1985 FORD GRANADA length
[x] Cancel search: lengthPage 75 of 255

9Inspect the valve springs, if possible
comparing their free length with new springs.
Renew the springs anyway if they have been in
use for 20 000 miles (32 000 km) or more.
10Use a straight-edge and feeler blades to
check that the cylinder head mating faces are
not distorted. If they are, have the heads
resurfaced by an engineering works.
11Commence reassembly by oiling a valve
stem and inserting the valve into its guide.
Cover the collet grooves with adhesive tape
and press the new valve stem oil seal down
the stem, using a suitable tube to press the
seals home. Note that the inlet valve seals are
rubber and the exhaust seals nylon. On the 2.8
litre engine, oversize exhaust valve seals must
be used when valves with oversize stems are
fitted. Remove the adhesive tape.
12Fit the valve spring and spring retainer.
Compress the spring and fit the collets, using
a dab of grease to hold them in position.
Carefully release the compressor.
13Tap the valve stem smartly with a mallet to
seat the components.
14Repeat the process on the remaining valves.
Refer to Part A, Section 28 of this Chapter.
The main bearing caps should be fitted, and
their bolts tightened to the specified torque,
when making bore measurements.
Refer to Part A, Section 29 of this Chapter.
1Refer to Part A, Section 27 of this Chapter for
the examination procedure. Note that regrinding
of this crankshaft is not permitted, so if significant
journal wear is present, a new crankshaft (and
new bearing shells) must be fitted.
2As with the SOHC engine, oversize main
bearing parent bores may be encountered.
These are marked with paint stripes on the
bearing caps, corresponding paint marks on
the bearing shells and identification codes on
the backs of the bearing shells.
3On the 2.4 litre engine, separate
thrustwashers are used to control crankshaft
endfloat. On the 2.9 litre engine, No 3 main
bearing shells have integral thrust flanges.
2.8 litre engine
1If oil pump wear is suspected, check the
cost and availability of new parts and the cost
of a new pump. Examine the pump and then
decide whether renewal or repair is the best
course of action (see illustration).2Remove the pick-up pipe and strainer.
3Note the position of the oil pump cover
relative to the body, then remove the bolts and
spring washers. Lift off the cover.
4Mark the rotor faces so that they can be
refitted the same way round, then remove
them from the body.
5Remove the pressure relief valve plug by
piercing it with a punch and levering it out.
Withdraw the spring and plunger.
6Thoroughly clean all parts in petrol or paraffin
and wipe dry using a non-fluffy rag. The
necessary clearances may now be checked
using a machined straight-edge (a good steel
rule) and a set of feeler blades. The critical
clearances are between the lobes of the centre
rotor and convex faces of the outer rotor;
between the rotor and pump body; and between
both rotors and the end cover plate (endfloat).
The clearances are given in the Specifications.
7Endfloat may be measured by refitting the
rotors, placing the straight-edge across the
bottom of the pump and measuring the clearance
between the two rotors and the straight-edge.
8New rotors are only available as a pair. If the
rotor-to-body clearance is excessive, a
complete new pump should be fitted.
9Commence reassembly by lubricating the
relief valve plunger. Fit the plunger and spring.
10Fit a new relief valve plug, flat side
outwards and seat it with a drift, until it is flush
with the pick-up pipe mating face.
11Lubricate the rotors and fit them,
observing the marks made when dismantling if
applicable.
12Fit the cover and secure it with the bolts
and spring washers. Tighten the bolts to the
specified torque.
13Fit the pick-up pipe and strainer, using a
new gasket.
14Temporarily insert the driveshaft into the
pump and make sure that the rotors turn freely.
15A new or overhauled pump must be
primed before fitting.2.4 & 2.9 litre engines
16Oil pump overhaul is essentially as
described for the 2.8 litre engine, noting the
differences in design of the components (see
illustrations).
27Oil pump - dismantling,
examination and reassembly
26Crankshaft and bearings -
examination
25Pistons and connecting rods
- examination and renovation
24Cylinder bores - examination
and renovation
2C•14V6 engines
27.16a Removing the pick-up from the oil
pump
27.1 Exploded view of the oil pump
1 Body
2 Bolt
3 Bolts
4 Lockwasher
5 Driveshaft
6 Toothed washer
7 Rotor set
8 Pressure relief valve plunger
9 Pressure relief valve spring
10 Pressure relief valve plug
11 Cover
12 Pick-up pipe and strainer
procarmanuals.com
Page 78 of 255

1Make sure that the oil pump and crankcase
mating faces are clean.
