1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM Index
[x] Cancel search: IndexPage 1743 of 2438

FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM INDEX
page page
Chassis Fuel Tubes ...................... 11
Flexible Fuel Components ................... 3
Fuel FilterÐAll Vehicles .................... 9
Fuel Hoses, Clamps, and Quick Connect Fittings . 10
Fuel Pump Assembly ...................... 5
Fuel Pump Module Installation ............... 9
Fuel Pump Module Removal ................. 8
Fuel Pump Pressure TestÐ2.2L/2.5L TBI and 3.0L MPI Engines ........................... 7
Fuel Pump Pressure TestÐAll Except 2.2L/2.5L TBI and 3.0L MPI ....................... 6
Fuel Pump Strainer Service .................. 9 Fuel System Pressure
...................... 6
Fuel System Pressure Release ProcedureÐ 2.2L/2.5L TBI ........................... 4
Fuel System Pressure Release ProcedureÐ3.0L . . 5
Fuel System Pressure Release ProcedureÐExcept 2.2L/2.5L TBI and 3.0L ................... 4
General Information ........................ 3
Identifying Flexible Fuel Components .......... 3
Mechanical Malfunctions .................... 8
Methanol Concentration SensorÐFlexible Fuel AA-Body .............................. 4
Service Precautions for Flexible Fuel Vehicles .... 3
GENERAL INFORMATION
Beginning this model year, Chrysler began produc-
ing AA-Body vehicles designed to operate on a mix-
ture of gasoline and methanol. These automobiles are
referred to as Flexible Fuel vehicles. Flexible fuel vehicles can operate on a mixture of
up to 85 percent methanol, 15 percent unleaded gas-
oline. These vehicles also operate on mixtures con-
taining a lower percentage of methanol or just pure
unleaded gasoline. In many cases, the procedures for servicing flexible
fuel components is identical to gasoline only compo-
nents. Refer to the particular Service Procedure in
this section. If the service procedure for flexible fuel
component differs from a gasoline only component,
the title of each service procedure identifies the ap-
plication.
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS FOR FLEXIBLE FUEL
VEHICLES
Methanol is more toxic than gasoline. Always re-
lease fuel system pressure before servicing fuel sys-
tem components and wear methanol resistant gloves
and eye protection. Avoid breathing methanol vapors or ingesting
methanol. Headaches, dizziness and even uncon-
sciousness could result from breathing these vapors.
Serious injury, blindness and even death could result
from ingesting methanol. Methanol vapors are extremely flammable and can
travel along the ground. Service vehicles in well ven-
tilated areas and avoid ignition sources. Never
smoke while servicing the vehicle. Do not allow methanol to contact skin. Prolonged
contact with methanol can cause dry skin or an al-
lergic skin reaction. Also, prolonged contact could re-
sult in absorption through the skin.
IDENTIFYING FLEXIBLE FUEL COMPONENTS
Flexible Fuel vehicles have unique methanol com-
patible fuel system components. Chrysler identifies
methanol compatible components that could be phys-
ically interchanged with gasoline only parts by color-
ing them green or applying a green label or tag to
them. Even though they may appear physically iden-
tical, components for gasoline only vehicles must not
be used on flexible fuel vehicles.
FLEXIBLE FUEL COMPONENTS
Flexible fuel AA-body vehicles uses many unique
fuel system components. The unique parts are green
in appearance or have a green tag or label attached
to them. While components used on gasoline only ve-
hicles may look similar or identical, they cannot be
used on flexible fuel vehicles. When servicing a com-
ponent, always use an original equipment or equiva-
lent flexible fuel replacement. The fuel system of flexible fuel AA-body vehicles
have the following unique components.
² Fuel pump module
² Fuel level sensor
² Fuel gauge (gauge cluster).
