1987 SUZUKI GRAND VITARA brake light
[x] Cancel search: brake lightPage 32 of 962
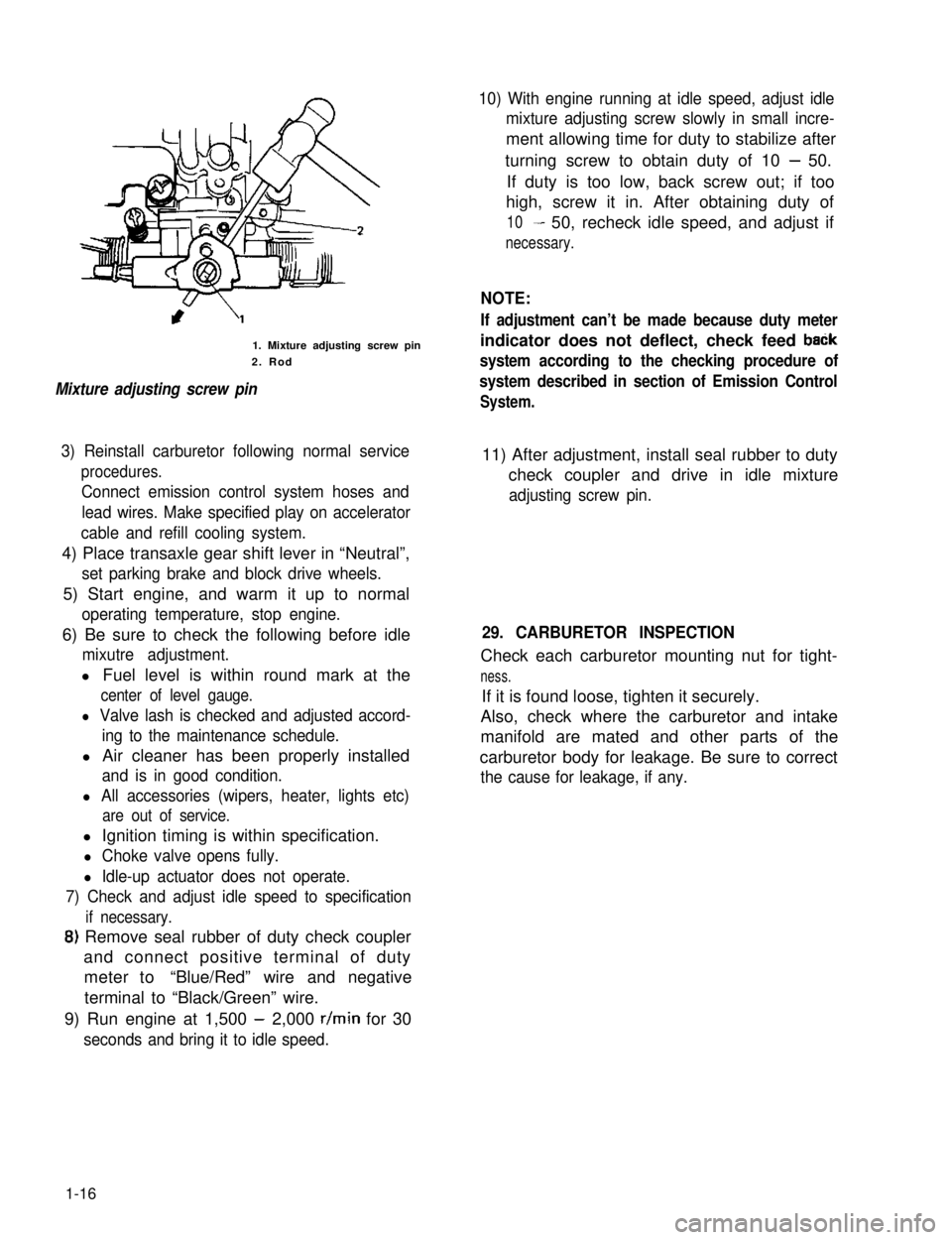
1. Mixture adjusting screw pin
2. Rod
Mixture adjusting screw pin
10) With engine running at idle speed, adjust idle
mixture adjusting screw slowly in small incre-
ment allowing time for duty to stabilize after
turning screw to obtain duty of 10 - 50.
If duty is too low, back screw out; if too
high, screw it in. After obtaining duty of
10- 50, recheck idle speed, and adjust if
necessary.
NOTE:
If adjustment can’t be made because duty meter
indicator does not deflect, check feed baCk
system according to the checking procedure of
system described in section of Emission Control
System.
