1988 OPEL CALIBRA check engine light
[x] Cancel search: check engine lightPage 213 of 525

32Release the securing clips and remove the
main outer timing belt cover, then unclip the
smaller outer timing belt cover from the
coolant pump.
33Turn the crankshaft through at least
quarter of a turn clockwise using a socket or
spanner on the crankshaft sprocket bolt.
34If the special gauge is available, place the
locked gauge at the centre of the belt run
between the coolant pump and the camshaft
sprocket. The gauge should locate on the
timing belt (see illustration).
35Slowly release the operating lever on the
gauge, then lightly tap the gauge two or three
times, and note the reading on the scale (see
illustration).
36If the reading is not as specified, loosen
the three coolant pump securing bolts, and
rotate the pump in the required direction to
achieve the desired reading on the gauge.
Rotate the pump clockwise to increase the
belt tension, or anti-clockwise to decrease the
tension.
37Lightly tighten the coolant pump securing
bolts.
38Remove the tensioning gauge, and turn
the crankshaft through one full turn clockwise.
39Re-check the belt tension as described in
paragraphs 4 and 5.
40If the tension is not as specified, repeat
paragraphs 6 to 9 inclusive until the desired,
consistent, reading is obtained.
41On completion of adjustment, remove the
checking gauge, tighten the coolant pump
bolts to the specified torque, and refit the
outer timing belt covers.
42If the special checking gauge is not
available, the timing belt tension can be
checked approximately by twisting the belt
between the thumb and forefinger, at the
centre of the run between the coolant pump
and the camshaft sprocket. It should just be
possible to twist the belt through 90°using
moderate pressure (see illustration). If
adjustment is necessary, continue as
described previously in this Section, but have
the belt tension checked by a Vauxhall dealer
using the special gauge at the earliest
opportunity. If in doubt, err on the tight side
when adjusting the tension, as if the belt is too
slack, it may jump on the sprockets, which
could result in serious engine damage.12Timing belt and tensioner 1.4
and 1.6 models (not C16 NZ2) -
removal, refitting and adjustment
3
Removal
1Remove the timing belt outer covers as
described in Section 11, paragraphs 1 to 5.
2To lock the tensioner in its slackest position
for removal and refitting, move the tensioner
indicator arm clockwise until the holes align in
the baseplate and the arm. Then insert a
close-fitting pin, such as a drift, to retain them
(see illustration). The tensioner can then be
unbolted, or the belt can be removed.
3Check that the tensioner roller rotates
smoothly and easily, with no noises or signs
of free play, roughness or notchy movement.
Check also that there is no sign of physical
wear or damage. If the tensioner is faulty in
any way, or if there is any reason to doubt the
continued efficiency of its spring, the
complete assembly must be renewed.
Refitting
4On refitting, ensure that the tensioner
baseplate lug engages with the hole in the oil
pump housing, then tighten the tensioner bolt
securely and remove the locking pin; the
tensioner should be quite free to move.
5Set the belt tension as described below.
Adjustment
6Whenever the timing belt is disturbed,
whether during belt renewal or any otherengine overhaul work, its tension must be set
on assembly - note that this procedure must
only be carried out on a cold engine.
7It is assumed that the belt has been
removed and refitted, i.e. that the crankshaft
pulley and timing belt outer covers are
removed, that the tensioner is unlocked (see
above) and that No 1 cylinder is in its firing
position (just before TDC on the compression
stroke). Temporarily refit the crankshaft pulley
bolt and remove the spark plugs so that the
crankshaft can be rotated easily.
8Note also that turning the coolant pump
with the precision required is a great deal
easier if a special spanner (Kent-Moore Part
No KM-421-A) is used. Alternatives are
available from manufacturers such as
Sykes-Pickavant (Part No 031300) (see
illustration).
9With the belt refitted and correctly routed
(see Section 11), ensure that the punch mark
on the crankshaft sprocket and the stamped
line on the camshaft sprocket are aligned with
their respective timing belt rear cover notches
(see illustrations).
10Tighten the belt by slackening its three
securing bolts, and turning the coolant pump
clockwise until the holes align in the tensioner
indicator arm and baseplate (the tensioner
indicator arm will then have moved fully
clockwise to its stop). Lightly tighten the
pump securing bolts, just sufficiently to
prevent the pump from moving.
