1983 FIAT UNO lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 36 of 303

17Screw in the camshaft front bearing
lockscrew (photo).
Oil pump
18Refit the oil pump as described in Sec-
tion 10.
Timing chain and sprockets
19Fit the timing chain and sprockets as
described in Section 6. Fit the Woodruff key
to the crankshaft nose.
20Using a new gasket, fit the timing chain
cover, but leave the bolts finger tight (photo).
21Apply grease to the lips of the timing
cover oil seal and then push the crankshaft
pulley into position.
22Move the timing cover if necessary so that
the pulley hub is centralised in the oil seal and
then tighten the cover bolts.
23Screw on the crankshaft pulley nut and
tighten to the specified torque (photo).
Piston/connecting rods
24Fit these as described in Section 9.
Sump pan
25Fit the sump pan as described in Sec-
tion 8.
Cylinder head
26Stand the engine upright and fit the
cylinder head as described in Section 7.
27Insert the pushrods in their original fitted
order.
28With the rocker arm adjuster screws fully
unscrewed, locate the rocker gear and screw
on the fixing nuts.
29Adjust the valve clearances as described
in Section 5.
30Locate a new gasket in position and fit the
rocker cover (photo).
31Screw on a new oil filter (Section 2).
21 Engine- refitting ancillary
components
1Refer to Chapter 5 and refit the clutch,
making sure to centralise the driven plate.
2Fit the coolant pump as described in
Chapter 2. Fit the thermostat housing if it was
removed noting the air cleaner mounting
bracket on the housing studs.
3Fit the alternator and drivebelt as described
in Chapter 9.
4Refer to Chapter 3 and fit the exhaust
manifold and hot air collector, the carburettor
and spacer and the fuel pump.
5Fit the distributor as described in Chapter
4. Fit the oil dipstick guide tube (photos).
22 Engine/transmission-
reconnection
1
1Support the weight of the transmission and
offer it squarely to the engine. The splined
input shaft should pass easily through the hub
of the driven plate, provided the plate has
been centralised as described in Chapter 5. It
may be necessary to align the splines with the
hub grooves, in which case have an assistant
turn the crankshaft pulley nut. The alignment
dowels will make the connection stiff, so
drawing the engine and transmission together
with two connecting bolts will ease it.
2Once the engine and transmission are fully
engaged, insert and tighten all the connecting
bolts. Locate the lifting eyes.
3Bolt on the flywheel housing cover plate
and the mounting brackets.
4Bolt on the starter motor.
23 Engine/transmission-
refitting
3
1The refitting operations are reversals of
those described in Section 13.
2Observe the following special points.
3Tighten the engine mounting and front
suspension (disconnected) bolts to the
specified torque when the hoist has been
1•22 903 cc engine
21.5B Dipstick guide tube support21.5A Dipstick guide tube20.30 Rocker cover nut and thrust plate
20.23 Tightening crankshaft pulley nut20.20 Timing cover20.17 Camshaft front bearing lockscrew
Hold the crankshaft against
rotation either by jamming
the starter ring gear or by
placing a block of wood
between a crankshaft web and the
inside of the crankcase.
Page 39 of 303

8Fit the new belt. Start at the crankshaft
drive pulley and, taking care not to kink or
strain the belt, slip it over the camshaft pulley.
The camshaft may have to be turned slightly
to mesh the pulley with the teeth on the belt.
Fit the belt on the tensioner pulley last; if this
is difficult, do not lever or force the belt on,
recheck the belt (photo).
9Release the tensioner nut and rotate the
crankshaft through two complete revolutions.
Retighten the nut. The belt tension may be
checked by twisting it through 90º with the
finger and thumb. It should just turn through
this angle without undue force. Note: The
above procedure serves only as a rough guide
to setting the belt tension - having it checked
by a FIAT dealer at the earliest opportunity is
recommended.
10Refit the timing belt cover (photo). Fit and
tension the alternator drivebelt (Chapter 2,
Section 8).
29 Cylinder head-
removal and refitting
3
1Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 2).
2Disconnect the battery.
