1985 FORD GRANADA engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 143 of 255

1Disconnect the battery negative terminal
then deplete the vacuum in the braking system
servo unit by depressing the footbrake several
times.
2Disconnect the wiring plug from the sensor
which is situated on the front of the vacuum
servo unit.
3Using a small flat-bladed screwdriver, prise
off the retaining circlip, then carefully withdraw
the sensor from the servo unit taking great
care not to displace the sealing O-ring (see
illustration).Note:If the O-ring becomes
displaced and falls into the servo unit it must
be recovered before the sensor is refitted.
4If the sensor is to be renewed, ensure that
the tip of the new sensor pushrod is the same
colour as that of the original.
5Fit a new O-ring to the sensor and apply asmear of clean engine oil to it to ease
installation.
6Ease the sensor into position in the servo
unit, taking care not to displace the O-ring,
and secure it in position with the circlip.
7Reconnect the sensor wiring connector and
the battery negative terminal.1Remove the driver’s seat as described in
Chapter 12.
2Carefully peel back the carpet from
immediately behind the crossmember to
reveal the G switch.
3Disconnect the wiring connector then undo
the two retaining screws and remove the
switch from the vehicle.
4Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
33G (gravity) switch (April 1992
on) - removal and refitting32Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS)
(April 1992 on) - removal and
refitting
10•14Braking system
32.3 Removing the Pedal Travel Sensor
(PTS) circlip - models from April 1992
procarmanuals.com
Page 145 of 255

11•2Steering and suspension
Front wheel alignment (continued)
Camber :
SOHC and 2.8 litre models:
Standard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0°23’ ±1°00’
Heavy duty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0°00’ ±1°00’
DOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-0°17’
2.4 litre low series models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-0°27’
2.4 litre high series and 2.9 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-0°21’
Tolerance:
DOHC, 2.4 and 2.9 litre models: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1°00’ to + 0°60’
Difference between left-hand and right-hand sides:
SOHC and 2.8 litre models:
Castor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1°00’ maximum
Camber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1°15’ maximum
DOHC, 2.4 and 2.9 litre models:
Castor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1°00’
Camber . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1°15’
Steering gear
Make:
Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Cam Gears
Power-assisted . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Cam Gears or ZF
Power steering fluid type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .ATF to Ford spec SQM-2C9010-A (Automatic Transmission
Fluid)
Tyres
Tyre sizes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175 SR/TR/HR 14, 185/70 HR/TR/VR 14, 195/65 HR 15, 205/60
VR 15
Tyre pressures: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .FrontRear
Normal load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.8 bar (26 lbf/in
2)1.8 bar (26 lbf/in2)
Full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.1 bar (30 lbf/in2)2.9 bar (42 lbf/in2)
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Steering
Steering gear-to-crossmember bolts:
Stage 1 (clamping) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Slacken, then Stage 2 (snug) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1511
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Tighten further 90°Tighten further 90°
Track rod end balljoint nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25 to 3018 to 22
Track rod end locknut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57 to 6842 to 50
Track rod inner balljoint nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7555
Intermediate shaft coupling pinch-bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
Pinion retaining nut (manual steering) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 10052 to 74
Pinion shaft nut (power steering) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37 to 4727 to 34
Slipper yoke plug (see text):
Manual steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4 to 53 to 4
Power steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 to 42 to 3
Steering wheel nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45 to 5533 to 41
Steering column mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2413 to 18
Steering column adjuster pivot nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10 to 137 to 10
Steering pump bracket to block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52 to 6438 to 47
Steering pump pulley hub bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10 to 127 to 9
Pressure hose to steering pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26 to 3119 to 23
Steering pump bracket-to-engine mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5830 to 43
Steering pump to bracket (V6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22 to 2916 to 21
Front suspension
Hub nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .390 to 450288 to 332
Lower arm balljoint nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65 to 8548 to 63
Top mount retaining nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2415 to 18
Stub axle carrier pinch-bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80 to 9059 to 66
Anti-roll bar clamps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 9052 to 66
Anti-roll bar to lower arms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 11052 to 81
Crossmember to frame . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 9052 to 66
Suspension strut to turret . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40 to 5230 to 38
Lower arm pivot:
Stage 1 (clamping) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Slacken. then Stage 2 (snug) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1511
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Tighten further 90°Tighten further 90°
procarmanuals.com
Page 146 of 255

The steering gear is of rack-and-pinion type.