² Fuel tank
² Fuel pressure regulator (including O-rings)
² Fuel rail
² Fuel injectors (including O-rings)
² Fuel tubes
² Fuel filter
² EVAP canister
² Fuel filler cap
² Fuel filler tube
² Pressure relief/Rollover valve
² All fuel system and emission system hoses and
tubes
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 3
Page 1754 of 2438

FUEL TANKS INDEX
page page
Flexible Fuel Vehicles ..................... 14
Fuel Pump Module ....................... 18
Fuel Reservoir ........................... 18
Fuel System Pressure Release ProcedureÐ 2.2L/2.5L TBI .......................... 15
Fuel System Pressure Release ProcedureÐ3.0L . 15
Fuel System Pressure Release ProcedureÐ Except 2.2L/2.5L TBI and 3.0L ............. 15 Fuel Tank
.............................. 16
Fuel Tank Level Sensor ................... 18
Fuel Tank Pressure Relief and Roll-Over Valve . . 20
General Information ....................... 14
Identifying Flexible Fuel Components .......... 14
Methanol Concentration Sensor .............. 18
Pressure Vacuum Fuel Filler Tube Cap ........ 14
Service Precautions for Flexible Fuel Vehicles . . . 14
GENERAL INFORMATION
The fuel tanks of Chrysler Corporation built vehi-
cles are equipped with fuel and vapor controls that
allow the vehicle to pass a full 360É rollover. The fuel delivery system used on front wheel drive
vehicles contains a fuel tank pressure relief/rollover
valve. The valve mounts on the top of the fuel tank.
The valve functions as a pressure relief valve while
the vehicle is upright. The valve also contains a
check valve that prevents fuel from escaping the fuel
tank if the vehicle turns over. The fuel filler cap also acts as a pressure/vacuum
valve. When pressure inside the fuel tank gets too
high or too low, the fuel filler cap opens to relieve
the difference in air pressure. An evaporation control system restricts fuel evapo-
ration into the atmosphere and reduces unburned hy-
drocarbons. Vapors from the fuel tank are collected
in a charcoal filled canister. The vapors are held in
the canister until the engine is operating. When the
engine operates, vapors are drawn through the in-
take manifold into the combustion chambers.
FLEXIBLE FUEL VEHICLES
Beginning this model year, Chrysler began produc-
ing AA-Body vehicles designed to operate on a mix-
ture of gasoline and methanol. These automobiles are
referred to as Flexible Fuel Vehicles. Flexible fuel vehicles can operate on a mixture of
up to 85 percent methanol, 15 percent unleaded gas-
oline. These vehicles also operate on mixtures con-
taining a lower percentage of methanol or just pure
unleaded gasoline. In many cases, the procedures for servicing flexible
fuel components is identical to gasoline only compo-
nents. Refer to the particular Service Procedure in
this section. If the service procedure for flexible fuel
component differs from a gasoline only component,
the title of each service procedure identifies the ap-
plication.
IDENTIFYING FLEXIBLE FUEL COMPONENTS
Flexible Fuel vehicles have unique methanol com-
patible fuel system components. Chrysler identifies
methanol compatible components that could be phys-
ically interchanged with gasoline only parts by color-
ing them green or applying a green label or tag to
them. Even though they may appear physically iden-
tical, components for gasoline only AA-body vehicles
must not be used on flexible fuel vehicles.
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS FOR FLEXIBLE FUEL
VEHICLES
Methanol is more toxic than gasoline. Always re-
lease fuel system pressure before servicing fuel sys-
tem components and wear methanol resistant gloves
and eye protection. Avoid breathing methanol vapors or ingesting
methanol. Headaches, dizziness and even uncon-
sciousness could result from breathing these vapors.
Serious injury, blindness and even death could result
from ingesting methanol. Methanol vapors are extremely flammable and can
travel along the ground. Service vehicles in well ven-
tilated areas and avoid ignition sources. Never
smoke while servicing the vehicle. Do not allow methanol to contact skin. Prolonged
contact with methanol can cause dry skin or an al-
lergic skin reaction. Also, prolonged contact could re-
sult in absorption through the skin.
PRESSURE VACUUM FUEL FILLER TUBE CAP
WARNING: REMOVE FUEL FILLER TUBE CAP TO
RELIEVE TANK PRESSURE BEFORE REMOVING
OR REPAIRING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
The loss of any fuel or vapor out of the filler tube
neck is prevented by the use of a safety filler cap.
The cap releases only under significant pressure 10.9
to 13.45 kPa (1.58 to 1.95 psi). The vacuum release
for all gas caps is between .97 and 2.0 kPa (.14 and
.29 psi). The cap must be replaced by a similar unit
in order for the system to remain effective.