11Using a spanner applied to the crankshaft
pulley bolt, turn the crankshaft smoothly
2A•16SOHC engine procedures
11.34 Tension blade KM-510-A correctly
positioned on timing belt. Belt must pass
through points A, B and C - SOHC engines11.42 Checking timing belt tension by
twisting belt through 90º between thumb
and forefinger
12.8 Using a special spanner to adjust the
timing belt by moving the coolant pump12.2 Using a close-fitting drift to lock the
tensioner. Note baseplate lug engaged in
oil pump housing (arrowed)
11.35 Note the reading on the scale of the
tension gauge -
1.6 litre engine
Page 214 of 525
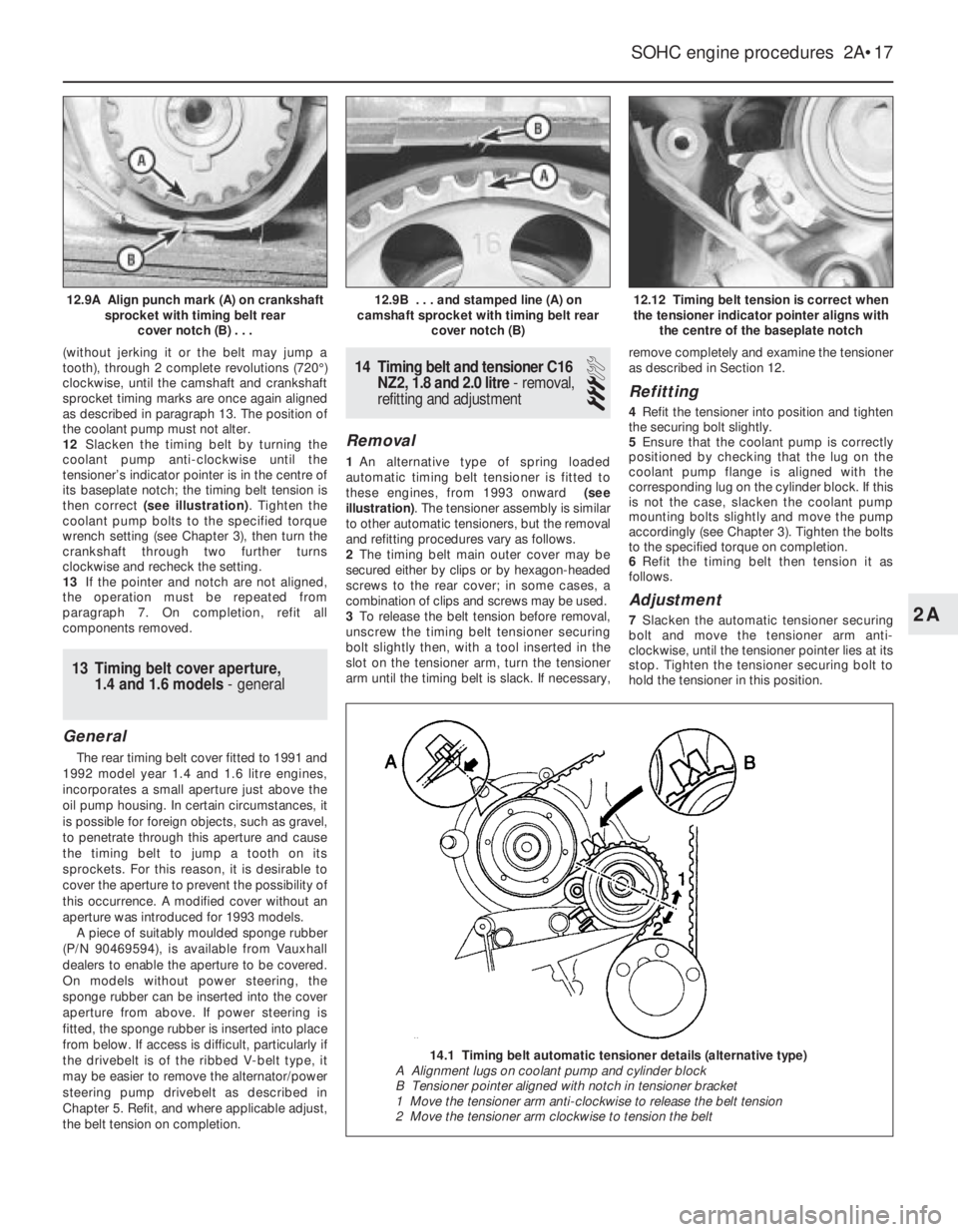
(without jerking it or the belt may jump a
tooth), through 2 complete revolutions (720°)
clockwise, until the camshaft and crankshaft
sprocket timing marks are once again aligned
as described in paragraph 13. The position of
the coolant pump must not alter.
12Slacken the timing belt by turning the
coolant pump anti-clockwise until the
tensioner’s indicator pointer is in the centre of
its baseplate notch; the timing belt tension is
then correct (see illustration). Tighten the
coolant pump bolts to the specified torque
wrench setting (see Chapter 3), then turn the
crankshaft through two further turns
clockwise and recheck the setting.
13If the pointer and notch are not aligned,
the operation must be repeated from
paragraph 7. On completion, refit all
components removed.
13Timing belt cover aperture,
1.4 and 1.6 models - general
General
The rear timing belt cover fitted to 1991 and
1992 model year 1.4 and 1.6 litre engines,
incorporates a small aperture just above the
oil pump housing. In certain circumstances, it
is possible for foreign objects, such as gravel,
to penetrate through this aperture and cause
the timing belt to jump a tooth on its
sprockets. For this reason, it is desirable to
cover the aperture to prevent the possibility of
this occurrence. A modified cover without an
aperture was introduced for 1993 models.
A piece of suitably moulded sponge rubber
(P/N 90469594), is available from Vauxhall
dealers to enable the aperture to be covered.
On models without power steering, the
sponge rubber can be inserted into the cover
aperture from above. If power steering is
fitted, the sponge rubber is inserted into place
from below. If access is difficult, particularly if
the drivebelt is of the ribbed V-belt type, it
may be easier to remove the alternator/power
steering pump drivebelt as described in
Chapter 5. Refit, and where applicable adjust,
the belt tension on completion.
14Timing belt and tensioner C16
NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre - removal,
refitting and adjustment
3
Removal
1An alternative type of spring loaded
automatic timing belt tensioner is fitted to
these engines, from 1993 onward (see
illustration). The tensioner assembly is similar
to other automatic tensioners, but the removal
and refitting procedures vary as follows.
2The timing belt main outer cover may be
secured either by clips or by hexagon-headed
screws to the rear cover; in some cases, a
combination of clips and screws may be used.
3To release the belt tension before removal,
unscrew the timing belt tensioner securing
bolt slightly then, with a tool inserted in the
slot on the tensioner arm, turn the tensioner
arm until the timing belt is slack. If necessary,remove completely and examine the tensioner
as described in Section 12.
Refitting
4Refit the tensioner into position and tighten
the securing bolt slightly.
5Ensure that the coolant pump is correctly
positioned by checking that the lug on the
coolant pump flange is aligned with the
corresponding lug on the cylinder block. If this
is not the case, slacken the coolant pump
mounting bolts slightly and move the pump
accordingly (see Chapter 3). Tighten the bolts
to the specified torque on completion.
