1989 FORD FIESTA air conditioning
[x] Cancel search: air conditioningPage 87 of 296

12After removal, reassemble the big-end
bearing caps and shells on their respective
connecting rods, and refit the bolts finger-
tight. Leaving the old shells in place until
reassembly will help prevent the bearing
recesses from being accidentally nicked or
gouged. New shells should be used on
reassembly.
Inspection
13 Before the inspection process can begin,
the piston/connecting rod assemblies must
be cleaned, and the original piston rings
removed from the pistons.
14 Carefully expand the old rings over the top
of the pistons. The use of two or three old feeler
blades will be helpful in preventing the rings
dropping into empty grooves (see illustration).
Be careful not to scratch the piston with the
ends of the ring. The rings are brittle, and will
snap if they are spread too far. They are also
very sharp - protect your hands and fingers.
Note that the third ring may incorporate an
expander. Always remove the rings from the top
of the piston. Keep each set of rings with its
piston if the old rings are to be re-used.
15 Scrape away all traces of carbon from the
top of the piston. A hand-held wire brush (or a
piece of fine emery cloth) can be used, once
the majority of the deposits have been
scraped away.
16 Remove the carbon from the ring grooves
in the piston using an old ring. Break the ring
in half to do this (be careful not to cut your
fingers - piston rings are sharp). Be careful to
remove only the carbon deposits - do not
remove any metal, and do not nick or scratch
the sides of the ring grooves.
17 Once the deposits have been removed,
clean the piston/connecting rod assembly
with paraffin or a suitable solvent, and dry
thoroughly. Make sure that the oil return holes
in the ring grooves are clear.
18 If the pistons and cylinder liners/bores are
not damaged or worn excessively, the original
pistons can be refitted. Normal piston wear
shows up as even vertical wear on the piston
thrust surfaces, and slight looseness of the
top ring in its groove. New piston rings should
always be used when the engine is
reassembled. 19
Carefully inspect each piston for cracks
around the skirt, around the gudgeon pin
holes, and at the piston ring “lands” (between
the ring grooves).
20 Look for scoring and scuffing on the
piston skirt, holes in the piston crown, and
burned areas at the edge of the crown. If the
skirt is scored or scuffed, the engine may
have been suffering from overheating, and/or
abnormal combustion which caused
excessively high operating temperatures. The
cooling and lubrication systems should be
checked thoroughly. Scorch marks on the
sides of the pistons show that blow-by has
occurred. A hole in the piston crown, or
burned areas at the edge of the piston crown,
indicates that abnormal combustion (pre-
ignition, knocking, or detonation) has been
occurring. If any of the above problems exist,
the causes must be investigated and
corrected, or the damage will occur again.
The causes may include incorrect ignition
timing, or a carburettor or fuel injection
system fault.
21 Corrosion of the piston, in the form of
pitting, indicates that coolant has been
leaking into the combustion chamber and/or
the crankcase. Again, the cause must be
corrected, or the problem may persist in the
rebuilt engine.
22 Check the piston-to-rod clearance by
twisting the piston and rod in opposite
directions. Any noticeable play indicates
excessive wear, which must be corrected. The
piston/connecting rod assemblies should be
taken to a Ford dealer or engine
reconditioning specialist to have the pistons,
gudgeon pins and rods checked, and new
components fitted as required.
23 Don’t attempt to separate the pistons
from the connecting rods (even if non-genuine
replacements are found elsewhere). This is a
task for a Ford dealer or similar engine
reconditioning specialist, due to the special
heating equipment, press, mandrels and
supports required to do the job. If the
piston/connecting rod assemblies do require
this sort of work, have the connecting rods
checked for bend and twist, since only such
engine repair specialists will have the facilities
for this purpose. 24
Check the connecting rods for cracks and
other damage. Also on CVH engines, check
that the oilway in the base of the connecting
rod is clear by probing with a piece of wire
(see illustration) . Temporarily remove the
big-end bearing caps and the old bearing
shells, wipe clean the rod and cap bearing
recesses, and inspect them for nicks, gouges
and scratches. After checking the rods,
replace the old shells, slip the caps into place,
and tighten the bolts finger-tight.
