1983 FIAT UNO lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 7 of 303
Roadside Repairs0•7
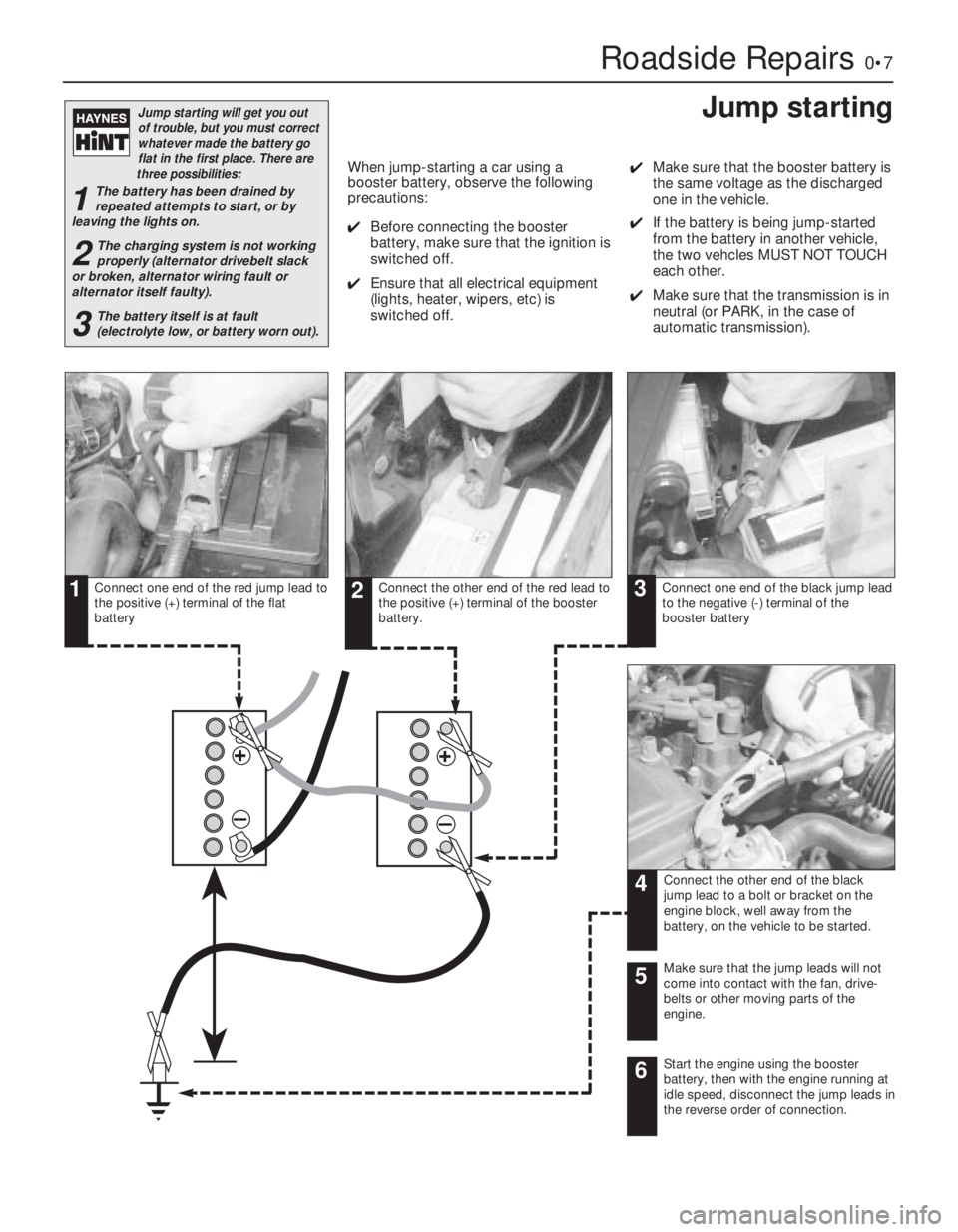
Connect one end of the red jump lead to
the positive (+) terminal of the flat
batteryConnect the other end of the red lead to
the positive (+) terminal of the booster
battery.Connect one end of the black jump lead
to the negative (-) terminal of the
booster battery
Connect the other end of the black
jump lead to a bolt or bracket on the
engine block, well away from the
battery, on the vehicle to be started.
