1985 FORD GRANADA heating
[x] Cancel search: heatingPage 8 of 255

to release any pressure. When pressure has
been released, carry on unscrewing the cap
and remove it.
9Top-up to the MAX mark with the specified
coolant (see illustration).In an emergency
plain water is better than nothing, but
remember that it is diluting the proper coolant.
Do not add cold water to an overheated
engine whilst it is still hot.
10Refit the expansion tank cap securely
when the level is correct. With a sealed type
cooling system like this, the addition of
coolant should only be necessary at very
infrequent intervals. If frequent topping-up is
required, it is likely there is a leak in the
system. Check the radiator, all hoses and joint
faces for any sign of staining or actual
wetness, and rectify as necessary. If no leaks
can be found, it is advisable to have the
pressure cap and the entire system pressure-
tested by a dealer or suitably-equipped
garage, as this will often show up a small leak
not previously apparent.
Brake fluid
Be sure to use only the specified brake
hydraulic fluid, since mixing different types of
fluid can cause damage to the system. See
“Lubricants, fluids and capacities”at the
beginning of this Chapter. When adding fluid,
it is a good idea to inspect the reservoir for
contamination. The system should be drained
and refilled if deposits, dirt particles or
contamination are seen in the fluid.
11Check the brake fluid level as follows.
12With the vehicle parked on level ground
and the ignition switched off, pump the brake
pedal at least 20 times or until the pedal feels
hard.
13Open the bonnet. Switch on the ignition:
the hydraulic unit pump will be heard running.
Wait until the pump stops, then switch off the
ignition.
14The fluid level in the reservoir should now
be between the MAX and MIN marks. If
topping-up is necessary, unplug the electrical
connectors from the cap, then unscrew and
remove it (see illustration).Catch the
hydraulic fluid which will drip off the level
sensor with a piece of rag.
15Top-up with fresh brake fluid of the
specified type (see illustration).Do not
overfill. Refit and reconnect the reservoir cap
immediately.16The fluid level in the reservoir will drop
slightly as the brake pads wear down during
normal operation. If the reservoir requires
repeated replenishment to maintain the proper
level, this is an indication of a hydraulic leak
somewhere in the system, which should be
investigated immediately.
Washer fluid
17When topping-up the windscreen or rear
screen washer fluid reservoir, a screenwash
additive should be added in the quantities
recommended on the bottle.
1On later models tyres may have tread wear
safety bands, which will appear when the
tread depth reaches approximately 1.6 mm.
Otherwise, tread wear can be monitored with a
simple, inexpensive device known as a tread
depth indicator gauge (see illustration).
2Wheels and tyres should give no real
problems in use, provided that a close eye is
kept on them with regard to excessive wear or
damage. To this end, the following points
should be noted.
3Ensure that the tyre pressures are checked
regularly and maintained correctly (see
illustration). Checking should be carried out
with the tyres cold, not immediately after the
vehicle has been in use. If the pressures are
checked with the tyres hot, an apparently-high
reading will be obtained, owing to heat
expansion. Under no circumstancesshould
an attempt be made to reduce the pressures
to the quoted cold reading in this instance, or
effective under-inflation will result.
4Note any abnormal tread wear (see
illustration). Tread pattern irregularities such
as feathering, flat spots, and more wear on
one side than the other, are indications of front
wheel alignment and/or balance problems. If
any of these conditions are noted, they should
be rectified as soon as possible.
5Under-inflation will cause overheating of the
tyre, owing to excessive flexing of the casing,
and the tread will not sit correctly on the road
surface. This will cause excessive wear, not to
mention the danger of sudden tyre failure due
to heat build-up.
4Tyre checks
1•7
1
Weekly checks
3.14 Removing the brake fluid reservoir cap3.15 Topping up the brake fluid reservoir
4.1 Checking the tyre tread depth4.3 Checking tyre pressure
3.9 Topping up the cooling system
Warning: Brake hydraulic fluid
can harm your eyes and damage
painted surfaces, so use extreme
caution when handling and
pouring it. Do not use fluid that has been
standing open for some time, as it absorbs
moisture from the air. Excess moisture can
cause a dangerous loss of braking
effectiveness.If any brake fluid gets onto
paintwork, wash it off
immediately with clean water.
procarmanuals.com
Page 37 of 255

(1.0 in) either side of the spreader gap. Fit the
tapered lower compression ring with the TOP
mark towards the top of the piston and the gap
150°from the spreader gap, then fit the upper
compression ring with the gap 150°on the
other side of the spreader gap. Note that the
compression rings are coated with a
molybdenum skin which must not be damaged.
7Note that the compression rings are made
of cast iron, and will snap if expanded too far.
Examine the surface of the camshaft
journals and lobes and the cam followers for
wear. If excessive, considerable noise would
have been noticed from the top of the engine
and a new camshaft and followers must be
fitted.
Check the camshaft bearings for wear and if
necessary have them renewed by a Ford
garage.
Check the camshaft lubrication tube for
obstructions and make sure that the jet holes
are clear. Obstruction of the holes can be due
to sludge build-up which occurs when regular
oil changes have been neglected.
