1993 CHEVROLET DYNASTY check engine light
[x] Cancel search: check engine lightPage 1655 of 2438
(3) Apply light coating of engine oil to the entire
circumference of oil seal lip. (4) Install seal assembly on cylinder block and
tighten bolts to 12 N Im (104 in. lbs.)
FRONT CRANKSHAFT OIL PUMP AND OIL
SEAL
(1) Install oil pump gasket and oil pump case
(Figs. 1 and 14). CAUTION: Install bolts, depending on length in lo-
cations shown in (Fig. 14).
(2) Using front crankshaft oil seal installer Special
Tool MB998306 install oil seal in oil pump (Fig. 15).
CYLINDER BLOCK
Inspect cylinder block for scratches, cracks and rust
or corrosion, and repair or replace as required.
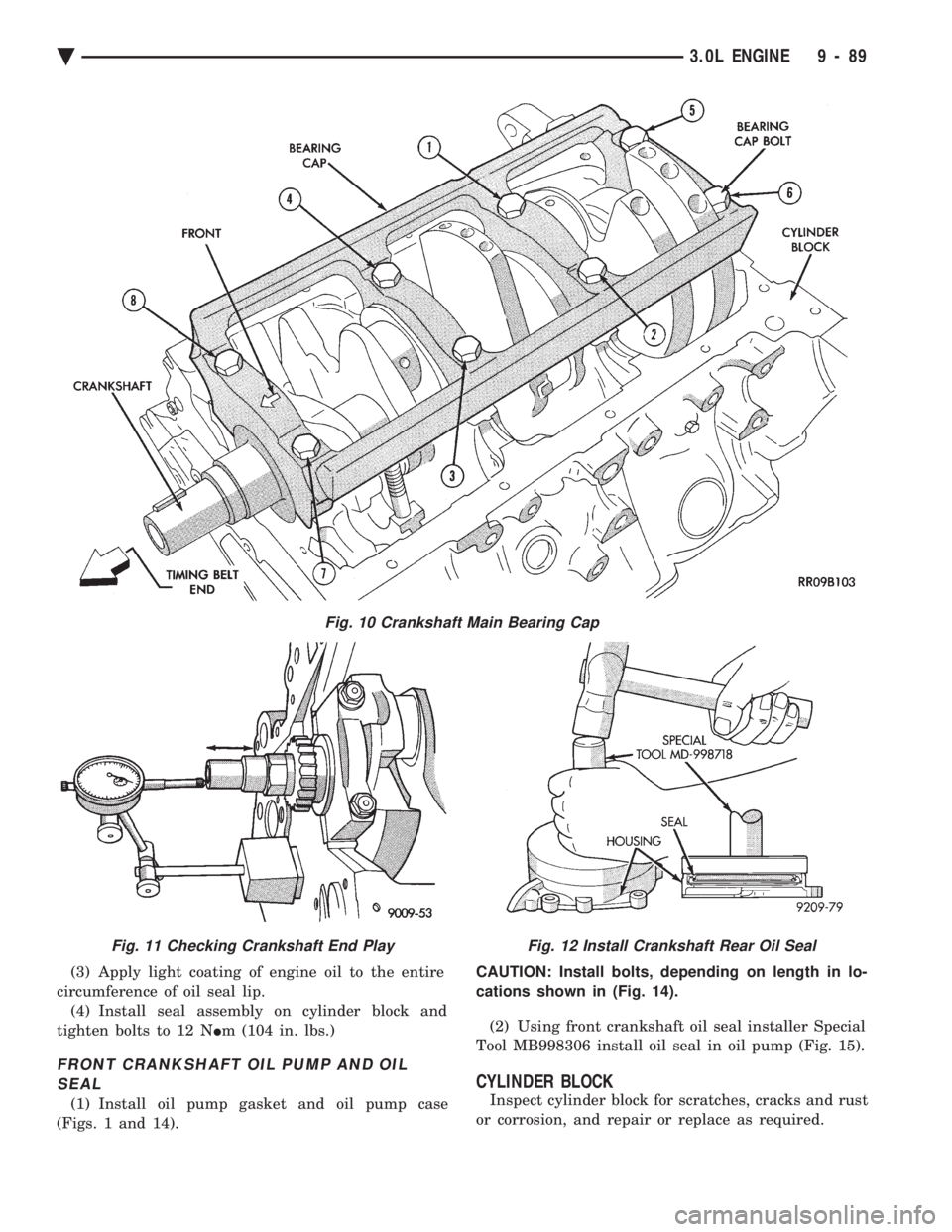
Fig. 10 Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap
Fig. 11 Checking Crankshaft End PlayFig. 12 Install Crankshaft Rear Oil Seal
Ä 3.0L ENGINE 9 - 89
Page 1669 of 2438

INSPECTION
(1) Before cleaning, check for leaks, damage and
cracks. (2) Clean cylinder head and oil passages.