–
+
+
–
123
4
Make sure that the jump leads will not
come into contact with the fan, drive-
belts or other moving parts of the
engine.5
Start the engine using the booster
battery, then with the engine running at
idle speed, disconnect the jump leads in
the reverse order of connection.6
Jump starting will get you out
of trouble, but you must correct
whatever made the battery go
flat in the first place. There are
three possibilities:
1The battery has been drained by
repeated attempts to start, or by
leaving the lights on.
2The charging system is not working
properly (alternator drivebelt slack
or broken, alternator wiring fault or
alternator itself faulty).
3The battery itself is at fault
(electrolyte low, or battery worn out).
Booster battery (jump) starting
When jump-starting a car using a
booster battery, observe the following
precautions:
4Before connecting the booster
battery, make sure that the ignition is
switched off.
4Ensure that all electrical equipment
(lights, heater, wipers, etc) is
switched off.4Make sure that the booster battery is
the same voltage as the discharged
one in the vehicle.
4If the battery is being jump-started
from the battery in another vehicle,
the two vehcles MUST NOT TOUCH
each other.
4Make sure that the transmission is in
neutral (or PARK, in the case of
automatic transmission).
Jump starting
Page 8 of 303

0•8Roadside Repairs
To avoid repetition, the procedure for
raising the vehicle, in order to carry out work
under it, is not included before each relevant
operation described in this Manual.
It is to be preferred, and it is certainly
recommended, that the vehicle is positioned
over an inspection pit or raised on a lift. Where
these facilities are not available, use ramps or
jack up the vehicle strictly in accordance with
the following guide. Once the vehicle is raised,
supplement the jack with axle stands.
Jacking
The jack supplied with the car should only
be used to change a wheel. Do not use this
jack when overhaul or repair work is being
carried out; employ a hydraulic or screw jack
and supplement it with axle stands.
Jacking points are located under the sills
for use with the jack supplied.To raise the front end with a garage jack,
locate the jack under the transmission lower
mounting, just below and slightly to the rear of
the transmission oil drain plug. Protect the
mounting by placing a block of wood between
the jack head and the mounting.
To raise the rear of the car, the jack should
be placed under the spare wheel housing as
far to the rear as possible. Place a wooden
bearer between the jack head and the
housing.
Towing
When being towed, use the left-hand front
towing eye.
When towing another vehicle, use the rear
towing eye adjacent to the exhaust tailpipe.
When being towed, remember that the
brake pedal will require heavier pressure due
to lack of servo assistance. Always turn theignition key to MAR to retain the steering in
the unlocked position.
Wheel changing
With the car on firm level ground, apply the
handbrake fully. Remove the hub cap or
wheel trim, if fitted.
Release, but do not remove, the bolts.
Chock the front and rear of the opposite
roadwheel and then raise the car using the sill
jack supplied with the car if it is being done at
the roadside. Alternatively use a workshop
jack supplemented with axle stands.
Remove the wheel bolts, change the wheel
and screw in the bolts finger tight. It is
recommended that the bolt threads are
smeared with multi-purpose grease. Lower
the car, remove the jack and tighten the wheel
bolts to the specified torque. Refit any wheel
trim that was removed.
Spare wheel and jack stowage
Front tow hook Rear tow hook
Jacking, towing and wheel changing
Page 10 of 303

0•10Routine maintenance
Maintenance is essential for ensuring safety and desirable for the
purpose of getting the best in terms of performance and economy
from the car. Over the years the need for periodic lubrication has been
greatly reduced if not totally eliminated. This has unfortunately tended
to lead some owners to think that because no such action is required
the items either no longer exist or will last forever. This is certainly not
the case; it is essential to carry out regular visual examinations as
comprehensively as possible in order to spot any possible defects at
an early stage before they develop into major and expensive repairs.