3) Reinstall carburetor following normal service
procedures.
Connect emission control system hoses and
lead wires. Make specified play on accelerator
cable and refill cooling system.
11) After adjustment, install seal rubber to duty
check coupler and drive in idle mixture
adjusting screw pin.
4) Place transaxle gear shift lever in “Neutral”,
set parking brake and block drive wheels.
5) Start engine, and warm it up to normal
operating temperature, stop engine.
6) Be sure to check the following before idle
mixutre adjustment.
l Fuel level is within round mark at the
center of level gauge.
l Valve lash is checked and adjusted accord-
ing to the maintenance schedule.
l Air cleaner has been properly installed
and is in good condition.
l All accessories (wipers, heater, lights etc)
are out of service.
29. CARBURETOR INSPECTION
Check each carburetor mounting nut for tight-
ness.
If it is found loose, tighten it securely.
Also, check where the carburetor and intake
manifold are mated and other parts of the
carburetor body for leakage. Be sure to correct
the cause for leakage, if any.
l Ignition timing is within specification.
l Choke valve opens fully.
l Idle-up actuator does not operate.
7) Check and adjust idle speed to specification
if necessary.
8) Remove seal rubber of duty check coupler
and connect positive terminal of duty
meter to“Blue/Red” wire and negative
terminal to “Black/Green” wire.
9) Run engine at 1,500 - 2,000 r/min for 30
seconds and bring it to idle speed.
1-16
Page 51 of 962
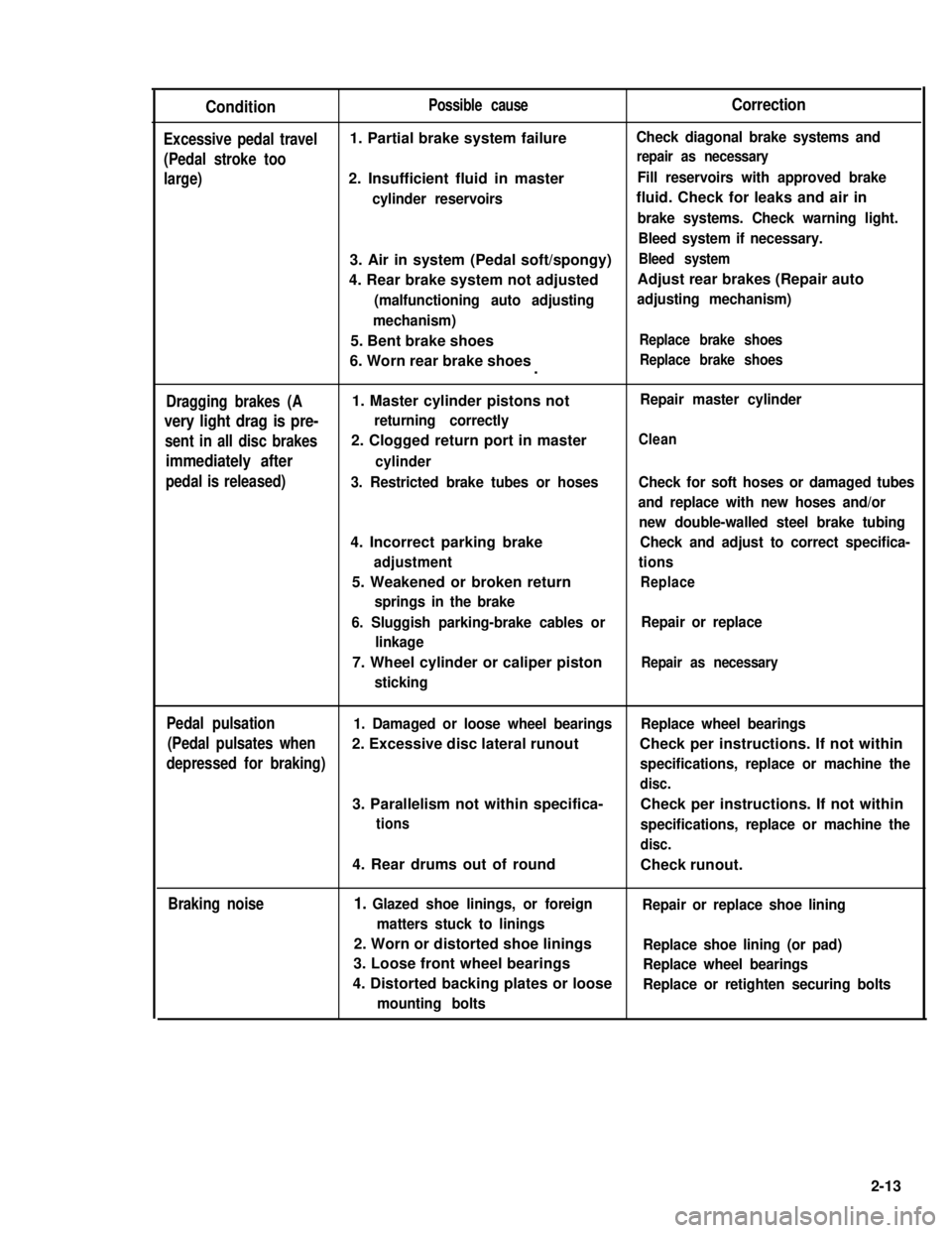
Condition
Excessive pedal travel
(Pedal stroke too
large)
Possible cause
1. Partial brake system failure
2. Insufficient fluid in master
cylinder reservoirs
Correction
Check diagonal brake systems and
repair as necessary
Fill reservoirs with approved brake
fluid. Check for leaks and air in
brake systems. Check warning light.