(3) Check cylinder head for flatness (Fig. 8).
(4) Inspect all surfaces with a straightedge if there is
any reason to suspect leakage. If out of flatness exceeds
.019mm (.00075 inch). times the span length in inches
in any direction, either replace head or lightly machine
the head surface. As an example, if a 12 inch span is
1mm (.004 inch) out of flat, allowable is 12 x .019mm
(.00075 inch) equals .22mm (.009 in.) This amount of
out of flat is acceptable. *Maximum of 0.2 mm (.008 inch) for grinding is
permitted.
CAUTION: This is a combined total dimension of
stock removal from cylinder head and block top
surface.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean all surfaces of cylinder block and cylinder
heads. (2) Install new gaskets on cylinder block (Fig. 9).
The Cylinder head bolts are torqued using the
torque yield method, they should be examined
BEFORE reuse. If the threads are necked down,
the bolts should be replaced (Fig. 10).
Necking can be checked by holding a scale or straight
edge against the threads. If all the threads do not
contact the scale the bolt should be replaced. (3) Tighten the cylinder head bolts 1 thru 8 in the
sequence shown in (Fig. 11). Using the 4 step torque
turn method, tighten according to the following values:
² First-All to 61 N Im (45 ft. lbs.)
² Second-All to 88 N Im (65 ft. lbs.)
² Third-All (again) to 88 N Im (65 ft. lbs.)
² Fourth + 1/4 Turn Do not use a torque wrench
for this step (4) Bolt torque after 1/4 turn should be over 122
N Im(90 ft. lbs.). If not, replace the bolt.
(5) Tighten head bolt number 9 (Fig. 11) to 33 N Im
(25 ft. lbs.) after head bolts 1 thru 8 have been tighten
to specifications. (6) Inspect push rods and replace worn or bent rods.
(7) Install push rods, rocker arm and shaft assem-
blies with the stamped steel retainers in the four
positions, tighten to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.) (Fig. 12).
Fig. 8 Check Cylinder Head
Fig. 9 Head Gasket Installation
Fig. 10 Checking Bolts for Stretching (Necking)
Fig. 11 Cylinder Head Tightening Sequence
Ä 3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 103
Page 1672 of 2438

REFACING VALVES AND VALVE SEATS
The intake and exhaust valves have a 44-1/2 to 45
degree face angle. The valve seats have a 45 to 45-
1/2 degree face angle. The valve face and valve seat
angles are shown in (Fig. 21).
VALVES
(1) Inspect the remaining margin after the valves
are refaced Refer to specifications (Fig. 20).
VALVE SEATS
CAUTION: Do not un-shroud cylinder head from
around the valve during valve seat refacing (Fig.
22).
(1) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be ob-
tained. (2) Measure the concentricity of valve seat using
dial indicator. Total runout should not exceed
.051mm (.002 inch) total indicator reading.
(3) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to de-
termine where the valve contacts the seat. To do this, coat valve seat
LIGHTLYwith Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to top edge of valve face,lower valve seat with a
15 degree stone. If the blue is transferred to the bottom
edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 65 degrees
stone. Valve seats which are worn or burned can be
reworked, provided that correct angle and seat
width are maintained. Otherwise cylinder head
must be replaced. (4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake seats should be 1.75 to 2.25mm (0.69 to .088
inch) The width of the exhaust seats should be 1.50 to
2.00mm (.059 to .078 inch) (Fig. 21) (5) Check the valve spring installed height after
refacing the valve and seat (Fig. 24).