14 - 14 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1761 of 2438

INSTALLATION
WARNING: FUEL PRESSURE RELIEF/ROLLOVER
VALVES DESIGNED FOR GASOLINE ONLY VEHI-
CLES CANNOT BE USED ON FLEXIBLE FUEL AA-
BODY VEHICLES. WHEN SERVICING THE FUEL
SYSTEM OF A FLEXIBLE FUEL VEHICLE, ONLY
USE ORIGINAL EQUIPMENT OR EQUIVALENT RE-
PLACEMENT COMPONENTS. (1) Install the rubber grommet in the fuel tank by
working it around the curled lip of the tank (Fig. 13).
CAUTION: Only use power steering fluid to lubri-
cate the pressure relief/rollover valve grommet.
(2) Lightly lubricate the grommet with power
steering fluid only and push the valve downward into
the grommet. Twist valve until properly positioned. (3) Install fuel tank (refer to fuel tank installa-
tion).
ACCELERATOR PEDAL AND THROTTLE CABLE INDEX
page page
Accelerator Pedal ........................ 21 Throttle Cable........................... 22
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
CAUTION: When servicing the accelerator pedal,
throttle cable or speed control cable, do not dam-
age or kink the control cable core wire.
REMOVAL
(1) Working from the engine compartment, hold
the throttle body throttle lever in the wide open po-
sition. Remove the throttle cable from the throttle
body cam. (2) From inside the vehicle, hold up the pedal and
remove the cable retainer and throttle cable from the
upper end of the pedal shaft (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2).
(3) Working from the engine compartment, remove
nuts from accelerator pedal assembly studs (Fig. 1).
Remove assembly from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position accelerator pedal assembly on dash
panel. Install retaining nuts. Tighten retaining nuts
to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 1 Accelerator Pedal and Throttle CableÐFront
View
Fig. 13 Installing Pressure Relief/Rollover Valve
Fig. 2 Accelerator Pedal and Throttle CableÐRearView
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 21
Page 1764 of 2438
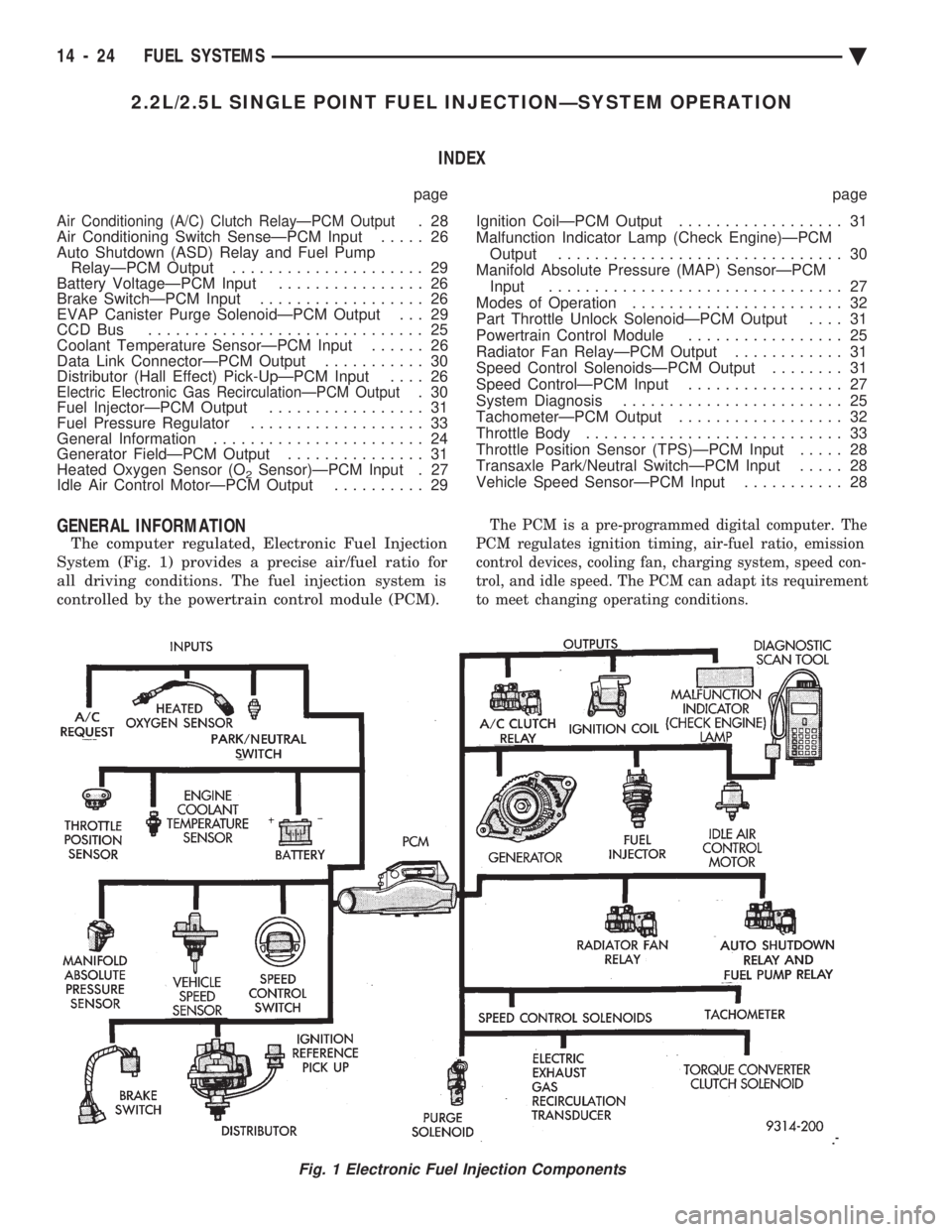
2.2L/2.5L SINGLE POINT FUEL INJECTIONÐSYSTEM OPERATION INDEX
page page
Air Conditioning (A/C) Clutch RelayÐPCM Output.28