12 Crankshaft -
removal and inspection
4
Removal
Note: The crankshaft can be removed only
after the engine has been removed from the
vehicle. It is assumed that the transmission,
flywheel/driveplate, timing belt/chain, cylinder
head, sump, oil pump pick-up/strainer, oil
baffle, oil pump, and piston/connecting rod
assemblies, have already been removed. The
crankshaft left-hand oil seal carrier/housing
must be unbolted from the cylinder
block/crankcase before proceeding with
crankshaft removal.
1 Before the crankshaft is removed, check
the endfloat. Mount a DTI (Dial Test Indicator,
or dial gauge) with the stem in line with the
crankshaft and just touching the crankshaft
(see illustration) .
2 Push the crankshaft fully away from the
gauge, and zero it. Next, lever the crankshaft
towards the gauge as far as possible, and
check the reading obtained. The distance that
the crankshaft moved is its endfloat; if it is
greater than specified, check the crankshaft
thrust surfaces for wear. If no wear is evident,
new thrustwashers should correct the
endfloat.
3 If no dial gauge is available, feeler gauges
can be used. Gently lever or push the
crankshaft all the way towards the right-hand
end of the engine. Slip feeler gauges between
the crankshaft and the main bearing
incorporating the thrustwashers to determine
the clearance.
2D•18 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
12.1 Checking crankshaft endfloat with a dial gauge11.24 Check that the connecting rodoilway on CVH engines is clear11.14 Using feeler gauge blades to remove piston rings
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 90 of 296

diameter from the bore measurement. If the
precision measuring tools shown are not
available, the condition of the pistons and
bores can be assessed, though not quite as
accurately, by using feeler gauges as follows.
Select a feeler gauge of thickness equal to the
specified piston-to-bore clearance, and slip it
into the cylinder along with the matching
piston. The piston must be positioned exactly
as it normally would be. The feeler gauge
must be between the piston and cylinder on
one of the thrust faces (at right-angles to the
gudgeon pin bore). The piston should slip
through the cylinder (with the feeler gauge in
place) with moderate pressure; if it falls
through or slides through easily, the clearance
is excessive, and a new piston will be
required. If the piston binds at the lower end
of the cylinder, and is loose toward the top,
the cylinder is tapered. If tight spots are
encountered as the piston/feeler gauge is
rotated in the cylinder, the cylinder is
out-of-round (oval).15 Repeat these procedures for the
remaining pistons and cylinder bores.
16 Compare the results with the
Specifications at the beginning of this
Chapter; if any measurement is beyond the
dimensions specified for that class (check the
piston crown marking to establish the class
of piston fitted), or if any bore measurement is
significantly different from the others
(indicating that the bore is tapered or oval),
the piston or bore is excessively-worn.
17 Worn pistons must be renewed; on some
engines, the pistons are available as Ford
replacement parts only as part of the
complete piston/connecting rod assembly.
See a Ford dealer or engine reconditioning
specialist for advice.
18 If any of the cylinder bores are badly
scuffed or scored, or if they are excessively-
worn, out-of-round or tapered, the usual
course of action would be to have the cylinder
block/crankcase rebored, and to fit new,
oversized, pistons on reassembly. See a Ford
dealer or engine reconditioning specialist for
advice.
19 If the bores are in reasonably good
condition and not excessively-worn, then it
may only be necessary to renew the piston
rings.
20 If this is the case, the bores should be
honed, to allow the new rings to bed in
correctly and provide the best possible seal.
Honing is an operation that will be carried out
for you by an engine reconditioning specialist.
21 After all the machining operations have
been carried out, the entire block/crankcase
must be washed very thoroughly with warm
soapy water to remove all traces of abrasive
grit produced during the machining
operations. When completely clean, rinse it
thoroughly and dry it, then lightly oil all
exposed machined surfaces to prevent
rusting.
22 The cylinder block/crankcase should now
be completely clean and dry, with all components checked for wear or damage,
and repaired or overhauled as necessary.
Refit as many ancillary components as
possible, for safekeeping. If reassembly is not
to start immediately, cover the block with a
large plastic bag to keep it clean.
14 Main and big-end bearings
-
inspection
4
1 Even though the main and big-end bearing
shells should be renewed during the engine
overhaul, the old shells should be retained for
close examination, as they may reveal
valuable information about the condition of
the engine (see illustration) .
2 Bearing failure occurs because of lack of
lubrication, the presence of dirt or other
foreign particles, overloading the engine, and
corrosion. Regardless of the cause of bearing
failure, it must be corrected before the engine
is reassembled, to prevent it from happening
again.