Power assistance is standard on V6 models
and optional on others. The power-assisted
steering gear has a “variable ratio” effect
which increases the steering ratio about the
straight-ahead position: this provides quick
lock-to-lock action without the penalty of
over-responsiveness in open road driving.
The steering wheel is adjustable both up-
and-down and fore-and-aft. Both steering
column and shaft are designed to collapse
under impact. The steering shaft is connected
to the pinion by an intermediate shaft, which
has a universal joint at its upper end and a
flexible coupling at the lower end.
Front suspension is independent, of the
MacPherson strut type, with coil springs and
concentric telescopic shock absorbers. The
struts are attached to the tops of the stub axle
carriers, which are located at their lower ends
by balljoints incorporated in the lower
suspension arms. The lower suspension arms
pivot at their inner ends, where they are
attached to a central crossmember. The anti-
roll bar is attached to the rear of the arms and
serves to control fore-and-aft movement as
well as reducing roll.
Suspension geometry has been designed to
give good steering “feel”, resistance to pulling
caused by uneven braking effort or tyre
deflation, and (in the case of manual steering)
acceptably low steering wheel effort at parking
speeds. Only toe is adjustable in service.
The rear suspension is also independent. It
is of the semi-trailing arm type, with coil
springs and separate telescopic shock
absorbers. An optionally-available ride height
control system keeps the rear suspension
height constant, regardless of vehicle load.
Both front and rear wheel bearings are of a
special taper-roller type and require no
periodic adjustment in service.1Refer to Chapter 1, Section 35, to check the
power steering fluid level.
2If the fluid level falls so low that air enters
the pump, or after component renewal, the
system must be bled as follows.
3Remove the reservoir filler cap. Top-up with
clean fluid to the appropriate “cold” level. It is
important that the fluid is free of air bubbles,
so do not shake the container when topping-
up, and pour the fluid slowly.
4Disconnect the negative LT lead from the
ignition coil. Have an assistant crank the
engine on the starter in two second bursts, at
the same time turning the steering wheel from
lock to lock. Keep the reservoir topped up
whilst this is going on.
5When air bubbles no longer appear in the
fluid, stop the cranking. Reconnect the coil
negative lead and run the engine for a few
seconds, then stop it and check the level
again. Refit the filler cap.
6Run the vehicle for a few miles to warm up
the fluid and expel any remaining air, then stop
the engine and make a final fluid level check.
Manual steering
1Position the steering in the straight-ahead
position, then remove the ignition key so that
the steering is locked.
2Slacken the front wheel nuts. Raise and
support the front of the vehicle and remove
the front wheels.
3Remove the pinch-bolt and nut which
secure the intermediate shaft flexible coupling
to the pinion shaft (see illustration).
4Slacken the track rod end locknuts by half a
turn each (see illustration).
5Remove the split pin from the track rod
balljoint nuts. Unscrew the nuts, break the
balljoint tapers using a separator tool anddisengage the track rod ends from the
steering arms.
6Remove the two bolts which secure the
steering gear to the crossmember. Lift out the
steering gear.
7Mark the positions of the track rod ends on
the track rods, using paint or sticky tape, so
that they can be refitted in approximately the
same positions. Unscrew the track rod ends
and locknuts.
8Commence refitting by screwing on the
locknuts and track rod ends, observing the
previously made position marks when
applicable.
9Bring the rack to the straight-ahead
position. Do this by counting the number of
turns of the pinion needed to go from lock to
lock, then applying half that number of turns
from full lock on one side.
10Offer the steering gear to the vehicle,
engaging the flexible coupling and loosely
fitting the securing bolts. Note that the master
spline on the pinion shaft mates with the
corresponding groove in the flexible coupling.
11Tighten the two steering gear-to-
crossmember bolts to the specified Stage 1
torque. Slacken the bolts and retighten to the
Stage 2 torque. Finally tighten the bolts
through the angle specified for Stage 3.
12Make sure that the flexible coupling and
pinion shaft are properly engaged, then fit the
pinch-bolt and nut. Tighten the pinch-bolt to
the specified torque.