Examine the auxiliary shaft for wear and
damage and renew it if necessary.
If the auxiliary shaft endfloat is outside the
limits given in the Specifications fit a new
thrust plate. If this does not bring the endfloat
within limits, renew the shaft.
Whenever the timing belt is removed it is
worthwhile renewing it, especially if it has
covered a high mileage. This is more important
on the 2.0 litre engine where stripped teeth on
the timing belt can cause the pistons to foul
the valves.If the ring gear is badly worn or has missing
teeth, it should be renewed. The old ring can
be removed from the flywheel by cutting a
notch between two teeth with a hacksaw and
then splitting it with a cold chisel. Wear eye
protection when doing this.
To fit a new ring gear requires heating the
ring to 204°C (400°F). This can be done by
polishing four equal sections of the gear,
laying it on a suitable heat resistant surface
(such as fire bricks) and heating it evenly with
a blow lamp or torch until the polished areas
turn a light yellow tinge. Do not overheat or the
hard wearing properties will be lost. The gear
has a chamfered inner edge which should go
against the shoulder when put on the flywheel.
When hot enough place the gear in position
quickly, tapping it home if necessary and let it
cool naturally, without quenching.
1This operation will normally only be required
at comparatively high mileages. However, if
persistent pinking occurs and performance
has deteriorated even though the engine
adjustments are correct, decarbonising and
valve grinding may be required.
2With the cylinder head removed, use a
scraper to remove the carbon from the
combustion chambers and ports. Remove all
traces of gasket from the cylinder head
surface, then wash it thoroughly with paraffin.
3Use a straight-edge and feeler blade to
check that the cylinder head surface is not
distorted. If it is, it must be resurfaced by a
suitably equipped engineering works.
4If the engine is still in the car, clean the
piston crowns and cylinder bore upper edges,
but make sure that no carbon drops between
the pistons and bores. To do this, locate two
of the pistons at the top of their bores and seal
off the remaining bores with paper and
masking tape. Press a little grease between
the two pistons and their bores to collect any
carbon dust; this can be wiped away when the
piston is lowered.5Examine the heads of the valves for pitting
and burning, especially the exhaust valve
heads. Renew any valve which is badly burnt.
Examine the valve seats at the same time. If
the pitting is very slight, it can be removed by
grinding the valve heads and seats together
with coarse, then fine, grinding paste.
6Where excessive pitting has occurred, the
valve seats must be recut or renewed by a
suitably equipped engineering works.
7Valve grinding is carried out as follows.
Place the cylinder head upside down on a
bench on blocks of wood.
8Smear a trace of coarse carborundum paste
on the seat face and press a suction grinding
tool onto the valve head. With a semi-rotary
action, grind the valve head to its seat, lifting
the valve occasionally to redistribute the
grinding paste. When a dull matt even surface
is produced on both the valve seat and the
valve, wipe off the paste and repeat the
process with fine carborundum paste as
before. A light spring placed under the valve
head will greatly ease this operation. When a
smooth unbroken ring of light grey matt finish
is produced on both the valve and seat, the
grinding operation is complete.
9Scrape away all carbon from the valve head
and stem, and clean away all traces of
grinding compound. Clean the valves and
seats with a paraffin soaked rag, then wipe
with a clean rag.
10If the guides are worn they will need
reboring for oversize valves or for fitting guide
inserts. The valve seats will also need
recutting to ensure that they are concentric
with the stems. This work should be given to
your Ford dealer or local engineering works.
11If the valve springs have been in use
for 20 000 miles (32 000 km) or more, renew
them. Always renew the valve stem oil seals
when the valves are removed.
1To ensure maximum life with minimum
trouble from a rebuilt engine, not only must
everything be correctly assembled, but it must
also be spotlessly clean. All oilways must be
clear, and locking washers and spring washers
must be fitted where indicated. Oil all bearings
and other working surfaces thoroughly with
engine oil during assembly.
2Before assembly begins, renew any bolts or
studs with damaged threads.
3Gather together a torque wrench, oil can,
clean rag, and a set of engine gaskets and oil
seals, together with a new oil filter.
4If they have been removed, new cylinder
head bolts and flywheel bolts will also be
required.
35Engine reassembly - general
information
34Cylinder head - decarbonising,
valve grinding and renovation
33Flywheel ring gear -
examination and renovation
32Timing belt - examination and
renovation
31Auxiliary shaft - examination
and renovation
30Camshaft and cam followers
- examination and renovation
2A•14SOHCengines
29.4a Checking a piston ring gap at the top
of the cylinder29.4b Checking a ring gap at the bottom of
the cylinder
To prevent carbon build-up,
polish the piston crown with
metal polish, but remove all
traces of the polish after.