3 When examining the bearing shells, remove
them from the cylinder block/crankcase and
main bearing caps, and from the connecting
rods and the big-end bearing caps, then lay
them out on a clean surface in the same
general position as their location in the
engine. This will enable you to match any
bearing problems with the corresponding
crankshaft journal. Do nottouch any shell’s
bearing surface with your fingers while
checking it, or the delicate surface may be
scratched.
4 Dirt or other foreign matter gets into the
engine in a variety of ways. It may be left in
the engine during assembly, or it may pass
through filters or the crankcase ventilation
system. It may get into the oil, and from there
into the bearings. Metal chips from machining
operations and normal engine wear are often
present. Abrasives are sometimes left in
engine components after reconditioning,
especially when parts are not thoroughly
cleaned using the proper cleaning methods.
Whatever the source, these foreign objects
often end up embedded in the soft bearing
material, and are easily recognised. Large
particles will not embed in the material, and
will score or gouge the shell and journal. The
best prevention for this cause of bearing
failure is to clean all parts thoroughly, and to
keep everything spotlessly-clean during
engine assembly. Frequent and regular engine
oil and filter changes are also recommended.
5 Lack of lubrication (or lubrication
breakdown) has a number of inter-related
causes. Excessive heat (which thins the oil),
overloading (which squeezes the oil from
the bearing face) and oil leakage (from
excessive bearing clearances, worn oil pump
or high engine speeds) all contribute to
lubrication breakdown. Blocked oil passages,
which usually are the result of misaligned oil
holes in a bearing shell, will also starve a bearing of oil, and destroy it. When lack of
lubrication is the cause of bearing failure, the
bearing material is wiped or extruded from the
shell’s steel backing. Temperatures may
increase to the point where the steel backing
turns blue from overheating.
6
Driving habits can have a definite effect on
bearing life. Full-throttle, low-speed operation
(labouring the engine) puts very high loads on
bearings, which tends to squeeze out the oil
film. These loads cause the shells to flex,
which produces fine cracks in the bearing
face (fatigue failure). Eventually, the bearing
material will loosen in pieces, and tear away
from the steel backing.
7 Short-distance driving leads to corrosion of
bearings, because insufficient engine heat is
produced to drive off condensed water and
corrosive gases. These products collect in the
engine oil, forming acid and sludge. As the oil
is carried to the engine bearings, the acid
attacks and corrodes the bearing material.
8 Incorrect shell refitting during engine
assembly will lead to bearing failure as well.
Tight-fitting shells leave insufficient bearing
running clearance, and will result in oil
starvation. Dirt or foreign particles trapped
behind a bearing shell result in high spots on
the bearing, which lead to failure.
9 Do not touch any shell’s bearing surface
with your fingers during reassembly; there is a
risk of scratching the delicate surface, or of
depositing particles of dirt on it.
15 Engine overhaul -
reassembly sequence
1 Before reassembly begins ensure that all
new parts have been obtained and that all
necessary tools are available. Read through
the entire procedure to familiarise yourself with
the work involved, and to ensure that all items
Engine removal and overhaul procedures 2D•21
14.1 Typical bearing failures
2D
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 91 of 296

necessary for reassembly of the engine are at
hand. In addition to all normal tools and
materials, jointing and thread locking
compound will be needed during engine
reassembly. For general-purpose applications,
it is recommended that Loctite 275 setting
sealer or Hylomar PL32M non-setting sealer
be used for joints where required, and
Loctite 270 for stud and bolt thread-locking.
For specific applications on Zetec engines,
Hylosil 102 for the cylinder block/crankcase-
to-sump/oil pump/oil seal carrier joints, and
Loctite 518 for the camshaft right-hand
bearing caps should be used. These are
recommended by, and obtained from, Ford
dealers. In all other cases, provided the
relevant mating surfaces are clean and flat,
new gaskets will be sufficient to ensure joints
are oil-tight. Do notuse any kind of silicone-
based sealant on any part of the fuel system or
inlet manifold, and neveruse exhaust sealants
upstream of the catalytic converter.
2 In order to save time and avoid problems,
engine reassembly can be carried out in the
following order (as applicable).
a) Engine ventilation cap (CVH and PTE engines).
b) Tappets and camshaft (HCS engines).
c) Crankshaft and main bearings.
d) Pistons and connecting rods.
e) Oil pump.
f) Sump.
g) Flywheel/driveplate.
h) Cylinder head.
i) Timing sprockets and chain/belt.
j) Engine external components.