3Steering gear - removal and
refitting
2Power steering fluid - level
check and bleeding1General information
Steering and suspension 11•3
11
3.3 Master spline and groove on pinion
shaft and coupling
Torque wrench settings (continued)Nmlbf ft
Rear suspension
Driveshaft stub axle nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .250 to 290180 to 210
Final drive mounting to floor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Final drive mounting to rear cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40 to 5030 to 37
Guide plate-to-floor bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Guide plate insulator bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69 to 8851 to 65
Lower arm to crossmember . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80 to 9559 to 70
Brake anchor plate to lower arm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52 to 6438 to 47
Anti-roll bar bracket bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Shock absorber mountings:
Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73 to 9754 to 72
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68 to 9250 to 68
Rear hub bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80 to 10059 to 74
Wheels
Wheel nuts (steel or alloy wheels) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 10052 to 74
procarmanuals.com
Page 149 of 255

3Depress the locking button with a small
screwdriver. Draw the lock barrel out of its
housing using the key (see illustration).
4Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1The intermediate shaft and flexible coupling
are not available separately, and so must be
renewed as a unit.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Position the steering straight-ahead.
4Remove the pinch-bolts which secure the
upper and lower ends of the intermediate
shaft. Free the universal joint from the column
shaft, then pull the flexible coupling off the
pinion shaft.
5When refitting, engage the master spline on
the pinion shaft with the groove in the flexible
coupling.
6Tighten the pinch-bolts to the specified
torque.
7Reconnect the battery.
Refer to Chapter 1, Section 21.
All engines except DOHC
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Wipe clean around the unions, then
disconnect the high pressure and return pipes
from the pump and the reservoir. Be prepared
for fluid spillage; take steps to keep fluid out of
the alternator.
3Remove the pump drivebelt(s).
4Remove the pump mounting, pivot and
adjustment bolts (as applicable) and lift the
pump from the engine (see illustration).
5If a new pump is to be fitted, recover the
pulley and mounting plate from the old pump.6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Adjust the drivebelt tension on completion and
bleed the steering hydraulic system.
DOHC engines
7The pump is mounted on a bracket on the
front right-hand side of the cylinder block. To
improve access to the pump, firmly apply the
handbrake then jack up the front of the car
and support it securely on axle stands (see
“Jacking”).
8Place a suitable container under the pump,
unscrew the fluid pipe unions, and drain the
fluid.
9Remove the drivebelt with reference to
Chapter 1.
10Prevent the pulley from rotating using a
strap wrench (which can be improvised using
an old drivebelt and a large socket and
wrench), and unscrew the three pulley
securing bolts (see illustration). Withdraw the
pulley.
11Unscrew the three pump securing bolts
from the front of the pump bracket, and the
single bolt from the rear of the bracket, and
withdraw the pump (see illustration).
12Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points:
a)Reconnect the fluid unions using new O-
rings.
b)On completion, top-up and bleed the
power steering fluid circuit.1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Clean around the hose unions on the
steering gear. Remove the single securing
bolt, withdraw the hoses and catch the fluid
which will drain from the reservoir.
3Clean around the hose unions on the pump.
Disconnect the unions and remove the hoses.
4Refit in the reverse order to removal, using
new O-rings.
5Top-up the steering fluid and bleed the
system.
1Slacken the front wheel nuts, raise and
support the vehicle and remove the front
wheel on the side concerned.
2Slacken the track rod end locknut by half a
turn.
3Remove the split pin from the track rod end
balljoint nut. Unscrew the nut a few turns (see
illustration).
4Break the balljoint taper with a proprietary
balljoint separator (see illustration). Remove
the separator and the nut and disengage the
track rod end from the steering arm.
5Unscrew the track rod end from the track
rod, being careful not to disturb the locknut.
13Track rod end - removal and
refitting
12Power steering hoses -
removal and refitting
11Power steering pump -
removal and refitting
10Power steering pump
drivebelt - removal, refitting
and tensioning
9Steering intermediate shaft
and flexible coupling - removal
and refitting
11•6Steering and suspension
8.3 Depress the column lock locking button
11.11 . . . for access to the front pump
securing bolts (arrowed)13.3 Track rod end balljoint nut unscrewed
11.4 Steering pump pivot bolt (arrowed) -
V6 model shown11.10 Unbolt the power steering pump
pulley . . .
procarmanuals.com
Page 150 of 255

6When refitting, screw the track rod end onto
the track rod as far as the locknut, then back it
off half a turn.