2Check that the washer on the oil pump
driveshaft is located correctly (see illustration).
3If a new or overhauled pump is being fitted,
prime it by injecting oil into it and turning it by
hand.
4Insert the oil pump driveshaft into the block
with the pointed end towards the distributor
(see illustration).
5Fit the assembled oil pump, using a new
gasket. Insert the pump-to-block bolts and
tighten them to the specified torque (see
illustration).
6Refit the sump.Refer to Part A, Section 40 of this Chapter.
2.8 litre engines
1Lubricate a new oil seal and fit it to the
timing cover (see illustration).
2If the Woodruff keys were removed from the
camshaft and crankshaft, refit them.
3Refit the crankshaft gear, if removed, using
a length of tube to drive it home.
4Position the camshaft and crankshaft so
that their keyways are facing each other(seeillustration).Slide the camshaft gear onto the
camshaft, rotating the shafts slightly if
necessary so that the marks on the two gears
are aligned. Remember that there are two
marks on the crankshaft gear.
5Fit the camshaft gear retaining bolt and
washer(see illustration).Tighten the bolt to
the specified torque.
6Apply sealant to the mating faces of the
timing cover and the intermediate plate.
7Position a new gasket on the intermediate
plate and fit the timing cover to the cylinder
block (see illustrations).
8Fit the timing cover bolts, but do not tighten
them yet.
9Oil the sealing face of the crankshaft pulley
or damper. Fit the pulley/damper and the
central bolt and washer, applying sealant to
the inboard face of the washer (see
illustration). Draw the pulley/damper into
36Timing cover and drive -
refitting
35Flywheel/driveplate and
adapter plate - refitting34Oil pump - refitting
V6 engines 2C•17
2C
34.2 Oil pump driveshaft washer location34.4 Fitting the oil pump driveshaft34.5 Oil pump in position
36.7a Timing cover gasket in position
36.1 Timing cover oil seal36.5 Camshaft gear washer and bolt36.4 Crankshaft and camshaft gears
correctly aligned
36.7b Fitting the timing cover36.9 Fitting the crankshaft pulley
procarmanuals.com
Page 90 of 255

See Chapter 1, Section 21.
1On 2.0 litre DOHC engines only, remove the
water pump/alternator drivebelt as described
in the previous Section.
2Loosen the alternator lower mounting
through-bolt, then remove the alternator upper
mounting bolt, and swing the alternator away
from the engine.
3Unscrew the central securing bolt, and
withdraw the drivebelt tensioner assembly.
4Commence refitting by positioning the
tensioner on the cylinder block, ensuring that
the lug on the rear of the tensioner bracket
engages with the corresponding hole in the
cylinder block (see illustration). Tighten the
securing bolt.
5Swing the alternator into position to align
the upper mounting bolt hole with the
corresponding hole in the drivebelt tensioner
assembly, then refit and tighten the upper
mounting bolt, then the lower throughbolt.
6Check the full length of the drivebelt for cracks
and deterioration and renew if necessary.
7Fit the drivebelt using a reversal of the
removal procedure, and release the tensioner
to tension the drivebelt.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Depressurize the cooling system by
unscrewing the expansion tank cap. Take
precautions against scalding if the system
is hot.
3Slacken the hose clips on all the hoses
which are connected to the tank. Pull off and
plug those hoses which are above the
waterline.4Remove the two screws which secure the
tank. Tilt the tank so that the coolant lies away
from the outlets, then disconnect and plug the
remaining hose.
5Disconnect the coolant level sensor, when
fitted, and remove the tank.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Top-up the cooling system on completion.
1The temperature gauge sender is located
towards the front of the engine. On SOHC
models it is just below the inlet manifold (see
illustration); on V6 models it is just below the
top hose connection on the front of the left-
hand cylinder head, and on DOHC models it is
located at the front of the inlet manifold (see
illustration).
2Slacken the expansion tank cap to release
pressure in the cooling system, taking
precautions against scalding if the system
is hot.Tighten the cap again to minimise
coolant loss.
3Disconnect the wiring from the sender unit.
Unscrew and remove it, being prepared for
some coolant spillage.
4Smear sealant on the sender unit threads
before refitting, then insert and tighten it.
Reconnect the wiring.
5Top-up the cooling system if necessary,
then run the engine and check the operation of
the temperature gauge.The cooling fan switch is located in the end
of the thermostat housing.
Removal and refitting of the switch is as
described for the temperature gauge sender in
the previous Section.
Models before April 1992
Front
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the instrument cluster (Chapter 13).
3Remove the facia top (Chapter 12).
4Unclip the two control cables from the
control levers (see illustration).