For information applicable to later models, see Supplement.
Every 250 miles (400 km), weekly,
or before a long journey
m mCheck engine oil level
m mCheck brake reservoir fluid level
m mCheck tyre pressures
m mCheck operation of all lights and horn
m mTop up washer fluid reservoirs, adding a screen
wash, and check operation of washers and wipers
m mCheck coolant level
m mCheck battery electrolyte level
Every 6000 miles (10 000 km)
or six months, whichever comes first
m mRenew engine oil and filter (Chapter 1, Section 2)
m mCheck drivebelt tension (Chapter 2, Section 8)
m mCheck carburettor idle speed and mixture
adjustments (Chapter 3)
m mCheck contact points and dwell angle (mechanical
breaker distributors) (Chapter 4, Section 3)
m mCheck tyre tread wear (Chapter 7, Section 7)
m mCheck disc pads for wear (Chapter 8, Section 3)
Every 36 000 miles (60 000 km)
or three years, whichever comes first
m mRenew the timing belt - 1116 and 1299/1301 cc
(Chapter 1, Section 28)
m mCheck exhaust system for corrosion (Chapter 3,
Section 19)
m mRenew contact breaker points and adjust dwell
angle (mechanical breaker distributors) (Chapter 4,
Section 3)
m mCheck and adjust ignition timing (Chapter 4,
Section 4)
m mRenew spark plugs (Chapter 4, Section 11)
m mCheck clutch adjustment (Chapter 5, Section 2)
m mCheck transmission oil level (Chapter 6, Section 2)
m mCheck driveshaft and steering rack gaiters for splits
(Chapters 7 and 10)
m mCheck rear brake shoe linings for wear (Chapter 8,
Section 4)
m mCheck handbrake travel (Chapter 8, Section 16)
m mCheck headlamp beam alignment (Chapter 9,
Section 17)
m mCheck balljoints for wear (Chapter 10, Section 2)
m mCheck front wheel alignment (Chapter 10, Section 8)
m mCheck suspension bushes for wear (Chapter 11,
Section 2)
m mCheck seat belts for fraying (Chapter 12, Section 23)
m mLubricate controls, hinges and locks
Every 24 000 miles (40 000 km)
or two years, whichever comes first
m mRenew coolant anti-freeze mixture (Chapter 2,
Section 3)
m mRenew transmission oil (Chapter 6, Section 2)
m mRenew brake hydraulic fluid (Chapter 8, Section 12)
m mCheck for underbody corrosion and clean out door
and sill drain holes (Chapter 12, Section 2)
Every 12 000 miles (20 000 km) or
12 months, whichever comes first
m mCheck and adjust valve clearances (Chapter 1,
Sections 5 and 26)
m mRenew air cleaner element (Chapter 3, Section 2)
Page 16 of 303

Cylinder block and crankcase
Material . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Cast-iron
Bore diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65.000 to 65.050 mm (2.5591 to 2.5610 in)
Diameter of camshaft bearing bores in crankcase timing gear end:
Grade B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50.505 to 50.515 mm (1.9882 to 1.9886 in)
Grade C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50.515 to 50.525 mm (1.9886 to 1.9890 in)
Grade D . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50.705 to 50.715 mm (1.9960 to 1.9964 in)
Grade E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50.715 to 50.725 mm (1.9964 to 1.9968 in)
Centre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46.420 to 46.450 mm (1.8275 to 1.8287 in)
Flywheel end . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35.921 to 35.951 mm (1.4142 to 1.4154 in)
Maximum cylinder bore taper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.015 mm (0.0006 in)
Maximum cylinder bore ovality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.015 mm (0.0006 in)
Pistons and piston rings
Piston diameter:
Grade A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64.940 to 64.950 mm (2.5566 to 2.5570 in)
Grade C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64.960 to 64.970 mm (2.5574 to 2.5578 in)
Grade E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64.980 to 64.990 mm (2.5582 to 2.5586 in)
Oversizes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 mm (0.008, 0.016, 0.024 in)
Piston clearance in cylinder bore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.050 to 0.070 mm (0.0020 to 0.0028 in)
Piston ring groove width:
Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.785 to 1.805 mm (0.0703 to 0.0711 in)
Second . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.015 to 2.035 mm (0.0793 to 0.0801 in)
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.975 to 3.977 mm (0.1566 to 0.1567 in)
Piston ring thickness:
Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.728 to 1.740 mm (0.0680 to 0.0685 in)
Second . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.978 to 1.990 mm (0.0779 to 0.0784 in)
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.925 to 3.937 mm (0.1545 to 0.1550 in)
Piston ring groove clearance:
Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.045 to 0.077 mm (0.0018 to 0.0030 in)
Second . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.025 to 0.057 mm (0.0010 to 0.0022 in)
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.020 to 0.052 mm (0.0008 to 0.0020 in)
Piston ring end gap:
Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.25 to 0.45 mm (0.0098 to 0.0177 in)
Second . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.20 to 0.35 mm (0.0078 to 0.0137 in)
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.20 to 0.45 mm (0.0078 to 0.0177 in)
Oversize piston rings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 mm (0.008, 0.016, 0.024 in)
Gudgeon pin diameter:
Grade 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19.970 to 19.974 mm (0.7862 to 0.7863 in)
Grade 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19.974 to 19.978 mm (0.7863 to 0.7865 in)
Grade 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19.978 to 19.982 mm (0.7865 to 0.7866 in)
Oversize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.2 mm (0.008 in)
Crankshaft
Journal diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50.785 to 50.805 mm (1.9994 to 2.0002 in)
Standard main bearing shell thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.832 to 1.837 mm (0.0721 to 0.0723 in)
Undersizes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.254, 0.508, 0.762,1.016 mm (0.010, 0.020. 0.030, 0.040 in)
Crankshaft endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.06 to 0.26 mm (0.0024 to 0.0102 in)
Crankpin diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39.985 to 40.005 mm (1.5741 to 1.5750 in)
Standard big-end shell bearing thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.807 to 1.813 mm (0.0712 to 0.0714 in)
Undersizes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.254, 0.508, 0.762, 1.016 mm (0.010, 0.020, 0.030, 0.040 in)
Camshaft
Diameter of camshaft journals:
Timing end . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37.975 to 38.000 mm (1.4951 to 1.4961 in)
Centre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43.348 to 43.373 mm (1.7079 to 1.7088 in)
Flywheel end . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30.975 to 31.000 mm (1.2194 to 1.2205 in)
Bush reamed diameters:
Timing gear end* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38.025 to 38.050 mm (1.4971 to 1.4981 in)
Centre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43.404 to 43.424 mm (1.7088 to 1.7096 in)
Flywheel end . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31.026 to 31.046 mm (1.2215 to 1.2223 in)
*Supplied reamed to size
Cam lift . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.1 mm (0.201 in)
Outside diameter of cam follower . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13.982 to 14.000 mm (0.5505 to 0.5512 in)
Oversizes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.05 to 0.010 mm (0.002 to 0.004 in)
Cam follower running clearance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.010 to 0.046 mm (0.0004 to 0.0018 in)
1•2 Engine – general
Page 20 of 303

Auxiliary shaft
Bearing internal diameter (reamed):
No. 1 (timing belt end) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35.664 to 35.684 mm (1.4052 to 1.4059 in)
No. 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32.000 to 32.020 mm (1.2608 to 1.2616 in)
Shaft journal diameter:
No. 1 (timing belt end) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35.593 to 35.618 mm (1.4024 to 1.4033 in)
No. 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31.940 to 31.960 mm (1.2584 to 1.2592 in)
Cylinder block and crankcase
Material . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Cast-iron
Bore diameter:
1116 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80.000 to 80.050 mm (3.152 to 3.154 in)
1301 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86.400 to 86.450 mm (3.404 to 3.406 in)
Maximum cylinder bore taper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.015 mm (0.0006 in)
Maximum cylinder bore ovality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.015 mm (0.0006 in)
