1989 MITSUBISHI GALANT brakes
[x] Cancel search: brakesPage 1 of 1273

BACKUP
Service Manual
GRLRNT
1989-1990-1991-1992-1993
Volume 1
Chassis & Mechanical
FOREWORD
This Service Manual has been prepared with thelatest service information available at the time of
publication. It is subdivided into various group cate-
gories and each section contains diagnostic, dis-
assembly, repair, and installation procedures along
with complete specifications and tightening ref-
erences. Use of this manual will aid in properly per-
forming any servicing necessary to maintain or res-
tore the high levels of performance and reliability
designed into these outstanding vehicles.
This BACKUP DSM manual is to be used DNLY as
a SACKUP. please DIJ NOT REDISTRIBUTEWHOLE SECTIONS. This BACKUP was sold to you under the fact that you do indeed
DWNa GENUINE DSM MANUAL. It CANNOT BE considered a REPLACEMENT (Unless your
original
manual was lost or
destroyed.) Please
See
README.TXT
or
README.HTML
for additional
information.
1kyou.
- Gjmpiemym_ay&?h
@
A
.
.”
WE SUPPORT
VOLUNTARY TECHNICIAN
CERTIFICATION THROUGH
Nallonal lnsrltule forAU~~~v3~;VPCT:VE
EXCELLENCE naiLcorn
MITSUBISHIMOTOR SALES OF AMERICA. Inc.
Mltsublshl Motors Corporat!on reserves the right to make changes indesign or to make additions to or Improvements In Its products
wlthout~mposng any obllgatlons upon Itself to install them on its productspreviously manufactured
0 1992 Mitsubishi Motors CorporationRcprintedinUSA
GROUP INDEXMOOAA-
General.........................................................
Engine...........................................................
Fuel................................................................
Cooling.........................................................
Intake and Exhaust..............................
Emission Control....................................
Clutch............................................................
Manual Transaxle..................................
Automatic Transaxle............................
Propeller Shaft........................................
Front Axle..................................................
Rear Axle....................................................
Wheel and Tire.......................................
Power Plant Mount..............................
Front Suspension...................................
Active-Electronic
Control Suspension..............................m
A
Rear Suspension....................................&
Service Brakes.........................................
Parking Brakes........................................
Alphabetical Index.................................
NOTE: Electrical system Information is contained in
Volume 2 “Electrical” of this paired Service Manual.
For overhaul procedures of engines or transmissions,
refer to the separately issued Engine
Service Manual
or Manual/Automatic Transmission Service Manual.
Page 32 of 1273

00-30GENERAL - Master Troubleshooting
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION Symptom Probable cause Reference page or remedy
1
r-Excessive 011 consumption
Oil leak Repair as necessary.I Valve
stem seal worn or damaged. Repair as necessary.
Valve stem worn. Repair as necessary.
Piston ring worn or damaged. Repair as necessary.
POOR FUEL MILEAGE Symptom
Poor fuel mtleage
Probable cause
Fuel leak
Air cleaner clogged. Ignition system problems.
Fuel injection system problems.
Compression too low.
Tires improperly inflated.
Clutch slips.Brakes drag. Reference page or remedy
Repair as necessary.
-
16-32
13-8, 119, 205
1 l-6
31-3 21-4
35-l 3
NOISE
SymptomNoise Probable cause
Loose bolts and nuts.
Engine noise Reference page or remedy
Retighten as necessary.
Repair as necessary.
HARD STEERING
Symptom
Hard steering Probable cause
Reference page or remedy
Loose power steering oil pump belt
37A-21
Low fluid level Replenish
Air in power steering system
37A-22
Low tire pressure31-3
Excessive turning resistance of lower arm ball33A-11
joint Excessively tightened of steering gear box 37A-33
rack support cover
Improper front wheel alignment
Excessive turning resistance of tie-rod ball
joint
Malfunctioning electronic controlled power
steering system
Sticky flow control valve
Bent rack in steering gear box
J
TSB RevisionI
33A-5
37A-15, 33 37A-9
37A-50,
51 37A-42
Page 728 of 1273

23-22 AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE
- Troubleshooting
Based upon use of the troubleshooting
guide, the probable location of the prob-
lem should be estimated.
Checks should be made of fluid levels
and the condition of the ATF, as well as
1 found to be necessary
.
the condition of the manual control ca-
bles; adjustments should then be made if
If a presumption has been made that
there is an abnormal condition some-
where in the electronic-control system,
check the fault code, in order to determine
the probable location of the problem, by using a scan tool or voltmeter.