Bleed system if necessary.
3. Air in system (Pedal soft/spongy)Bleed system
4. Rear brake system not adjustedAdjust rear brakes (Repair auto
(malfunctioning auto adjustingadjusting mechanism)
mechanism)
5. Bent brake shoesReplace brake shoes
6. Worn rear brake shoesReplace brake shoes.
Dragging brakes (A
very light drag is pre-
sent in all disc brakes
immediately after
pedal is released)
1. Master cylinder pistons not
returning correctly
2. Clogged return port in master
cylinder
3. Restricted brake tubes or hoses
4. Incorrect parking brake
adjustment
5. Weakened or broken return
springs in the brake
Repair master cylinder
Clean
Check for soft hoses or damaged tubes
and replace with new hoses and/or
new double-walled steel brake tubing
Check and adjust to correct specifica-
tions
Replace
6. Sluggish parking-brake cables or
linkage
Repair or replace
7. Wheel cylinder or caliper piston
sticking
Repair as necessary
Pedal pulsation1. Damaged or loose wheel bearingsReplace wheel bearings
(Pedal pulsates when2. Excessive disc lateral runout Check per instructions. If not within
depressed for braking)specifications, replace or machine the
disc.
3. Parallelism not within specifica-Check per instructions. If not within
tionsspecifications, replace or machine the
disc.
4. Rear drums out of roundCheck runout.
Braking noise1. Glazed shoe linings, or foreignRepair or replace shoe lining
matters stuck to linings
2. Worn or distorted shoe liningsReplace shoe lining (or pad)
3. Loose front wheel bearingsReplace wheel bearings
4. Distorted backing plates or looseReplace or retighten securing bolts
mounting bolts
2-13
Page 141 of 962
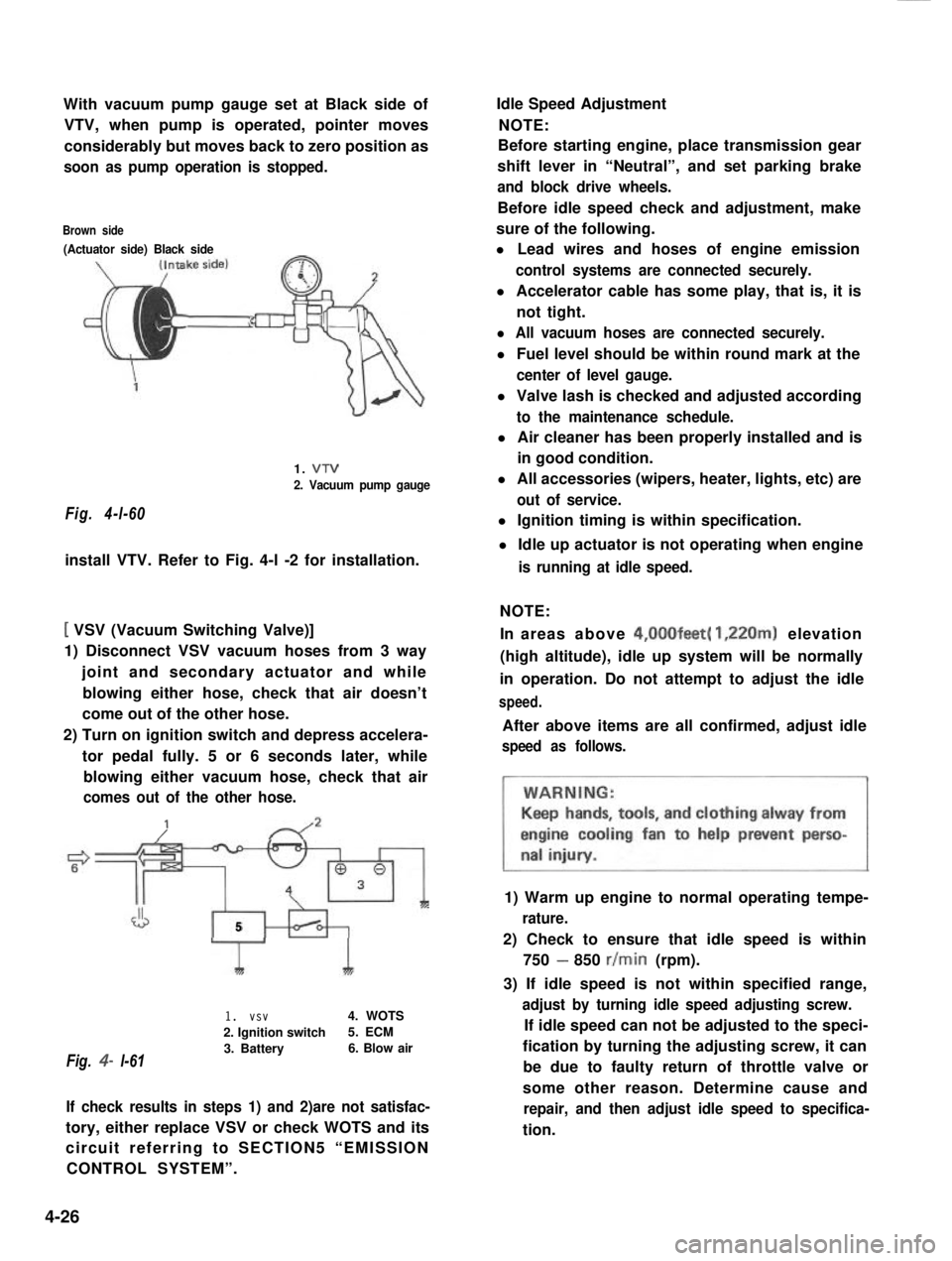
With vacuum pump gauge set at Black side of
VTV, when pump is operated, pointer moves
considerably but moves back to zero position as
soon as pump operation is stopped.
Brown side
(Actuator side) Black side
Fig. 4-l-60
1. VTV
2. Vacuum pump gauge
install VTV. Refer to Fig. 4-l -2 for installation.
[ VSV (Vacuum Switching Valve)]