6Refit the timing belt then tension it as
follows.
Adjustment
7Slacken the automatic tensioner securing
bolt and move the tensioner arm anti-
clockwise, until the tensioner pointer lies at its
stop. Tighten the tensioner securing bolt to
hold the tensioner in this position.
SOHC engine procedures 2A•17
12.12 Timing belt tension is correct when
the tensioner indicator pointer aligns with
the centre of the baseplate notch12.9B . . . and stamped line (A) on
camshaft sprocket with timing belt rear
cover notch (B)12.9A Align punch mark (A) on crankshaft
sprocket with timing belt rear
cover notch (B) . . .
2A
14.1 Timing belt automatic tensioner details (alternative type)
A Alignment lugs on coolant pump and cylinder block
B Tensioner pointer aligned with notch in tensioner bracket
1 Move the tensioner arm anti-clockwise to release the belt tension
2 Move the tensioner arm clockwise to tension the belt
Page 219 of 525

40Refit the camshaft sprocket and the
timing belt and tension the timing belt as
described in Section 11.
41Where applicable, refit the manifolds to
the cylinder head, with reference to Chapter
4A, 4B or 4C, using new gaskets.
42Reconnect the exhaust downpipe to the
manifold, using a new gasket, referring to
Chapter 4C, if necessary.
43Refit the upper alternator mounting to the
inlet manifold, then adjust the alternator
drivebelt tension, as described in Chapter 5.
44Refill the cooling system, as described in
Chapter 3.
45On completion, check that all relevant
hoses, pipes and wires, etc., have been
reconnected.
46When the engine is started, check for
signs of leaks.
47Once the engine has reached normal
operating temperature, check and if
necessary adjust the idle speed (where
applicable) and the mixture (where
applicable), with reference to Chapter 4A or
4B.
21Cylinder head - removal and
refitting (engine removed)
4
Note: New cylinder head bolts and a new
cylinder head gasket must be used on
refitting, and sealer will be required when
refitting the camshaft housing.
The torque settings stated are only applicable
to latest specification head bolts, available
from Vauxhall. Earlier type or alternative make,
head bolts may require different torques.
Consult your supplier.
Removal
1The cylinder head can be removed
complete with the manifolds, or the manifolds
can be detached from the cylinder head
before removal, with reference Chapter 4A,
4B or 4C.
2Remove the timing belt and the camshaft
sprocket, as described in Section 11.
3Unscrew the two upper rear timing belt
cover securing bolts from the camshaft
housing (see illustration).4Disconnect the HT leads from the spark
plugs, labelling them if necessary to aid
refitting, and remove the distributor cap
referring to Chapter 5.
5If not already done, disconnect the stub
hose that connects the crankcase breather
tube to the camshaft housing. If applicable,
unscrew the bolt securing the crankcase
breather tube bracket to the end of the
cylinder head.
6Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected.
Refitting
7Proceed as described in Section 21,
paragraphs 23 to 41 inclusive, but in addition
note the following.
8On completion check that all relevant
hoses, pipes and wires, etc., have been
reconnected.
22Cylinder head -dismantling
and reassembly
4
Note: A valve spring compressor tool will be
required for this operation. New valve stem oil
seals must be used on reassembly
Dismantling
1With the cylinder head removed as
described in Section 21, clean away all
external dirt.
2If not already done, remove the thermostat
housing, and on 1.4 and 1.6 litre models, thethermostat, as described in Chapter 3.
Remove the manifolds as described in
Chapter 4A, 4B or 4C. Remove the spark
plugs if not already done.
3To remove a valve, fit a valve spring
compressor tool. Ensure that the arms of the
compressor tool are securely positioned on
the head of the valve and the spring cap (see
illustration).
4Compress the valve spring to relieve the
pressure of the spring cap acting on the
collets. If the spring cap sticks on the valve
stem, support the compressor tool and give
the end a light tap with a hammer to help free
the spring cap.
5Extract the two split collets, then slowly
release the compressor tool.
6Remove the spring cap, spring, valve stem
oil seal, and the spring seat, then withdraw
the valve.
2A•22SOHC engine procedures
20.36 Fit new cylinder head bolts, ensuring
that the washers are in place20.37B Tighten the cylinder head bolts to
the specified torque . . .
22.3 Valve spring compressor tool fitted to
No 1 exhaust valve - 2.0 litre engine21.3 Upper rear timing belt cover securing
bolts (arrowed) - 1.6 litre engine
20.37C . . .then through the specified
angle - 2.0 litre engine
20.37A Cylinder head bolt tightening
sequence - SOHC engines
Page 221 of 525

23Cylinder head - inspection
and renovation
4
Note: Refer to a dealer for advice before
attempting to carry out valve grinding or valve
seat reciting operations, as these operations
may not be possible for the DIY mechanic.
This is due to the fitment of hardened valve
seats for use with unleaded petrol
Inspection
1Remember that the cylinder head is of light
alloy construction and is easily damaged, use
a blunt scraper or rotary wire brush to clean all
traces of carbon deposits from the
combustion spaces and the ports. The valve
stems and valve guides should also be freed
from any carbon deposits. Wash the
combustion spaces and ports down with
paraffin and scrape the cylinder head surface
free of any foreign matter with the side of a
steel rule, or a similar article.
2If the engine is installed in the car, clean the
pistons and the top of the cylinder bores. If
the pistons are still in the block, it is essential
that great care is taken to ensure that no
carbon gets into the cylinder bores. This could
scratch the cylinder walls or cause damage to
the pistons and rings. To ensure this does not
happen, first turn the crankshaft so that two of
the pistons are at the top of their bores. Insert
rag into the other two bores or seal them off
with paper and masking tape. The waterways
should also be covered with small pieces of
masking tape, to prevent particles of carbon
entering the cooling system and damaging the
coolant pump.