When the abnormal system is discovered,
check each element (sensors, etc.) one by
one, and make repairs as necessary.
When the abnormal condition is pre- sumed to be in the oil-pressure-control
When the result of the oil-pressure test does not satisfy the specified pressure,
1 passages for leakage, etc
.
check each system at places related to
the valve body, check the oil-pressure
If the problem is unusually dirty ATF,
abnormal noises, oil leakage, or slippage
L##t he traniaxle.1
of the clutch or brakes or an abnormal
condition of the transaxle Itself,
disassem-
TROUBLESHOOTING
Functional malfunctions of the ELGWT can lead to other
problems,
such
as those described
below:
(1) Improper
maintenance
and/or
adjustments
(2) Malfunctions of the electronic control functions
(3) Malfunctions of mechanical functions
(4) Malfunctions of hydraulic control functions
(5) Malfunctions of engine performance
etc.
In order
to properly
determine (“Troubleshoot”)
the
source
of
these
malfunctions,
it is first essential
to methodically ques-
tion
the
user
concerning
the details
of the problem,
such as
the
condition of
the
problem,
the
situation at
the
time the
problem
occurred,
and any other relevant
information, all in as much detail
as possible.
The user
should
also be asked
whether or not the problem has occurred more than once,
and under
what conditions. Subsequently,
certain
tests should
be conducted in a certain
order,
as described
at
the
left.
1 TSB Revision
Page 732 of 1273
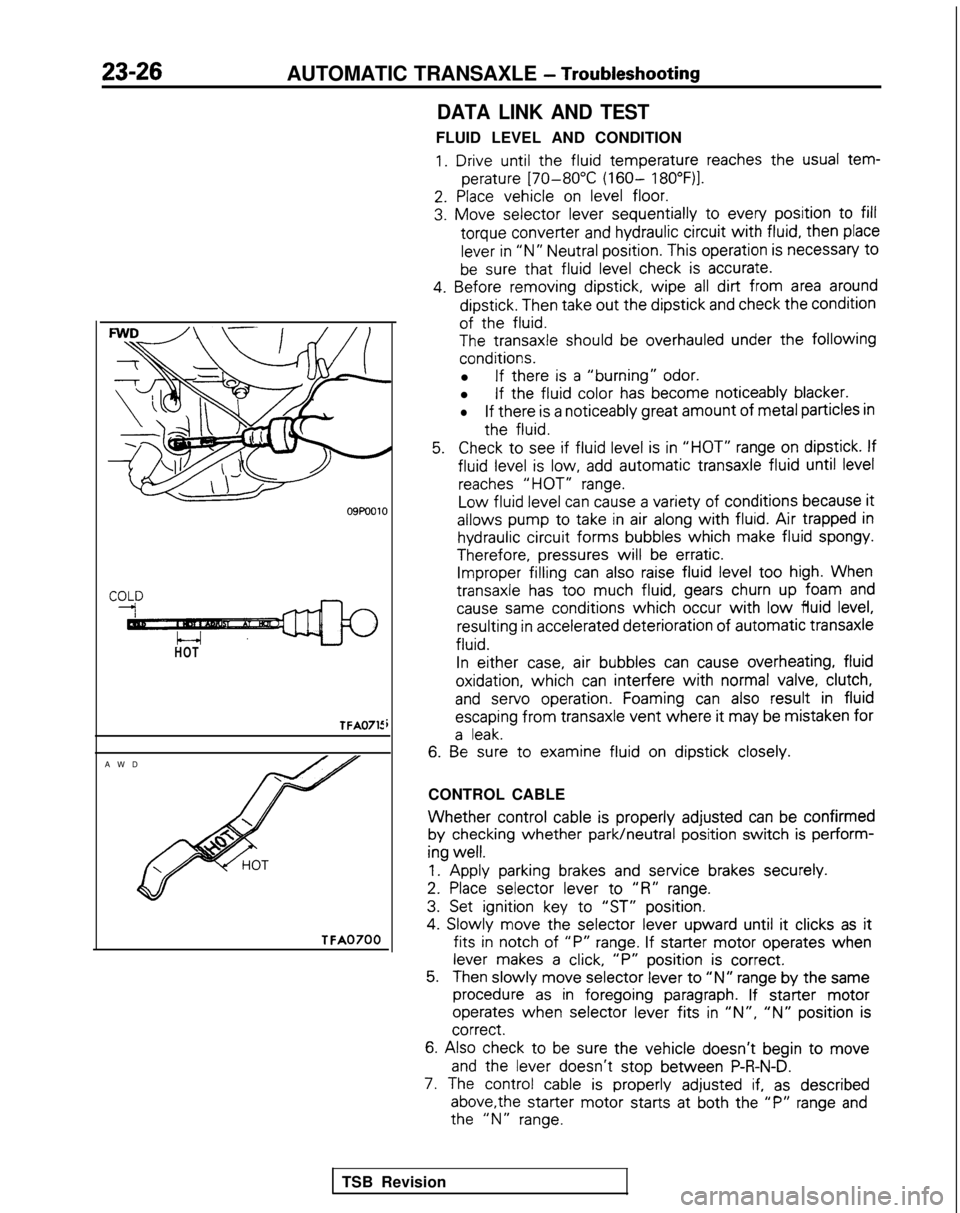
23-26AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Troubleshooting
HOT
TFA0715
AW
D
TFA0700
DATA LINK AND TEST
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
1. Drive until the
fluid
temperature
reaches the
usual tem-
perature
[70-80°C (160- 18O”F)l.