3 Ensure that everything is clean prior to
reassembly. As mentioned previously, dirt and
metal particles can quickly destroy bearings
and result in major engine damage. Use clean
engine oil to lubricate during reassembly.
16 Piston rings - refitting
2
1Before installing new piston rings, check
the end gaps. Lay out each piston set with a
piston/connecting rod assembly, and keep them together as a matched set from now on.
2
Insert the top compression ring into the first
cylinder, and square it up with the cylinder
walls by pushing it in with the top of the
piston. The ring should be near the bottom of
the cylinder, at the lower limit of ring travel.
3 To measure the end gap, slip feeler gauges
between the ends of the ring, until a gauge
equal to the gap width is found. The feeler
gauge should slide between the ring ends
with a slight amount of drag. Compare the
measurement to the value given in the
Specifications in this Chapter; if the gap is
larger or smaller than specified, double-check to make sure you have the correct rings
before proceeding. If you are assessing the
condition of used rings, have the cylinder
bores checked and measured by a Ford
dealer or similar engine reconditioning
specialist, so that you can be sure of exactly
which component is worn, and seek advice as
to the best course of action to take.
4 If the end gap is still too small, it must be
opened up by careful filing of the ring ends
using a fine file. If it is too large, this is not as
serious, unless the specified limit is exceeded,
in which case very careful checking is
required of the dimensions of all components,
as well as of the new parts.
5 Repeat the procedure for each ring that will
be installed in the first cylinder, and for each
ring in the remaining cylinders. Remember to
keep rings, pistons and cylinders matched up.
6 Refit the piston rings as follows. Where the
original rings are being refitted, use the marks
or notes made on removal, to ensure that
each ring is refitted to its original groove and
the same way up. New rings generally have
their top surfaces identified by markings
(often an indication of size, such as “STD”, or
the word “TOP”) - the rings must be fitted with
such markings uppermost (see illustration) .
Note: Always follow the instructions printed
on the ring package or box - different
manufacturers may require different
approaches. Do not mix up the top and
second compression rings, as they usually
have different cross-sections.
7 The oil control ring (lowest one on the
piston) is usually installed first. It is composed
of three separate elements. Slip the
spacer/expander into the groove. If an
anti- rotation tang is used, make sure it is
inserted into the drilled hole in the ring groove.
Next, install the lower side rail. Don’t use a
piston ring installation tool on the oil ring side
rails, as they may be damaged. Instead, place
one end of the side rail into the groove
between the spacer/expander and the ring
land, hold it firmly in place, and slide a finger
around the piston while pushing the rail into
the groove. Next, install the upper side rail in
the same manner.
8 After the three oil ring components have
been installed, check that both the upper and
lower side rails can be turned smoothly in the
ring groove.
9 The second compression (middle) ring is installed next, followed by the top
compression ring - ensure their marks are
uppermost, and be careful not to confuse
them. Don’t expand either ring any more than
necessary to slide it over the top of the piston.
10
On HCS engines, when all of the rings are
fitted to each piston, arrange them so that the
gaps are positioned as described in the
Specifications at the start of this Chapter.
11 On the CVH and PTE engines, when all of
the rings are fitted to each piston, arrange
them so that the gaps are spaced at 120º
intervals, with no gaps positioned above the
gudgeon pin hole.
12 On Zetec engines, when all the rings are
fitted to each piston, space the ring gaps
(including the elements of the oil control ring)
uniformly around the piston at 120º intervals.
17 Crankshaft - refitting and
main bearing running
clearance check
4
1 It is assumed at this point that the cylinder
block/crankcase and crankshaft have been
cleaned, inspected and repaired or
reconditioned as necessary. Position the
engine upside-down.
2 Remove the main bearing cap bolts, and lift
out the caps. Lay the caps out in the proper
order, to ensure correct installation.
3 If they’re still in place, remove the old
bearing shells from the block and the main
bearing caps. Wipe the bearing recesses of
the block and caps with a clean, lint-free
cloth. They must be kept spotlessly-clean!
Main bearing running clearance
check
HCS engines
4 Wipe clean the main bearing shell seats in
the crankcase, and clean the backs of the
bearing shells. Insert the respective upper
shells (dry) into position in the crankcase.
Note that the upper shells have grooves in
them (the lower shells are plain, and have a
wider location lug). Where the old main
bearings are being refitted, ensure that they
are located in their original positions. Make
sure that the tab on each bearing shell fits into
the notch in the block or cap.