3Press a little grease into the gap between
the cylinder walls and the two pistons that are
to be worked on. With a blunt scraper,
carefully scrape away the carbon from the
piston crown, taking great care not to scratch
the aluminium. Also scrape away the carbon
from the surrounding lip of the cylinder wall.
When all carbon has been removed, scrape
away the grease that will now be
contaminated with carbon particles, taking
care not to press any into the bores. To assist
prevention of carbon build-up, the piston
crown can be polished with a metal polish.
Remove the rags or masking tape from the
other two cylinders, and turn the crankshaft
so that the two pistons that were at thebottom are now at the top. Place rag or
masking tape in the cylinders that have been
decarbonised, and continue as just described.
4Examine the heads of the valves for pitting
and burning, especially the heads of the
exhaust valves. The valve seatings should be
examined at the same time. If the pitting on
the valve and seat is very slight, the marks
can be removed by grinding the seats and
valves together with coarse, and then fine,
valve grinding paste.
5Where bad pitting has occurred to the valve
seats, it will be necessary to recut them and fit
new valves. This latter job should be entrusted
to the local dealer or engineering works. In
practice it is very seldom that the seats are so
badly worn. Normally it is the valve that is too
badly worn for refitting, and the owner can
easily buy a new set of valves and match
them to the seats by valve grinding.
Renovation
6Valve grinding is carried out as follows.
Smear a trace of coarse carborundum paste
on the seat face and apply a suction grinder
tool to the valve head. With a semi-rotary
motion, grind the valve head to its seat, lifting
the valve occasionally to redistribute the
grinding paste. When a dull matt even surface
is produced on both the valve seat and the
valve, wipe off the paste and repeat the
process with fine carborundum paste, lifting
and turning the valve to redistribute the paste
as before. A light spring placed under the
valve head will greatly ease this operation.
When a smooth unbroken ring of light grey
matt finish is produced, on both valve and
valve seat faces, the grinding operation is
complete. Carefully clean away every trace of
grinding compound, taking great care to leave
none in the ports or in the valve guides. Clean
the valves and valve seats with a
paraffin-soaked rag, then with a clean rag,
and finally, if an air line is available, blow the
valves, valve guides and valve ports clean.
7Check that all valve springs are intact. If any
one is broken, all should be renewed. Check
the free height of the springs against new
ones. If some springs are not long enough,
replace them all. Springs suffer from fatigue
and it is a good idea to renew them even if
they look serviceable. 8The cylinder head can be checked for
warping either by placing it on a piece of plate
glass or using a straight-edge and feeler
blades. If there is any doubt or if its block face
is corroded, have it re-faced by your dealer or
motor engineering works.
9On 1.8 and 2.0 litre, always renew the
sealing ring between the cylinder head and
the thermostat housing when the head is
removed for overhaul (see illustration).
Reference to Chapter 21 will show that a
considerable amount of work is involved if it is
wished to renew the sealing ring with the
cylinder head installed.
10If the oil pressure regulating valve in the
cylinder head is to be renewed, access is
gained through the circular plug covering the
end of the valve (see illustration). The old
valve must be crushed, then its remains
extracted, and a thread (M10) cut in the valve
seat to allow removal using a bolt. A new
valve and plug can then be driven into
position. In view of the intricacies of this
operation, it is probably best to have the valve
renewed by a Vauxhall dealer if necessary.
24Hydraulic valve lifters -
inspection
4
Inspection
1On engines that have covered a high
mileage, or for which the service history
(particularly oil changes) is suspect, it is
possible for the valve lifters to suffer internal
contamination. In extreme cases this may
result in increased engine top end noise and
wear. To minimise the possibility of problems
occurring later in the life of the engine, it is
advisable to dismantle and clean the hydraulic
valve lifters as follows whenever the cylinder
head is overhauled. Note that no spare parts
are available for the valve lifters, and if any of
the components are unserviceable, the
complete assembly must be renewed (see
illustration).
2With the cylinder head removed and
dismantled as described in Sections 21 and
23, first inspect the valve lifter bores in the
2A•24SOHC engine procedures
23.10 Oil pressure regulating valve (1) and
plug (2) - 2.0 litre engine23.9 Renewing the thermostat housing
sealing ring - 2.0 litre engine
Warning: The exhaust valves
fitted to 20 XEJ and C 20 XE
(DOHC) models are fitted with
sodium to improve their heat
transfer. Sodium is a highly reactive
metal, which will ignite or explode
spontaneously on contact with water
(including water vapour in the air). These
must NOT be disposed of with ordinary
scrap. Seek advice from a Vauxhall dealer
or your Local Authority, if the valves are to
be disposed of.
Page 223 of 525

25Flywheel -removal, inspection
and refitting
4
Note: New flywheel securing bolts must he
used on refitting. Certain models are fitted
with a ‘Pot type’ flywheel. Although, it has a
deeply recessed surface for the clutch disc,
the operations below are the same.
Removal
1If not already done, remove the clutch,
(Chapter 6), and the starter motor, (Chapter 5).
2If the engine is in the vehicle, remove the
clutch release bearing and its guide sleeve, as
described in Chapter 6.
3Although the flywheel bolt holes are offset
so that the flywheel can only be fitted in one
position, it will make refitting easier if
alignment marks are made between the
flywheel and the end of the crankshaft.
4Prevent the flywheel from turning by
jamming the ring gear teeth using a large
screwdriver or similar tool. Access is most
easily obtained through the starter motor
aperture if the engine is in the vehicle.