3Disconnect and plug the carburettor fuel
hoses.
4Disconnect the throttle and choke linkage
from the carburettor. 5Disconnect the HT leads from the spark
plugs.
6Disconnect the brake servo vacuum hose
from the intake manifold.
7Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
thermostat housing.
8Disconnect the crankcase ventilation
system hoses from the rocker cover and
carburettor.
9Unbolt and remove the timing belt cover.
10Release the timing belt tensioner pulley
bolt, then lever the pulley against the spring
plunger and retighten the bolt to retain the
tensioner pulley in the non-tensioned position.
Slip the belt from the camshaft sprocket.
11Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
carburettor and intake manifold.
12Disconnect the exhaust downpipes from
the manifold.
13If a crowfoot type wrench is available, the
cylinder head nuts and bolts can be removed
and the complete cylinder head camshaft
carrier assembly withdrawn (photo).
14If this type of wrench is not available
however, remove the carrier first as described
in Section 27.
15If a crowfoot is available, unscrew the
cylinder head nuts and bolts evenly and
progressively starting with the centre ones
and working towards both ends.
16Rock the cylinder head by gripping the
manifolds. Note: Do not insert a lever in
the gasket joint to prise the head from the
block.17Pull the head off the studs and remove it
to the bench. Remove and discard the old
cylinder head gasket.
18Unbolt and remove the hot air collecting
shield for the air cleaner from the exhaust
manifold. The exhaust and inlet manifolds can
now be unbolted. The carburettor may remain
on the inlet manifold.
19Overhaul and decarbonising of the
cylinder head is described in Section 39.
20Refitting is a reversal of the removal
process, but make sure the crankshaft and
camshaft timing marks are set as described in
Section 28 to avoid the valve heads digging
into the piston crowns when the head is
refitted.
21Always use new gaskets. The cylinder
1116 cc and 1301 cc engine 1•25
Fig. 1.29 Timing belt arrangement (Sec 28)
1 Camshaft sprocket
2 Tensioner pulley locknut
3 Timing mark on crankshaft front oil seal
retainer
4 Crankshaft sprocket
5 Crankshaft sprocket timing mark
6 Auxiliary shaft sprocket
7 Tensioner bracket bolt
8 Tensioner pulley
9 Timing belt
10 Tensioner bracket
11 Tensioner spring
28.8 Slipping timing belt onto tensioner
pulleyFig. 1.28 TDC marks (1) at front of engine
(Sec 28)
Fig. 1.30 Cylinder head bolt tightening
sequence (Sec 29)28.10 Tightening timing belt cover nut29.13 Using a crowfoot type wrench on a
cylinder head bolt
1
Page 40 of 303

head gasket must be fitted (ALTO visible) so
that the oil pressure hole in the block is
central in the copper ringed cut-out in the
gasket (photos). Make sure that the gasket
surfaces on head and block are perfectly
clean and free from oil, otherwise the heat
sealing (polymerisation) process of the gasket
cannot take place.
22Tighten the cylinder head nuts and bolts
to the specified torque, in the sequence
shown in Fig. 1.30. Follow the procedure very
carefully owing to the special type (ASTADUR)
of gasket used which hardens in use. Always
keep a new cylinder head gasket in its
nylon cover until just before it is required for
use.
23Oil the cylinder head bolts and
washers and allow them to drain for thirty
minutes.
24Tighten the bolts in the following
stages:
Stage 1 20 Nm (15 lbf ft)
Stage 2 40 Nm (30 lbf ft)
Stage 3 Through 90º
Stage 4 Through 90º (photo)
Retightening the bolts after a running-in
mileage is not required.
25Fit the timing belt (Section 28).
26Check the valve clearances (Section 26)
after the camshaft carrier has been fitted
(Section 27).
27Bolt on the camshaft carrier cover.
28Reconnect all hoses, leads and controls.
29Reconnect the battery and refill the
cooling system.
30 Sump pan-
removal and refitting
1
1Position the car over an inspection pit or
raise the front wheels on ramps.
2Disconnect the battery.