procarmanuals.com
Page 84 of 255

Chapter 3
Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
Air conditioning system - component renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Cooling fan switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Cooling system - draining . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Cooling system - filling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Cooling system - flushing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Electric cooling fan(s) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Expansion tank - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
General information and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Heater assembly - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Heater control cables - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Heater controls - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Heater coolant valve - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21Heater matrix - dismantling and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Radiator - inspection and repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Radiator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Temperature gauge sender - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Thermostat - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Thermostat - testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Viscous-coupled fan - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Water pump/alternator drivebelt(s) - inspection, renewal and
adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Water pump/alternator drivebelt tensioner - removal and refitting .13
Water pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
General
System type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Sealed, pressurised, thermostatically controlled
Fan type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Mechanical temperature-sensitive viscous clutch, or electric
(DOHC)
Coolant
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See “Lubricants and fluids”
Capacity:
SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.0 litres (14.1 pints) approx
DOHC:
Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.9 litres (13.9 pints) approx
Fuel injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.3 litres (12.8 pints) approx
V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8.5 litres (15.0 pints) approx
Specific gravity at 45 to 50% antifreeze concentration . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.069 to 1.077
Expansion tank cap
Opening pressure:
SOHC and V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.85 to 1.10 bar
DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 to 1.4 bar
Thermostat
Nominal rating:.
SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88°C (190°F)
DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102°C (216°F)
V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82°C (180°F)
Actual opening temperature:
SOHC and DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85° to 89°C (185° to 192°F)
V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79° to 83°C (174° to 181°F)
Water pump drivebelt
Deflection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 mm (0.4 in) approx under normal fingertip pressure at mid-
point of longest run
3•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
3
procarmanuals.com
Page 85 of 255
Cooling system
The cooling system is of pressurised type
and includes a front mounted crossflow
radiator, belt-driven water pump, temperature-
sensitive thermo-viscous fan (on DOHC
models, an electrically-operated cooling fan is
fitted, operated by a switch in the thermostat
housing), wax type thermostat, and an
expansion and degas tank.
The radiator matrix is of copper and brass
construction and the end tanks are of plastic.
On automatic transmission models the right-
hand side end tank incorporates the
transmission oil cooler.
The thermostat is located behind the water
outlet elbow at the front of the cylinder head
on OHCmodels, and on the front of the water
pump on V6 models. Its purpose is to ensure
rapid engine warm-up by restricting the flow of
coolant in the engine when cold, and also to
assist in regulating the normal operating
temperature of the engine.
The expansion tank incorporates a pressure
cap which effectively pressurises the cooling
system as the coolant temperature rises,
thereby increasing the boiling point of the
coolant. The tank also has a further degas
function. Any accumulation of air bubbles in
the coolant, in particular in the thermostat
housing and the radiator, is returned to the
tank and released in the air space thus
maintaining the efficiency of the coolant.
On models fitted with the auxiliary warning
system, the expansion tank contains a level
sensor which operates a warning light if the
coolant level falls significantly.
When the engine is started from cold, the
water pump circulates coolant around the
cylinder block, cylinder head(s) and inlet
manifold. The warm coolant passes through
the automatic choke housing (when
applicable) and through the heater matrix
before returning to the engine. As the coolant
expands, the level in the expansion tank rises.
Circulation of coolant through the radiator is
prevented while the thermostat is shut. When
the coolant reaches the predeterminedtemperature the thermostat opens and hot
water passes through the top hose to the top
of the radiator. As the water circulates down
through the radiator, it is cooled by the
passage of air past the radiator when the car is
in forward motion, supplemented by the action
of the thermo-viscous fan when necessary.
Having reached the bottom of the radiator, the
water is now cool and the cycle is repeated.
Circulation of water continues through the
expansion tank, inlet manifold and heater at all
times; the heater temperature control being by
an air flap.
The thermo-viscous fan is controlled by the
temperature of air behind the radiator. When
the air temperature reaches a predetermined
level, a bi-metallic coil commences to open a
valve within the unit and silicon fluid is fed
through a system of vanes. Half of the vanes
are driven directly by the water pump and the
remaining half are connected to the fan blades.
The vanes are arranged so that drive is
transmitted to the fan blades in relation to the
drag or viscosity of the fluid, and this in turn
depends on ambient temperature and engine
speed. The fan is therefore only operated when
required, and compared with direct drive type
fan represents a considerable improvement in
fuel economy, drivebelt wear and fan noise.
Air conditioning
Air conditioning is fitted as standard on
Scorpio models and is optionally available on
some other models. In conjunction with the
heater, the system enables any reasonable air
temperature to be achieved inside the car, it
also reduces the humidity of the incoming air,
aiding demisting even when cooling is not
required.
The refrigeration side of the air conditioning
system functions in a similar way to a
domestic refrigerator. A compressor, belt-
driven from the crankshaft pulley, draws
refrigerant in its gaseous phase from an
evaporator. The compressed refrigerant
passes through a condenser where it loses
heat and enters its liquid phase. After
dehydration the refrigerant returns to the
evaporator where it absorbs heat from air
passing over the evaporator fins. The
refrigerant becomes a gas again and the cycle
is repeated.Various subsidiary controls and sensors
protect the system against excessive
temperature and pressures. Additionally,
engine idle speed is increased when the
system is in use to compensate for the
additional load imposed by the compressor.
