake manifold, tighten
bolts to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.). Refill cooling system
(see Refilling System ).
COOLANT
The cooling system is designed around the coolant.
The coolant must accept heat from engine metal, in
the cylinder head area near the exhaust valves. Then
carry this heat to the radiator where the tube/fin as-
semblies of these components can give it up to the
air.
PERFORMANCE
Performance is measurable. For heat transfer pure
water excels (Formul a = 1 btu per minute for each
degree of temperature rise for each pound of water).
This formula is altered when necessary additives to
control boiling, freezing, and corrosion are added as
follows:
² Pure Water (1 btu) boils at 100ÉC (212ÉF) and
freezes at 0ÉC (32ÉF).
² 100 Percent Glycol (.7 btu) can cause a hot engine
and detonation and will raise the freeze point to 22ÉC
(-8ÉF).
² 50/50 Glycol and Water (.82 btu) is the recom-
mended combination that provides a freeze point of
-37ÉC(-35ÉF).The radiator, water pump, engine water
jacket, radiator pressure cap, thermostat, tempera-
ture gauge, sending unit and heater are all designed
for 50/50 glycol. Where required, a 56 percent glycol and 44 percent
water mixture will provide a freeze point of-59ÉC
(-50ÉF).
CAUTION: Richer mixtures cannot be measured
with field equipment which can lead to problems
associated with 100 percent glycol.
SELECTION AND ADDITIVES
The use of aluminum cylinder heads, intake mani-
folds, and water pumps requires special corrosion
protection. Mopar Antifreeze, Prestone II, Peak or
antifreeze containing Alugard 340-2, or their equiva-
lent are recommended for best engine cooling with-
out corrosion. When mixed only to a freeze point of
Fig. 11 Thermostat, Housing, and Water BoxÐ3.0L Engine
Fig. 12 Thermostat InstalledÐ3.0L Engine
Fig. 13 Thermostat, Housing and WaterboxÐ3.3Land 3.8L Engine
7 - 14 COOLING SYSTEM Ä