1) Disconnect VSV vacuum hoses from 3 way
joint and secondary actuator and while
blowing either hose, check that air doesn’t
come out of the other hose.
2) Turn on ignition switch and depress accelera-
tor pedal fully. 5 or 6 seconds later, while
blowing either vacuum hose, check that air
comes out of the other hose.
J5
Fig. 4- l-61
1I
1. vsv4. WOTS
2. Ignition switch5. ECM
3. Battery6. Blow air
If check results in steps 1) and 2)are not satisfac-
tory, either replace VSV or check WOTS and its
circuit referring to SECTION5 “EMISSION
CONTROL SYSTEM”.
Idle Speed Adjustment
NOTE:
Before starting engine, place transmission gear
shift lever in “Neutral”, and set parking brake
and block drive wheels.
Before idle speed check and adjustment, make
sure of the following.
l Lead wires and hoses of engine emission
control systems are connected securely.
l Accelerator cable has some play, that is, it is
not tight.
l All vacuum hoses are connected securely.
l Fuel level should be within round mark at the
center of level gauge.
l Valve lash is checked and adjusted according
to the maintenance schedule.
l Air cleaner has been properly installed and is
in good condition.
l All accessories (wipers, heater, lights, etc) are
out of service.
l Ignition timing is within specification.
l Idle up actuator is not operating when engine
is running at idle speed.
NOTE:
In areas above 4,00Ofeet( 1,220m) elevation
(high altitude), idle up system will be normally
in operation. Do not attempt to adjust the idle
speed.
After above items are all confirmed, adjust idle
speed as follows.
1) Warm up engine to normal operating tempe-
rature.
2) Check to ensure that idle speed is within
750 - 850 r/min (rpm).
3) If idle speed is not within specified range,
adjust by turning idle speed adjusting screw.
If idle speed can not be adjusted to the speci-
fication by turning the adjusting screw, it can
be due to faulty return of throttle valve or
some other reason. Determine cause and
repair, and then adjust idle speed to specifica-
tion.