Precautions
Antifreeze mixture
Antifreeze mixture is poisonous. Keep it out
of reach of children and pets. Wash splashes
off skin and clothing with plenty of water.
Wash splashes off vehicle paintwork to avoid
discolouration.
Antifreeze/water mixture must be renewed
every two years to preserve its anti-corrosive
properties. In climates where antifreeze
protection is unnecessary, a corrosion
inhibitor may be used instead - consult a Ford
dealer. Never run the engine for long periods
with plain water as coolant. Only use the
specified antifreeze, as inferior brands may not
contain the necessary corrosion inhibitors, or
may break down at high temperatures.
Antifreeze containing methanol is particularly
to be avoided, as the methanol evaporates.
The specified mixture is 45 to 50%
antifreeze and 50 to 55% clean soft water (by
volume). Mix the required quantity in a clean
container.
Air conditioning refrigerant
Although the refrigerant is not itself toxic, in
the presence of a naked flame (or a lighted
cigarette) it forms a highly toxic gas. Liquid
refrigerant spilled on the skin will cause
frostbite. If refrigerant enters the eyes, rinse
them with a dilute solution of boric acid and
seek medical advice immediately.
In view of the above points, and of the need
for specialised equipment for evacuating and
recharging the system, any work which
requires the disconnection of a refrigerant line
must be left to a specialist.
Do not allow refrigerant lines to be exposed
to temperatures above 110°C (230°F) - eg
during welding or paint drying operations and
do not operate the air conditioning system if it
is known to be short of refrigerant, or further
damage may result.
1General information and
precautions
3•2Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Radiator lower mountings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 126 to 9
Thermostat housing bolts:
SOHC, DOHC and 2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2013 to 15
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 105 to 7
Water pump bolts:
SOHC, M8 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2113 to 16
SOHC, M10 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4226 to 31
DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2816 to 21
2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 to 137 to 10
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 105 to 7
Water pump pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2616 to 19
Water pump/alternator drivebelt tensioner bolt (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 9752 to 72
Fan-to-viscous clutch bolts:
SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 106 to 7
V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2313 to 17
Fan shroud bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Cylinder block drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2516 to 18
procarmanuals.com
Page 86 of 255

See Chapter 1, Section 46.
See Chapter 1, Section 46.
See Chapter 1, Section 46.
1Drain the radiator. There is no need to drain
the cylinder block. On DOHC engines the
electric cooling fan assembly must be removed
to gain the clearance to remove the radiator.
2Disconnect the top and bottom hoses from
the radiator by slackening the hose clips and
pulling off the hoses with a twisting motion
(see illustrations). Do not use excessive force
- the radiator side tanks are made of plastic.
3On OHCmodels, disconnect the small hose
running from the expansion tank to the radiator.
4On automatic transmission models, clean
around the transmission fluid cooler unions on
the radiator and disconnect them (seeillustration). Be prepared for fluid spillage;
plug or cap the cooler lines to keep dirt out.
5On models with air conditioning, disconnect
the auxiliary fan thermo-switch. If the thermo-
switch is mounted in the radiator, remove It.
6Remove the upper half of the fan shroud by
removing the two bolts and two clips (see
illustration), and the lower half which is
secured by two bolts.
7Release the two radiator top mounting clips
by pulling out the plastic plugs (see illustration).
8Raise and support the front of the vehicle.
Support the radiator and remove the two
bottom mounting bolts (see illustration).
9Carefully lower the radiator slightly to free
the top mountings, then remove it from under
the vehicle.
10If a new radiator is being fitted, transfer the
fan shrouds and mountings from the old one.
11Refit by reversing the removal operations,
then refill the cooling system.
12On automatic transmission models, check
the transmission fluid level.
1If the radiator has been removed because of
suspected blockage, reverse-flush it.
2Clean dirt and debris from the radiator fins,
using an air jet, or water and a soft brush. Be
careful not to damage the fins, or cut your
fingers. 3A radiator specialist can perform a “flow
test” on the radiator to establish whether an
internal blockage exists.
4A leaking radiator must be referred to a
specialist for permanent repair. Do not attempt
to weld or solder a leaking radiator, as
damage to the plastic parts may result.
5In an emergency, minor leaks from the
radiator can be cured by using a radiator
sealant while the radiator is in situ.
SOHC engines
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Drain the cooling system. As it is not
necessary to completely drain the radiator, the
bottom hose can be disconnected from the
water pump.