5Unscrew the securing bolts, and remove
the flywheel (see illustration). Take care, as
the flywheel is heavy!
Inspection
6With the flywheel removed, it can be
inspected as follows.
7If the teeth on the flywheel starter ring are
badly worn, or if some are missing, then it will
be necessary to remove the ring and fit a new
one.
8The old ring can be split with a cold chisel,
after making a cut with a hacksaw blade
between two gear teeth. Take great care not
to damage the flywheel during this operation,
and use eye protectors always. Once the ring
has been split, it will spread apart and can be
lifted from the flywheel.
9The new ring gear must be heated to 180 to
230°C (356 to 446°F) and unless facilities for
heating by oven or flame are available, leave
the fitting to a dealer or motor engineering
works. The new ring gear must not be
overheated during this work, or the temper of
the metal will be altered.10The ring should be tapped gently down
onto its register, and left to cool naturally -the
contraction of the metal on cooling will ensure
that it is a secure and permanent fit.
11If the clutch friction disc contact surface
of the flywheel is scored, or on close
inspection, show’s evidence of small hairline
cracks (caused by overheating), it may be
possible to have the flywheel surface ground.
This is provided that the overall thickness of
the flywheel is not reduced too much. Consult
a specialist engine repairer and if it is not
possible, renew the flywheel complete.
Refitting
12Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
13Align the previously made marks on the
flywheel and crankshaft, and fit new flywheel
securing bolts. Tighten them to the specified
torque in the two stages given in the Specifi-
cations, whilst preventing the flywheel from
turning, as during removal (see illustrations).
14Where applicable, refit the clutch release
bearing, guide sleeve, and the clutch, as
described in Chapter 6.
26Flexplate (automatic
transmission) -removal and
refitting
4
Removal
1Remove the transmission (Chapter 7B).
2Prevent the flexplate from turning by
jamming its ring gear teeth using a large
screwdriver or similar tool.
3Unbolt and remove the flexplate. Examine
the bolts and renew them all as a set if there is
the slightest doubt about their condition.
4The ring gear can be checked, and renewed
if necessary, as described in Section 25.
Refitting
5Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. If the bolts are to be re-used, use a
wire brush to clean their threads, apply a few
drops of thread-locking compound (Vauxhall
Part No 90167347, or equivalent) to the
threads of each bolt on refitting. Tighten the
bolts to the specified torque wrench setting.6Refit the transmission, refer to Chapter 7B if
necessary.
27Crankshaft front oil seal -
renewal
3
Renewal
1Remove the timing belt and the rear timing
belt cover, as described in Section 11.
2Ensure that the Woodruff key is removed
from the end of the crankshaft.
3Punch or drill a small hole in the centre of
the now-exposed oil seal. Screw in a
self-tapping screw, and pull on the screw with
pliers to extract the seal. Several attempts
may be necessary. Be careful not to damage
the sealing face of the crankshaft.
4Clean the oil seal seat with a wooden or
plastic scraper.
5Before fitting the new oil seal, steps must
be taken to protect the oil seal lips from
damage, and from turning back on the
shoulder at the front end of the crankshaft.
Grease the seal lips, and then wind tape
around the end of the crankshaft to form a
gentle taper.
6Tap the seal into position using a large
socket or tube, until the seal is flush with the
outer face of the oil pump housing.
7Refit the rear timing belt cover and the
timing belt tension the timing belt as
described in Section 11.
2A•26SOHC engine procedures
25.13C . . .and then through the
specified angle -
1.6 litre engine25.13B Tighten the flywheel securing bolts
to the specified toque . . .25.13A Tool for locking flywheel fitted to
engine-to-transmission bolt hole -
1.6 litre engine
25.5 Removing the flywheel -
1.6 litre engine
Page 229 of 525
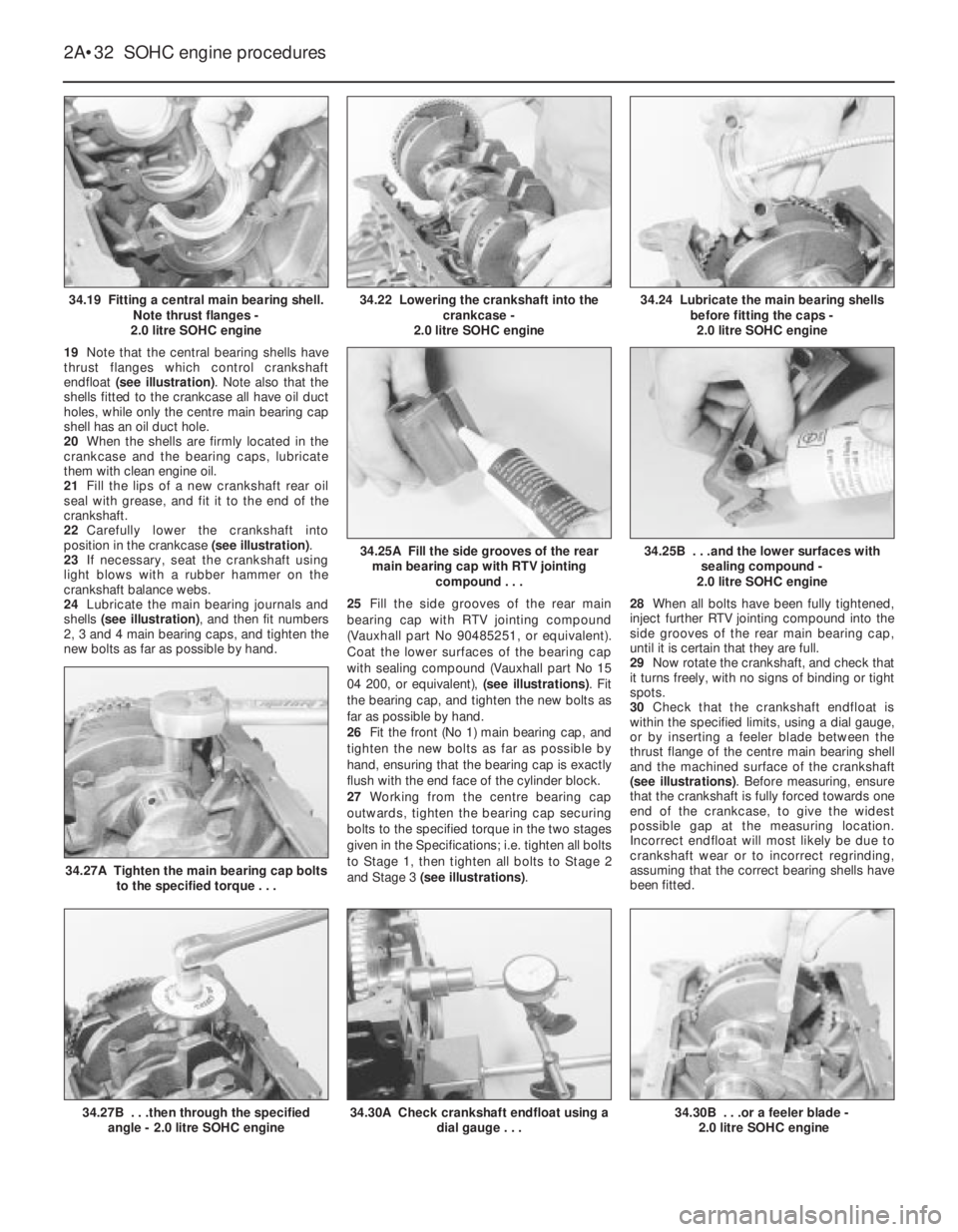