7Insert the ball-pin into the steering arm.
Tighten the balljoint nut to the specified torque
and secure with a new split pin. Nip up the
track rod end locknut, but do not tighten it fully
yet.
8Refit the roadwheel, lower the vehicle and
tighten the wheel nuts to the specified torque.
9Check the toe setting as described in the
following Section. (This may not be strictly
necessary if the same track rod end has been
refitted, but is certainly advisable if any
components have been renewed.)
10Tighten the track rod end locknut when
toe is correct.
1Front wheel alignment is defined by camber,
castor, steering axis inclination and toe
setting. The first three factors are determined
in production; only toe can be adjusted in
service. Incorrect toe will cause rapid tyre
wear (see illustration).
2Toe is defined as the amount by which the
distance between the front wheels, measured
at hub height, differs from the front edges to
the rear edges. If the distance between the
front edges is less than that at the rear, the
wheels are said to toe-in; the opposite case is
known as toe-out.3To measure toe, it will be necessary to
obtain or make a tracking gauge. These are
available in motor accessory shops, or one
can be made from a length of rigid pipe or bar
with some kind of threaded adjustment facility
at one end. Many tyre specialists will also
check toe free, or for a nominal sum.
4Before measuring toe, check that all
steering and suspension components are
undamaged and that tyre pressures are
correct. The vehicle must be at approximately
kerb weight, with the spare wheel and jack in
their normal positions and any abnormal loads
removed.
5Park the vehicle on level ground and bounce
it a few times to settle the suspension.
6Use the tracking gauge to measure the
distance between the inside faces of the front
wheel rims, at hub height, at the rear of the
front wheels. Record this distance; call it
measurement A.
7Push the vehicle forwards or backwards so
that the wheels rotate exactly 180°(half a turn).
Measure the distance between the front wheel
rims again, this time at the front of the wheels.
Record this distance; call it measurement B.
8Subtract measurement B from
measurement A. If the answer is positive it is
the amount of toe-in; if negative it is the
amount of toe-out. Permissible values are
given in the Specifications.
9If adjustment is necessary loosen the track
rod end locknuts and the outer bellows clips,
then rotate each track rod by equal amounts
until the setting is correct. Hold the track rod
ends in their horizontal position with a spanner
while making the adjustment.
10Tighten the locknuts and outer bellows
clips.
11Provided the track rods have been
adjusted by equal amounts the steering wheel
should be central when moving straight-
ahead. The amount of visible thread on each
track rod should also be equal.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Raise and securely support the front of the
vehicle.
3Remove the suspension lower arm pivot
nuts and bolts (see illustration). Disengage
the arms from the crossmember.
4Disconnect the steering column shaft from
the intermediate shaft universal joint.
5Remove the two bolts which secure the
steering gear to the crossmember. Draw the
steering gear forwards so that it is clear of the
crossmember and support it by wiring it to the
frame rails.
6It is now necessary to support the engine,
preferably from above, using a hoist or an
adjustable support bar resting on the wings or
suspension turrets. Alternatively a jack and
some wooden blocks may be used frombelow, but this is bound to obstruct access to
some extent.
7Remove the engine mounting lower
securing nuts. Raise the engine until the
mountings are just clear of the crossmember.
8Release the brake pipe clips from the
crossmember and slide the brake pipes from
their slots. Be careful not to strain the pipes.
9Support the crossmember and remove its
four securing bolts. Lower the crossmember
and remove it from the vehicle.
10Commence refitting by offering the
crossmember to the frame rails. Insert the four
securing bolts and tighten them to the
specified torque.
11Secure the brake pipes to the
crossmember.
12Refit the steering gear to the
crossmember. Tighten its securing bolts to the
specified torque.
13Insert the suspension arms into the
crossmember and secure them with the pivot
bolts and nuts. Do not tighten the nuts and
bolts yet, just nip them up.
14Lower the engine onto the crossmember.