3Disconnect the top hose from the
thermostat housing at the front of the cylinder
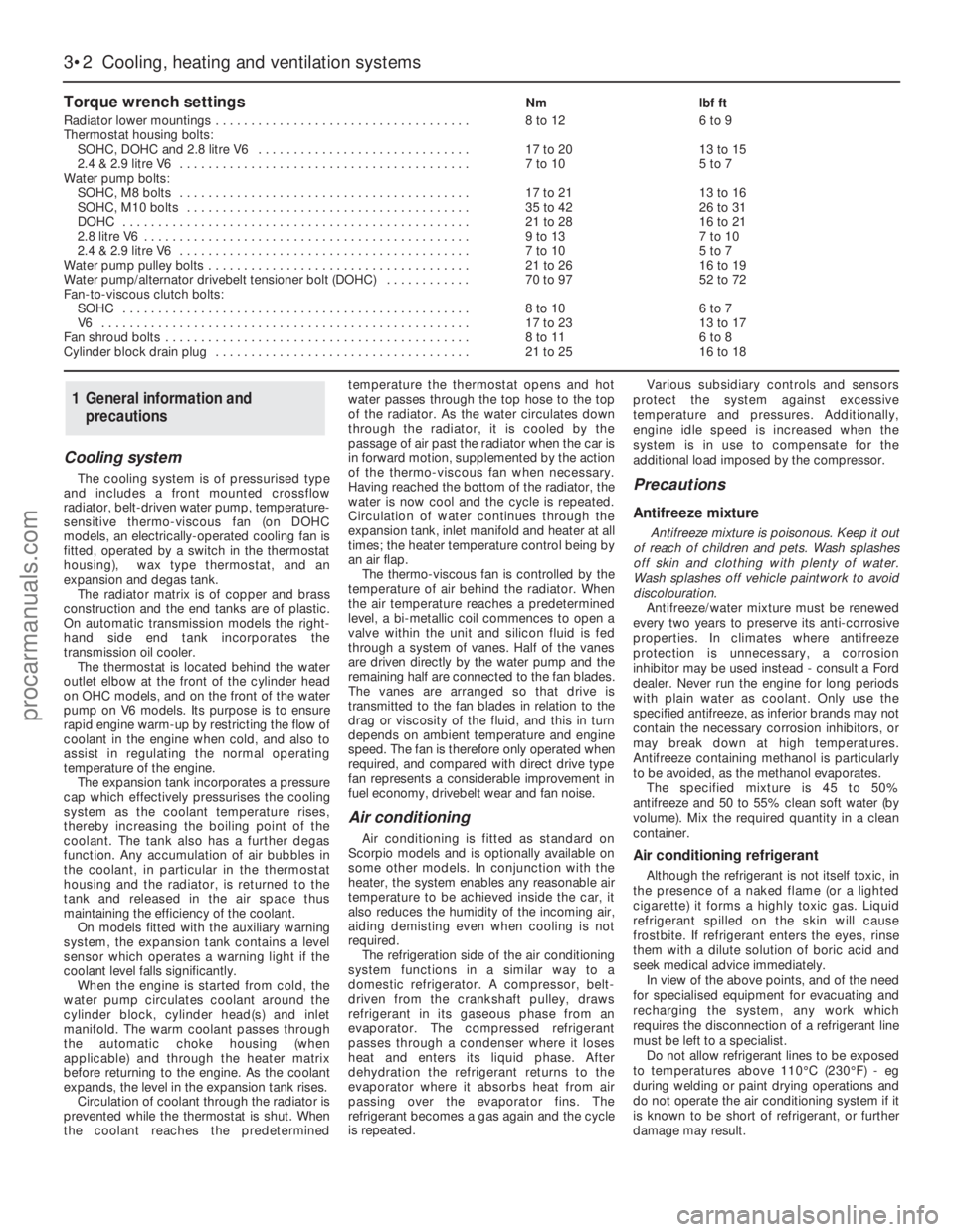
head (see illustration).
4Unscrew the bolts and remove the housing
and gasket (see illustration).
5Using a screwdriver, prise the retaining clip
from the housing, and extract the thermostat
and sealing ring (see illustrations).
6Clean the thermostat housing and cylinder
head mating surfaces. Obtain a new gasket for
reassembly, and if necessary a new sealing
ring too.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations.