4-26
Page 143 of 962
3) Reinstall carburetor following normal service
procedures.
Connect emission control system hoses and
lead wires. Make specified play on accelerator
cable and refill cooling system.
4) Place transaxle gear shift lever in “Neutral”,
set parking brake and block drive wheels.
5) Start engine, and warm it up to normal
operating temperature, stop engine.
6) Be sure to check the following before idle
mixture adjustment.
l Fuel level is within round mark at the
center of level gauge.
l Valve lash is checked and adjusted accord-
ing to the maintenance schedule.
l Air cleaner has been properly installed
and is in good condition.
l All accessories (wipers, heater, lights etc)
are out of service.
l Ignition timing is within specification.
l Choke valve opens fully.
l Idle-up actuator does not operate.
7) Check and adjust idle speed to specification
if necessary.
8) Remove seal rubber of duty check coupler
and connect positive terminal of duty
meter to“Blue/Red” wire and negative
terminal to “Black/Green” wire.
9) Run engine at 1,500 - 2,000 r/min for 30
seconds and bring it to idle speed.
10) With engine running at idle speed, adjust idle
mixture adjusting screw slowly in small incre-
ment allowing time for duty to stabilize after
turning screw to obtain duty of 10 - 50.
If duty is too low, back screw out; if too
high, screw it in. After obtaining duty of
10 - 50, recheck idle speed, and adjust if
necessary.
NOTE:
If adjustment can’t be made because duty meter
indicator does not deflect, check feed back
system according to the checking procedure of
system described in section of Emission Control
System.
11) After adjustment, install seal rubber to duty
check coupler and drive in idle mixture
adjusting screw pin.
4-28
Page 244 of 962
![SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 1987 Service Repair Manual [Carrier and hold-down]
The battery carrier and hold-down clamp should
be clean and free from corrosion before instal-
ling the battery. The carrier should be in good
condition so that it will support SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 1987 Service Repair Manual [Carrier and hold-down]
The battery carrier and hold-down clamp should
be clean and free from corrosion before instal-
ling the battery. The carrier should be in good
condition so that it will support](/manual-img/20/57437/w960_57437-243.png)
[Carrier and hold-down]
The battery carrier and hold-down clamp should
be clean and free from corrosion before instal-
ling the battery. The carrier should be in good
condition so that it will support the battery
securely and keep it level.
Make certain there are no parts in carrier before
installing the battery.
To prevent the battery from shaking in its
carrier, the hold-down bolts should be tight but
not over tightened.
[Visual inspection]
Check for obvious damage, such as cracked or
broken case or cover, that could permit loss of
electrolyte. If obvious damage is noted, replace
the battery. Determine cause of damage and
correct as needed.
Check the battery terminal and cords for corro-
sion. If any, it should be cleaned.
[Built-in indicator]
This sealed battery has a built-in temperature
compensated indicator in the top of the battery.
This indicator is to be used with the following
diagnostic procedure. When observing the
indicator, make sure that the battery has a clean
top. A light may be needed in some poorly-lit
areas.
Under normal operation, two indications can
be seen
2
Clear
RedCHARGING
NECESSARY
Fig. lo-23
l Clear with Red Dot
This means the discharging battery. In this case,
charge the battery until the indicator will be
blue with red dot. The charging and electrical
systems should also be checked at this time. If
any defective is found, correct it. While charging
it, if the battery feels hot 52°C (125” F), or if
violent gassing or spewing of electrolyte through
the vent hole occurs, discontinue charging or
reduce charging rate.
[Jump starting in case of emergency with
auxiliary (booster) battery]
NOTE:
l Do not push or tow the vehicle to start.
Damage to the emission system and/or to
other parts of the vehicle may result.
8 Both booster and discharged battery should
be treated carefully when using jumper cables.
Follow the procedure outlined below, being
careful not to cause sparks:
CAUTION:
l Departure from these conditions or the
procedure below could result in: (1)
Serious personal injury (particularly to
eyes) or property damage from such
causes as battery explosion, battery acid,
or electrical burns; and/or (2) damage to
electronic components of either vehicle.
l Never expose battery to open flame or
electric spark-batteries generate a gas
which is flammable and explosive.
l Remove rings,watches,and other
jewelry. Wear approved eye protection.
l Do not allow battery fluid to contact
eyes, skin, fabrics, or painted surfaces -
fluid is a corrosive acid. Flush any con-
tacted area with water immediately and
thoroughly. Be careful that metal tools
or jumper cables do not contact the
positive battery terminal (or metal in
contact with it) and any other metal on
the car, because a short circuit could
occur. Batteries should always be kept
out of the reach of children.