2. Place
vehicle
on level floor.
3. Move
selector
lever sequentially
to
every
position
to fill
torque
converter
and hydraulic circuit
with fluid,
then
place
lever in “N” Neutral position.
This operation is necessary
t0
be sure that fluid
level check is accurate.
4. Before
removing
dipstick,
wipe all dirt from area around
dipstick.
Then take out
the
dipstick
and check the
condition
of the
fluid.
The
transaxle
should be overhauled under the following
conditions.
l If there
is a “burning” odor.
l If the
fluid
color
has become
noticeably
blacker.
lIf there
is a noticeably
great
amount
of metal particles in
the
fluid.
5.Check to
see if fluid
level is in “HOT” range on dipstick.
If
fluid
level is low, add automatic
transaxle
fluid
until level
reaches “HOT” range.
Low
fluid
level can cause a variety of
conditions
because it
allows
pump
to
take
in air along with fluid. Air trapped in
hydraulic circuit
forms
bubbles
which
make fluid
spongy.
Therefore,
pressures
will be erratic. Improper filling
can also raise fluid level too
high. When
transaxle
has too
much fluid,
gears churn up foam and
cause same
conditions
which occur with low fluid
level, resulting
in accelerated deterioration
of
automatic
transaxle
fluid.
In
either
case, air bubbles
can cause overheating,
fluid
oxidation,
which can interfere
with normal valve, clutch,
and
servo
operation.
Foaming can also result
in fluid
escaping
from
transaxle
vent where it
may be mistaken
for
a leak.
6. Be
sure to
examine
fluid
on dipstick
closely.
CONTROL CABLE
Whether control
cable is properly
adjusted
can be confirmed
by
checking
whether park/neutral
position
switch is perform-
ing
well.
1.
Apply
parking brakes and service
brakes securely.
2. Place
selector
lever
to
“R” range.
3. Set ignition
key to
“ST” position.
4.
Slowly
move
the
selector
lever
upward
until it
clicks as it
fits in
notch of “P” range. If starter
motor
operates
when
lever makes a click, “P”
position
is correct.
5.Then slowly
move
selector
lever to “N” range by
the
same
procedure as in foregoing
paragraph. If starter
motor
operates
when selector
lever
fits in ‘IN”, “N” position
is correct.
6.
Also check to be sure the
vehicle
doesn’t
begin to move
and
the
lever
doesn’t
stop
between
P-R-N-D.
7. The control
cable is properly
adjusted if, as described
above,the
starter
motor
starts
at both the
“P” range and the
“N” range.