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Cylinder head bolts:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 15
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 30
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Turn through 90º Turn through 90º
Stage 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Turn through 90º Turn through 90º
Camshaft carrier to cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 15
Main bearing cap bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80 59
Big-end cap nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51 38
Flywheel mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83 61
Camshaft sprocket bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83 61
Belt tensioner bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44 32
Exhaust manifold nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 21
Auxiliary shaft sprocket bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83 61
Flexible mounting bracket bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59 44
Flexible mounting centre nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 36
Oil pressure switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 24
Spark plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Roadwheel bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86 63
Driveshaft/hub nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272 200
Tie-rod end balljoint nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34 25
Brake caliper mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53 39
Front strut lower clamp bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 36
Driveshaft inboard boot retainer bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 7
Crankshaft pulley nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98 7
1•6 Engine – general
Part 1: General
1 Description
1The Uno may be powered by one of three
engines depending upon the particular model.
903 cc
2This is of four cylinder overhead valve type
with a light alloy cylinder head and a cast-iron
block and crankcase.
3A three bearing crankshaft is used and the
chain-driven camshaft runs in three steel
backed white metal bearings.
4The light alloy pistons are fitted with two
compression and one oil control ring. The
gudgeon pin is an interference fit in the small
end of the connecting rod.
5Lubrication is provided by an oil pump
within the sump pan and both the pump and
the distributor are driven from a gear on the
camshaft. Pressurised oil passes through acartridge type oil filter. An oil pressure relief
valve is incorporated in the oil pump. The
engine oil is independent of the transmission
lubricant.
1116 cc and 1301 cc
6These engines are of single overhead
camshaft type, the camshaft being driven by a
toothed belt.
7The difference in engine capacity is
achieved by increasing the cylinder bore on
the 1301 cc engine.
8The cylinder head is of light alloy while the
cylinder block and crankcase are of cast-iron
construction.
9A five bearing crankshaft is used and the
camshaft runs in a similar number of bearings,
but as these are in-line bored directly in the
camshaft carrier, no repair is possible.
10The pistons are of light alloy with two
compression and one oil control ring. The
gudgeon pin is an interference fit in the small
end of the connecting rod.
11An auxiliary shaft, driven by the timing belt
is used to drive the distributor, oil pump and
fuel pump.12The oil pump is located within the sump
pan and incorporates a pressure relief valve.
13Pressurised oil passes through a cartridge
type oil filter.
14The crankshaft main bearings are
supplied under pressure from drillings in the
crankcase from the main oil gallery whilst the
connecting rod big-end bearings are
lubricated from the main bearings by oil
forced through the crankshaft oilways. The
camshaft bearings are fed from a drilling from
the main oil gallery. The cams and tappets are
lubricated by oil mist from outlets in the
camshaft bearings.
15The cylinder walls, pistons and gudgeon
pins are lubricated by oil splashed up by the
crankshaft webs. An oil pressure warning light
is fitted to indicate when the pressure is too
low.
All engines
16The engine is mounted transversely with
the transmission at the front of the car.
17The engine oil is independent of the
transmission lubricant.