Make sure that the engine mountings locate
correctly into the holes in the crossmember.
Tighten the engine mounting nuts. The engine
support bar or hoist can now be removed.
15Reconnect the steering column shaft to
the intermediate shaft. Tighten the pinch-bolt
to the specified torque.
16Lower the vehicle onto its wheels, then
tighten the lower arm pivot bolts to the
specified torque.
17Reconnect the battery.
1Slacken the front wheel nuts. Raise and
support the front of the vehicle and remove
the front wheel.
2Separate the track rod end from the steering
arm.
3Unbolt the brake caliper, pull it off the disc
and tie it up out of the way. Do not allow it to
hang by its hose.
4Remove the split pin from the suspension
lower arm balljoint nut. Slacken the nut a few
16Front stub axle carrier -
removal and refitting
15Front suspension
crossmember - removal and
refitting
14Front wheel alignment -
checking and adjusting
Steering and suspension 11•7
11
13.4 Using a balljoint separator
14.1 Front wheel toe-in (greatly
exaggerated)15.3 Front suspension lower arm pivot bolt
procarmanuals.com
Page 156 of 255
cornering or braking. Control circuitry also
prevents the compressor being energised for
more than five minutes continuously, as could
otherwise happen if the system sprang a leak.
No repairs to individual components are
possible. Apparent control faults should be
referred to a Ford dealer before embarking on
an expensive programme of testing by
substitution. Always use new O-rings on the
pipe unions once they have been disturbed.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Raise and support the front of the vehicle.
3Remove the compressor cover (front left-hand
side of engine) which is secured by four screws.
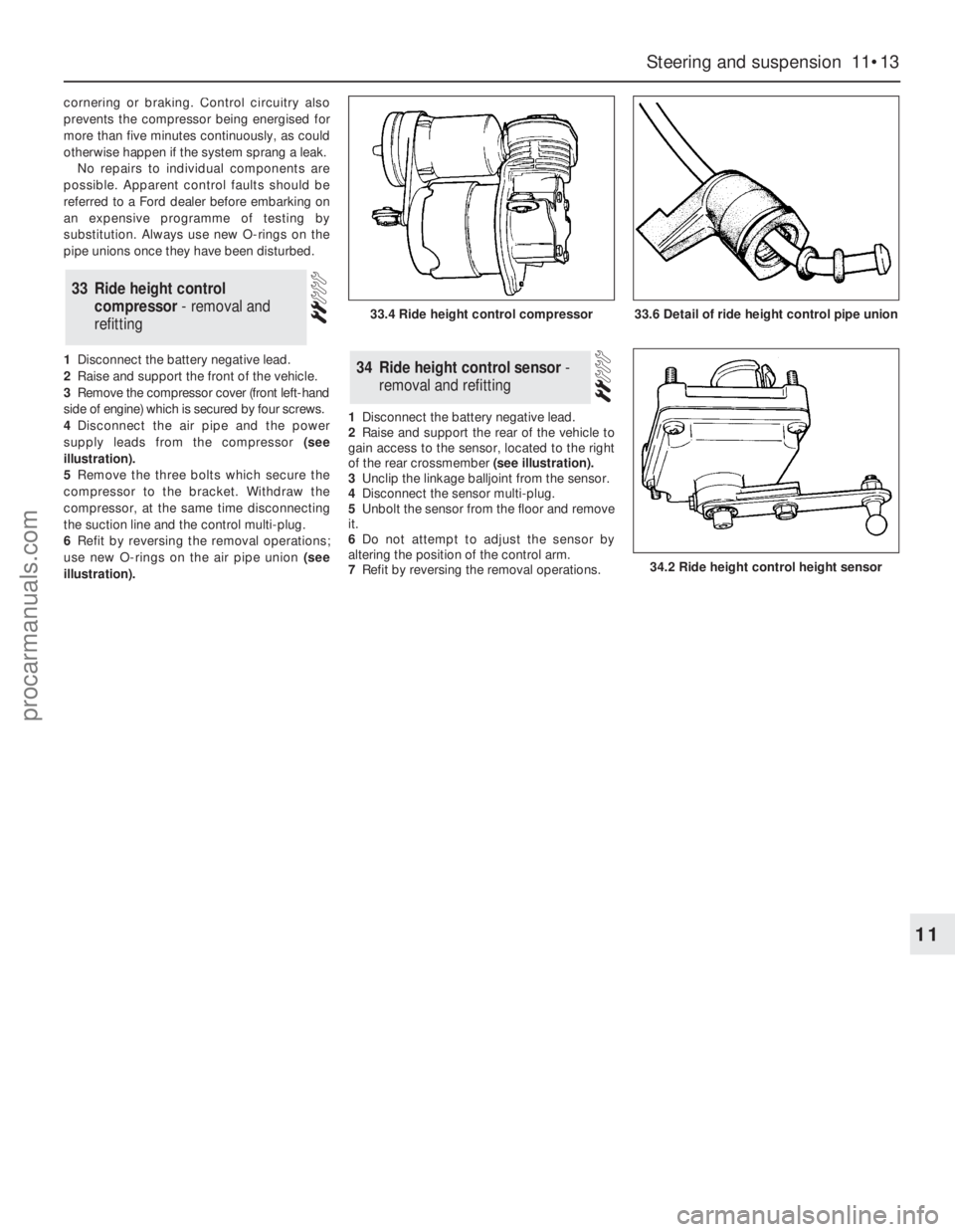
4Disconnect the air pipe and the power
supply leads from the compressor (see
illustration).
5Remove the three bolts which secure the
compressor to the bracket. Withdraw the
compressor, at the same time disconnecting
the suction line and the control multi-plug.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations;
use new O-rings on the air pipe union(see
illustration).1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Raise and support the rear of the vehicle to
gain access to the sensor, located to the right
of the rear crossmember (see illustration).
3Unclip the linkage balljoint from the sensor.
4Disconnect the sensor multi-plug.
5Unbolt the sensor from the floor and remove
it.
6Do not attempt to adjust the sensor by
altering the position of the control arm.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations.
34Ride height control sensor -
removal and refitting
33Ride height control
compressor - removal and
refitting
Steering and suspension 11•13
11
33.4 Ride height control compressor33.6 Detail of ride height control pipe union
34.2 Ride height control height sensor