TSB Revision
Page 757 of 1273
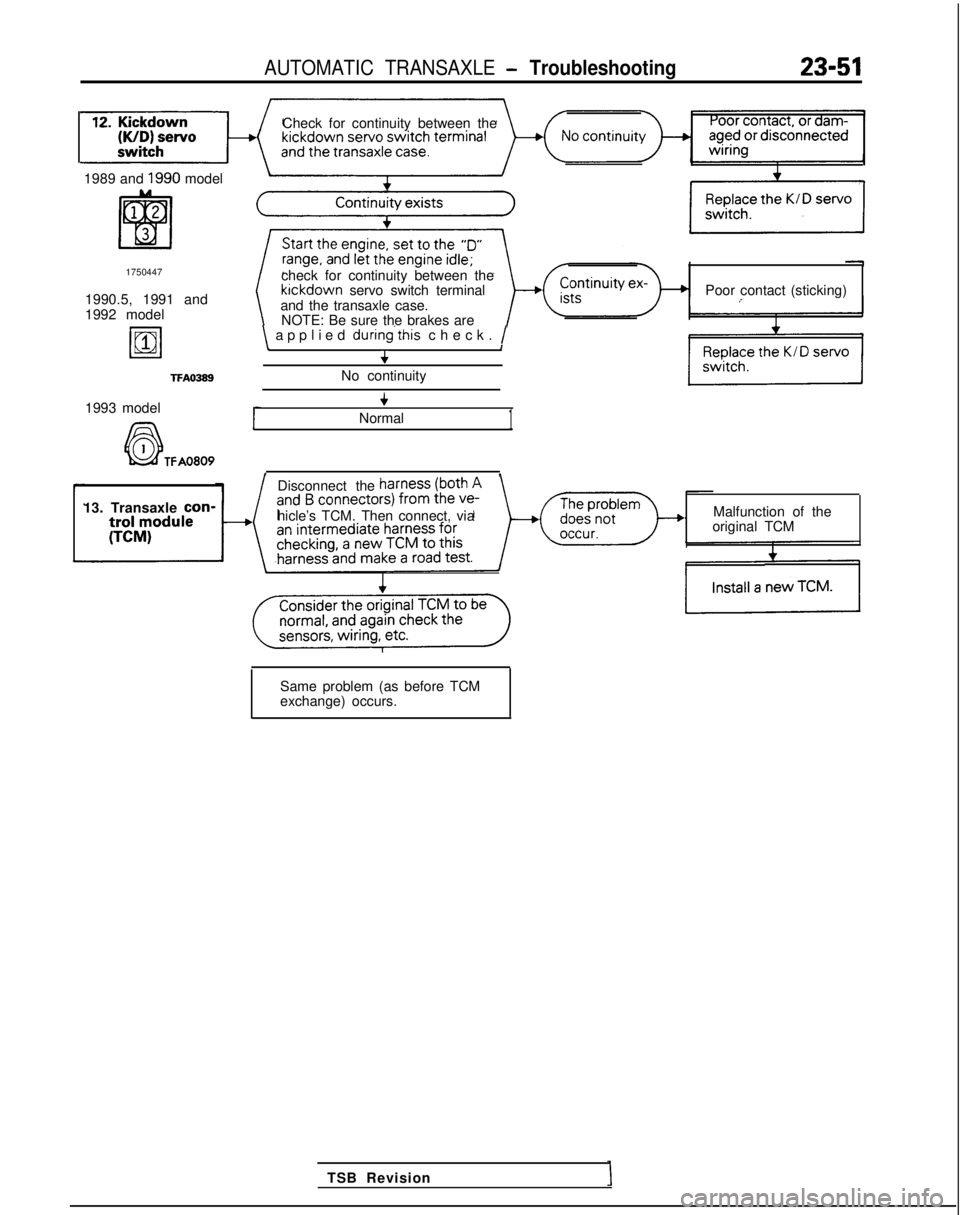
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Troubleshooting23-51
Check for continuity between the
1989 and
1990 model
1750447
1990.5, 1991 and
1992 model
19811
TFAO389
check for continuity between the kickdown
servo switch terminal
and the transaxle case. Poor contact (sticking)
NOTE: Be sure the brakes are
\ applied during’this
check. /\I+
No continuity
1993 model
A6-l
+
Normal1
k&f TFA0809, ,
Disconnect the
13. Transaxle con-
hicle’s TCM. Then connect, via Malfunction of the
original TCM
TSB Revision
Same problem (as before TCM
exchange) occurs.
Page 765 of 1273

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Troubleshooting23-59
ring
brake
CONVERTER STALL TEST
Stall test consist of determining maximum engine
speed obtained at full throttle in “D” and “R”
positions. This test checks torque converter stator
overrunning clutch operation, and holding ability of
transaxle clutches and low-reserve brake.
Caution
During this test, make sure that no one stand in
front of or behind vehicle.
1. Check transaxle fluid level. Fluid should be at
normal operating temperature [70-80°C (160-
18O”F)j. Engine coolant should also be at normal
operating temperature
[80-90°C (180-19O”F)l.