5On air conditioned models, disconnect the
hoses from the vacuum switch.
6Remove the four screws which secure the
heater control assembly. Withdraw the
assembly from the facia.
7When refitting, secure the control assembly
with the four screws. Reconnect the vacuum
switch (when applicable) and the control
cables. Adjust the control cables if necessary
by altering the positions of the cable clips.
8When satisfied with the operation of the
cables, refit the other disturbed components.
Rear
9Remove the centre console (Chapter 12).
10Unclip the control cables and remove the
control unit.
11Refit in the reverse order to removal.
Models from April 1992
12Undo the two instrument panel surround
retaining screws, then carefully release the
retaining clips and remove the surround from
the facia.
13Pull off the three knobs from the heater
and ventilation controls to gain access to the
two hidden central vent panel retaining
screws. Slacken and remove the four panel
retaining screws and partially withdraw the
17Heater controls - removal and
refitting
16Cooling fan switch - removal
and refitting
15Temperature gauge sender -
removal and refitting
14Expansion tank - removal and
refitting
13Water pump/alternator
drivebelt tensioner - removal
and refitting
12Water pump/alternator
drivebelt(s) - inspection,
renewal and adjustment
Cooling, heating and ventilation systems 3•7
3
13.4 On refitting, ensure the drivebelt
tensioner lug (A) engages with hole in the
mounting bracket (B)15.1a Temperature gauge sender (manifold
removed)15.1b Temperature gauge sender unit
location (arrowed)
17.4 Heater control cable clip (arrowed)
viewed through windscreen
procarmanuals.com
Page 106 of 255
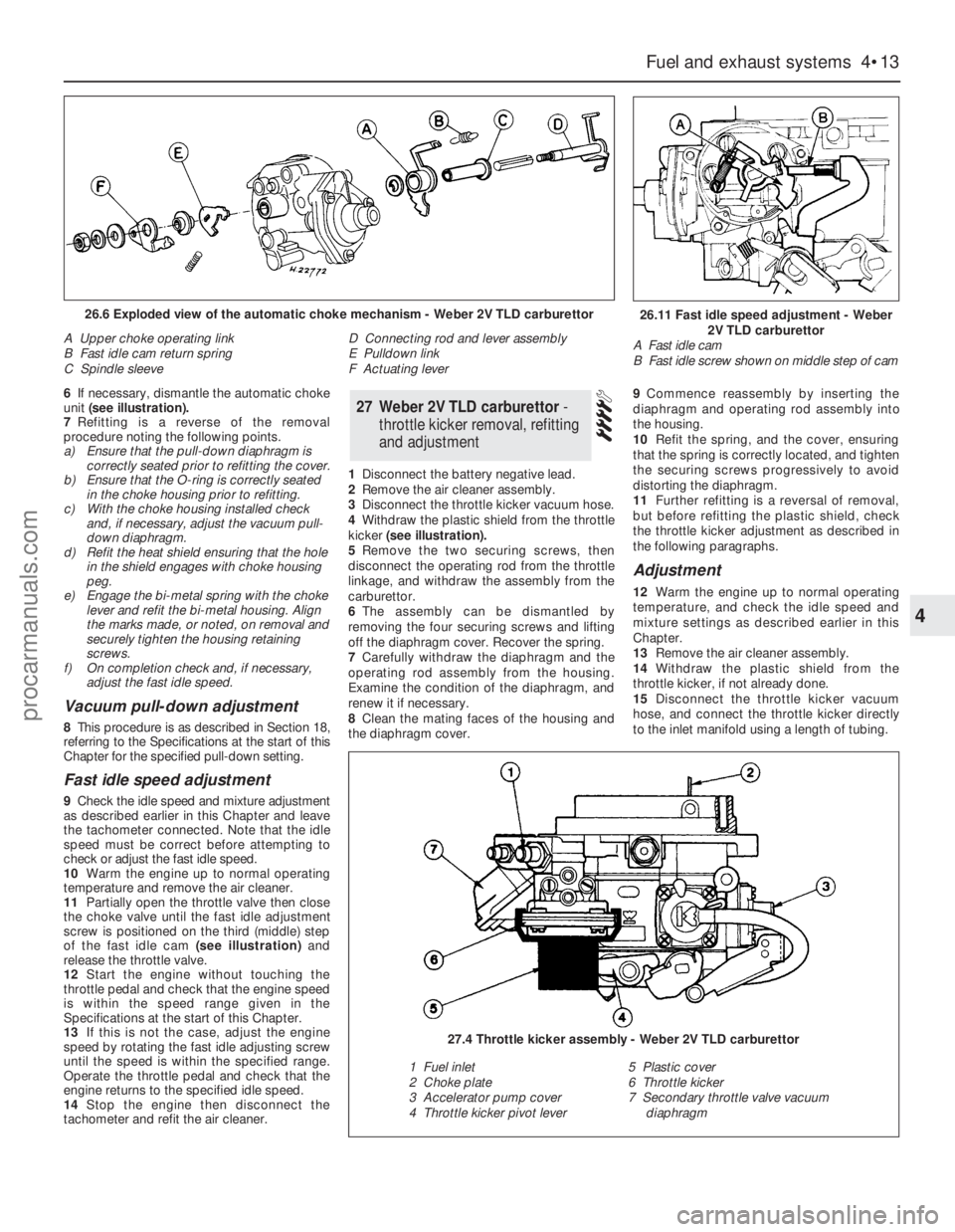
6If necessary, dismantle the automatic choke
unit (see illustration).