TESTING VALVE SPRINGS
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should be
tested (Fig. 23). As an example; the compression
Fig. 23 Testing Valve Spring with Tool C-647
Fig. 20 Valve Dimensions
Fig. 21 Valve Seats
Fig. 22 Refacing Valve Seats
9 - 106 3.3/3.8L ENGINE Ä
Page 1674 of 2438

(15) Install rocker arm covers tighten screws to 14
N Im (120 in. lbs.) and connector to ignition coils.
(16) Install Intake Manifold; Refer to Intake Mani-
fold Installation 3.3/3.8L Engine, Group 11 Exhaust
System and Intake Manifold.
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
The valve train includes roller tappet assemblies,
aligning yokes and yoke retainer. Roller tappet alignment is maintained by machined
flats on tappet body being fitted in pairs into six
aligning yokes. The yokes are secured by an alignment
yoke retainer (Fig. 26).
PRELIMINARY STEP TO CHECKING THE HY- DRAULIC TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to cor-
rect tappet noise, read the oil pressure at the gauge.
Install a reliable gauge at pressure sending unit if
vehicle has no oil pressure gauge and check the oil level
in the oil pan. The pressure should be between 30 and
80 psi (206.8 to 551.6 kPa) at 2000 rpm. The oil level in the pan should never be above the
MAX mark on dipstick, or below the MIN mark. Either
of these two conditions could be responsible for noisy
tappets. Oil Level Check: stop engine after reach-
ing normal operating temperature . Allow 5 min-
utes to stabilize oil level, check dipstick.
OIL LEVEL TOO HIGH
If oil level is above the MAX mark on dip stick, it is
possible for the connecting rods to dip into the oil while
engine is running and create foam. Foam in oil pan
would be fed to the hydraulic tappets by the oil pump
causing them to become soft and allow valves to seat
noisily.
OIL LEVEL TOO LOW
Low oil level may allow pump to take in air which
when fed to the tappets, causes them to become soft
and allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake
side of pump through which air can be drawn will
create the same tappet action. Check the lubri- cation system from the intake strainer to the pump
cover, including the relief valve retainer cap. When
tappet noise is due to aeration, it may be intermittent
or constant, and usually more than one tappet will be
noisy. When oil level and leaks have been corrected,
engine should be operated at fast idle to allow all of the
air inside of the tappets to be bled out.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE DIAGNOSIS
To determine source of valve train noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed and
listen for source of the noise. Worn valve guides or cocked springs are some-
times mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is the
case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not appre-
ciably reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in
the tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod
sockets and push rod ends for wear. Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a heavy
click. A light noise is usually caused by excessive
leakdown around the unit plunger which will necessi-
tate replacing the tappet, or by the plunger partially
sticking in the tappet body cylinder. A heavy click is
caused either by a tappet check valve not seating, or by
foreign particles becoming wedged between the
plunger and the tappet body causing the plunger to
stick in the down position. This heavy click will be
accompanied by excessive clearance between the valve
stem and rocker arm as valve closes. In either case,
tappet assembly should be removed for inspection and
cleaning.
TAPPET REMOVAL
(1) Refer to Cylinder Head Removal of this section to
remove intake manifold and cylinder heads for access
to tappets for service. (2) Remove yoke retainer and aligning yokes.
(3) Use Tool C-4129 to remove tappets from their
bores. If all tappets are to be removed, identify tappets
to insure installation in original location. If the tappet or bore in cylinder block is scored,
scuffed, or shows signs of sticking, ream the bore
to next oversize and replace with oversize tap-
pet.
CAUTION: The plunger and tappet bodies are not
interchangeable. The plunger and valve must always
be fitted to the original body. It is advisable to work on
one tappet at a time to avoid mixing of parts. Mixed
parts are not compatible. Do not disassemble a tap-
pet on a dirty work bench.
DISASSEMBLY (FIG. 27)
(1) Pry out plunger retainer spring clip.
Fig. 26 Roller Tappets Aligning Yoke and Retainer
9 - 108 3.3/3.8L ENGINE Ä
Page 1685 of 2438

before installation. Bearing shells are available in
standard and the following undersizes: 0.025mm (.001
inch), .051mm (.002 inch), .076mm (.003 inch), .254mm
(.010 inch), and .305mm (.012 inch). Never install an
undersize bearing that will reduce clearance below
specifications.