Caution: Don’t hammer the shells into
place, and don’t nick or gouge the bearing
faces. No lubrication should be used at
this time.
5 Place the crankshaft thrustwashers into
position in the crankcase, so that their oil
grooves are facing outwards (away from the
central web) (see illustration) .
CVH and PTE engines
6Wipe clean the main bearing shell seats in
the crankcase, and clean the backs of the
bearing shells. Insert the respective upper
shells (dry) into position in the crankcase.
Note that with the exception of the front main
bearing, the upper shells have grooves in
2D•22 Engine removal and overhaul procedures
16.6 Look for etched markings (“STD” -
indicating a standard-sized ring - shown
here) identifying piston ring top surface
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 289 of 296
1595 Ford Fiesta Remake
Glossary of technical termsREF•23
REF
CamshaftA rotating shaft on which a series
of cam lobes operate the valve mechanisms.
The camshaft may be driven by gears, by
spr ockets and chain or by sprockets and a
belt.
Canister A container in an evaporative
emission control system; contains activated
char coal granules to trap vapours from the
fuel system.
Carburettor A device which mixes fuel with
air in the proper proportions to provide a
desir ed power output from a spark ignition
inter nal combustion engine.
Castellated Resembling the parapets along
the top of a castle wall. For example, a
castellated balljoint stud nut.
Castor In wheel alignment, the backward or
forwar d tilt of the steering axis. Castor is
positive when the steering axis is inclined
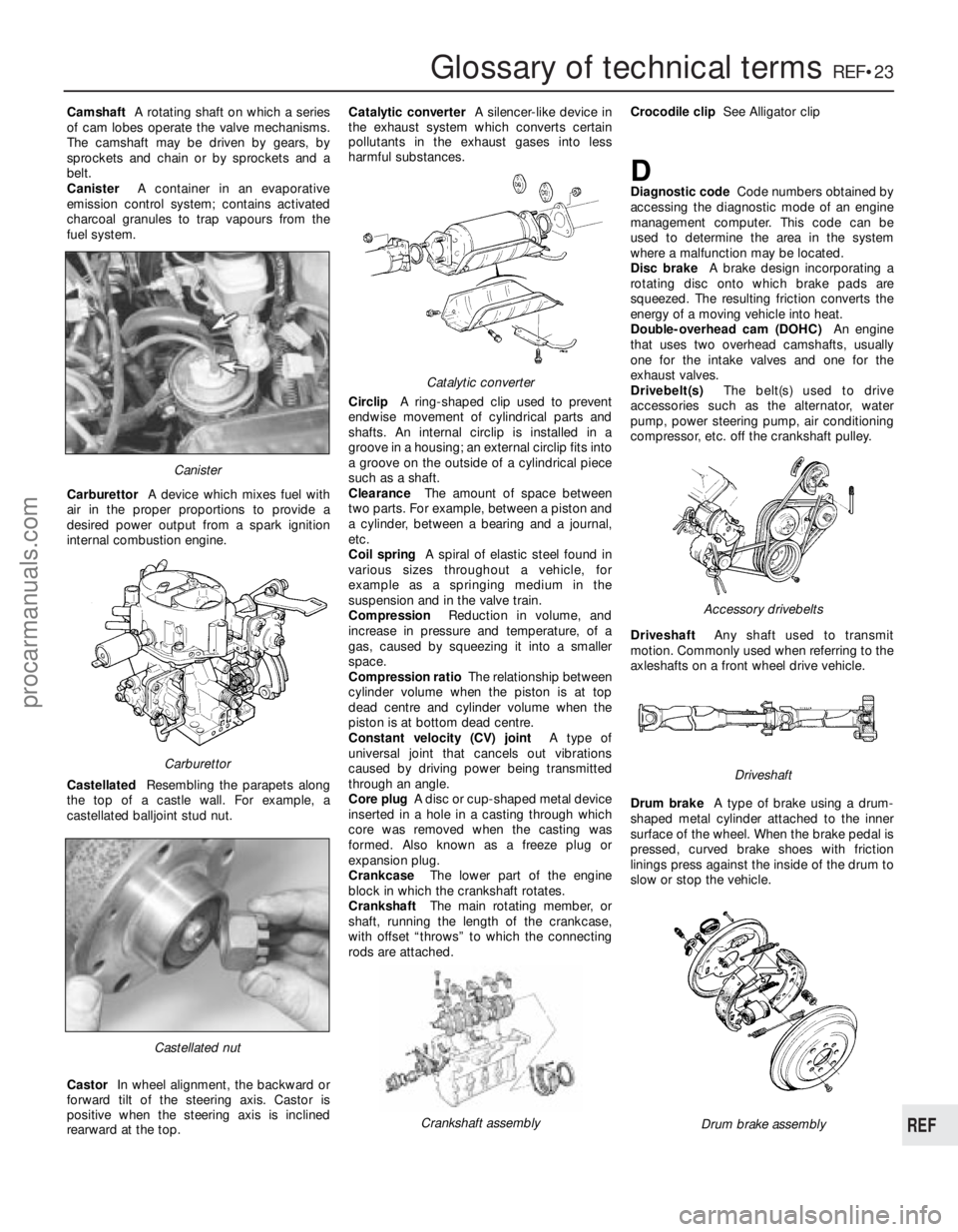
rearwar d at the top. Catalytic converter
A silencer-like device in
the exhaust system which converts certain
pollutants in the exhaust gases into less
harmful substances.