3Drain the engine oil. Unbolt and remove the
flywheel housing lower cover plate.
4Unbolt the sump pan and remove it
together with its gasket.
5Refitting is a reversal of removal. Always
use a new gasket locating it on clean mating
flanges and tighten the fixing bolts evenly and
progressively (photo).
6Fill the engine with oil and reconnect the
battery.
31 Oil pump-
removal and refitting
1
1Remove the sump pan as described in the
preceding Section.
2Unbolt the oil pump and withdraw it
complete with driveshaft.
3Use a new gasket when refitting the pump
and prime the pump by pouring engine oil
through the pick-up filter screen (photo).
32 Pistons/connecting rod-
removal and refitting
3
1Remove the sump pan and the oil pump as
described in Sections 30 and 31.
1•26 1116 cc and 1301 cc engine
Fig. 1.31 Piston/connecting rod assembly
diagram (Sec 32)
1 Matching numbers
2 Gudgeon pin offset
3 Auxiliary shaft
Arrow indicates direction of rotation of
crankshaft viewed from timing belt end
29.24 Tightening a cylinder head bolt
through 90º using a protractor
31.3 Bolting on the oil pump30.5 Locating the sump pan gasket
29.21C Lowering cylinder onto block29.21B Cylinder head gasket in position -
cylinder block drain plug arrowed29.21A Cylinder head gasket top face
marking
Page 41 of 303

2The big-end bearing shells can be renewed
without having to remove the cylinder head if
the caps are unbolted and the
piston/connecting rod pushed gently about
one inch up the bore (the crankpin being at its
lowest point). If these shells are worn,
however, the main bearing shells will almost
certainly be worn as well. In this case, the
engine should be removed for complete
overhaul including crankshaft removal.
3To remove the piston/connecting rods,
remove the cylinder head as described in
Section 29.
4Grip the oil pick-up pipe and twist or rock it
from its hole in the crankcase. It is an
interference fit in the hole.
5Unscrew the nuts from the big-end caps,
then remove the caps with their bearing
shells. The caps and their connecting rods are
numbered 1, 2, 3 and 4 from the timing cover
end of the engine. The numbers are adjacent
at the big-end cap joint and on the side of the
crankcase furthest from the auxiliary shaft.
6If the bearing shells are to be used again,
tape them to their respective big-end caps.
7Push each connecting rod/piston assembly
up the bore and out of the cylinder block.
There is one reservation; if a wear ridge has
developed at the top of the bores, remove this
by careful scraping before trying to remove
the piston/rod assemblies. The ridge will
otherwise prevent removal or break the piston
rings during the attempt.
8If the connecting rod bearing shells are to
be used again, tape the shells to their
respective rods.
9Dismantling the piston/connecting rod is
described in Section 18.
Refitting
10Fit the new shells into the connecting rod
and caps, ensuring the surfaces on which the
shells seat, are clean and dry.
11Check that the piston ring gaps are evenly
spaced at 120º intervals. Liberally oil the rings
and the cylinder bores.
12Fit a piston ring clamp to compress the
rings.
13Insert the piston/connecting rod into the
cylinder bore, checking that the rod assembly
is correct for that particular bore. The cap and
rod matching numbers must be furthest away
from the auxiliary shaft (Fig. 1.31).14Push the piston into the bore until the
piston ring clamp is against the cylinder block
and then tap the crown of the piston lightly to
push it out of the ring clamp and into the bore
(photo).
15Oil the crankshaft journal and fit the
big-end of the connecting rod to the journal.
Fit the big-end cap and nuts, checking that
the cap is the right way round (photo).
16Tighten the big-end nuts to the specified
torque. The correct torque is important as the
nuts have no locking arrangement. After
tightening each big-end, check the crankshaft
rotates smoothly (photo).
17Refit the oil pick-up pipe, the cylinder
head, oil pump and sump pan, all as
described earlier.
18Refill the engine with oil and coolant.
33 Engine mountings-
renewal
1
1Three engine/transmission flexible
mountings are used.