REMOVAL (1) Remove oil pan and identify bearing caps before
removal. (2) Remove bearing caps one at a time. Remove
upper half of bearing by inserting Special Main Bear-
ing Tool C-3059. (Fig. 3) into the oil hole of crankshaft. (3) Slowly rotate crankshaft clockwise, forcing out
upper half of bearing shell.
INSTALLATION Only one main bearing should be selectively
fitted while all other main bearing caps are prop-
erly tightened. When installing a new upper bearing shell, slightly
chamfer the sharp edges from the plain side. (1) Start bearing in place, and insert Main Bearing
Tool C-3059 into oil hole of crankshaft (Fig. 3). (2) Slowly rotate crankshaft counter-clockwise slid-
ing the bearing into position. Remove Special Main
Bearing Tool C-3059. (3) Install each main cap and tighten bolts finger
tight. (4) Tighten number 1, 3 and 4 main cap bolts to 41
N Im + 1/4 Turn (30 ft. lbs.+ 1/4 Turn).
(5) Rotate the crankshaft until number 6 piston is
at TDC. (6) To ensure correct thrust bearing alignment the
following procedure must be done: (a) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel. (b) Then, move crankshaft all the way to the
front of its travel. (c) Wedge a appropriate tool between the rear of
the cylinder block and rear crankshaft counter-
weight. This will hold the crankshaft in it's most
forward position. (d) Tighten the #2 Thrust Bearing cap bolts to
41 N Im + 1/4 Turn (30 ft. lbs.+ 1/4 Turn). Remove
the holding tool.
CHECKING CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
(1) Mount a dial indicator to front of engine, locat-
ing probe on nose of crankshaft (Fig. 4). (2) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel. (3) Zero the dial indicator.
(4) Move crankshaft all the way to the front and
read the dial indicator. Refer to (Fig. 5) for specifica-
tion.
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY CHECKÐOPTIONAL
(1) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel using a lever inserted between a main bearing
Fig. 3 Removing and Installing Upper Main Bearing With Special Tool C-3059Fig. 1 Main Bearing Cap Identification
Fig. 2 Main Bearing Identification
Ä 3.3/3.8L ENGINE 9 - 119
Page 1703 of 2438

CLEANING AND INSPECTION
(1) Discard gaskets and clean all gasket surfaces
on both manifolds and on cylinder head. (2) Test gasket surfaces of manifolds for flatness
with a straight edge. Surfaces must be flat within
0.15mm per 300mm (.006 in. per foot) of manifold
length. (3) Inspect manifolds for cracks and distortion.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install a new intake and exhaust manifold gas-
ket. Coat steel gasket lightly with Gasket Sealer on
manifold side. Do notcoat composition gasket with
(any) sealer. (2) Set exhaust manifold in place. Tighten retain-
ing nuts starting at center and progressing outward
in both directions to 23 N Im (200 in. lbs.) torque. Re-
peat this procedure until all nuts are at specified
torque. (3) Set intake manifold in place.
(4) Raise vehicle and tighten retaining screws
starting at center and progressing outward in both
directions to 23 N Im (200 in. lbs.) torque (Fig. 3). Re-
peat this procedure until all screws are at specified
torque. (5) Reverse removal procedures 1-9 for installation.
(6) With the DRBII Scan Tool use ASD Fuel Sys-
tem Test to pressurize system to check for leaks.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay will remain ener-
gized for 7 minutes or until the ignition switch is
turned to the OFF position, or Stop All Test is se-
lected.
INTAKE AND EXHAUST MANIFOLDSÐFLEXIBLE
FUEL ENGINE
INTAKE MANIFOLD
The manifold is die-cast aluminum with upper ple-
num and 4 tubes lower runners. These attach to the
cylinder head, with each runner leading directly to a
cylinder. The manifold is also machined for fuel rail attach-
ment and injector installation. The throttle body is
installed on the upper plenum of the manifold.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
All high strength iron casting that intermesh with
the intake manifold. For standard engines a four
branch design collects and directs exhaust gases to
the conical (articulated joint connection) outlet.