procarmanuals.com
Page 159 of 255

important also to keep watch on those parts of
the vehicle not immediately visible, for
instance the underside, inside all the wheel
arches, and the lower part of the engine
compartment.
The basic maintenance routine for the
bodywork is washing - preferably with a lot of
water, from a hose. This will remove all the
loose solids which may have stuck to the
vehicle. It is important to flush these off in
such a way as to prevent grit from scratching
the finish. The wheel arches and underframe
need washing in the same way, to remove any
accumulated mud, which will retain moisture
and tend to encourage rust. Paradoxically
enough, the best time to clean the underframe
and wheel arches is in wet weather, when the
mud is thoroughly wet and soft. In very wet
weather, the underframe is usually cleaned of
large accumulations automatically, and this is
a good time for inspection.
Periodically, except on vehicles with a wax-
based underbody protective coating, it is a
good idea to have the whole of the underframe
of the vehicle steam-cleaned, engine
compartment included, so that a thorough
inspection can be carried out to see what
minor repairs and renovations are necessary.
Steam-cleaning is available at many garages,
and is necessary for the removal of the
accumulation of oily grime, which sometimes
is allowed to become thick in certain areas. If
steam-cleaning facilities are not available,
there are some excellent grease solvents
available which can be brush-applied; the dirt
can then be simply hosed off. Note that these
methods should not be used on vehicles with
wax-based underbody protective coating, or
the coating will be removed. Such vehicles
should be inspected annually, preferably just
prior to Winter, when the underbody should be
washed down, and any damage to the wax
coating repaired. Ideally, a completely fresh
coat should be applied. It would also be worth
considering the use of such wax-based
protection for injection into door panels, sills,
box sections, etc, as an additional safeguard
against rust damage, where such protection is
not provided by the vehicle manufacturer.
After washing paintwork, wipe off with a
chamois leather to give an unspotted clear
finish. A coat of clear protective wax polish will
give added protection against chemical
pollutants in the air. If the paintwork sheen has
dulled or oxidised, use a cleaner/polisher
combination to restore the brilliance of the
shine. This requires a little effort, but such
dulling is usually caused because regular
washing has been neglected. Care needs to
be taken with metallic paintwork, as special
non-abrasive cleaner/polisher is required to
avoid damage to the finish. Always check that
the door and ventilator opening drain holes
and pipes are completely clear, so that water
can be drained out. Brightwork should be
treated in the same way as paintwork.