1) Set parking brake and place transmission in
neutral. Turn off the ignition, turn off lights
and all other electrical loads.
2) Check electrolyte level. If level is below low
level line, replace battery.
NOTE:
When jump starting an engine with charging
equipment, be sure equipment used is 12volt
and negative ground. Do not use 24volt charging
equipment. Using each equipment can cause
serious damage to the electrical system or
electronic parts.
10-11
Page 406 of 962
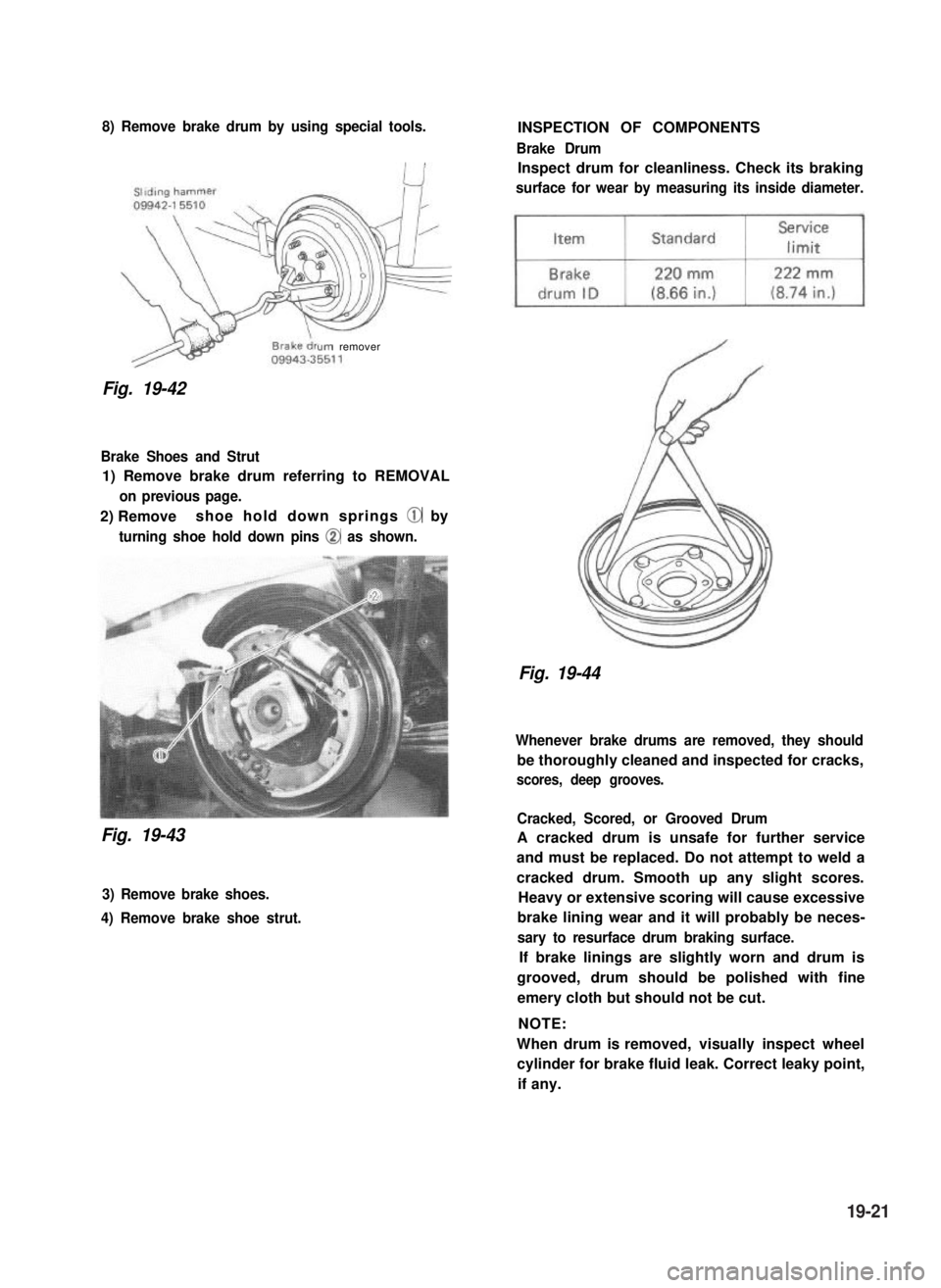
8) Remove brake drum by using special tools.
urn remover
Fig. 19-42
Brake Shoes and Strut
1) Remove brake drum referring to REMOVAL
on previous page.