2To renew a mounting, support the weight of
the engine/transmission on a hoist or jack and
unbolt and remove the mounting.
3In the unlikely event of all three mountings
requiring renewal at the same time, only
disconnect them and renew them one at a
time.
34 Engine- method of removal
1The engine complete with transmission
should be removed by lowering it to the floor
and withdrawing it from under the front of the
car which will have been raised to provide
adequate clearance.
35 Engine/transmission-
removal and separation
3
1Open the bonnet, disconnect the
windscreen washer tube.
2Mark the hinge positions on the undersideof the bonnet and then with the help of an
assistant to support its weight unbolt and
remove the bonnet to a safe place.
3Disconnect the battery negative lead.
4Drain the cooling system and the engine
and transmission oils.
5Remove the air cleaner.
6From the rear of the alternator disconnect
the electrical leads.
7Disconnect the leads from the starter
motor, oil pressure and coolant temperature
switches, also the oil temperature switch.
8Disconnect the LT lead from the distributor
and the HT lead from the ignition coil.
9Disconnect the clutch cable from the
release lever at the transmission. Also
disconnect the speedometer drive cable
(knurled ring).
10Pull the leads from the reversing lamp
switch.
11Disconnect all coolant hoses from the
engine. Also disconnect the brake servo hose
from the intake manifold.
12Disconnect the choke and throttle
controls from the carburettor.
13Disconnect the inlet hose from the fuel
pump and plug the hose.
14Disconnect the fuel return hose from the
carburettor.
15Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
carburettor throttle block.
16Raise the front of the car and remove the
front roadwheels.
17Unscrew and remove the driveshaft to
hub nuts. These are very tight and a long
knuckle bar will be required when unscrewing
them. Have an assistant apply the brake pedal
hard to prevent the hub from turning.
18Working under the car, remove the inner
wing protective shields and then disconnect
the exhaust downpipe from the manifold.
19Disconnect the exhaust pipe sections by
removing the socket clamp just forward of the
rear axle beam. Remove the front section.
20Disconnect the forward ends of the
gearchange rods by prising their sockets from
the ballstuds.
21Unscrew the nuts on the steering tie-rod
end balljoints and then using a suitable
“splitter” tool, separate the balljoints from the
steering arms.
22Unbolt the front brake hose support clips
1116 cc and 1301 cc engine 1•27
32.16 Tightening a big-end cap nut32.15 Fitting a big-end cap32.14 Fitting piston into cylinder bore
1
Page 42 of 303

from the suspension struts and then remove
the bolts which secure the hub carriers to the
U-clamps at the base of the suspension
struts.
23Pull the tops of the hub carriers down and
then outwards and push the driveshafts from
them.
24Unbolt the driveshaft inboard boot
retainers and then remove the driveshafts
from the transmission.
25Support the engine on a hoist or use a
trolley jack under the engine/transmission.
Remove the bottom mounting and then the
upper left and right-hand ones.
26Lower the power unit to the floor by
pushing it to the left-hand side to clear the
right-hand mounting bracket and then swivel
the gearbox towards the rear of the car.
Withdraw the engine/transmission from under
the car.
27External dirt and grease should now be
removed using paraffin and a stiff brush or a
water-soluble solvent.
28Unbolt and remove the engine mounting
brackets and the starter motor.
29Unbolt and remove the cover plate with
the gearchange ball stud strut from the lower
front face of the flywheel housing.
30With the engine resting squarely on its
sump pan, unscrew the flywheel housing
connecting bolts, noting the location of any
lifting lugs and hose and wiring clips.
31Support the weight of the transmission
and withdraw it in a straight line from the
engine.
36 Engine- dismantling (general)
Refer to Section 14, Part 2.
37 Engine ancillary components
- removal
Refer to Section 15, Part 2 and also remove
the intake manifold.
38 Engine-
complete dismantling
3
1Have the engine resting squarely and
supported securely on the work surface.
2Unbolt and remove the timing belt cover.
3Grip the now exposed timing belt with the
hands and loosen the camshaft sprocket.