7Refitting is a reverse of the removal
procedure noting the following points.
a)Ensure that the pull-down diaphragm is
correctly seated prior to refitting the cover.
b)Ensure that the O-ring is correctly seated
in the choke housing prior to refitting.
c)With the choke housing installed check
and, if necessary, adjust the vacuum pull-
down diaphragm.
d)Refit the heat shield ensuring that the hole
in the shield engages with choke housing
peg.
e)Engage the bi-metal spring with the choke
lever and refit the bi-metal housing. Align
the marks made, or noted, on removal and
securely tighten the housing retaining
screws.
f)On completion check and, if necessary,
adjust the fast idle speed.
Vacuum pull-down adjustment
8This procedure is as described in Section 18,
referring to the Specifications at the start of this
Chapter for the specified pull-down setting.
Fast idle speed adjustment
9Check the idle speed and mixture adjustment
as described earlier in this Chapter and leave
the tachometer connected. Note that the idle
speed must be correct before attempting to
check or adjust the fast idle speed.
10Warm the engine up to normal operating
temperature and remove the air cleaner.
11Partially open the throttle valve then close
the choke valve until the fast idle adjustment
screw is positioned on the third (middle) step
of the fast idle cam(see illustration)and
release the throttle valve.
12Start the engine without touching the
throttle pedal and check that the engine speed
is within the speed range given in the
Specifications at the start of this Chapter.
13If this is not the case, adjust the engine
speed by rotating the fast idle adjusting screw
until the speed is within the specified range.
Operate the throttle pedal and check that the
engine returns to the specified idle speed.
14Stop the engine then disconnect the
tachometer and refit the air cleaner.1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the air cleaner assembly.
3Disconnect the throttle kicker vacuum hose.
4Withdraw the plastic shield from the throttle
kicker(see illustration).
5Remove the two securing screws, then
disconnect the operating rod from the throttle
linkage, and withdraw the assembly from the
carburettor.
6The assembly can be dismantled by
removing the four securing screws and lifting
off the diaphragm cover. Recover the spring.
7Carefully withdraw the diaphragm and the
operating rod assembly from the housing.
Examine the condition of the diaphragm, and
renew it if necessary.
8Clean the mating faces of the housing and
the diaphragm cover.9Commence reassembly by inserting the
diaphragm and operating rod assembly into
the housing.
10Refit the spring, and the cover, ensuring
that the spring is correctly located, and tighten
the securing screws progressively to avoid
distorting the diaphragm.
11Further refitting is a reversal of removal,
but before refitting the plastic shield, check
the throttle kicker adjustment as described in
the following paragraphs.
Adjustment
12Warm the engine up to normal operating
temperature, and check the idle speed and
mixture settings as described earlier in this
Chapter.
13Remove the air cleaner assembly.
14Withdraw the plastic shield from the
throttle kicker, if not already done.
15Disconnect the throttle kicker vacuum
hose, and connect the throttle kicker directly
to the inlet manifold using a length of tubing.
27Weber 2V TLD carburettor -
throttle kicker removal, refitting
and adjustment
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•13
4
26.11 Fast idle speed adjustment - Weber
2V TLD carburettor
A Fast idle cam
B Fast idle screw shown on middle step of cam26.6 Exploded view of the automatic choke mechanism - Weber 2V TLD carburettor
A Upper choke operating link
B Fast idle cam return spring
C Spindle sleeveD Connecting rod and lever assembly
E Pulldown link
F Actuating lever
27.4 Throttle kicker assembly - Weber 2V TLD carburettor
1 Fuel inlet
2 Choke plate
3 Accelerator pump cover
4 Throttle kicker pivot lever5 Plastic cover
6 Throttle kicker
7 Secondary throttle valve vacuum
diaphragm
procarmanuals.com
Page 121 of 255

1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead.