19Note that the central bearing shells have
thrust flanges which control crankshaft
endfloat (see illustration). Note also that the
shells fitted to the crankcase all have oil duct
holes, while only the centre main bearing cap
shell has an oil duct hole.
20When the shells are firmly located in the
crankcase and the bearing caps, lubricate
them with clean engine oil.
21Fill the lips of a new crankshaft rear oil
seal with grease, and fit it to the end of the
crankshaft.
22Carefully lower the crankshaft into
position in the crankcase (see illustration).
23If necessary, seat the crankshaft using
light blows with a rubber hammer on the
crankshaft balance webs.
24Lubricate the main bearing journals and
shells (see illustration), and then fit numbers
2, 3 and 4 main bearing caps, and tighten the
new bolts as far as possible by hand.25Fill the side grooves of the rear main
bearing cap with RTV jointing compound
(Vauxhall part No 90485251, or equivalent).
Coat the lower surfaces of the bearing cap
with sealing compound (Vauxhall part No 15
04 200, or equivalent), (see illustrations). Fit
the bearing cap, and tighten the new bolts as
far as possible by hand.
26Fit the front (No 1) main bearing cap, and
tighten the new bolts as far as possible by
hand, ensuring that the bearing cap is exactly
flush with the end face of the cylinder block.
27Working from the centre bearing cap
outwards, tighten the bearing cap securing
bolts to the specified torque in the two stages
given in the Specifications; i.e. tighten all bolts
to Stage 1, then tighten all bolts to Stage 2
and Stage 3 (see illustrations).28When all bolts have been fully tightened,
inject further RTV jointing compound into the
side grooves of the rear main bearing cap,
until it is certain that they are full.
29Now rotate the crankshaft, and check that
it turns freely, with no signs of binding or tight
spots.
30Check that the crankshaft endfloat is
within the specified limits, using a dial gauge,
or by inserting a feeler blade between the
thrust flange of the centre main bearing shell
and the machined surface of the crankshaft
(see illustrations). Before measuring, ensure
that the crankshaft is fully forced towards one
end of the crankcase, to give the widest
possible gap at the measuring location.
Incorrect endfloat will most likely be due to
crankshaft wear or to incorrect regrinding,
assuming that the correct bearing shells have
been fitted.
2A•32SOHC engine procedures
34.19 Fitting a central main bearing shell.
Note thrust flanges -
2.0 litre SOHC engine34.24 Lubricate the main bearing shells
before fitting the caps -
2.0 litre SOHC engine
34.30B . . .or a feeler blade -
2.0 litre SOHC engine
34.27A Tighten the main bearing cap bolts
to the specified torque . . .
34.27B . . .then through the specified
angle - 2.0 litre SOHC engine34.30A Check crankshaft endfloat using a
dial gauge . . .
34.25B . . .and the lower surfaces with
sealing compound -
2.0 litre SOHC engine34.25A Fill the side grooves of the rear
main bearing cap with RTV jointing
compound . . .
34.22 Lowering the crankshaft into the
crankcase -
2.0 litre SOHC engine
Page 230 of 525

31Refit the previously removed
components, referring to the relevant
Sections of this Chapter.
35Crankshaft and bearings -
examination
4
Examination
1Examine the crankpin and main journal
surfaces for signs of scoring or scratches, and
check the ovality and taper of the crankpins
and main journals. If the bearing surface
dimensions do not fall within the tolerance
ranges given in the Specifications at the
beginning of this Chapter, the crankpins
and/or main journals will have to be reground.
2Big-end and crankpin wear is accompanied
by distinct metallic knocking, particularly
noticeable when the engine is pulling from low
revs, and some loss of oil pressure.
3Main bearing and main journal wear is
accompanied by severe engine vibration rumble
- getting progressively worse as engine rev’s
increase - and again by loss of oil pressure.
4If the crankshaft requires regrinding, take it
to an engine reconditioning specialist, who
will machine it for you and supply the correct
undersize bearing shells.