Circlip A ring-shaped clip used to prevent
endwise movement of cylindrical parts and
shafts. An internal circlip is installed in a
gr oove in a housing; an external circlip fits into
a groove on the outside of a cylindrical piece
such as a shaft.
Clearance The amount of space between
two parts. For example, between a piston and
a cylinder, between a bearing and a journal,
etc.
Coil spring A spiral of elastic steel found in
various sizes throughout a vehicle, for
example as a springing medium in the
suspension and in the valve train.
Compression Reduction in volume, and
incr ease in pressure and temperature, of a
gas, caused by squeezing it into a smaller
space.
Compr ession ratio The relationship between
cylinder volume when the piston is at top
dead centre and cylinder volume when the
piston is at bottom dead centre.
Constant velocity (CV) joint A type of
universal joint that cancels out vibrations
caused by driving power being transmitted
thr ough an angle.
Cor e plug A disc or cup-shaped metal device
inserted in a hole in a casting through which
cor e was removed when the casting was
formed. Also known as a freeze plug or
expansion plug.
Crankcase The lower part of the engine
block in which the crankshaft rotates.
Crankshaft The main rotating member, or
shaft, running the length of the crankcase,
with offset “throws” to which the connecting
r ods are attached. Crocodile clip
See Alligator clip
DDiagnostic code Code numbers obtained by
accessing the diagnostic mode of an engine
management computer. This code can be
used to determine the area in the system
wher e a malfunction may be located.
Disc brake A brake design incorporating a
r otating disc onto which brake pads are
squeezed. The resulting friction converts the
ener gy of a moving vehicle into heat.
Double-overhead cam (DOHC) An engine
that uses two overhead camshafts, usually
one for the intake valves and one for the
exhaust valves.
Drivebelt(s) The belt(s) used to drive
accessories such as the alternator, water
pump, power steering pump, air conditioning
compressor , etc. off the crankshaft pulley.
Driveshaft Any shaft used to transmit
motion. Commonly used when referring to the
axleshafts on a front wheel drive vehicle.
Drum brake A type of brake using a drum-
shaped metal cylinder attached to the inner
surface of the wheel. When the brake pedal is
pr essed, curved brake shoes with friction
linings press against the inside of the drum to
slow or stop the vehicle.
Castellated nut
Catalytic converter
Crankshaft assembly
Carburettor
Canister
Drum brake assembly
Accessor y drivebelts
Driveshaft
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 291 of 296

1595 Ford Fiesta Remake
Glossary of technical termsREF•25
REF
JJump startStarting the engine of a vehicle
with a discharged or weak battery by
attaching jump leads from the weak battery to
a charged or helper battery.
LLoad Sensing Proportioning Valve (LSPV) A
brake hydraulic system control valve that
works like a proportioning valve, but also
takes into consideration the amount of weight
carried by the rear axle.
Locknut A nut used to lock an adjustment
nut, or other threaded component, in place.
For example, a locknut is employed to keep
the adjusting nut on the rocker arm in
position.
Lockwasher A form of washer designed to
pr event an attaching nut from working loose.