Windscreens and windows can be kept clear
of the smeary film which often appears, by theuse of proprietary glass cleaner. Never use
any form of wax or other body or chromium
polish on glass.
Mats and carpets should be brushed or
vacuum-cleaned regularly, to keep them free
of grit. If they are badly stained, remove them
from the vehicle for scrubbing or sponging,
and make quite sure they are dry before
refitting. Seats and interior trim panels can be
kept clean by wiping with a damp cloth. If they
do become stained (which can be more
apparent on light-coloured upholstery), use a
little liquid detergent and a soft nail brush to
scour the grime out of the grain of the material.
Do not forget to keep the headlining clean in
the same way as the upholstery. When using
liquid cleaners inside the vehicle, do not over-
wet the surfaces being cleaned. Excessive
damp could get into the seams and padded
interior, causing stains, offensive odours or
even rot. If the inside of the vehicle gets wet
accidentally, it is worthwhile taking some
trouble to dry it out properly, particularly
where carpets are involved. Do not leave oil or
electric heaters inside the vehicle for this
purpose.
Repairs of minor scratches in
bodywork
If the scratch is very superficial, and does
not penetrate to the metal of the bodywork,
repair is very simple. Lightly rub the area of the
scratch with a paintwork renovator, or a very
fine cutting paste, to remove loose paint from
the scratch, and to clear the surrounding
bodywork of wax polish. Rinse the area with
clean water.
Apply touch-up paint to the scratch using a
fine paint brush; continue to apply fine layers
of paint until the surface of the paint in the
scratch is level with the surrounding
paintwork. Allow the new paint at least two
weeks to harden, then blend it into the
surrounding paintwork by rubbing the scratch
area with a paintwork renovator or a very fine
cutting paste. Finally, apply wax polish.
Where the scratch has penetrated right
through to the metal of the bodywork, causing
the metal to rust, a different repair technique is
required. Remove any loose rust from the
bottom of the scratch with a penknife, then
apply rust-inhibiting paint to prevent the
formation of rust in the future. Using a rubber
or nylon applicator, fill the scratch with
bodystopper paste. If required, this paste can
be mixed with cellulose thinners to provide a
very thin paste which is ideal for filling narrow
scratches. Before the stopper-paste in the
scratch hardens, wrap a piece of smoothcotton rag around the top of a finger. Dip the
finger in cellulose thinners, and quickly sweep
it across the surface of the stopper-paste in
the scratch; this will ensure that the surface of
the stopper-paste is slightly hollowed. The
scratch can now be painted over as described
earlier in this Section.
Repairs of dents in bodywork
When deep denting of the vehicle’s
bodywork has taken place, the first task is to
pull the dent out, until the affected bodywork
almost attains its original shape. There is little
point in trying to restore the original shape
completely, as the metal in the damaged area
will have stretched on impact, and cannot be
reshaped fully to its original contour. It is
better to bring the level of the dent up to a
point which is about 3 mm below the level of
the surrounding bodywork. In cases where the
dent is very shallow anyway, it is not worth
trying to pull it out at all. If the underside of the
dent is accessible, it can be hammered out
gently from behind, using a mallet with a
wooden or plastic head. Whilst doing this,
hold a suitable block of wood firmly against
the outside of the panel, to absorb the impact
from the hammer blows and thus prevent a
large area of the bodywork from being “belled-
out”.
Should the dent be in a section of the
bodywork which has a double skin, or some
other factor making it inaccessible from
behind, a different technique is called for. Drill
several small holes through the metal inside
the area - particularly in the deeper section.
Then screw long self-tapping screws into the
holes, just sufficiently for them to gain a good
purchase in the metal. Now the dent can be
pulled out by pulling on the protruding heads
of the screws with a pair of pliers.