Page 23 of 303

Cylinder head - removal and refitting
Sump pan - removal and refitting
Pistons/connecting rods - removal and
refitting
Oil pump - removal and refitting
Engine mountings - renewal
1116 cc and 1301 cc engines
Valve clearances - checking and adjusting
Camshaft and camshaft carrier - removal
and refitting
Timing belt - removal and refitting
Cylinder head - removal and refitting
Sump pan - removal and refitting
Oil pump - removal and refitting
Pistons/connecting rods - removal and
refitting
Engine mountings - renewal
Part 2:
903 cc engine
5 Valve clearances-
adjustment
2
1Adjust the valves when the engine is cold.
2Unbolt and remove the rocker cover.
3It is important that the clearance is set
when the cam follower of the valve being
adjusted is on the heel of the cam (ie;
opposite the peak). This can be done by
carrying out the adjustments in the following
order, which also avoids turning the
crankshaft more than necessary.
4Turn the crankshaft either using a spanner
on the pulley nut or by raising a front
roadwheel, engaging a gear (3rd or 4th) and
turning the wheel in the forward direction of
travel. It will be easier to turn the engine if the
spark plugs are first removed.
Valve fully open Check and adjust
Valve No. 8 EX Valve No. 1 EX
Valve No. 6 IN Valve No. 3 IN
Valve No. 4 EX Valve No. 5 EX
Valve No. 7 IN Valve No. 2 IN
Valve No. 1 EX Valve No. 8 EX
Valve No. 3 IN Valve No. 6 IN
Valve No. 5 EX Valve No. 4 EX
Valve No. 2 IN Valve No. 7 IN5Count the valves from the timing cover end
of the engine.
6Remember, the inlet and exhaust valve
clearances are different.
7Insert the appropriate feeler gauge between
the end of the valve stem and the rocker arm.
It should be a stiff sliding fit (photo).
8If the clearance is incorrect, release the
rocker arm adjuster screw locknut using a ring
spanner. Turn the adjuster screw using a
small open-ended spanner, but tie something
to it in case it is inadvertently dropped
through one of the pushrod holes.
9Once the clearance is correct, tighten the
locknut without moving the position of the
adjuster screw.
10Repeat the operations on the remaining
seven valves.
11Re-check all the clearances. Make sure
that the rocker cover gasket is in good
condition and fit the rocker cover.
6 Timing chain and sprockets
- removal and refitting
3
1Remove the alternator drivebelt as
described in Chapter 2.
2Unscrew and remove the crankshaft pulley
nut.3Disconnect the hoses from the fuel pump.
4Unbolt and remove the fuel pump with
spacer and rod.
5Support the engine on a hoist or under the
sump and disconnect and remove the
right-hand mounting. Then unscrew and
remove the timing cover bolts. The base of
the cover is secured by the front two sump
pan studs. Unbolt and lower the front end of
the sump. Avoid breaking the gasket. Remove
the timing cover.
6Undo and remove the camshaft sprocket
securing bolt; this will also release the fuel
pump drive cam from the end of the camshaft.
Note the timing marks on the camshaft and
crankshaft sprockets.
7Using two tyre levers, carefully ease the two
sprockets forwards away from the crankcase.
Lift away the two sprockets and timing chain.
8Remove the Woodruff key from the
crankshaft nose with a pair of pliers and note
how the channel in the pulley is designed to fit
over it. Place the Woodruff key in a container
as it is a very small part and can easily
become lost. The camshaft sprocket is
located on the camshaft by a dowel peg.Refitting
9Fit the Woodruff key to the front of the
crankshaft.
10Tap the crankshaft sprocket onto the front
of the crankshaft.
11Turn the sprocket so that the Woodruff
key is uppermost.
12Turn the camshaft until it is in such a
position that if the sprocket was fitted the
dimple timing mark on the sprocket would be
nearest to and in alignment with, the one on
the crankshaft sprocket.
903 cc engine 1•9
5.7 Adjusting a valve clearance
1 Sprocket retaining bolt
2 Fuel pump eccentric cam
3 Timing chain4 Camshaft sprocket
5 Sprocket locating dowel
6 Camshaft7 Woodruff key
8 Crankshaft
9 Crankshaft sprocket
Fig. 1.6 Timing chain and sprockets (Sec 6)
1
To prevent the crankshaft
rotating, either select a gear
and have an assistant apply
the footbrake hard or
remove the starter motor and lock the
ring gear teeth with a large cold chisel
or screwdriver.