INTAKE/EXHAUST MANIFOLDS
SERVICEÐFLEXIBLE FUEL ENGINES
Intake and exhaust manifolds use a one piece gas-
ket. Service procedures requiring removal and instal-
lation of either must include both manifolds.
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
Methanol is more toxic than gasoline. Always re-
lease fuel system pressure before servicing fuel sys-
tem components and wear methanol resistant gloves
and eye protection. Avoid breathing methanol vapors or ingesting
methanol. Headaches, dizziness and even uncon-
sciousness could result from breathing these vapors.
Serious injury, blindness and even death could result
from ingesting methanol. Methanol vapors are extremely flammable and can
travel along the ground. Service vehicles in well ven-
tilated areas and avoid ignition sources. Never
smoke while servicing the vehicle. Do not allow methanol to contact skin. Prolonged
contact with methanol can cause dry skin or an al-
lergic skin reaction. Also, prolonged contact could re-
sult in absorption through the skin.
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
WEAR METHANOL RESISTANT GLOVES AND EYE
PROTECTION WHILE SERVICING THE FUEL SYS-
TEM.
(a) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(b) Remove fuel filler cap.
(c) Remove the protective cap from the fuel pres-
sure test port on the fuel rail (Fig. 4).
(d) Place the open end of fuel pressure release
hose, tool number C-4799-1, into an approved gas-
oline container. Connect the other end of hose
C-4799-1 to the fuel pressure test port (Fig. 5).
Fuel pressure will bleed off through the hose into
the gasoline container. Fuel gauge C-4799-A con-
tains hose C-4799-1.
Fig. 4 Fuel Pressure Test Port
Ä EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11 - 7
Page 1758 of 2438

INSTALLATION
WARNING: FUEL TANKS DESIGNED FOR GASO-
LINE ONLY VEHICLES CANNOT BE USED ON
FLEXIBLE FUEL AA-BODY VEHICLES. WHEN SER-
VICING THE FUEL SYSTEM OF A FLEXIBLE FUEL
VEHICLE, ONLY USE ORIGINAL EQUIPMENT OR
EQUIVALENT REPLACEMENT COMPONENTS. (1) Position fuel tank on transmission jack. Con-
nect vapor separator/rollover valve hose and position
insulator pad on fuel tank. Position vapor vent so
that it is not pinched between tank and floor pan
during installation. (2) Raise tank and fuel filler tube carefully into
position. Use a light coating of power steering fluid
to ease fuel filler tube installation. Ensure filler tube
grommet is not damaged. Verify that the tube is in-
stalled correctly. (3) Tighten fuel tank strap nuts to 23 N Im (250 in.
lbs.) torque. Remove transmission jack. Ensure
straps are not twisted or bent. (4) Lubricate the metal tubes on the fuel pump
with clean 30 weight engine oil. Install the quick
connect fuel fittings. Refer to Quick Connect Fittings
in the Fuel Delivery section of this Group. (5) Attach electrical connector to fuel pump mod-
ule and level sensor unit. (6) Lower the vehicle.
(7) Attach filler tube to filler neck opening in
quarter panel. Tighten quarter panel screws to 2
N Im (17 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Fill fuel tank, install filler cap, and connect
battery cable.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or un-
til the ignition switch is turned to the Off position.
(9) Use the DRBII scan tool ASD Fuel System Test
to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
FUEL PUMP MODULE
Refer to the Fuel Delivery section of this group.
METHANOL CONCENTRATION SENSOR
Refer to the Fuel Delivery section of this group.
FUEL RESERVOIR
The fuel reservoir is internal to the fuel pump as-
sembly (Fig. 6). The purpose is to provide fuel at the
fuel pump intake during all driving conditions, espe-
cially when low fuel levels are present.
FUEL TANK LEVEL SENSOR
DIAGNOSIS
This procedure test the resistance of the level sen-
sor itself. It does not test the level sensor circuit. Re-
fer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams for circuit
identification and Group 8E, Instrument Panel and
Gauges for fuel gauge information. The level sensor is a variable resistor. Its resis-
tance changes with the amount of fuel in the tank.