4Release the timing belt tensioner pulley
centre bolt, then slip the belt from the pulley
and sprockets to remove it. Note which way
round the belt is fitted, usually so that the
lettering on the belt can be read from the
crankshaft pulley end of the engine.
5Remove the camshaft sprocket.6Unbolt and remove the camshaft timing belt
cover backing plate.
7Unbolt and remove the camshaft carrier
cover.
8Unbolt the camshaft carrier and lift it off
very slowly, at the same time pushing the cam
followers and their shims down with the
fingers securely onto their respective valve
springs. It is easy to remove the camshaft
carrier too quickly with some of the cam
followers stuck in it and as the carrier is lifted
away, the cam followers will fall out. If this
happens, the valve clearances will be upset as
the cam followers and shims cannot be
returned, with any certainty, to their original
positions. Keep the cam followers and shims
in their originally fitted order.
9Unscrew and remove the cylinder head
bolts and nuts, grip the manifold, rock the
head and remove the complete cylinder
head/manifold/carburettor assembly. Remove
and discard the cylinder head gasket.
10Unbolt the coolant pump from the side of
the cylinder block and remove it complete
with coolant distribution pipe. Remove the
crankcase breather.
11Remove the distributor/oil pump
driveshaft. This is simply carried out by
inserting a finger into the hole vacated by the
distributor and wedging it in the hole in the
end of the driveshaft. Lift the shaft out of
mesh with the auxiliary shaft. Where the
distributor is driven by the camshaft, a cover
plate retains the oil pump driveshaft in
position.
12Unbolt and remove the sprocket from the
end of the auxiliary shaft. The sprocket is held
to the shaft with a Woodruff key.
13Unbolt the auxiliary shaft retainer and
withdraw the shaft from the crankcase.
14Unscrew and remove the crankshaft
pulley nut. This is very tight and the flywheel
starter ring gear will have to be jammed with a
cold chisel or a suitably bent piece of steel to
prevent the crankshaft rotating.
15Withdraw the crankshaft sprocket, which
is located by the Woodruff key.
16Unbolt the front engine mounting bracket
from the cylinder block, together with the
timing belt cover screw anchor bush. Unbolt
and remove the timing belt tensioner pulley.
17Unscrew the flywheel securing bolts. Thestarter ring gear will again have to be jammed
to prevent the crankshaft rotating as the bolts
are unscrewed. Mark the flywheel position in
relation to the crankshaft mounting flange,
then remove it.
18Unbolt the front and rear crankshaft oil
seal retainer bolts from the crankcase and the
sump. Remove the oil seal retainers.
19Turn the engine on its side, extract the
remaining sump bolts and remove the sump.
If it is stuck, try tapping it gently with a
soft-faced hammer. If this fails, cut all round
the sump-to-gasket flange with a sharp knife.
Do not try prising with a large screwdriver; this
will only distort the sump mating flange.
20With the sump removed, unbolt and
remove the oil pump.
21Grip the oil pick-up pipe and twist or rock
it from its hole in the crankcase. It is an
interference fit in the hole.
22Remove the piston/connecting rods as
described in Section 32.
23Before unbolting the main bearing caps,
note that they are marked with one, two, three
or four notches. No. 5 main bearing cap is
unmarked. Note that the notches are nearer
the auxiliary shaft side.
24Unbolt and remove the main bearing
caps. If the bearing shells are to be used
again, tape them to their respective caps. The
bearing shell at the centre position is plain,
the others have a lubricating groove.
25Carefully, lift the crankshaft from the
crankcase, noting the thrust washers at No. 5
main bearing. These control the crankshaft
endfloat.
39 Cylinder head- dismantling
and decarbonising
4
1The operations are similar to those
described for the ohv engine in Section 17 in
respect of decarbonising and valve grinding.
2To remove a valve, use a valve spring
compressor to compress the first valve and
then extract the split collets (photo).
3Release the valve spring compressor.
4Withdraw the valve spring cap and the
double valve springs (photos).
5Remove the valve (photo).