The next stage of the repair is the removal
of the paint from the damaged area, and from
an inch or so of the surrounding “sound”
bodywork. This is accomplished most easily
by using a wire brush or abrasive pad on a
power drill, although it can be done just as
effectively by hand, using sheets of abrasive
paper. To complete the preparation for filling,
score the surface of the bare metal with a
screwdriver or the tang of a file, or
alternatively, drill small holes in the affected
area. This will provide a really good “key” for
the filler paste.
To complete the repair, see the Section on
filling and respraying.
Repairs of rust holes or gashes in
bodywork
Remove all paint from the affected area, and
from an inch or so of the surrounding “sound”
bodywork, using an abrasive pad or a wire
brush on a power drill. If these are not
available, a few sheets of abrasive paper will
do the job most effectively. With the paint
removed, you will be able to judge the severity
of the corrosion, and therefore decide whether
to renew the whole panel (if this is possible) or
4Minor body damage - repair
3Maintenance - upholstery and
carpets
12•2Bodywork and fittings
procarmanuals.com
Page 161 of 255

Where serious damage has occurred or
large areas need renewal due to neglect, it
means certainly that completely new sections
or panels will need welding in and this is best
left to professionals. If the damage is due to
impact, it will also be necessary to completely
check the alignment of the bodyshell
structure. Due to the principle of construction,
the strength and shape of the whole car can
be affected by damage to one part. In such
instances the services of a Ford agent with
specialist checking jigs are essential. If a body
is left misaligned, it is first of all dangerous as
the car will not handle properly, and secondly
uneven stresses will be imposed on the
steering, engine and transmission, causing
abnormal wear or complete failure. Tyre wear
may also be excessive.
1Open and prop the bonnet.
2Mark around the bonnet hinge bolts, using
soft pencil or a washable marker pen, to
provide a guide when refitting (see
illustration).
3Disconnect the windscreen washer hose atthe non-return valve or washer pump. Be
prepared for fluid spillage.
4Disconnect the under-bonnet light (when
fitted).
5Free the insulation from around the left-
hand hinge bolts. With the help of an assistant,
support the bonnet and remove the hinge
bolts. Unhook the bonnet from the pump and
remove it.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Make sure that the gap between the bonnet
and the wings is equal on both sides when the
bonnet is shut; adjust if necessary at the hinge
bolts.
7Adjust the bump stops and bonnet lock
striker if necessary to obtain satisfactory
opening and closing of the bonnet (see
illustration).
Later models
8The operation for later models is essentially
as described above, noting thatit will be
necessary to unclip the insulation panel from
the underside of the bonnet to gain access to
the windscreen washer hose and washer
nozzle heater wiring plugs (see illustration).
9Disconnect the wiring plugs and hose and
free them from the retaining clips on the right-
hand side of the bonnet before removal.
10On refitting ensure that the hose and
wiring are correctly routed and retained by all
the necessary clips before refitting the
insulation panel (see illustrations).1Open the door and disconnect the wiring
multi-plug from the door pillar (see
illustration).
2Unbolt the door check strap.
3Slacken, but do not remove, the hinge
cotter pin nuts (see illustration).
4Open the door to approximately 60°from
the vehicle body and lift it off the hinges. If the
door is reluctant to move, make sure that it is
opened to the correct angle and that the cotter
pin nuts are adequately slackened.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Adjust the door striker plate if necessary as
described in Section 12.
6If a new door is to be fitted, new hinges will
have to be welded to it after trial fitting.
Consult a Ford dealer for details.
Hatchback models
1Open the tailgate and remove the interior
trim panel, which is retained by eleven screws.
2Disconnect the wiring from the heated rear
window, aerial pre-amplifier and lock solenoid.
3Repeat paragraph 2 for the rear wiper motor
and the rear washer tube, and any other
electrical equipment.
8Tailgate - removal and refitting
7Door - removal and refitting
6Bonnet - removal and refitting
5Major body damage - repair
12•4Bodywork and fittings
6.2 Left-hand hinge bolts (arrowed) are
obscured by insulation
6.10 On refitting ensure the wiring and
hoses are correctly routed and secured by
all necessary retaining clips
7.1 Door wiring multi-plug7.3 One of the hinge cotter pins (arrowed)
6.7 Bonnet lock striker and safety catch6.8 On later models disconnect the washer
nozzle heater wiring plugs before removing
the bonnet
procarmanuals.com