7Thermostat - removal and
refitting
6Radiator - inspection and repair
5Radiator - removal and refitting
4Cooling system - filling
3Cooling system - flushing
2Cooling system - draining
Cooling, heating and ventilation systems 3•3
3
5.2a Radiator top hose5.2b Radiator bottom hose (A)
Also shown are automatic transmission fluid
cooler lower union (B) and hose to expansion
tank (C)5.4 Transmission fluid cooler upper union
5.6 Fan shroud clip5.7 Pull out the plug to release the radiator
top mounting5.8 One of the radiator bottom mounting
bolts (arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
Page 87 of 255
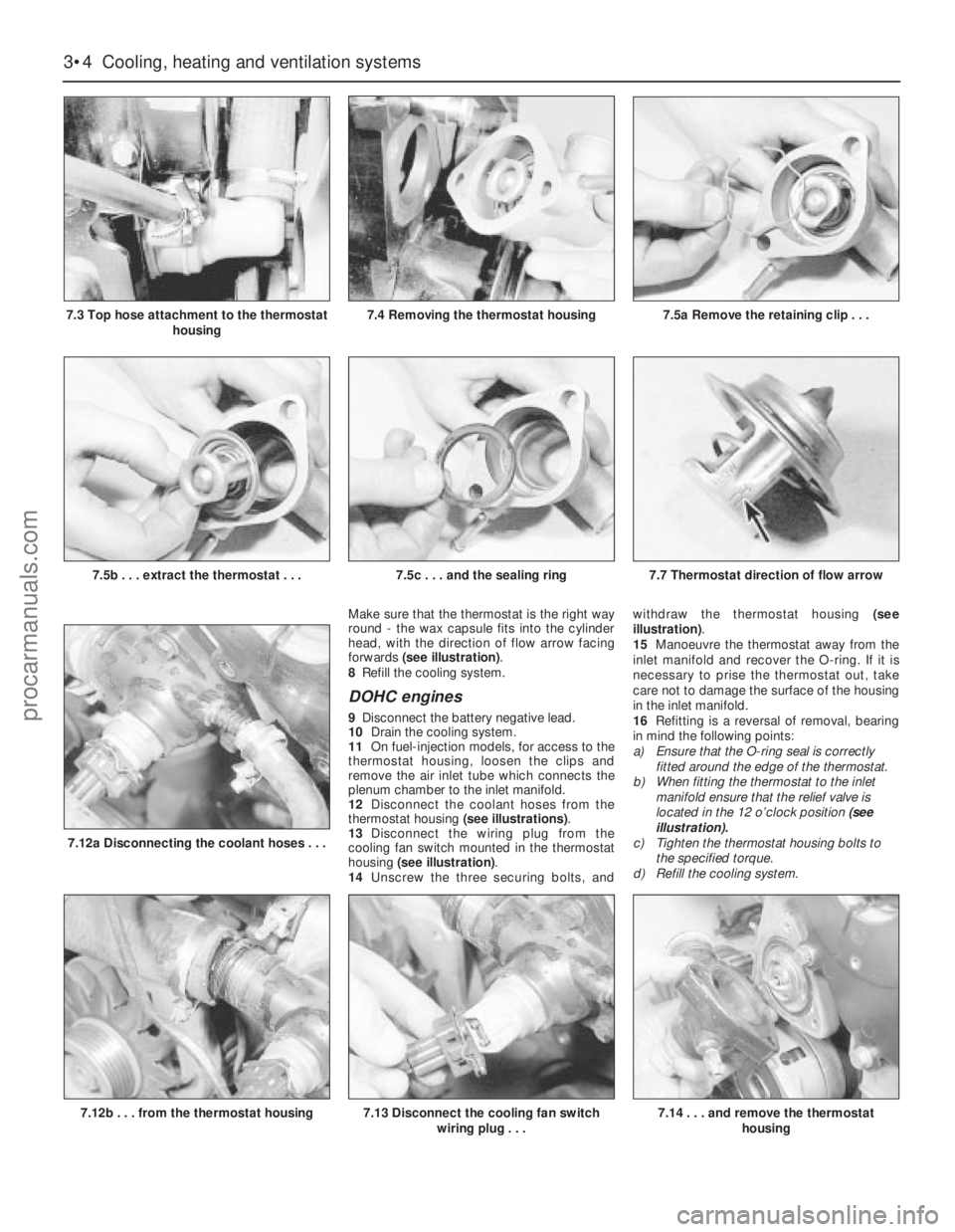
Make sure that the thermostat is the right way
round - the wax capsule fits into the cylinder
head, with the direction of flow arrow facing
forwards (see illustration).
8Refill the cooling system.
DOHC engines
9Disconnect the battery negative lead.
10Drain the cooling system.
11On fuel-injection models, for access to the
thermostat housing, loosen the clips and
remove the air inlet tube which connects the
plenum chamber to the inlet manifold.
12Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
thermostat housing (see illustrations).
13Disconnect the wiring plug from the
cooling fan switch mounted in the thermostat
housing (see illustration).
14Unscrew the three securing bolts, andwithdraw the thermostat housing (see
illustration).
15Manoeuvre the thermostat away from the
inlet manifold and recover the O-ring. If it is
necessary to prise the thermostat out, take
care not to damage the surface of the housing
in the inlet manifold.
16Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points:
a)Ensure that the O-ring seal is correctly
fitted around the edge of the thermostat.
b)When fitting the thermostat to the inlet
manifold ensure that the relief valve is
located in the 12 o’clock position (see
illustration).
c)Tighten the thermostat housing bolts to
the specified torque.
d)Refill the cooling system.
3•4Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
7.3 Top hose attachment to the thermostat
housing
7.12b . . . from the thermostat housing
7.5b . . . extract the thermostat . . .7.5c . . . and the sealing ring7.7 Thermostat direction of flow arrow
7.12a Disconnecting the coolant hoses . . .
7.13 Disconnect the cooling fan switch
wiring plug . . .7.14 . . . and remove the thermostat
housing
7.4 Removing the thermostat housing7.5a Remove the retaining clip . . .
procarmanuals.com
Page 88 of 255

V6 engines
17The thermostat is removed in the course
of water pump removal.
1A rough test of the thermostat may be made
by suspending it with a piece of string in a
saucepan full of water(see illustration).Bring
the water to the boil. The thermostat most
open by the time the water boils. If not, renew
it.