Air Conditioning Switch SenseÐPCM Input ..... 26
Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay and Fuel Pump RelayÐPCM Output ..................... 29
Battery VoltageÐPCM Input ................ 26
Brake SwitchÐPCM Input .................. 26
EVAP Canister Purge SolenoidÐPCM Output . . . 29
CCD Bus .............................. 25
Coolant Temperature SensorÐPCM Input ...... 26
Data Link ConnectorÐPCM Output ........... 30
Distributor (Hall Effect) Pick-UpÐPCM Input .... 26
Electric Electronic Gas RecirculationÐPCM Output.30
Fuel InjectorÐPCM Output ................. 31
Fuel Pressure Regulator ................... 33
General Information ....................... 24
Generator FieldÐPCM Output ............... 31
Heated Oxygen Sensor (O
2Sensor)ÐPCM Input . 27
Idle Air Control MotorÐPCM Output .......... 29 Ignition CoilÐPCM Output
.................. 31
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine)ÐPCM Output ............................... 30
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorÐPCM Input ................................ 27
Modes of Operation ....................... 32
Part Throttle Unlock SolenoidÐPCM Output .... 31
Powertrain Control Module ................. 25
Radiator Fan RelayÐPCM Output ............ 31
Speed Control SolenoidsÐPCM Output ........ 31
Speed ControlÐPCM Input ................. 27
System Diagnosis ........................ 25
TachometerÐPCM Output .................. 32
Throttle Body ............................ 33
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)ÐPCM Input ..... 28
Transaxle Park/Neutral SwitchÐPCM Input ..... 28
Vehicle Speed SensorÐPCM Input ........... 28
GENERAL INFORMATION
The computer regulated, Electronic Fuel Injection
System (Fig. 1) provides a precise air/fuel ratio for
all driving conditions. The fuel injection system is
controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM).
The PCM is a pre-programmed digital computer. The
PCM regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio, emission
control devices, cooling fan, charging system, speed con-
trol, and idle speed. The PCM can adapt its requirement
to meet changing operating conditions.