1•28 1116 cc and 1301 cc engine
39.4A Valve spring cap39.2 Valve spring compressor and split
collets
Page 43 of 303

6Remove the spring seat (photo).
7Discard the valve stem oil seal and fit a new
one (photo).
8Remove the remaining valves in a similar
way and keep the components in their
originally fitted sequence.
9Reassembly is a reversal of removal. Refit
the components to their original positions, but
renew the valve springs if their free length is
less than that of a new spring or if the
springs have been in operation for more than
80 000 km (50 000 miles).
10The original valve clearance adjusting
shims will no longer provide the correct
clearances if the valves have been ground in
or the seats recut. Only where dismantling of
a valve was carried out to renew a spring is
there any purpose in returning the shims to
their original locations. Try to obtain the loan
of eight thin shims from your dealer and insert
them into the tappets (cam followers) before
assembling the cam followers to the carrier,
where they should be retained with thick
grease (photo).
11Fit the camshaft carrier, complete with
cam followers and shims to the cylinder head.
12Adjust the valve clearances as described
in Section 26.
40 Examination and renovation
4
1The procedures are similar to those
described in Section 18 covering the
following:
Cylinder block and crankcase
Crankshaft and bearings
Pistons and piston rings
Flywheel
2The following additional items must also be
examined.
Oil pump
3Carefully, clamp the pump housing in a
vice, shaft downwards.
4Take off the pump cover, with the suction
pipe. This will release the oil pressure relief
valve inside. Also inside is a filter.
5Remove the internal cover plate.6Take out the driveshaft and the gears.
7Clean and examine all the parts. Measure
the clearances against the Specifications. The
end clearance is measured by putting a
straight-edge across the cover face.
8The oil pump should only need
replacements after very long mileage, when
the rest of the engine is showing great signs
of wear.
9The length of a new gear can be measured
against the old gear to see if a new gear will
restore the end clearance to the Specifica-
tions. Otherwise the housing must be
changed.
10The driven gear shaft is mounted in the
housing with an interference fit. If there is any
slackness, a new housing (which will come
with shaft fitted) must be used.
11The oil pump shares its drive with the
distributor.
Camshaft, cam followers and
shims
12The camshaft journals and cams should
be smooth, without grooves or scores.
13Wear in the camshaft carrier bearings can
only be rectified by renewal of the carrier.
14Cam follower wear is usually very small
and when they show slackness in their bores,
it is probably the light alloy of the camshaft
carrier which has worn.
15Always measure the thickness of the valve
clearance shims using a metric micrometer.
Any grooving or wear marks in the shims
should be rectified by renewal with ones of
similar thickness.
Auxiliary shaft
16The shaft journals, the fuel pump
eccentric, and the drivegear for the distributor
and oil pump should be smooth and shiny. If
not, the shaft will have to be renewed.
17The bushes should still be tight in the
cylinder block, their oil holes lined up with
those in the block.
18Measure the bearing clearance. If
excessive, the bushes will have to be
renewed. They are a press fit, and require
reaming with a special reamer after fitting.
This is a job best done by a Fiat agent with the
special tools.
19Ensure the new bushes are fitted with the
oil holes lined up.
20Also check the driven gear and its bush.
21It is recommended a new oil seal is fitted
in the endplate. Hold the shaft in a vice, and
remove the pulley. Fit the new oil seal in the
endplate, lips inwards.
Timing belt tensioner
22Check the bearing revolves smoothly and
freely, and has no play. Do not immerse it in
cleaning fluid, as it is partially sealed. Wipe
the outside, and then smear in some new
general purpose grease.
23The action of the spring will have been felt
when the belt was taken off. It should be
cleaned, and oiled, to prevent seizure through
dirt and rust.
24Note the circlip on the engine right-hand
mounting bracket. This retains the timing belt
tensioner plunger.
1116 cc and 1301 cc engine 1•29
39.6 Valve spring seat39.5 Removing a valve39.4B Double valve springs
39.10 Cam followers fitted to camshaft
carrier39.7 Valve stem oil seal
1
Page 45 of 303

plate to the crankcase, using a new gasket
(photos).