2) Removeshoe hold down springs @ by
turning shoe hold down pins @ as shown.
Fig. 19-43
3) Remove brake shoes.
4) Remove brake shoe strut.
INSPECTION OF COMPONENTS
Brake Drum
Inspect drum for cleanliness. Check its braking
surface for wear by measuring its inside diameter.
Fig. 19-44
Whenever brake drums are removed, they should
be thoroughly cleaned and inspected for cracks,
scores, deep grooves.
Cracked, Scored, or Grooved Drum
A cracked drum is unsafe for further service
and must be replaced. Do not attempt to weld a
cracked drum. Smooth up any slight scores.
Heavy or extensive scoring will cause excessive
brake lining wear and it will probably be neces-
sary to resurface drum braking surface.
If brake linings are slightly worn and drum is
grooved, drum should be polished with fine
emery cloth but should not be cut.
NOTE:
When drum is removed, visually inspect wheel
cylinder for brake fluid leak. Correct leaky point,
if any.
19-21
Page 427 of 962
19-8. MAINTENANCE SERVICE
ROAD TESTING BRAKES
Brakes should be tested on dry, clean, smooth
and reasonably level roadway which is not
crowned. Road test brakes by making brake
applications with both light and heavy pedal
forces at various speeds to determine if the car
stops evenly and effectively.
Also drive car to see if it leads to one side or the
other without brake application. If it does,
check tire pressure, front end alignment and
front suspension attachments for looseness.
See diagnosis chart for other causes.
BRAKE FLUID LEAKS
Check master cylinder fluid levels. While a slight
drop in reservoir level does result from normal
lining wear, an abnormally low level indicates a
leak in the system.In such a case, check the
entire brake system for leakage. If even a slight
evidence of leakage is noted, the cause should be
corrected or defective parts should be replaced.
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL INSPECTION
Be sure to use particular brake fluid either as
marked on reservoir cap of that car or recom-
mended in owner’s manual which comes along
with that car.
Use of any other fluid is strictly prohibited.
Fluid level should be between MIN and MAX
lines marked on reservoir.
When warning light lights sometimes during
driving, replenish fluid to MAX line.
When fluid decreases quickly, inspect brake
system for leakage. Correct leaky points and
then refill to specified level.
FILL RESERVOIR
CAUTION:
Do not use shock absorber fluid or any
other fluid which contains mineral oil. Do
not use a container which has been used for
mineral oil or a container which is wet
from water. Mineral oil will cause swelling
and distortion of rubber parts in the hy-
draulic brake system and water will mix
with brake fluid, lowering the fluid boiling
point. Keep all fluid containers capped to
prevent contamination.
Fluid to fill reservoir which is indicated on
reservoir cap of the car with embossed letters or
in owner’s manual supplied with the car.
Add fluid up to MAX line.
Fig. 19-8-2
Fig. 19-8-1
19-42
Page 428 of 962
BRAKE PEDAL FREE HEIGHT ADJUSTMENT
Brake pedal height is normal if brake pedal is
as high as clutch pedal.
1) When booster push rod clevis has been
reinstalled, it is important that measurement
between booster mounting surface (with a
gasket attached) and the center of clevis
pin hole is adjusted within 125.5 mm -
126.5 mm (4.94 - 4.98 in.). (See page
19-37.)
2) When stop light switch has been removed,
refer to the following STOP LIGHT SWITCH
ADJUSTMENT for proper installation.
The services in above steps 1) and 2) may
affect brake pedal height.