2Disconnect the battery positive leads. These
may be protected by a plastic cover. Do not
allow the spanner to bridge the positive and
negative terminals.
3Release the battery hold-down clamp. Lift
out the battery. Keep it upright and be careful
not to drop it - it is heavy.
4Commence by placing the battery in its tray,
making sure it is the right way round. Secure it
with the hold-down clamp.
5Clean the battery terminals if necessary
then reconnect them. Connect the positive
lead first, then the negative lead.
1Should it appear that the alternator is not
charging the battery, check first that the
drivebelt is intact and in good condition and
that its tension is correct. Also check the
condition and security of the alternator
electrical connections and the battery leads.
2Accurate assessment of alternator output
requires special equipment and a degree of
skill. A rough idea of whether output is
adequate can be gained by using a voltmeter
(range 0 to 15 or 0 to 20 volts) as follows.
3Connect the voltmeter across the battery
terminals. Switch on the headlights and note
the voltage reading: it should be between 12
and 13 volts.
4Start the engine and run it at a fast idle
(approx 1500 rpm). Read the voltmeter: it
should indicate 13 to 14 volts.
5With the engine still running at a fast idle,
switch on as many electrical consumers as
possible (heated rear window, heater blower
etc). The voltage at the battery should be
maintained at 13 to 14 volts. Increase the
engine speed slightly if necessary to keep the
voltage up.
6If alternator output is low or zero, check the
brushes. If the brushes are OK, seek expert
advice.7Occasionally the condition may arise where
the alternator output is excessive. Clues to this
condition are constantly blowing bulbs;
brightness of lights vary considerably with
engine speed; overheating of alternator and
battery, possible with steam or fumes coming
from the battery. This condition is almost
certainly due to a defective voltage regulator,
but expert advice should be sought.
8Note that the alternator voltage regulator
can be renewed without removing the
alternator from the vehicle. The procedure is
part of brush renewal.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the multi-plug from the rear of
the alternator. It may be secured by a wire clip.
3Slacken the alternator adjusting and pivot
nut(s), bolt(s)and washer(s)(see illustration).
Swing the alternator towards the engine and
slip the drivebelt(s) off the pulley.
4Support the alternator. Remove the
adjusting and pivot nuts, bolts and washers,
noting the fitted positions of the washers. Lift
out the alternator. Do not drop it, it is fragile.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Tension the drivebelt(s) then tighten the
adjustment strap bolt followed by the pivot nut
and bolt. If there are two pivot bolts, tighten
the front one first.
6Refit the multi-plug and reconnect the
battery.
1The alternator brushes can be inspected or
renewed without removing the alternator from
the vehicle, but disconnect the battery
negative lead first.
2From the rear of the alternator remove the
two screws which secure the voltage
regulator/brush carrier assembly. Withdraw
the assembly (see illustration).
3Measure the length of each brush
protruding from the carrier (see illustration). If
they are worn down to, or below, the minimumspecified, the old brushes will have to be
unsoldered and new ones soldered into place.
Some skill with a soldering iron will be
required; excess heat from the soldering iron
could damage the voltage regulator. When
fitted, the new brushes must move freely in
their holders.
4Clean the slip rings with a cloth moistened
with methylated spirit (see illustration). If they
are badly burnt or damaged, seek expert
advice.
5Refit the assembled brush carrier/voltage
regulator and secure it with the two screws. If
the alternator is on the vehicle, reconnect the
battery negative lead.
1If the starter motor fails to operate, first
check that the battery is charged by switching
on the headlights. If the headlights do not
come on, or rapidly become dim, the battery
or its connections are at fault.
2Check the security and condition of the
battery and starter solenoid connections.
Remember that the heavy lead to the solenoid
is always “live” - disconnect the battery
negative lead before using tools on the
solenoid connections.
8Starter motor - testing on the
vehicle7Alternator - brush renewal
6Alternator - removal and
refitting
5Alternator - testing on the
vehicle
4Battery - removal and refitting
5•4Engine electrical systems
7.3 Measuring brush protrusion7.4 Clean the slip rings (arrowed)
6.3 Alternator mounting details
A Large washer
B Small washer (not always fitted)
C Mounting bracket
D Alternator
Some models have a single pivot bolt
7.2 Removing the voltage regulator/brush
carrier
procarmanuals.com
Page 132 of 255

Note: Hydraulic fluid is poisonous; wash off
immediately and thoroughly in the case of skin
contact and seek immediate medical advice if
any fluid is swallowed or gets into the eyes.