2. Apply chocks to both rear wheels.
3. Attach engine tachometer.
4. Apply parking and service brakes fully.
5. Start engine.
6. With selector lever in “D” position, depress
accelerator pedal fully to read engine maximum
rpm. Do not hold throttle wide open any longer
than is necessary to obtain maximum engine
rpm reading, and never longer than 5 seconds at
a time. If more than one stall test is required,
operate engine at approximatey 1,000 rpm in
TRANSAXLE CONTROL
neutral for 2 minutes to cool transaxle fluid
between tests.
Stall speed: 1,800-3,200
rpm
7.Place selector lever to “R” position and perform
stall test by the same procedure as in foregoing
item.
Stall Speed Above Specification in “D”
If stall speed is higher than specification, rear clutch
or overrunning clutch of transaxle is slipping. In this
case, perform hydraulic test to locate cause of
slippage.
Stall Speed Above Specification in “I?”
If stall speed is higher than specification, front
clutch of transaxle or low-reverse brake is slipping. In this case, perform hydraulic test to locate cause
of slippage.
Stall Speed Below Specification in “D” and “R”
If stall speed is lower than specification, insufficient
engine output or faulty torque converter is sus-
pected. Check for engine misfiring, ignition timing,
valve clearance etc. If these are good, torque
converter is faulty. Svmotom
Probable cause
Remedy
Selector lever operation is Incorrect adjustment of sleeve
1 Adjust
stiff
Starter motor does not oper-
Incorrect adjustment of control cable
Excessive wear of detent plate
Worn contact surfaces of pushbutton and sleeve
Malfunction in park/neutral position switch Replace
Replace
ate with the selector lever in
the
“N” or “P” position Malfunction of starter relayI
Incorrect adjustment of control cable
AdjustI
W
ill not shift to 4-speed
( Malfunction of OD switch) ReplaceI
TSB Revision
Page 788 of 1273
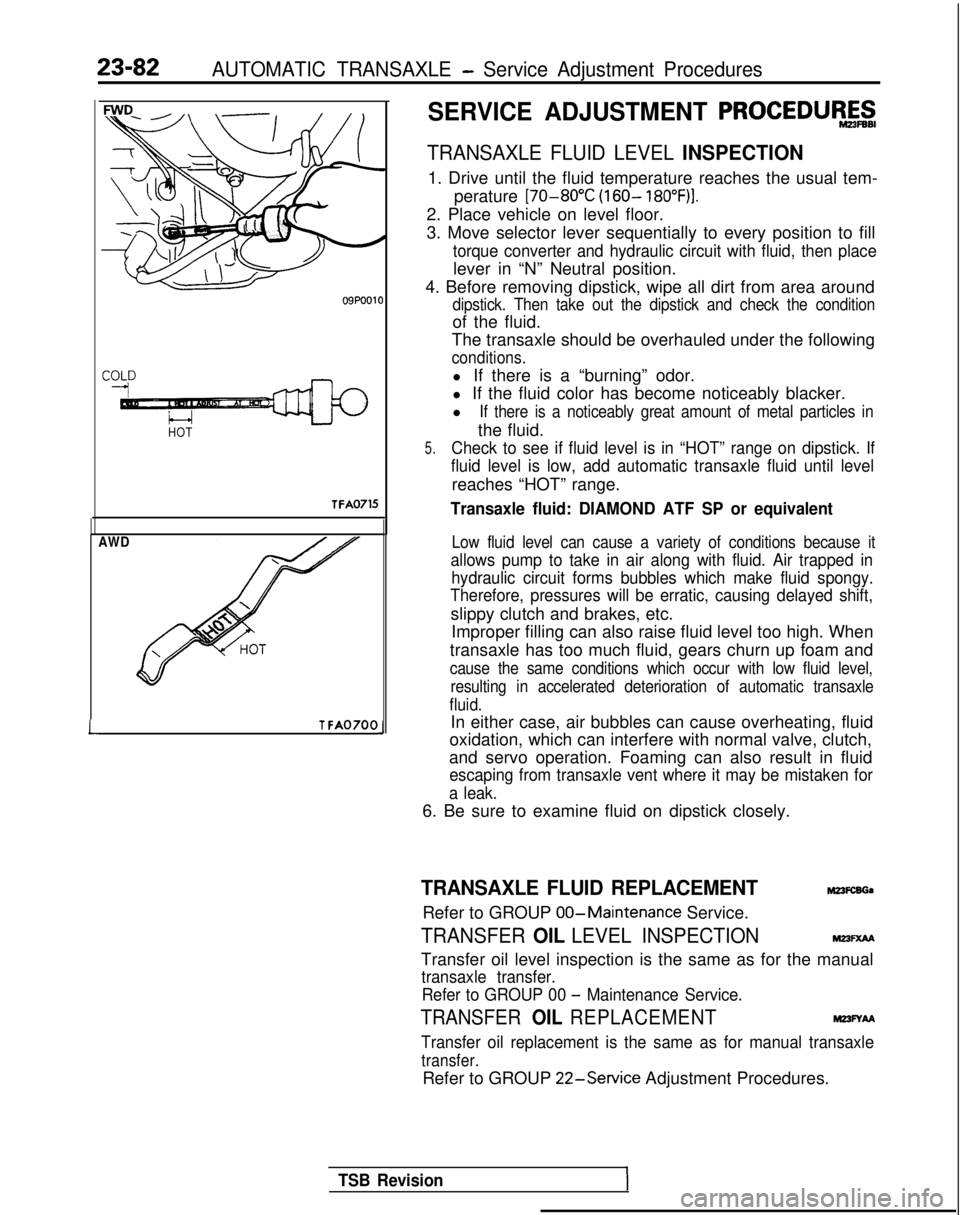
23-82AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE - Service Adjustment Procedures
HOTTFA0715
AWD
LT FA0700J
SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDUR&g