The float arm attached to the sensor moves as the
fuel level changes. To test the level sensor, connect
an ohmmeter across the sensor signal and sensor
ground terminals of the fuel level sensor connector
(Fig. 7 or Fig. 8). Move the float lever to the full stop
and empty stop positions shown in the resistance
chart (Fig. 7 or Fig. 8). Record the resistance at each
point. Replace the level sensor if the resistance is not
within specifications. The low fuel warning light specifications determine
if the level sensor portion of the warning light circuit
functions properly. It does not test the complete
warning light circuit. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams for circuit
identification and Group 8E, Instrument Panel and
Gauges for fuel gauge information.
REMOVAL
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
WHEN SERVICING FLEXIBLE FUEL VEHICLES,
WEAR METHANOL RESISTANT GLOVES AND EYE
PROTECTION AND AVOID BREATHING FUMES. DO
NOT ALLOW METHANOL/GASOLINE MIXTURES TO
CONTACT SKIN. SERVICE VEHICLES IN WELL VEN-
TILATED AREAS AND AVOID IGNITION SOURCES.
NEVER SMOKE WHILE SERVICING THE VEHICLE.
Fig. 6 Fuel Reservoir
14 - 18 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1785 of 2438

SYSTEMS TEST
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING A TEST
WITH THE ENGINE OPERATING.
OBTAINING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(1) Connect DRBII scan tool to the data link con-
nector located in the engine compartment near the
powertrain control module (PCM). (2) Start the engine if possible, cycle the transaxle
selector and the A/Cswitch if applicable. Shut off
the engine. (3) Turn the ignition switch on, access Read Fault
Screen. Record all the fault messages shown on the
DRBII scan tool. Observe the malfunction indicator
lamp (check engine lamp on the instrument panel).
The lamp should light for 3 seconds then go out (bulb
check).
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs used by the powertrain control
module (PCM) have only two recognized states,
HIGH and LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot
recognize the difference between a selected switch po-
sition versus an open circuit, a short circuit, or a de-
fective switch. If the change is displayed, it can be
assumed that the entire switch circuit to the PCM is
functional. From the state display screen access ei-
ther State Display Inputs and Outputs or State Dis-
play Sensors.
STATE DISPLAY INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the State Display screen. Then access Inputs and
Outputs. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Inputs and
Outputs screen. Park/Neutral Switch (automatic transaxle only)
Speed Control Resume
Brake Switch
Speed Control On/Off
Speed Control Set
A/C Switch Sense
S/C (Speed Control) Vent Solenoid
S/C (Speed Control) Vacuum Solenoid
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid (3 speed auto-
matic transaxle)
A/C Clutch Relay
EGR Solenoid
Auto Shutdown Relay
Radiator Fan Relay
Purge Solenoid
Malfunction Indicator (Check Engine) Lamp
STATE DISPLAY SENSORS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the State Display screen. Then access Sensor
Display. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Sensor Dis-
play screen. Oxygen Sensor Signal
Coolant Temperature
Coolant Temp Sensor
Throttle Position
Minimum Throttle
Battery Voltage
MAP Sensor Reading
Idle Air Control Motor Position
Added Adaptive Fuel
Adaptive Fuel Factor
Barometric Pressure
Min Airflow Idl Spd
Engine Speed
Fault #1 Key-On Info
Module Spark Advance
Speed Control Target
Fault #2 Key-On Info
Fault #3 Key-On Info
Speed Control Status
Charging System Goal
Theft Alarm Status
Speed Control Switch Voltage
Map Sensor Voltage
Vehicle Speed
Oxygen Sensor State
MAP Gauge Reading
Throttle Opening (percentage)
Total Spark Advance
CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST MODE
The circuit actuation test mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices which the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) cannot internally rec-
ognize. The PCM can attempt to activate these
outputs and allow an observer to verify proper oper-
ation. Most of the tests provide an audible or visual
indication of device operation (click of relay contacts,
spray fuel, etc.). With the exception of an intermit-
tent condition, if a device functions properly during
its test, it can be assumed that the device, its associ-
ated wiring, and its driver circuit are in working or-
der.
OBTAINING CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the Actuators screen. The following is a list of
the engine control system functions accessible
through Actuators screens. Stop All Tests
Ignition Coil #1
Fuel Injector #1
Idle Air Control Motor Open/Close
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 45