Certain types of hydraulic fluid are inflammable
and may ignite when allowed into contact with
hot components; when servicing any hydraulic
system it is safest to assume that the fluid is
inflammable and to take precautions against
the risk of fire as though it is petrol that is
being handled. Finally, it is hygroscopic (it
absorbs moisture from the air) old fluid may be
contaminated and unfit for further use. When
topping-up or renewing the fluid, always use
the recommended type and ensure that it
comes from a freshly-opened sealed container
1Bleeding is necessary whenever air has
entered the hydraulic system - for instance
after component renewal. Because the
hydraulic circuits are split, if only the front or
rear circuit has been disturbed it will normally
only be necessary to bleed the front or rear
calipers. If the hydraulic unit has been
disturbed or the fluid level has been allowed to
fall so low that air has entered the system,
both front and rear circuits must be bled,
starting with the front
2The services of an assistant will be required.
As far as is known, pressure bleeding or other
“one-man” equipment cannot be used. In
addition a supply of fresh brake fluid of the
correct type will be needed, together with a
length of flexible tube to fit the bleed screws
and a clean glass or plastic container.
3Do not allow the hydraulic unit pump motor
to run for more than two minutes at a time. The
motor must be allowed to cool (with the
ignition off) for at least ten minutes after each
two minute spell of running.
4Remember that brake fluid is poisonous and
that the rear brake hydraulic system may be
under considerable pressure. Take care not to
allow hydraulic fluid to spray into the face or
eyes.
5Keep the reservoir topped up to the MAX
mark during bleeding.
6Discard the fluid bled out of the system as it
is unfit for re-use.
Models before April 1992
Front brakes
7Remove the dust cap (if fitted) from the left-
hand caliper bleed screw. Slacken the bleed
screw, then nip it up again. Make sure that the
ignition is off.8Fit the bleed tube over the bleed screw.
Place the other end of the tube in the bleed jar
(glass or plastic container). Pour sufficient
brake fluid into the jar to cover the end of the
tube.
9Open the bleed screw one full turn. Have
the assistant depress the brake pedal as far as
it will go, and hold it depressed. Tighten the
bleed screw, then tell the assistant to release
the pedal.
10Repeat paragraph 9 until clean fluid, free
of air bubbles, flows from the bleed screw
during the downstrokes. Remember to keep
the fluid reservoir topped up.
11Repeat the operations on the right-hand
caliper. Refit the bleed screw dust caps (if
applicable) on completion.
Rear brakes
12Remove the dust cap (if fitted) from the
rear left-hand caliper bleed screw. Open the
bleed screw one full turn.
13Fit the bleed tube over the bleed screw.
Place the other end of the tube in the bleed jar
(see illustration).
14Have the assistant depress the brake
pedal as far as it will go and hold it down.
Switch on the ignition: the hydraulic unit pump
will start and fluid will flow from the bleed
screw.
15When clean fluid, free of air bubbles,
emerges from the bleed screw, tighten the
bleed screw and have the assistant release the
pedal.
16Wait for the hydraulic unit pump to stop,
then top-up the reservoir and repeat the
procedure on the right-hand caliper. This time
the brake pedal should only be depressed
half-way.
17Switch off the ignition, top-up the reservoir
again and refit the reservoir cap. Refit the
bleed screw dust caps (if applicable).
Models from April 1992
18This operation can be carried out using the
information given above inparagraphs 1 to 10,
ignoring the reference to the hydraulic unit
pump and bearing in mind the following.
19Note that if only one circuit is disturbed it
will only be necessary to bleed that relevant
circuit on completion.20If the complete system is to be bled, it
should be done in the following order.
a)Left-hand front caliper.
b)Right-hand front brake caliper.
c)Left-hand rear caliper.
d)Right-hand rear caliper.
See Chapter 1, Section 44.
1Whenever the brake pads are inspected,
also inspect the brake discs for deep
scratches, scores or cracks. Light scoring is
normal and may be ignored. A cracked disc
must be renewed; scratches and scores can
sometimes be machined out, provided that the
thickness of the disc is not reduced below the
specified minimum.
2When the brake pads are renewed, or if
brake judder or snatch is noticed, check the
discs for run-out and thickness variation. (Note
that wheel bearing wear can cause disc run-
out.)
3Position a dial test indicator probe against
the disc wear face, approximately 15 mm (0.6 in)
in from the outer circumference. Zero the
indicator, rotate the disc and read the run-out
from the indicator(see illustration).Maximum
run-out is given in the Specifications. If a dial
test indicator is not available, use a fixed
pointer and feeler blades.