11Fit the belt sprocket and partially tighten
its bolt. Then, using an oil filter strap wrench
or similar device to hold the sprocket against
rotation, tighten the bolt to the specified
torque. Take care not to damage the teeth of
the sprocket, which is of fibre construction
(photo).
Oil sump, sump pan and
breather
12Fit the oil drain pipe by tapping it into
place, squarely in its hole in the crankcase.
Tighten its retaining bolt (photo).
13Bolt up the oil pump, using a new gasket
at its mounting flange (photo).14Fit the sump (using a new gasket) and
tighten the securing screws to the specified
torque. Note the reinforcement washers
(photo).
15Insert the oil pump/driveshaft into the
distributor hole. This does not have to be
specially positioned as the distributor is
splined to the shaft and can be set by moving
its location in the splines (refer to Chapter 4)
(photo).
16Push the breather into its crankcase
recess and tighten its securing bolt (photos).Flywheel, crankshaft sprocket
and pulley
17Make sure that the flywheel-to-crankshaft
mounting flange surfaces are clean. Althoughthe bolt holes have unequal distances
between them, it is possible to fit the flywheel
in one of two alternative positions at 180º
difference. Therefore if the original flywheel is
being refitted, align the marks made before
removal.
18If a new flywheel is being fitted, or if
alignment marks were not made before
dismantling, set No. 1 position at TDC
(crankshaft front Woodruff key pointing
vertically). Fit the flywheel to its mounting
flange so that its timing dimple is uppermost
and in alignment with the relative position of
the TDC mark on the flywheel housing
inspection window.
19Insert the bolts and tighten them to the
specified torque, jamming the ring gear to
1116 cc and 1301 cc engine 1•31
42.11 Tightening camshaft sprocket bolt.
Note sprocket locking device42.10B Tightening auxiliary shaft end plate
bolt42.10A Auxiliary shaft end plate and
gasket
42.16B Crankcase breather and retaining
bolt42.16A Crankcase breather seal42.15 Fitting oil pump driveshaft
42.14 Tightening sump pan bolt42.13 Locating oil pump and gasket42.12 Tightening oil drain pipe bolt