5Inspect the big-end and main bearing shells
for signs of general wear, scoring, pitting and
scratches. The bearings should be matt grey
in colour. With leadindium bearings, should a
trace of copper colour be noticed, the
bearings are badly worn, as the lead bearing
material has worn away to expose the indium
underlay. Renew the bearings if they are in
this condition, or if there are any signs of
scoring or pitting. You are strongly advised
to renew the bearings - regardless of their
condition at time of major overhaul.
Refitting used bearings is a false economy.
6The undersizes available are designed to
correspond with crankshaft regrind sizes. Thebearings are in fact, slightly more than the
stated undersize, as running clearances have
been allowed for during their manufacture.
7Main and big-end bearing shells can be
identified as to size by the marking on the
back of the shell. Standard size shell bearings
are marked STD or .00, undersize shells are
marked with the undersize such as 0.020 u/s.
This marking method applies only to
replacement bearing shells, and not to those
used during production.
8An accurate method of determining bearing
wear is by using a Plastigage. The crankshaft
is located in the main bearings (and, if
necessary, the big-end bearings), and the
Plastigage filament is located across the
journal. Vauxhall recommend that the
crankshaft journal and bearing shells are
lightly lubricated, to prevent the Plastigage
from tearing as the bearing cap is removed.
The bearing cap should be fitted, and the
bolts tightened to the specified torque. The
cap is then removed, and the width of the
filament is checked against a scale that shows
the bearing running clearance. The clearance
should be compared with that given in the
Specifications.
9Where applicable, check the teeth of the
crankshaft TDC sensor wheel for damage
(see illustration). If evident, the crankshaft
must be renewed.
10Similarly, check the condition of the pins
in the front crankshaft balance weight, which
serve as detect points for the plug-in
diagnostic sensor used by Vauxhall dealers
(see illustration).
36Cylinder block and bores -
examination and renovation
4
Examination
1Examine the cylinder bores for taper,
ovality, scoring and scratches. Start bycarefully examining the top of the cylinder
bores. If they are at all worn, a very slight
ridge will be found on the thrust side. This
marks the top of the piston ring travel. The
owner will have a good indication of the bore
wear before dismantling the engine, or
removing the cylinder head. Excessive oil
consumption, accompanied by blue smoke
from the exhaust, is a sure sign of worn
cylinder bores and piston rings.
2Measure the bore diameter across the
block, and just below any ridge. This can be
done with an internal micrometer or a dial
gauge. Compare this with the diameter of the
bottom of the bore, which is not subject to
wear. If no measuring instruments are
available, use a piston from which the rings
have been removed, and measure the gap
between it and the cylinder wall with a feeler
blade. Refer to the Specifications. If the
cylinder wear exceeds the permitted
tolerances, then the cylinders will need
reboring, in which case note the following
points:
a)Piston and cylinder bores are closely
matched in production. The actual
diameter of the piston is indicated by
numbers on its crown; the same numbers
stamped on the crankcase indicate the
bore diameter
b)After reboring has taken place, the
cylinder bores should be measured
accurately and oversize pistons selected
from the grades available to give the
specified piston-to-bore clearance
c)For grading purposes, the piston diameter
is measured across the bottom of the skirt
3If the wear is marginal and within the
tolerances given, new special piston rings can
be fitted to offset the wear.
4Thoroughly examine the crankcase and
cylinder block for cracks and damage, and
use a piece of wire to probe all oilways and
waterways to ensure that they are
unobstructed.
SOHC engine procedures 2A•33
35.10 Check the condition of the pins (arrowed) in the front
crankshaft balance weight - 2.0 litre SOHC engine35.9 Check the condition of the TDC sensor wheel teeth at the
front of the crankshaft - 2.0 litre SOHC engine
2A
Page 236 of 525
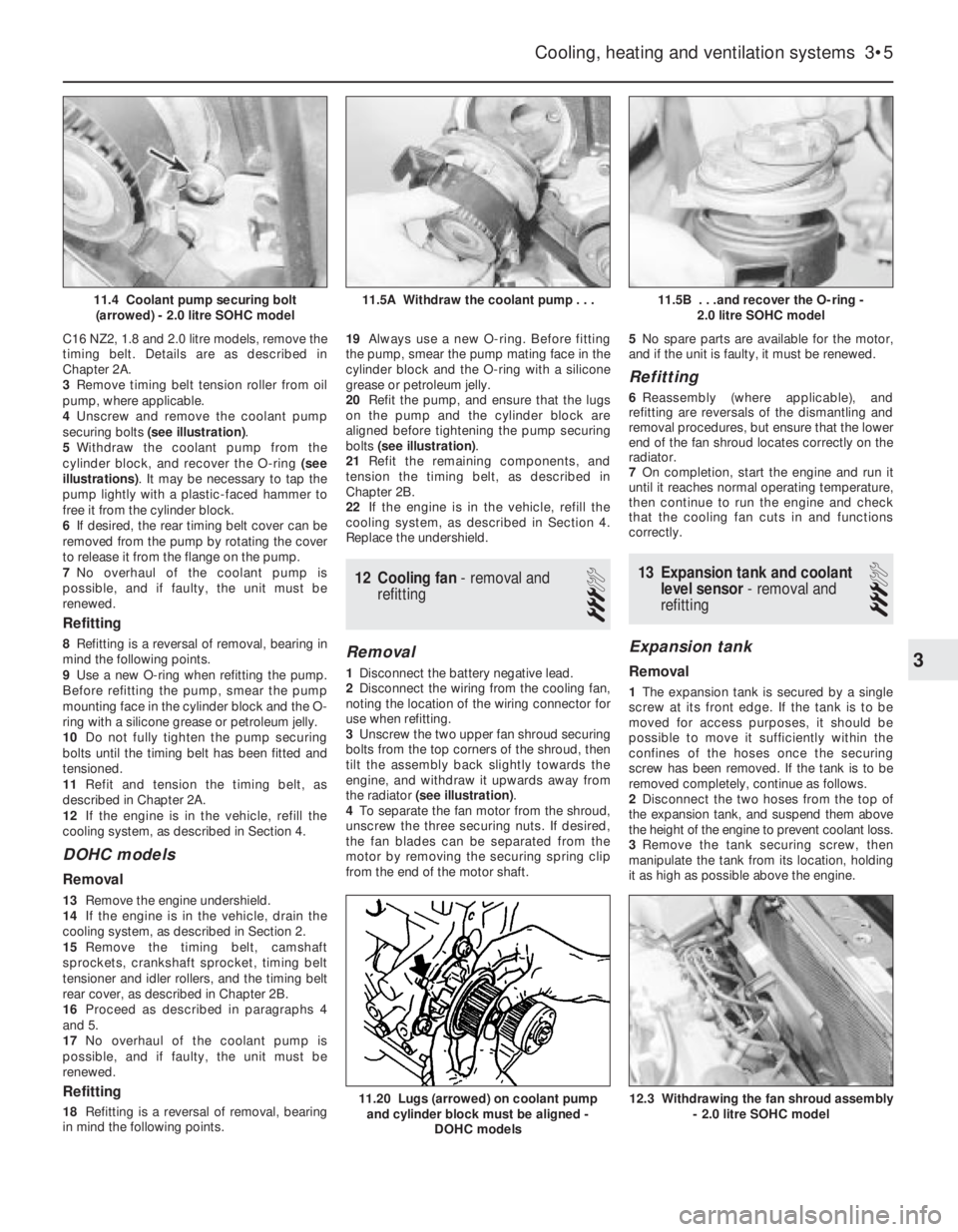