2If a thermometer is available, the precise
opening temperature of the thermostat may be
determined and compared with that given in
the Specifications.
3A thermostat which fails to close as the
water cools must also be renewed.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the upper half of the fan shroud
(two bolts, four clips).
3Undo the nut which secures the fan clutch
to the water pump.This nut has a left-hand
thread, ie it is undone in a clockwise direction.
A thin cranked spanner, 32 mm (OHC) or 36
mm (V6) AF is needed(see illustration);
alternatively, if two of the pulley bolts are
removed, a normal thickness or even anadjustable spanner can be used (see
illustrations). Tap the spanner with a mallet if
need be to release the nut.
4The fan can now be unbolted from the
viscous clutch if required. Do not overtighten
the bolts when refitting.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2To provide additional clearance when
removing the cooling fan shroud assembly
(which is removed from below the vehicle),
apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking”).
3Disconnect the wiring plug(s) from the
motor(s), and where applicable, unclip the
wiring from the fan shroud.
4Unclip the expansion tank hose from the fan
shroud.
5Unscrew the two nuts securing the fan shroud
to the top of the radiator, then tilt the top of theshroud away from the radiator, and lift the
shroud to release the lower securing clips.
Withdraw the assembly from below the vehicle.
6To remove the fan blades, prise the
securing clip from the end of the motor shaft.
7The motor can be separated from the fan
shroud by unscrewing the three securing nuts
and bolts.
8Note that two cooling fans may be fitted,
depending on model. Both fans are secured to
the shroud in the same manner.
9Refitting is a reversal of removal, but when
fitting the fan blades, ensure that the drive dog
on the motor shaft engages with the slot in the
rear of the fan blades.
SOHC engines
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Drain the cooling system.
3Remove the fan and viscous coupling.
4If not already done, remove the pump
drivebelt(s), then unbolt and remove the water
pump pulley (see illustration).
5Disconnect the radiator bottom hose and
the heater return hose from the pump.
6Remove the timing belt cover, which is
secured by three bolts.
11Water pump - removal and
refitting
10Electric cooling fan(s) -
removal and refitting
9Viscous-coupled fan - removal
and refitting
8Thermostat - testing
Cooling, heating and ventilation systems 3•5
3
7.16 Thermostat relief valve (arrowed)
positioned in the 12 o’clock position8.1 Checking the thermostat opening
temperature9.3a Dimensions of spanner for undoing
fan clutch nut. Spanner thickness must not
exceed 5 mm (0.2 in)
9.3b Undoing the viscous fan clutch nut9.3c Removing the fan and clutch11.4 Undoing a water pump pulley bolt
X = 10 mm (0.4 in)
Y = 10 mm (0.4 in)Z = 50 mm (2.0 in)
If problems are experienced
with the pulley turning as the
nut is undone, remove the
drivebelt and clamp an old
drivebelt round the pulley to restrain it,
using self-locking pliers.
procarmanuals.com
Page 89 of 255
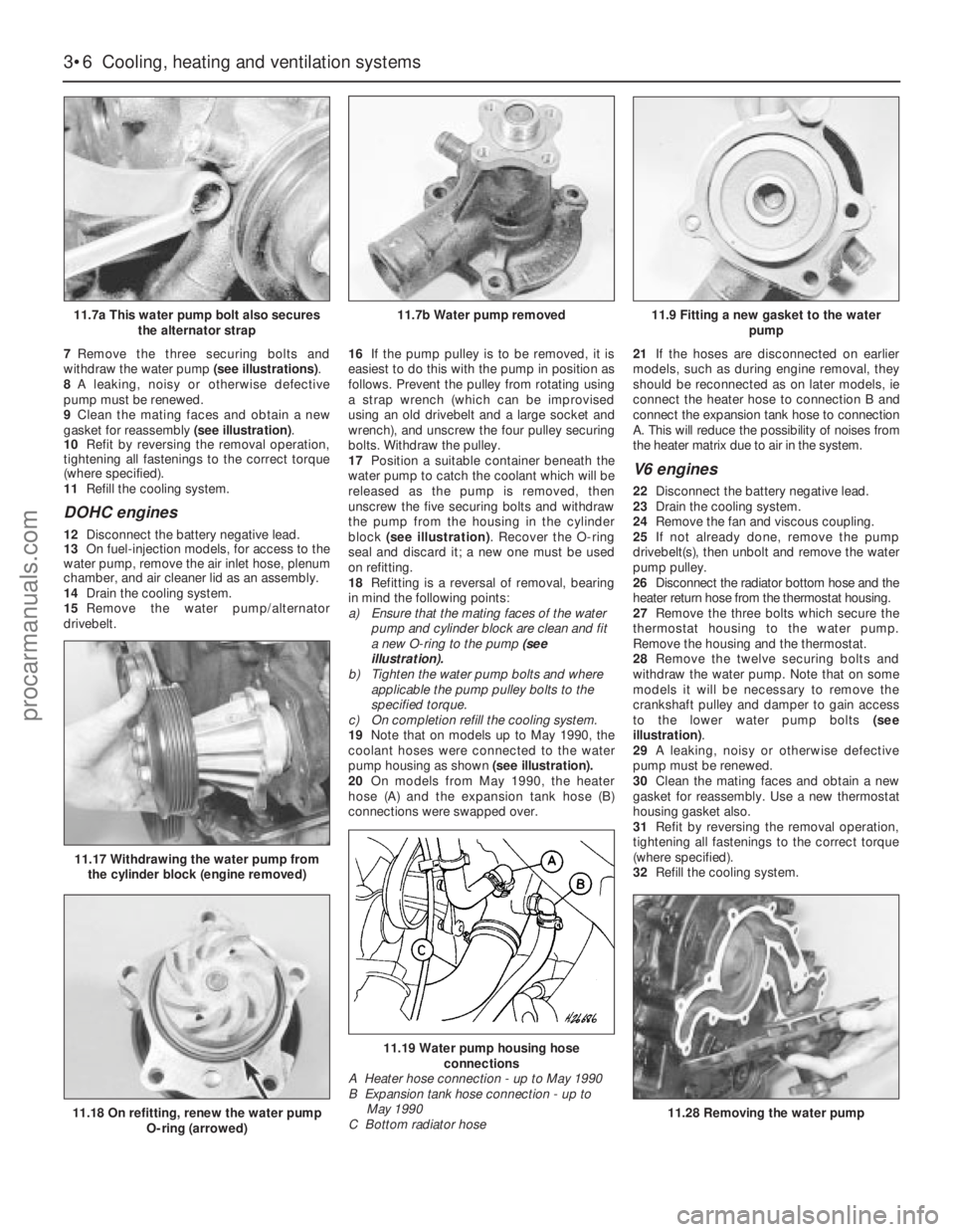
7Remove the three securing bolts and
withdraw the water pump (see illustrations).
8A leaking, noisy or otherwise defective
pump must be renewed.
9Clean the mating faces and obtain a new
gasket for reassembly (see illustration).