1
Page 47 of 303
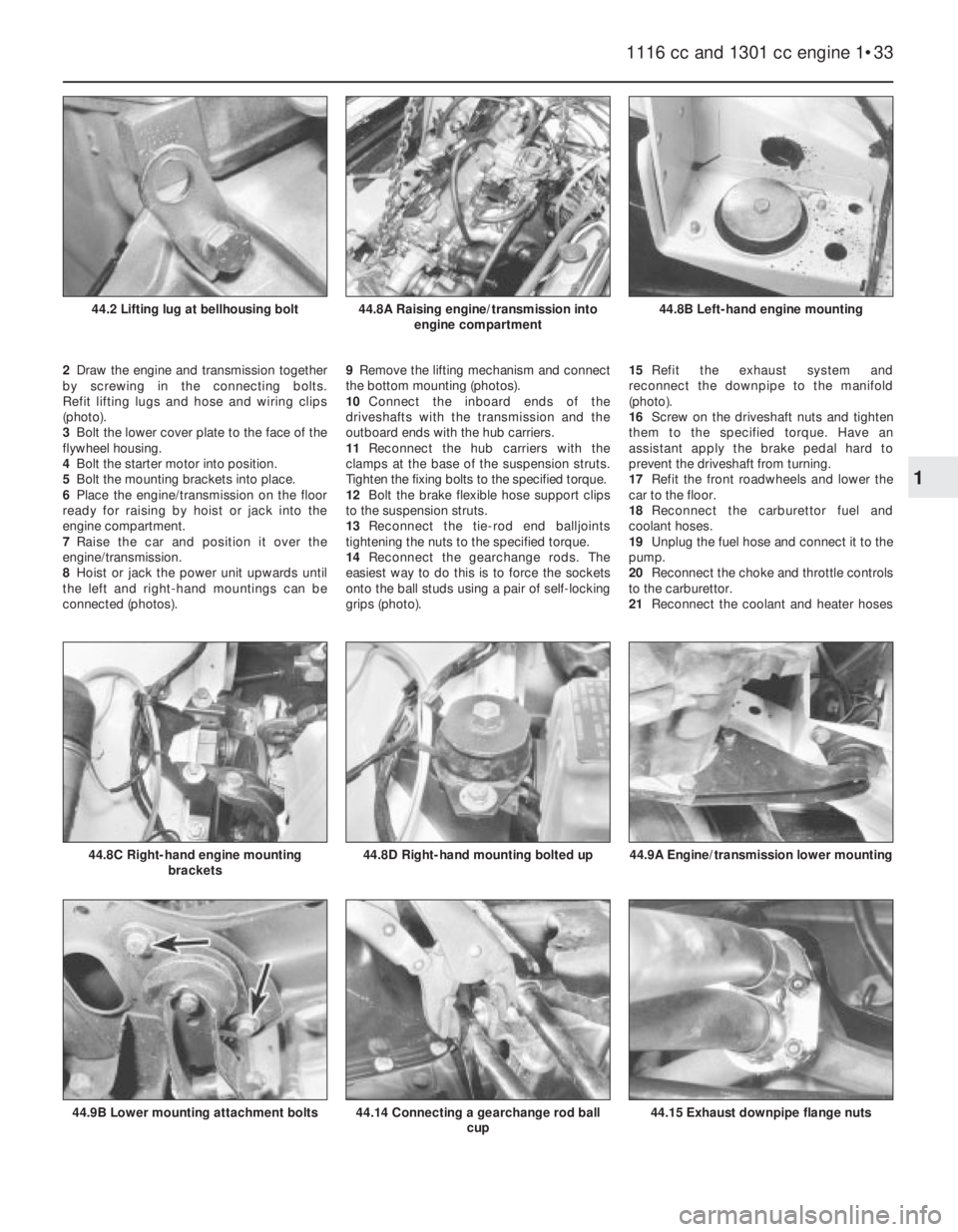
2Draw the engine and transmission together
by screwing in the connecting bolts.
Refit lifting lugs and hose and wiring clips
(photo).
3Bolt the lower cover plate to the face of the
flywheel housing.
4Bolt the starter motor into position.
5Bolt the mounting brackets into place.
6Place the engine/transmission on the floor
ready for raising by hoist or jack into the
engine compartment.
7Raise the car and position it over the
engine/transmission.
8Hoist or jack the power unit upwards until
the left and right-hand mountings can be
connected (photos).9Remove the lifting mechanism and connect
the bottom mounting (photos).
10Connect the inboard ends of the
driveshafts with the transmission and the
outboard ends with the hub carriers.
11Reconnect the hub carriers with the
clamps at the base of the suspension struts.
Tighten the fixing bolts to the specified torque.
12Bolt the brake flexible hose support clips
to the suspension struts.
13Reconnect the tie-rod end balljoints
tightening the nuts to the specified torque.
14Reconnect the gearchange rods. The
easiest way to do this is to force the sockets
onto the ball studs using a pair of self-locking
grips (photo).15Refit the exhaust system and
reconnect the downpipe to the manifold
(photo).
16Screw on the driveshaft nuts and tighten
them to the specified torque. Have an
assistant apply the brake pedal hard to
prevent the driveshaft from turning.
17Refit the front roadwheels and lower the
car to the floor.
18Reconnect the carburettor fuel and
coolant hoses.
19Unplug the fuel hose and connect it to the
pump.
20Reconnect the choke and throttle controls
to the carburettor.
21Reconnect the coolant and heater hoses
1116 cc and 1301 cc engine 1•33
44.8B Left-hand engine mounting44.8A Raising engine/transmission into
engine compartment44.2 Lifting lug at bellhousing bolt
44.15 Exhaust downpipe flange nuts44.14 Connecting a gearchange rod ball
cup44.9B Lower mounting attachment bolts
44.9A Engine/transmission lower mounting44.8D Right-hand mounting bolted up44.8C Right-hand engine mounting
brackets
1