MMacPherson strut A type of front
suspension system devised by Earle
MacPherson at Ford of England. In its original
form, a simple lateral link with the anti-roll bar
cr eates the lower control arm. A long strut - an
integral coil spring and shock absorber - is
mounted between the body and the steering
knuckle. Many modern so-called MacPherson
strut systems use a conventional lower A-arm
and don’t rely on the anti-roll bar for location. Multimeter An electrical test instrument with
the capability to measure voltage, current and
resistance.
NNOx Oxides of Nitrogen. A common toxic
pollutant emitted by petrol and diesel engines
at higher temperatures.
OOhm The unit of electrical resistance. One
volt applied to a resistance of one ohm will
pr oduce a current of one amp.
Ohmmeter An instrument for measuring
electrical resistance.
O-ring A type of sealing ring made of a
special rubber-like material; in use, the O-ring
is compressed into a groove to provide the
sealing action. Overhead cam (ohc) engine
An engine with
the camshaft(s) located on top of the cylinder
head(s).
Overhead valve (ohv) engine An engine with
the valves located in the cylinder head, but
with the camshaft located in the engine block.
Oxygen sensor A device installed in the
engine exhaust manifold, which senses the
oxygen content in the exhaust and converts
this information into an electric current. Also
called a Lambda sensor.
PPhillips screw A type of screw head having a
cr oss instead of a slot for a corresponding
type of screwdriver.
Plastigage A thin strip of plastic thread,
available in different sizes, used for measuring clearances. For example, a strip of Plastigage
is laid across a bearing journal. The parts areassembled and dismantled; the width of the
crushed strip indicates the clearance between
jour nal and bearing.
Pr opeller shaft The long hollow tube with
universal joints at both ends that carries
power from the transmission to the differential on front-engined rear wheel drive vehicles.
Pr oportioning valve A hydraulic control
valve which limits the amount of pressure to
the rear brakes during panic stops to prevent
wheel lock-up.
RRack-and-pinion steering A steering system
with a pinion gear on the end of the steering
shaft that mates with a rack (think of a geared
wheel opened up and laid flat). When the
steering wheel is turned, the pinion turns,
moving the rack to the left or right. This
movement is transmitted through the track
r ods to the steering arms at the wheels.
Radiator A liquid-to-air heat transfer device
designed to reduce the temperature of the
coolant in an internal combustion engine
cooling system.
Refrigerant Any substance used as a heat
transfer agent in an air-conditioning system.
R-12 has been the principle refrigerant for
many years; recently, however, manufacturers
have begun using R-134a, a non-CFC
substance that is considered less harmful to the ozone in the upper atmosphere.
Rocker arm
A lever arm that rocks on a shaft
or pivots on a stud. In an overhead valve
engine, the rocker arm converts the upward
movement of the pushrod into a downward
movement to open a valve.
Rotor In a distributor, the rotating device
inside the cap that connects the centre
electr ode and the outer terminals as it turns,
distributing the high voltage from the coil
secondary winding to the proper spark plug.
Also, that part of an alternator which rotates
inside the stator. Also, the rotating assembly
of a turbocharger, including the compressor
wheel, shaft and turbine wheel.
Runout The amount of wobble (in-and-out
movement) of a gear or wheel as it’ s rotated.
The amount a shaft rotates “out-of-true.” The
out-of-r ound condition of a rotating part.
SSealant A liquid or paste used to prevent
leakage at a joint. Sometimes used in
conjunction with a gasket.
Sealed beam lamp An older headlight design
which integrates the reflector, lens and
filaments into a hermetically-sealed one-piece
unit. When a filament burns out or the lens
cracks, the entire unit is simply replaced.
Serpentine drivebelt A single, long, wide
accessory drivebelt that’s used on some
newer vehicles to drive all the accessories,
instead of a series of smaller, shorter belts.
Serpentine drivebelts are usually tensioned by
an automatic tensioner.
Shim Thin spacer, commonly used to adjust
the clearance or relative positions between
two parts. For example, shims inserted into or
under bucket tappets control valve
clearances. Clearance is adjusted by
changing the thickness of the shim.
Slide hammer A special puller that screws
into or hooks onto a component such as a
shaft or bearing; a heavy sliding handle on the
shaft bottoms against the end of the shaft to
knock the component free.
Sprocket A tooth or projection on the
periphery of a wheel, shaped to engage with a
chain or drivebelt. Commonly used to refer to
the sprocket wheel itself.
Starter inhibitor switch On vehicles with an
O-ring
Serpentine drivebelt
Plastigage
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su