TRANSAXLE FLUID LEVEL INSPECTION
1. Drive until the fluid temperature reaches the usual tem-
perature [70-80°C
(160- 18O”F)I.
2. Place vehicle on level floor.
3. Move selector lever sequentially to every position to fill
torque converter and hydraulic circuit with fluid, then place
lever in “N” Neutral position.
4. Before removing dipstick, wipe all dirt from area around
dipstick. Then take out the dipstick and check the condition
of the fluid.
The transaxle should be overhauled under the following
conditions.
l If there is a “burning” odor.
l If the fluid color has become noticeably blacker.
l
If there is a noticeably great amount of metal particles in
the fluid.
5.Check to see if fluid level is in “HOT” range on dipstick. If
fluid level is low, add automatic transaxle fluid until level
reaches “HOT” range.
Transaxle fluid: DIAMOND ATF SP or equivalent
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions because it
allows pump to take in air along with fluid. Air trapped in hydraulic circuit forms bubbles which make fluid spongy.
Therefore, pressures will be erratic, causing delayed shift,
slippy clutch and brakes, etc.
Improper filling can also raise fluid level too high. When
transaxle has too much fluid, gears churn up foam and
cause the same conditions which occur with low fluid level, resulting in accelerated deterioration of automatic transaxle
fluid.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating, fluid
oxidation, which can interfere with normal valve, clutch,
and servo operation. Foaming can also result in fluid
escaping from transaxle vent where it may be mistaken for
a leak.
6. Be sure to examine fluid on dipstick closely.
TRANSAXLE FLUID REPLACEMENTM23FcsGa
Refer to GROUP 00-Maintenance
Service.
TRANSFER OIL LEVEL INSPECTIONMm=xM
Transfer oil level inspection is the same as for the manual
transaxle transfer.
Refer to GROUP 00
- Maintenance Service.
TRANSFER OIL REPLACEMENTM23FYAA
Transfer oil replacement is the same as for manual transaxle
transfer.
Refer to GROUP 22-Service
Adjustment Procedures.