Fig. 1 Electronic Fuel Injection Components
14 - 24 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1775 of 2438
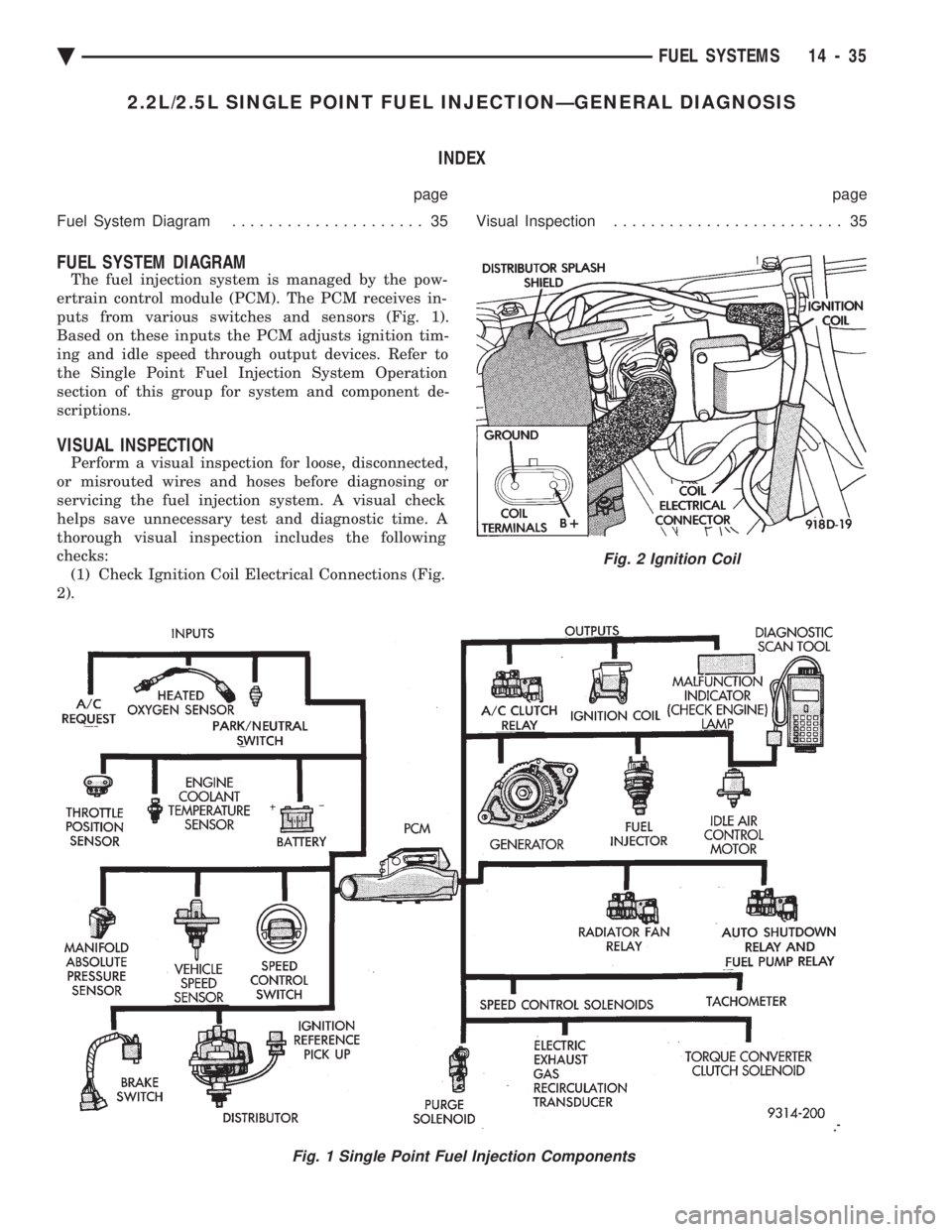
2.2L/2.5L SINGLE POINT FUEL INJECTIONÐGENERAL DIAGNOSIS INDEX
page page
Fuel System Diagram ..................... 35 Visual Inspection......................... 35
FUEL SYSTEM DIAGRAM
The fuel injection system is managed by the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM). The PCM receives in-
puts from various switches and sensors (Fig. 1).
Based on these inputs the PCM adjusts ignition tim-
ing and idle speed through output devices. Refer to
the Single Point Fuel Injection System Operation
section of this group for system and component de-
scriptions.
VISUAL INSPECTION
Perform a visual inspection for loose, disconnected,
or misrouted wires and hoses before diagnosing or
servicing the fuel injection system. A visual check
helps save unnecessary test and diagnostic time. A
thorough visual inspection includes the following
checks: (1) Check Ignition Coil Electrical Connections (Fig.
2).