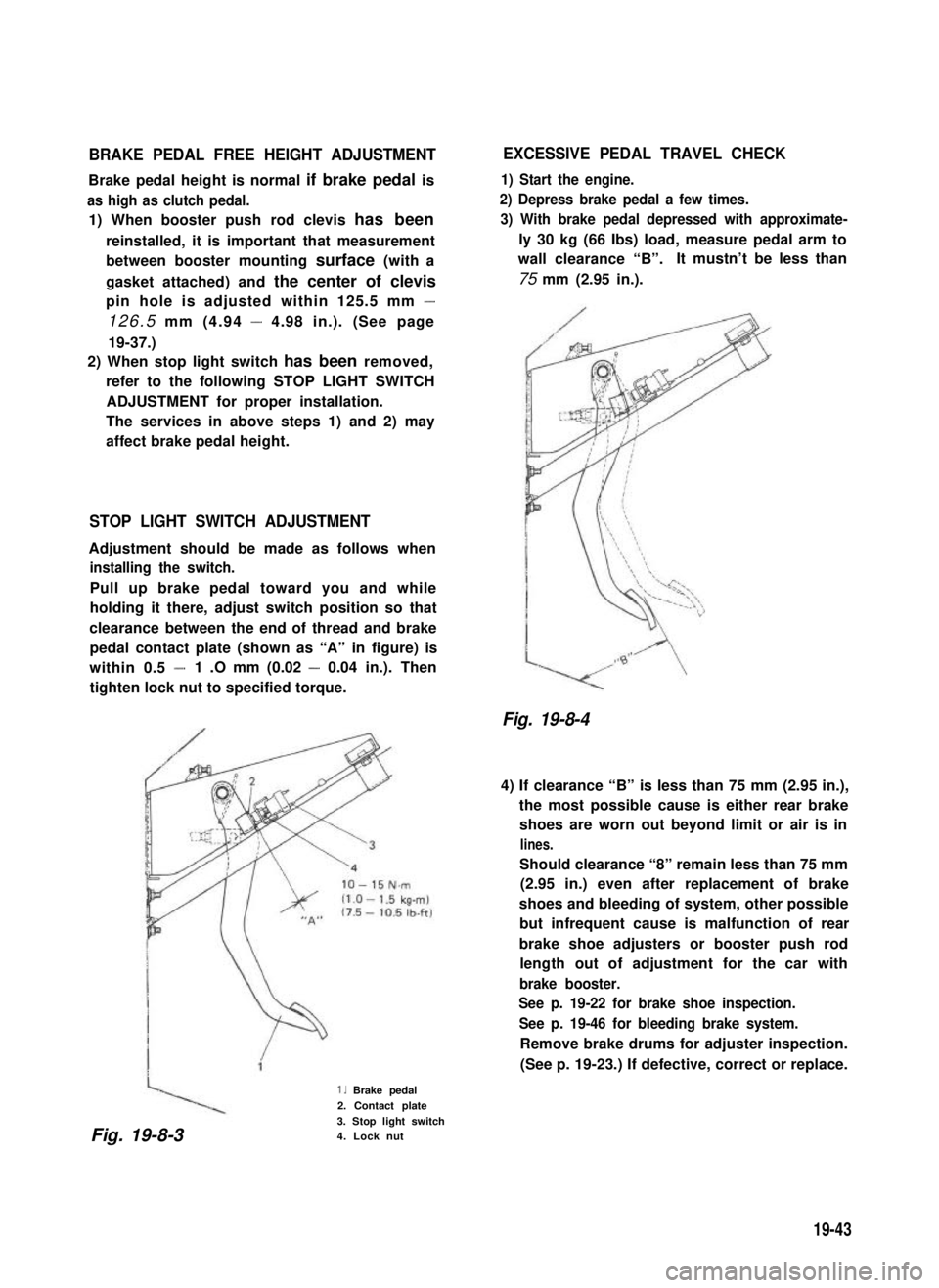
STOP LIGHT SWITCH ADJUSTMENT
Adjustment should be made as follows when
installing the switch.
Pull up brake pedal toward you and while
holding it there, adjust switch position so that
clearance between the end of thread and brake
pedal contact plate (shown as “A” in figure) is
within 0.5 -1 .O mm (0.02 - 0.04 in.). Then
tighten lock nut to specified torque.
1. Brake pedal
2. Contact plate
3. Stop light switch4. Lock nut
EXCESSIVE PEDAL TRAVEL CHECK
1) Start the engine.
2) Depress brake pedal a few times.
3) With brake pedal depressed with approximate-
ly 30 kg (66 Ibs) load, measure pedal arm to
wall clearance “B”.It mustn’t be less than
75 mm (2.95 in.).
Fig. 19-8-4
4) If clearance “B” is less than 75 mm (2.95 in.),
the most possible cause is either rear brake
shoes are worn out beyond limit or air is in
lines.
Should clearance “8” remain less than 75 mm
(2.95 in.) even after replacement of brake
shoes and bleeding of system, other possible
but infrequent cause is malfunction of rear
brake shoe adjusters or booster push rod
length out of adjustment for the car with
brake booster.
See p. 19-22 for brake shoe inspection.
See p. 19-46 for bleeding brake system.
Remove brake drums for adjuster inspection.
(See p. 19-23.) If defective, correct or replace.
Fig. 19-8-3
19-43