4Measure the thickness of the disc, using a
micrometer, in eight evenly spaced positions
around the disc. Maximum thickness variation
is given in the Specifications. Renew the disc if
the variation is out of limits.
1Slacken the front wheel nuts, raise and
support the vehicle and remove the relevant
front wheel.
2Remove the two bolts which hold the caliper
bracket to the stub axle carrier. Lift the caliper
5Front brake disc - removal and
refitting
4Brake discs - inspection
3Brake hydraulic system - fluid
renewal
2Brake hydraulic system -
bleeding
Braking system 10•3
10
2.13 Bleeding a rear brake caliper
4.3 Measuring brake disc run-out
Hydraulic fluid is an effective
paint stripper and will attack
plastics; if any is spilt, it
should be washed off
immediately using copious quantities of
fresh water.
procarmanuals.com
Page 148 of 255

reference to horn switch plate retaining
screws. Note that the wheel is retained by a
bolt, not a nut as on earlier models. To gain
access to the bolt, prise out the horn button
and disconnect the wiring connectors.
1This operation is for correcting small errors
in steering wheel centralisation - up to 60°. For
larger errors, remove the steering wheel and
make a rough correction by repositioning the
wheel on refitting.
2Drive the vehicle in a straight line on a level
surface. Note the angle by which the steering
wheel deviates from the desired straight-
ahead position.
3Raise the front of the vehicle by driving it
onto ramps, or with a jack and axle stands
(see “Jacking”).
4Slacken both track rod end locknuts. Also
slacken the steering rack bellows outer clips.
5Make alignment marks between each track
rod end and its rod, so that the amount of
rotation applied can be accurately determined.
6Turn both track rodsin the same direction
to correct the steering wheel position. As a
rough guide, 19°of track rod rotation will
change the steering wheel position by 1°. To
correct error at the steering wheel, rotate both
track rods anti-clockwise (viewed from the
left-hand side of the vehicle), and the reverse
to correct as anti-clockwise errors. Both track
rods must be rotated by the same amount.
7Tighten the bellows clips and the track rod
end locknuts when adjustment is correct.
Lower the vehicle.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Position the steering in the straight-ahead
position.
3Remove the steering wheel. This is not
essential, but will improve access.
4Working under the bonnet, disconnect the
intermediate shaft universal joint from the
steering column shaft.5Remove the steering column shrouds and
disconnect the switch multi-plugs. Do not
forget the ignition/starter switch.
6Disconnect the bonnet release cable from the
operating lever on the underside of the column.
7Prise out the driver’s side air vent. Remove
the under-dash insulation and trim panel on
the driver’s side, unclipping the bulb failure
module, where applicable.
8Remove the three nuts which secure the
column height adjuster to the mounting bracket
(see illustration). Remove the column assembly
by drawing it into the vehicle. Do not drop it or
otherwise mistreat it if it is to be re-used.9When refitting, have an assistant guide the
column shaft into the intermediate shaft
universal joint. Secure the column with the
three nuts inside the vehicle and adjust it to
the minimum length position, then tighten the
coupling pinch-bolt.
10Complete refitting by reversing the
removal operations.
1Remove the steering column (see
illustration).
2Insert the key into the lock and turn it to
position 1. (If the lock has failed so that the key
will not enter, destructive methods will have to
be used.)
8Steering column lock - removal
and refitting
7Steering column - removal and
refitting
6Steering wheel - centralising
Steering and suspension 11•5
11
7.8 Two of the three nuts (arrowed) which
secure the column height adjuster
8.1 View of steering wheel and column
A Steering wheel
B Mounting bracket and
spring
C Thrust washer and spring
D Lower bearingE Height adjuster
F Column shaft and spire
washer
G Multi-function switchH Ignition/steering lock
I Horn brush unit
J Upper bearing
K Multi-function switch
Make alignment marks
between the two shafts for
reference when reassembling.
procarmanuals.com
Page 150 of 255

6When refitting, screw the track rod end onto
the track rod as far as the locknut, then back it
off half a turn.
7Insert the ball-pin into the steering arm.
Tighten the balljoint nut to the specified torque
and secure with a new split pin. Nip up the
track rod end locknut, but do not tighten it fully
yet.
8Refit the roadwheel, lower the vehicle and
tighten the wheel nuts to the specified torque.
9Check the toe setting as described in the
following Section. (This may not be strictly
necessary if the same track rod end has been
refitted, but is certainly advisable if any
components have been renewed.)