Page 24 of 303

13Engage the timing chain with the teeth of
the crankshaft sprocket. Then locate the
camshaft sprocket within the upper loop of
the chain in such a way that when the
sprocket is pushed onto the camshaft, the
timing marks will be in alignment. Make sure
that the self-tensioning links are on the inside
of the chain against the cylinder block
(photos).
14Place the camshaft sprocket onto the
camshaft so that its positioning dowel
engages.
15Secure the camshaft sprocket by fitting
the special cam, that drives the fuel pump, on
its locating dowel. Fit the camshaft sprocket
retaining bolt (photo).
16Tighten the sprocket bolt to the specified
torque.
17If the timing cover oil seal showed signs of
leaking before engine overhaul the old seal
should be removed and a new one fitted.
18Using a screwdriver, carefully remove the
old oil seal, working from the rear of the cover.
Fit the new seal making sure it is inserted
squarely, and tap home with a hammer.
19Lubricate the oil seal with engine oil.
20With all traces of old gasket and jointing
compound removed from the timing cover
and cylinder block mating faces, smear a little
grease onto the timing cover mating face and
fit a new gasket in position.
21Fit the timing cover to the cylinder block
and finger tighten the securing bolts, and
spring washer. Ensure that the fuel pump
pushrod bush is in place in the cover.22Wipe the hub of the pulley and carefully
place into position on the crankshaft. It should
locate on the Woodruff key. It may be
necessary to adjust the position of the timing
cover slightly in order to centralise the oil seal
relative to the pulley hub.
23Tighten the timing cover securing bolts in
a diagonal and progressive manner.
24Tighten the crankshaft pulley nut to the
specified torque again holding the crankshaft
against rotation as previously described
(paragraph 2) this Section.
25Refit the fuel pump and alternator
drivebelt.
7 Cylinder head-
removal and refitting
3
1For safety reasons, disconnect the battery
negative lead.
2Refer to Chapter 2 and drain the cooling
system.
3Refer to Chapter 3 and remove the
carburettor, air cleaner and spacer block.
4Undo and remove the five nuts and
washers securing the exhaust manifold and
hot air ducting to the cylinder head.
5Detach the cable from the temperature
indicator sender unit.
6Refer to Chapter 4 and disconnect the
distributor LT lead and the coil HT lead.
7Refer to Chapter 2 and remove the
thermostat housing from the cylinder head.
8Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
cylinder head.
9Note the electrical connections to the rear
of the alternator and disconnect them.
10Disconnect the mounting and adjuster link
bolts and remove the alternator from the
engine.
11Unscrew the four nuts securing the rocker
cover to the top of the cylinder head and lift
away the spring washers and metal packing
pieces. Remove the rocker cover and cork
gasket.
12Unscrew the four rocker pedestal
securing nuts in a progressive manner. Lift
away the four nuts and spring washers andease the valve rocker assembly from the
cylinder head studs.
13Remove the pushrods, keeping them in
the relative order in which they were removed.
The easiest way to do this is to push them
through a sheet of thick paper or thin card in
the correct sequence.
14Unscrew the cylinder head securing bolts
half a turn at a time in the reverse order to that
shown in Fig. 1.7; don’t forget the one within
the inlet manifold. When all the bolts are no
longer under tension they may be unscrewed
from the cylinder head one at a time. This will
also release a section of the cooling system
pipe secured by two of the bolts. All the bolts
have washers.