TSB Revision
Page 837 of 1273
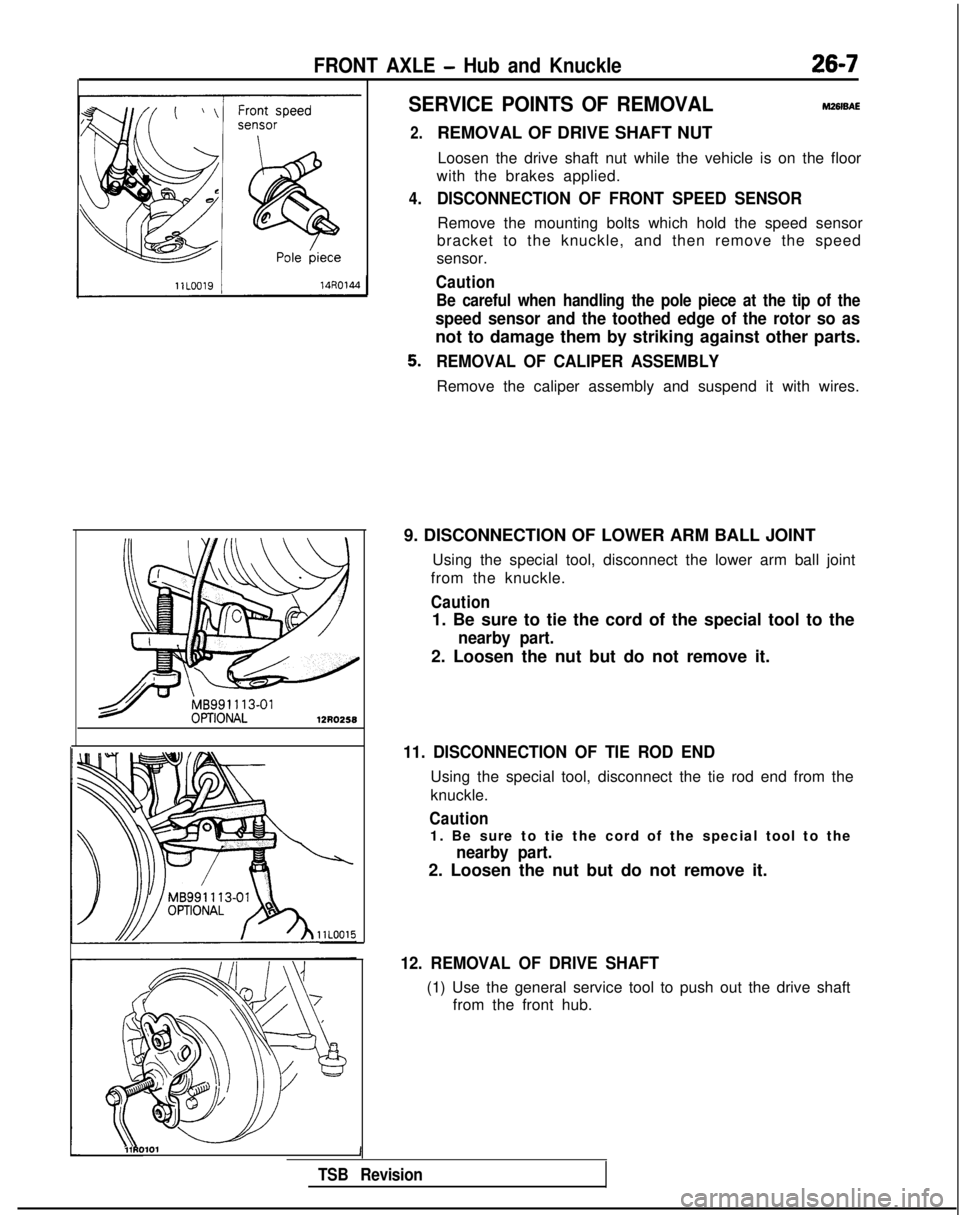
FRONT AXLE - Hub and Knuckle26-7
SERVICE POINTS OF REMOVALM261sAE
2.
4.
REMOVAL OF DRIVE SHAFT NUTLoosen the drive shaft nut while the vehicle is on the floor
with the brakes applied.
DISCONNECTION OF FRONT SPEED SENSOR
Remove the mounting bolts which hold the speed sensor
bracket to the knuckle, and then remove the speed
sensor.
Caution
Be careful when handling the pole piece at the tip of the
speed sensor and the toothed edge of the rotor so as
not to damage them by striking against other parts.
REMOVAL OF CALIPER ASSEMBLY
Remove the caliper assembly and suspend it with wires.
9. DISCONNECTION OF LOWER ARM BALL JOINT Using the special tool, disconnect the lower arm ball joint
from the knuckle.
Caution
1. Be sure to tie the cord of the special tool to the
nearby part.
2. Loosen the nut but do not remove it.
11. DISCONNECTION OF TIE ROD END
Using the special tool, disconnect the tie rod end from the
knuckle.
Caution
1. Be sure to tie the cord of the special tool to the
nearby part.
2. Loosen the nut but do not remove it.
12. REMOVAL OF DRIVE SHAFT
(1) Use the general service tool to push out the drive shaft from the front hub.
l\\11RO101 1
TSB Revision