10Refit by reversing the removal operation,
tightening all fastenings to the correct torque
(where specified).
11Refill the cooling system.
DOHC engines
12Disconnect the battery negative lead.
13On fuel-injection models, for access to the
water pump, remove the air inlet hose, plenum
chamber, and air cleaner lid as an assembly.
14Drain the cooling system.
15Remove the water pump/alternator
drivebelt.16If the pump pulley is to be removed, it is
easiest to do this with the pump in position as
follows. Prevent the pulley from rotating using
a strap wrench (which can be improvised
using an old drivebelt and a large socket and
wrench), and unscrew the four pulley securing
bolts. Withdraw the pulley.
17Position a suitable container beneath the
water pump to catch the coolant which will be
released as the pump is removed, then
unscrew the five securing bolts and withdraw
the pump from the housing in the cylinder
block (see illustration). Recover the O-ring
seal and discard it; a new one must be used
on refitting.
18Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points:
a)Ensure that the mating faces of the water
pump and cylinder block are clean and fit
a new O-ring to the pump (see
illustration).
b)Tighten the water pump bolts and where
applicable the pump pulley bolts to the
specified torque.
c)On completion refill the cooling system.
19Note that on models up to May 1990, the
coolant hoses were connected to the water
pump housing as shown(see illustration).
20On models from May 1990, the heater
hose (A) and the expansion tank hose (B)
connections were swapped over.21If the hoses are disconnected on earlier
models, such as during engine removal, they
should be reconnected as on later models, ie
connect the heater hose to connection B and
connect the expansion tank hose to connection
A. This will reduce the possibility of noises from
the heater matrix due to air in the system.
V6 engines
22Disconnect the battery negative lead.
23Drain the cooling system.
24Remove the fan and viscous coupling.
25If not already done, remove the pump
drivebelt(s), then unbolt and remove the water
pump pulley.
26Disconnect the radiator bottom hose and the
heater return hose from the thermostat housing.
27Remove the three bolts which secure the
thermostat housing to the water pump.
Remove the housing and the thermostat.
28Remove the twelve securing bolts and
withdraw the water pump. Note that on some
models it will be necessary to remove the
crankshaft pulley and damper to gain access
to the lower water pump bolts (see
illustration).
29A leaking, noisy or otherwise defective
pump must be renewed.
30Clean the mating faces and obtain a new
gasket for reassembly. Use a new thermostat
housing gasket also.
31Refit by reversing the removal operation,
tightening all fastenings to the correct torque
(where specified).
32Refill the cooling system.
3•6Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
11.7a This water pump bolt also secures
the alternator strap
11.18 On refitting, renew the water pump
O-ring (arrowed)
11.17 Withdrawing the water pump from
the cylinder block (engine removed)
11.19 Water pump housing hose
connections
A Heater hose connection - up to May 1990
B Expansion tank hose connection - up to
May 1990
C Bottom radiator hose
11.28 Removing the water pump
11.7b Water pump removed11.9 Fitting a new gasket to the water
pump
procarmanuals.com