10Tighten the track rod end locknut when
toe is correct.
1Front wheel alignment is defined by camber,
castor, steering axis inclination and toe
setting. The first three factors are determined
in production; only toe can be adjusted in
service. Incorrect toe will cause rapid tyre
wear (see illustration).
2Toe is defined as the amount by which the
distance between the front wheels, measured
at hub height, differs from the front edges to
the rear edges. If the distance between the
front edges is less than that at the rear, the
wheels are said to toe-in; the opposite case is
known as toe-out.3To measure toe, it will be necessary to
obtain or make a tracking gauge. These are
available in motor accessory shops, or one
can be made from a length of rigid pipe or bar
with some kind of threaded adjustment facility
at one end. Many tyre specialists will also
check toe free, or for a nominal sum.
4Before measuring toe, check that all
steering and suspension components are
undamaged and that tyre pressures are
correct. The vehicle must be at approximately
kerb weight, with the spare wheel and jack in
their normal positions and any abnormal loads
removed.
5Park the vehicle on level ground and bounce
it a few times to settle the suspension.
6Use the tracking gauge to measure the
distance between the inside faces of the front
wheel rims, at hub height, at the rear of the
front wheels. Record this distance; call it
measurement A.
7Push the vehicle forwards or backwards so
that the wheels rotate exactly 180°(half a turn).
Measure the distance between the front wheel
rims again, this time at the front of the wheels.
Record this distance; call it measurement B.
8Subtract measurement B from
measurement A. If the answer is positive it is
the amount of toe-in; if negative it is the
amount of toe-out. Permissible values are
given in the Specifications.
9If adjustment is necessary loosen the track
rod end locknuts and the outer bellows clips,
then rotate each track rod by equal amounts
until the setting is correct. Hold the track rod
ends in their horizontal position with a spanner
while making the adjustment.
10Tighten the locknuts and outer bellows
clips.
11Provided the track rods have been
adjusted by equal amounts the steering wheel
should be central when moving straight-
ahead. The amount of visible thread on each
track rod should also be equal.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Raise and securely support the front of the
vehicle.
3Remove the suspension lower arm pivot
nuts and bolts (see illustration). Disengage
the arms from the crossmember.
4Disconnect the steering column shaft from
the intermediate shaft universal joint.
5Remove the two bolts which secure the
steering gear to the crossmember. Draw the
steering gear forwards so that it is clear of the
crossmember and support it by wiring it to the
frame rails.
6It is now necessary to support the engine,
preferably from above, using a hoist or an
adjustable support bar resting on the wings or
suspension turrets. Alternatively a jack and
some wooden blocks may be used frombelow, but this is bound to obstruct access to
some extent.
7Remove the engine mounting lower
securing nuts. Raise the engine until the
mountings are just clear of the crossmember.
8Release the brake pipe clips from the
crossmember and slide the brake pipes from
their slots. Be careful not to strain the pipes.
9Support the crossmember and remove its
four securing bolts. Lower the crossmember
and remove it from the vehicle.
10Commence refitting by offering the
crossmember to the frame rails. Insert the four
securing bolts and tighten them to the
specified torque.
11Secure the brake pipes to the
crossmember.
12Refit the steering gear to the
crossmember. Tighten its securing bolts to the
specified torque.
13Insert the suspension arms into the
crossmember and secure them with the pivot
bolts and nuts. Do not tighten the nuts and
bolts yet, just nip them up.
14Lower the engine onto the crossmember.
Make sure that the engine mountings locate
correctly into the holes in the crossmember.
Tighten the engine mounting nuts. The engine
support bar or hoist can now be removed.
15Reconnect the steering column shaft to
the intermediate shaft. Tighten the pinch-bolt
to the specified torque.
16Lower the vehicle onto its wheels, then
tighten the lower arm pivot bolts to the
specified torque.
17Reconnect the battery.
1Slacken the front wheel nuts. Raise and
support the front of the vehicle and remove
the front wheel.
2Separate the track rod end from the steering
arm.
3Unbolt the brake caliper, pull it off the disc
and tie it up out of the way. Do not allow it to
hang by its hose.
4Remove the split pin from the suspension
lower arm balljoint nut. Slacken the nut a few
16Front stub axle carrier -
removal and refitting
15Front suspension
crossmember - removal and
refitting
14Front wheel alignment -
checking and adjusting
Steering and suspension 11•7
11
13.4 Using a balljoint separator
14.1 Front wheel toe-in (greatly
exaggerated)15.3 Front suspension lower arm pivot bolt
procarmanuals.com