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, remove the
timing belt. Details are as described in
Chapter 2A.
3Remove timing belt tension roller from oil
pump, where applicable.
4Unscrew and remove the coolant pump
securing bolts (see illustration).
5Withdraw the coolant pump from the
cylinder block, and recover the O-ring (see
illustrations). It may be necessary to tap the
pump lightly with a plastic-faced hammer to
free it from the cylinder block.
6If desired, the rear timing belt cover can be
removed from the pump by rotating the cover
to release it from the flange on the pump.
7No overhaul of the coolant pump is
possible, and if faulty, the unit must be
renewed.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing in
mind the following points.
9Use a new O-ring when refitting the pump.
Before refitting the pump, smear the pump
mounting face in the cylinder block and the O-
ring with a silicone grease or petroleum jelly.
10Do not fully tighten the pump securing
bolts until the timing belt has been fitted and
tensioned.
11Refit and tension the timing belt, as
described in Chapter 2A.
12If the engine is in the vehicle, refill the
cooling system, as described in Section 4.
DOHC models
Removal
13Remove the engine undershield.
14If the engine is in the vehicle, drain the
cooling system, as described in Section 2.
15Remove the timing belt, camshaft
sprockets, crankshaft sprocket, timing belt
tensioner and idler rollers, and the timing belt
rear cover, as described in Chapter 2B.
16Proceed as described in paragraphs 4
and 5.
17No overhaul of the coolant pump is
possible, and if faulty, the unit must be
renewed.
Refitting
18Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points.19Always use a new O-ring. Before fitting
the pump, smear the pump mating face in the
cylinder block and the O-ring with a silicone
grease or petroleum jelly.
20Refit the pump, and ensure that the lugs
on the pump and the cylinder block are
aligned before tightening the pump securing
bolts (see illustration).
21Refit the remaining components, and
tension the timing belt, as described in
Chapter 2B.
22If the engine is in the vehicle, refill the
cooling system, as described in Section 4.
Replace the undershield.
12Cooling fan - removal and
refitting
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the wiring from the cooling fan,
noting the location of the wiring connector for
use when refitting.
3Unscrew the two upper fan shroud securing
bolts from the top corners of the shroud, then
tilt the assembly back slightly towards the
engine, and withdraw it upwards away from
the radiator (see illustration).
4To separate the fan motor from the shroud,
unscrew the three securing nuts. If desired,
the fan blades can be separated from the
motor by removing the securing spring clip
from the end of the motor shaft.5No spare parts are available for the motor,
and if the unit is faulty, it must be renewed.
Refitting
6Reassembly (where applicable), and
refitting are reversals of the dismantling and
removal procedures, but ensure that the lower
end of the fan shroud locates correctly on the
radiator.
7On completion, start the engine and run it
until it reaches normal operating temperature,
then continue to run the engine and check
that the cooling fan cuts in and functions
correctly.
13Expansion tank and coolant
level sensor -removal and
refitting
3
Expansion tank
Removal
1The expansion tank is secured by a single
screw at its front edge. If the tank is to be
moved for access purposes, it should be
possible to move it sufficiently within the
confines of the hoses once the securing
screw has been removed. If the tank is to be
removed completely, continue as follows.
2Disconnect the two hoses from the top of
the expansion tank, and suspend them above
the height of the engine to prevent coolant loss.
3Remove the tank securing screw, then
manipulate the tank from its location, holding
it as high as possible above the engine.
Cooling, heating and ventilation systems 3•5
11.5B . . .and recover the O-ring -
2.0 litre SOHC model
12.3 Withdrawing the fan shroud assembly
- 2.0 litre SOHC model11.20 Lugs (arrowed) on coolant pump
and cylinder block must be aligned -
DOHC models
11.5A Withdraw the coolant pump . . .11.4 Coolant pump securing bolt
(arrowed) - 2.0 litre SOHC model
3