15The cylinder head may now be lifted off. If
the head is jammed, try to rock it to break the
seal. Under no circumstances try to prise it
apart from the cylinder block with a
screwdriver or cold chisel as damage may be
done to the faces of the head or block. If this
or the Hint, fail to work, strike the head
sharply with a plastic headed hammer, or with
a wooden hammer, or with a metal hammer
with an interposed piece of wood to cushion
the blows. Under no circumstances hit the
head directly with a metal hammer as this may
cause the casting to fracture. Several sharp
taps with the hammer, at the same time
pulling upwards, should free the head. Lift the
head off and place on one side.
16The cylinder head may now be de-
carbonised or dismantled, refer to Section 17.
Refitting
17After checking that both the cylinder block
and cylinder head mating surfaces are
perfectly clean, generously lubricate each
cylinder with engine oil.
18Always use a new cylinder head gasket as
the old gasket will be compressed and not
capable of giving a good seal.
1•10 903 cc engine
6.15 Fitting fuel pump drive cam and
sprocket bolt
6.13C Self-tensioning links on inside of
chain6.13B Timing mark alignment6.13A Fitting the sprockets and timing
chain
If the head will not readily
free, turn the crankshaft.
The compression generated
in the cylinders will often
break the gasket joint
Page 25 of 303

19Never smear grease on the gasket as,
when the engine heats up, the grease will melt
and may allow compression leaks to develop.
20The cylinder head gasket cannot be fitted
incorrectly due to its asymmetrical shape, but
the word ALTO should be uppermost in any
event (photo).
21The locating dowels should be refitted to
the front right and left-hand side cylinder head
securing bolt holes.
22Carefully fit the cylinder head gasket to
the top of the cylinder block.
23Lower the cylinder head onto the gasket,
taking care not to move the position of the
gasket.
24Screw in the cylinder head bolts finger
tight, remembering the bolt within the intake
manifold and the metal coolant pipe which is
held by the two cylinder head bolts adjacent to
the coolant temperature sender unit (photos).
25Tighten the cylinder head bolts in two
stages, in the specified sequence to the
torque given in Specifications.
26With the cylinder head in position, fit the
pushrods in the same order in which they
were removed. Ensure that they locate
properly in the stems of the tappets and
lubricate the pushrod ends before fitment
(photo).
27Unscrew the rocker arm adjuster screws
as far as they will go.
28Fit the rocker gear over the four studs in
the cylinder head and lower onto the cylinder
head. Make sure the ball ends of the rockers
locate in the cups of the pushrods.29Fit the four nuts and washers to the rocker
shaft pedestal studs and tighten in a
progressive manner to the torque wrench
setting given in the Specifications.
30Adjust the valve clearances as described
in Section 5.
31Fit the exhaust manifold, thermostat
housing and alternator, also the rocker cover
(photo).
32Fit the carburettor, air cleaner and
distributor (Chapter 4).
33Reconnect all hoses and electrical leads,
including the battery.
34Refill the cooling system.
8 Sump pan-
removal and refitting
1
1Drain the engine oil.
2Unscrew and remove the four nuts and
twelve bolts and lift away the sump pan. If it
has stuck on the gasket carefully tap the side
of the mating flange to break the seal.
Remove the gasket and clean away any
pieces of gasket cement which are adhering
to the flanges.
3Remove the sealing strips from the
recesses at either end of the sump pan.
Refitting
4Fit the new sealing strips and if necessary,
trim their ends until they are just proud of the
sump pan flange (photo).5Using thick grease, stick the gasket side
strips to the crankcase.
6Apply a blob of jointing compound at the
points of overlap of the side gaskets and
strips.
7Offer up the sump pan, screw in and tighten
the bolts and nuts progressively (photos).
8Refill the engine with oil.
903 cc engine 1•11
7.24B Cylinder head bolts holding coolant
pipe7.24A Cylinder head bolt in intake manifold7.20 Cylinder head gasket
7.31 Fitting the rocker cover
7.26 Fitting a pushrod
Fig. 1.7 Cylinder head bolt tightening
sequence (Sec 7)1
8.4 Sump pan sealing strip8.7A Fitting the sump pan