Fig. 1 Single Point Fuel Injection Components
Fig. 2 Ignition Coil
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 35
Page 1781 of 2438

2.2L/2.5L SINGLE POINT FUEL INJECTIONÐON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS INDEX
page page
60-Way PCM Wiring Connector .............. 46
Circuit Actuation Test Mode ................ 45
Diagnostic Trouble Code Description .......... 42
General Information ....................... 41
High and Low Limits ...................... 42
Ignition Timing Procedure .................. 46 Monitored Circuits
........................ 41
Non-Monitored Circuits .................... 42
State Display Test Mode ................... 45
Systems Test ........................... 45
Throttle Body Minimum Air Flow Check Procedure.46
GENERAL INFORMATION
The powertrain control module (PCM) has been
programmed to monitor many different circuits of the
fuel injection system. If a problem is sensed with a
monitored circuit often enough to indicate an actual
problem, the PCM stores a fault. If the problem is re-
paired or ceases to exist, the PCM cancels the Diag-
nostic Trouble Code after 50 to 100 vehicle key on/off
cycles. Certain criteria must be met for a diagnostic trou-
ble code to be entered into powertrain control module
(PCM) memory. The criteria may be a specific range
of engine RPM, engine temperature, and/or input
voltage to the PCM. It is possible that a diagnostic trouble code for a
monitored circuit may not be entered into memory
even though a malfunction has occurred. This may
happen because one of the diagnostic trouble code
criteria for the circuit has not been met. For exam-
ple , assume that one of the diagnostic trouble code
criteria for a certain sensor circuit is that the engine
must be operating between 750 and 2000 RPM to be
monitored for a diagnostic trouble code. If the sensor
output circuit shorts to ground when engine RPM is
above 2400 RPM (resulting i n a 0 volt input to the
PCM) a diagnostic trouble code will not be entered
into memory. This is because the condition does not
occur within the specified RPM range. There are several operating conditions for which
the PCM does not monitor and set diagnostic trouble
codes. Refer to Monitored Circuits and Non-Moni-
tored Circuits in this section. Stored diagnostic trouble codes can be displayed by
cycling the ignition key On - Off - On - Off - On.
Also, the technician can display fault information us-
ing the DRB II scan tool. The DRBII scan tool con-
nects to the data link connector in the vehicle (Fig.
1,2or3).
MONITORED CIRCUITS
The powertrain control module (PCM) can detect
certain fault conditions in the fuel injection system. Open or Shorted Circuit - The PCM can deter-
mine if the sensor output (input to PCM) is within
proper range, and if the circuit is open or shorted. Output Device Current Flow
- The PCM senses
whether the output devices are hooked up. If there is
a problem with the circuit, the PCM senses whether
the circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted
high. Oxygen Sensor - The PCM can determine if the
oxygen sensor is switching between rich and lean
Fig. 1 Data Link Connector LocationÐAA and AP Vehicles
Fig. 2 Data Link Connector LocationÐAC Vehicles
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 41
Page 1782 of 2438

once the system has entered closed loop. Refer to
Modes of Operation in this section for an explanation
of closed loop operation.
NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems and conditions that could have malfunctions
that result in driveability problems. Diagnostic trou-
ble codes may not be displayed for these conditions.
However, problems with these systems may cause di-
agnostic trouble codes to be displayed for other sys-
tems. For example, a fuel pressure problem will not
register a fault directly, but could cause a rich or
lean condition. This could cause an oxygen sensor
fault to be stored in the PCM. Fuel Pressure - Fuel pressure is controlled by the
fuel pressure regulator. The PCM cannot detect a
clogged fuel pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel fil-
ter, or a pinched fuel supply or return line. However,
these could result in a rich or lean condition causing
an oxygen sensor fault. Secondary Ignition Circuit - The PCM cannot
detect an inoperative ignition coil, fouled or worn
spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or open spark plug
cables. Engine Timing - The PCM cannot detect an incor-
rectly indexed timing chain, camshaft sprocket and
crankshaft sprocket. The PCM also cannot detect an
incorrectly indexed distributor. However, these could
result in a rich or lean condition causing an oxygen
sensor fault to be stored in the PCM. Cylinder Compression - The PCM cannot detect
uneven, low, or high engine cylinder compression. Exhaust System
- The PCM cannot detect a
plugged, restricted or leaking exhaust system. Fuel Injector Malfunctions - The PCM cannot
determine if the fuel injector is clogged, the pintle is
sticking or the wrong injector is installed. However,
these could result in a rich or lean condition causing
an oxygen sensor fault to be stored in the PCM. Excessive Oil Consumption - Although the PCM
monitors the exhaust stream oxygen content through
the oxygen sensor when the system is in closed loop,
it cannot determine excessive oil consumption. Throttle Body Air Flow - The PCM cannot detect
a clogged or restricted air cleaner inlet or filter ele-
ment. Evaporative System - The PCM will not detect a
restricted, plugged or loaded evaporative purge can-
ister. Vacuum Assist - Leaks or restrictions in the vac-
uum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control sys-
tem devices are not monitored by the PCM. However,
these could result in a MAP sensor fault being stored
in the PCM. PCM System Ground - The PCM cannot deter-
mine a poor system ground. However, a diagnostic
trouble code may be generated as a result of this con-
dition. PCM Connector Engagement - The PCM cannot
determine spread or damaged connector pins. How-
ever, a diagnostic trouble code may be generated as a
result of this condition.
HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The powertrain control module (PCM) compares in-
put signal voltages from each input device with es-
tablished high and low limits that are programmed
into it for that device. If the input voltage is not
within specifications and other diagnostic trouble
code criteria are met, a diagnostic trouble code will
be stored in memory. Other diagnostic trouble code
criteria might include engine RPM limits or input
voltages from other sensors or switches that must be
present before a fault condition can be verified.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTION
When a diagnostic trouble code appears, it indi-
cates the powertrain control module (PCM) has rec-
ognized an abnormal condition in the system.
Diagnostic trouble codes can be obtained from the
malfunction indicator lamp (instrument panel Check
Engine lamp) on the Instrument Panel or from the
DRBII scan tool. Diagnostic trouble codes indicate
the results of a failure but do not identify the failed
component directly.
Fig. 3 Data Link Connector LocationÐAG and AJ Vehicles
14 - 42 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1788 of 2438

2.2L/2.5L SINGLE POINT FUEL INJECTIONÐSERVICE PROCEDURES INDEX
page page
Canister Purge Solenoid ................... 53
Electric Exhaust Gas Recirculation Transducer (EET) Service ............................... 53
Fuel Fitting ............................. 50
Fuel Injector ............................ 51
Fuel Lines and Hoses ..................... 48
Fuel Pressure Regulator ................... 51 Fuel System Pressure Release Procedure
...... 48
Heated Oxygen Sensor (O
2Sensor) .......... 54
Idle Air Control Motor ..................... 53
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor ........... 53
PCM Service ............................ 54
Throttle Body ............................ 48
Throttle Position Sensor ................... 52
FUEL LINES AND HOSES
Perform the Fuel System Pressure Relief Procedure
before servicing the fuel system. The procedure must
be done to bleed fuel pressure from the system before
removing clamps or hoses. Use care when removing fuel hoses to prevent dam-
age to hose or hose nipple. Always use new hose
clamps, of the correct type, during reassembly. Tighten
hose clamps to 1 N Im (10 in. lbs.) torque. Do not use
aviation style clamps on this system or hose
damage may result.
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE
CAUTION: Before servicing the fuel pump, fuel lines,
fuel filter, throttle body, or fuel injector, release fuel
system pressure.
(1) Loosen fuel filler cap to release fuel tank pres-
sure. (2) Disconnect injector wiring harness connector at
edge of throttle body (Fig. 1). (3) Connect a jumper wire between terminal Num-
ber 1 of the injector harness and engine ground. (4) Connect a jumper wire to the positive terminal
Number 2 of the injector harness and touch the battery
positive post for no longer than 5 seconds . This
releases system pressure. (5) Remove jumper wires.
(6) Continue fuel system service.
THROTTLE BODY
CAUTION: The fuel system is under a constant pres-
sure of 270 kPa (39 psi). When servicing the fuel
portion of the throttle body, release fuel pressure
before disconnecting any tubes. Refer to the fuel
pressure release procedure.
Always reassemble throttle body components with
new O-rings and seals where applicable. Never use
silicone lubricants on O-rings or seals, damage may
result. Use care when removing fuel tubes to prevent
damage to quick connect fittings or tube ends. Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps, and Quick Connect Fittings
in the Fuel Delivery Section of this Group.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove air cleaner (Fig. 2).
(2) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure.
(3) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(4) Disconnect vacuum hoses and electrical connec-
tors (Fig. 3).
Fig. 1 Injector Harness Connector
Fig. 2 Throttle Body and Air Cleaner Assembly
14 - 48 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä