1983 FIAT UNO heater
[x] Cancel search: heaterPage 7 of 303
Roadside Repairs0•7
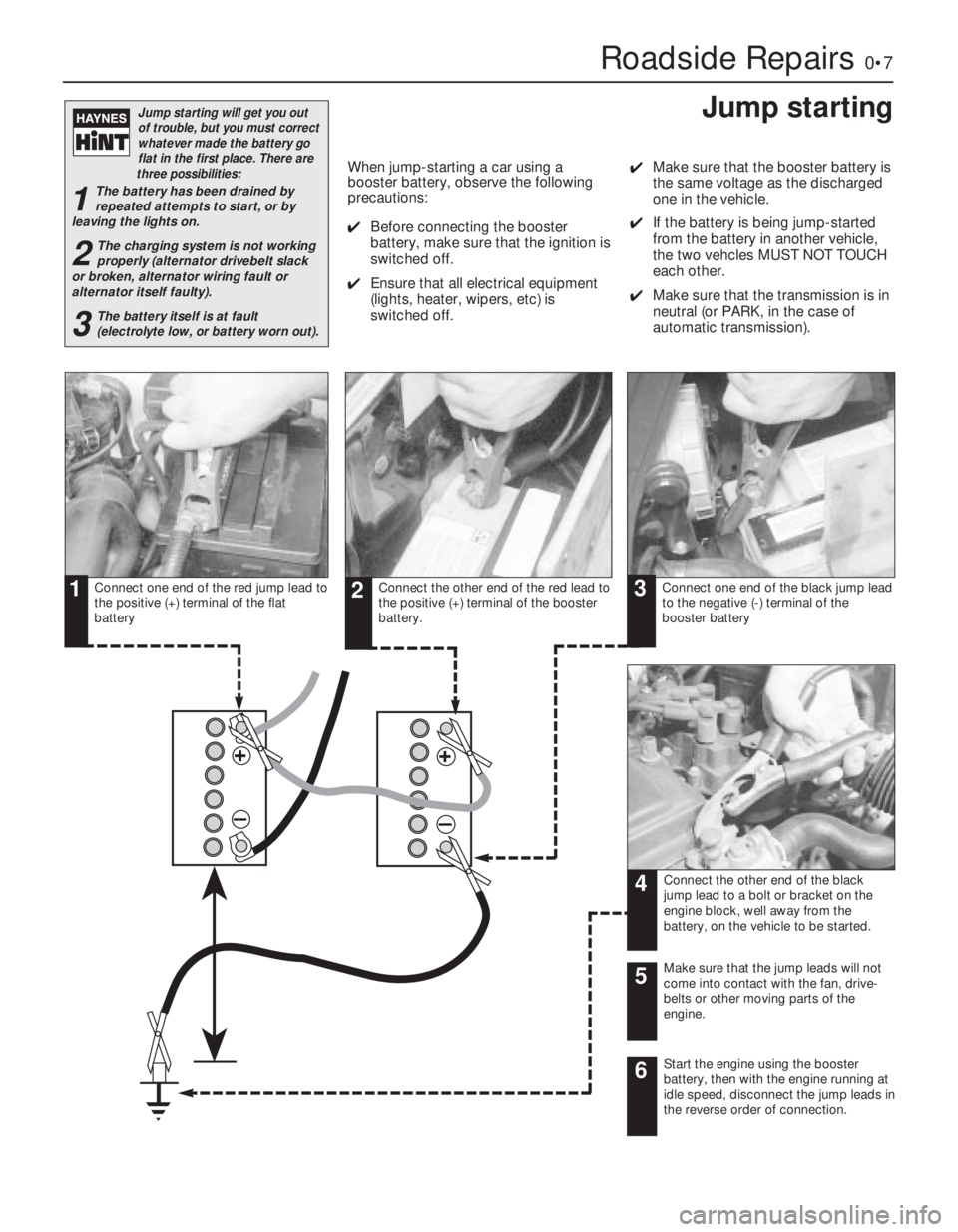
Connect one end of the red jump lead to
the positive (+) terminal of the flat
batteryConnect the other end of the red lead to
the positive (+) terminal of the booster
battery.Connect one end of the black jump lead
to the negative (-) terminal of the
booster battery
Connect the other end of the black
jump lead to a bolt or bracket on the
engine block, well away from the
battery, on the vehicle to be started.
–
+
+
–
123
4
Make sure that the jump leads will not
come into contact with the fan, drive-
belts or other moving parts of the
engine.5
Start the engine using the booster
battery, then with the engine running at
idle speed, disconnect the jump leads in
the reverse order of connection.6
Jump starting will get you out
of trouble, but you must correct
whatever made the battery go
flat in the first place. There are
three possibilities:
1The battery has been drained by
repeated attempts to start, or by
leaving the lights on.
2The charging system is not working
properly (alternator drivebelt slack
or broken, alternator wiring fault or
alternator itself faulty).
3The battery itself is at fault
(electrolyte low, or battery worn out).
Booster battery (jump) starting
When jump-starting a car using a
booster battery, observe the following
precautions:
4Before connecting the booster
battery, make sure that the ignition is
switched off.
4Ensure that all electrical equipment
(lights, heater, wipers, etc) is
switched off.4Make sure that the booster battery is
the same voltage as the discharged
one in the vehicle.
4If the battery is being jump-started
from the battery in another vehicle,
the two vehcles MUST NOT TOUCH
each other.
4Make sure that the transmission is in
neutral (or PARK, in the case of
automatic transmission).
Jump starting
Page 28 of 303
Fig. 1.20 Flywheel housing cover plate
removed (Sec 13)
Fig. 1.19 Left-hand flexible
mounting (Sec 13)
10Disconnect the leads from the reversing
lamp switch.
11Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
cylinder head and coolant pump.
12Disconnect the fuel inlet hose from the
fuel pump. Plug the hose.
13Disconnect the throttle and choke
controls from the carburettor.
14Disconnect the heater hoses from the
engine.
15Disconnect the fuel return hose from the
carburettor.
16Disconnect the exhaust downpipe from
the manifold.
17Raise the front end of the car and support
it securely on axle stands. Remove the
roadwheels.
18Unscrew the driveshaft to hub nuts. These
are very tight and a long knuckle bar will be
required when unscrewing them. Have anassistant apply the brakes hard to prevent the
hub turning.
19Working under the car, remove the
protective shields and disconnect the exhaust
system mountings and withdraw it to the
rear.
20Disconnect the forward ends of the
gearchange rods by prising their sockets from
the ballstuds.
21Unscrew the nuts on the steering tie-rod
end balljoints and using a suitable “splitter”
tool separate the balljoints from the steering
arms. Unbolt the brake calipers and tie them
up out of the way.
22Unscrew and remove the bolts which
secure the hub carriers to the U-clamps at the
base of the suspension struts (photo).
23Pull the tops of the hub carriers from the
clamps and release the driveshafts from the
hub carriers.24Tie the driveshafts in a horizontal plane
with lengths of wire.
25Support the engine on a hoist or use a
trolley jack under the engine/transmission and
remove the bottom mounting and then the
upper left and right-hand ones (photo).
26Carefully lower the power unit to the floor
and withdraw it from under the car.
27External dirt and grease should now be
removed using paraffin and a stiff brush or a
water-soluble solvent.
28Unbolt and remove the engine mounting
brackets and the starter motor.
29Unbolt and remove the cover plate and
gearchange ball stud strut from the lower front
face of the flywheel housing.
30With the engine resting squarely on its
sump pan unscrew the flywheel housing
connecting bolts noting the location of any
lifting lugs and hose and wiring brackets.
1•14 903 cc engine
13.25 Right-hand engine mounting
Fig. 1.18 Hub carrier detached
from strut clamp (Sec 13)
13.22 Hub carrier strut clamp
Fig. 1.17 Tie-rod end balljoint
disconnected (Sec 13)Fig. 1.16 Gearchange rods
disconnected (Sec 13)
Fig. 1.15 Fuel return hose
disconnected from carburettor
(Sec 13)Fig. 1.14 Fuel inlet hose
disconnected from pump
(Sec 13)Fig. 1.13 Coolant hose at rear
of coolant pump (Sec 13)Fig. 1.12 Coolant hoses at
thermostat housing (Sec 13)
Page 47 of 303
2Draw the engine and transmission together
by screwing in the connecting bolts.
Refit lifting lugs and hose and wiring clips
(photo).
3Bolt the lower cover plate to the face of the
flywheel housing.
4Bolt the starter motor into position.
5Bolt the mounting brackets into place.
6Place the engine/transmission on the floor
ready for raising by hoist or jack into the
engine compartment.
7Raise the car and position it over the
engine/transmission.
8Hoist or jack the power unit upwards until
the left and right-hand mountings can be
connected (photos).9Remove the lifting mechanism and connect
the bottom mounting (photos).
10Connect the inboard ends of the
driveshafts with the transmission and the
outboard ends with the hub carriers.
11Reconnect the hub carriers with the
clamps at the base of the suspension struts.
Tighten the fixing bolts to the specified torque.
12Bolt the brake flexible hose support clips
to the suspension struts.
13Reconnect the tie-rod end balljoints
tightening the nuts to the specified torque.
14Reconnect the gearchange rods. The
easiest way to do this is to force the sockets
onto the ball studs using a pair of self-locking
grips (photo).15Refit the exhaust system and
reconnect the downpipe to the manifold
(photo).
16Screw on the driveshaft nuts and tighten
them to the specified torque. Have an
assistant apply the brake pedal hard to
prevent the driveshaft from turning.
17Refit the front roadwheels and lower the
car to the floor.
18Reconnect the carburettor fuel and
coolant hoses.
19Unplug the fuel hose and connect it to the
pump.
20Reconnect the choke and throttle controls
to the carburettor.
21Reconnect the coolant and heater hoses
1116 cc and 1301 cc engine 1•33
44.8B Left-hand engine mounting44.8A Raising engine/transmission into
engine compartment44.2 Lifting lug at bellhousing bolt
44.15 Exhaust downpipe flange nuts44.14 Connecting a gearchange rod ball
cup44.9B Lower mounting attachment bolts
44.9A Engine/transmission lower mounting44.8D Right-hand mounting bolted up44.8C Right-hand engine mounting
brackets
1
Page 48 of 303

to the engine. Also reconnect the brake servo
hose to the intake manifold (photos).
22Reconnect the leads to the reversing lamp
switch. Reconnect the transmission earth lead
(photos).
23Reconnect the clutch cable and adjust as
described in Chapter 5.
24Reconnect the speedometer drive cable
to the transmission and tighten the knurled
retaining ring.
25Reconnect the low tension lead to the
distributor and the high tension lead to the
ignition coil.
26Reconnnect the electrical leads to thestarter motor, the oil pressure and
temperature switches and the coolant
temperature switch.
27Connect the leads to the alternator.
28Refit the air cleaner.
29Refill the cooling system. Refill the engine
with oil.
30Reconnect the battery.
31Refit the bonnet and connect the
windscreen washer tube.
32Fit the inner wing protective shields
(photo).
45 Engine- initial start-up after
major overhaul
4
1If new bearings and rings have been fitted,
it is likely that the engine will be stiff to turn so
make sure the battery is well charged.
2Switch on the ignition and check that
appropriate warning lights come on.
3Start up the engine. If it refuses to start,
refer to the “Fault Finding” Section in the
Reference section of this Manual.
4Watch the oil pressure warning light and
alternator charging indicator light. If there is
no charge or if the oil pressure warning light
does not go out after a second or two, havinghad time to fill the new oil filter, switch off and
recheck.
5If the warning lights go out, set the engine
to run on fast idle and check the engine for
leaks.
6Check the coolant level; it will probably go
down as air locks are filled.
7Keep the engine running at a fast idle and
bring it up to normal working temperature. As
the engine warms up, there will be some odd
smells and smoke from parts getting hot and
burning off oil deposits.
8When the engine running temperature has
been reached, adjust the idling speed, as
described in Chapter 3. Check and, if
necessary, adjust the ignition timing using a
stroboscope (see Chapter 4).
9Stop the engine and wait a few minutes;
check to see if there are any coolant or oil
leaks.
10Road test the car to check that the engine
is running with the correct smoothness and
power. If it does not, refer to “Fault finding” in
the Reference section of this Manual. Do not
race the engine. If new bearings and/or
pistons and rings have been fitted, it should
be treated as a new engine and run it at
reduced speed for at east 800 km (500 miles).
11After 800 km (500 miles) change the
engine oil and filter.
1•34 1116 cc and 1301 cc engine
44.32 Inner wing protective shield44.26B Coolant temperature switch44.26A Oil pressure warning switch
44.22B Transmission earth lead
44.22A Reversing lamp switch on
transmission44.21B Brake servo hose at manifold44.21A Heater hose at manifold
Page 51 of 303

2
System type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . “No loss” with radiator and integral expansion tank. Electric cooling
fan, belt-driven coolant pump, thermostat on cylinder head
General
Radiator fan cuts in . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90 to 94ºC (194 to 201ºF)
Radiator fan switches off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85 to 89ºC (185 to 192ºF)
Thermostat opens:
903 cc engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85 to 89ºC (185 to 192ºF)
1116 cc and 1301 cc engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83 to 87ºC (181 to 188.6ºF)
Fully open:
903 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100ºC (212ºF)
1116 cc and 1301 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95ºC (203ºF)
Expansion tank pressure cap rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.78 bar (11 lbf/in2)
Coolant
Capacity:
903 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.6 litre (8.1 pint)
1116 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.0 litre (10.6 pint)
1301 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.2 litre (10.9 pint)
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ethylene glycol based antifreeze
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Temperature sender switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 36
Coolant pump mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34 25
Alternator adjuster and mountings nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 36
Chapter 2 Cooling and heating systems
For modifications, and information applicable to later models, see Supplement at end of manual
Coolant mixtures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Coolant pump - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Cooling system - draining, flushing and refilling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Cooling system sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Description and maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Drivebelt - tensioning and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Fault finding - cooling and heating . . . . . . . . . . . . See end of ChapterHeater - dismantling, overhaul and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Heater unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Heating and ventilation system - description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Radiator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Radiator fan thermostatic switch - removal, checking and refitting . 5
Radiator fan - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Thermostat - removal, testing and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2•1
Specifications Contents
1 Description and
maintenance
1
1The cooling system consists of a
front-mounted radiator with built-in expansion
tank, a coolant pump (belt-driven from the
crankshaft pulley) and a thermostatically-
controlled electric cooling fan.
2In order to assist rapid warm-up, athermostat is located in a housing at the
left-hand end of the cylinder head. The hose
connections to the thermostat housing vary
according to model.
3The heater is supplied with coolant from the
engine and incorporates a matrix and blower
with the necessary controls.
4The throttle valve plate block of the
carburettor is coolant-heated as a means of
improving fuel atomisation.
5Maintenance is minimal as in theory no
coolant should ever be lost from theexpansion tank. Regularly check that the
coolant level is between 50.0 and 70.0 mm
(1.97 and 2.8 in) above the MIN mark on the
tank with the engine cold. The need for
regular topping up will indicate a leak
somewhere in the system. If one cannot be
found suspect an internal leak in the engine
although this is usually confirmed by a rise in
the engine oil level and water on the dipstick
(photo). Any topping-up should be done using
an antifreeze mixture (see Section 3), not plain
water.
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 52 of 303

6Avoid unscrewing the expansion tank cap
when the engine is hot, but if this must be
done, cover the cap with a cloth to avoid
scalding by escaping steam.
7Periodically, check the condition of all
coolant hoses and tighten the clips.
2 Cooling system- draining,
flushing and refilling
1
1Set the heater temperature lever to
maximum.
2Unscrew the cap from the expansion tank.
3Disconnect the radiator bottom hose and
unscrew the cylinder block drain plug (1116
cc and 1301 cc engines) and allow the coolant
to drain. Refer to photo 29.21B, page 64.
4If the system is in good condition with no
sign of rust or dirt in the drained coolant, then
it may be refilled immediately. If the system
has been neglected and the antifreeze has notbeen regularly renewed and there is evidence
of rust and sediment in the drained liquid then
flush the system through with a cold water
hose.
5If the radiator should appear to be clogged,
it may be necessary to remove it (Section 7)
invert it and reverse flush it using a cold water
hose. If, after a reasonable period the water
still does not run clear, the radiator should be
flushed with a good proprietary cleaning
system. Extensive damage should be repaired
by a specialist or the unit exchanged for a
new or reconditioned radiator.
6Reconnect the bottom hose and screw in
the drain plug.
7Remove the plug (B) (Fig. 2.2) from the
bleed hole in the heater hose.
8Remove the plug (D) (Fig. 2.3) from the
bleed hole in the expansion tank.
9Pour antifreeze mixture slowly into the filler
neck of the expansion tank until it is seen to
come out of the expansion tank plug hole.
Screw in the plug.
10Add further coolant until it is seen todribble out of the hole in the heater hose.
Screw in the plug.
11Top up the expansion tank to the
specified level and screw on the tank cap.
12Start the engine and run it until the cooling
fan cuts in. Switch off, allow to cool and top
up if necessary to the specified mark on the
expansion tank.
3 Coolant mixtures
1In cold climates, antifreeze is needed for
two reasons. In extreme cases, if the coolant
in the engine freezes solid it could crack the
cylinder block or head. But also in cold
weather, with the circulation restricted by the
thermostat, and any warm water that is
getting to the radiator being at the top, the
bottom of the radiator could freeze, and so
block circulation completely, making the
coolant trapped in the engine boil.
2The antifreeze should be mixed in the
proportions advocated by the makers,
according to the climate. There are two levels
of protection. The first cuts risk of damage, as
the antifreeze goes mushy before freezing.
The second, valid all year round, is the
corrosion protection it offers - see below. The
normal proportion in a temperate climate to
provide maximum protection against freezing
and corrosion is 50% antifreeze and
50% water.
3Use only ethylene glycol based antifreeze
and preferably soft water.
4Antifreeze should be left in through the
summer. It has an important secondary
function, to act as an inhibitor against
corrosion. In the cooling system are many
different metals, in particular the aluminium of
the cylinder head. In contact with the coolant
this sets up electrolytic corrosion,
accentuated by any dirt in the system. This
corrosion can be catastrophically fast.
5After about two years, the effectiveness of
the antifreeze’s inhibitor is used up. It must
then be discarded, and the system refilled
with new coolant.
6In warm climates free from frost, an
2•2 Cooling and heating systems
Fig. 2.3 Plug (D) in expansion tank (Sec 2)Fig. 2.2 Plug (B) in heater hose (Sec 2)
1.5 Expansion tank cap
Fig. 2.1 Cooling system on 903 cc engine (Sec 1)
Page 55 of 303

fluid. They are “sealed”. Liquid will get in, but
a thorough clean will be impracticable, and it
will be impossible to get new grease in.
17Check all the parts, get a new gland, two
new grommets, (1116 cc and 1301 cc) and a
new gasket. Scrape all deposits out of the
housing and off the impeller.
18To reassemble, start by inserting the new
grommets (1116 cc and 1301 cc) in the
grooves by each bearing. Fit the circlip to the
shaft, then the shouldered ring, bearings and
spacer. Fit the shaft and bearing assembly
into the cover. Fit the stop screw. Press on
the pulley.
19Fit the new gland (seal), seating it in its
location in the cover. Press the impeller onto
the shaft. The impeller must be put on part
way, and then the housing held in place to see
how far the impeller must go down the shaft
to give the correct clearance, which is 0.8 to
1.3 mm (0.03 to 0.05 in) as shown in Figs. 2.4
and 2.5.
20The impeller clearance can be checked
through the coolant passage in the side of the
pump.
21Refitting is a reversal of the removal
process, but use a new flange gasket and
tension the drivebelt as described in Section 8
(photo).
22Refill the cooling system.
10 Cooling system sensors
1A coolant temperature sender switch is
located in the cylinder head (above No. 1
spark plug) on 903 cc engines and adjacent to
No. 2 spark plug on 1116 cc and 1301 cc
engines.
2The switch operates the coolant
temperature gauge and an excessive
temperature warning lamp.
3On some models, a level sensor is screwed
into the side of the expansion tank. This
sensor consists of a pair of reed switches
within a capsule which are kept closed by the
strong magnetic flux generated by the
hydrostatic force inspired by the action of the
coolant against the float.
4If the coolant level drops then the magneticflux is weakened and the switches open.
5In the event of a fault developing, before
assuming that the cause is the sensor, check
all connecting wiring.
11 Heating and ventilation
system- description
1The heater is centrally mounted under the
facia and is of fresh air type.2Air is drawn in through the grille at the base
of the windscreen. It then passes through the
coolant heated matrix when it can then be
distributed through selective outlets
according to the setting of the control levers.
3A booster fan is provided for use when the
car is stationary or is travelling too slowly to
provide sufficient air ram effect.
4Fresh air outlets are provided at each end
and centrally on the facia panel.
12 Heater unit-
removal and refitting
1
1Drain the cooling system.
2Disconnect the heater hoses at the engine
compartment rear bulkhead.
3Working within the car under the facia
panel, disconnect the leads from the
heater blower by pulling the connecting plug
apart.
4If a radio is fitted, disconnect the
aerial, earth, speaker and power leads from
it.
Cooling and heating systems 2•5
Fig. 2.6 Checking impeller clearance
(Sec 9)9.21 Fitting coolant pump (1116 cc engine)
Fig. 2.7 Heater and ventilation system (Sec 11)
A Fresh air inlet flap
B Air distribution flap
C Coolant valveD Blower
E MatrixF Control levers
G Footwell air duct
2
Page 56 of 303
5Pull off the knobs from the control levers
(photo).
6Extract the screws and take off the control
indicator plate (photos). Disconnect the leads
from the cigar lighter and carefully detach the
fibre optic which provides the panel
illumination.
7Unscrew and remove the screws which
hold the console to the heater unit and
withdraw the console.
8The control cables can be disconnected
from the arms of the control flap valves
(photos).
9Unscrew the single screw from the upper
face of the facia panel. This screw secures theupper part of the heater casing (photo).
10Unscrew the mounting nuts which hold
the heater to the bulkhead (photo).
11Lower the heater to the floor, taking care
not to allow coolant to spill on the carpet.
12Refitting is a reversal of removal. Fill the
cooling system.
13 Heater- dismantling, overhaul
and reassembly
1
1Remove the heater from the car as
described in the preceding Section.
2•6 Cooling and heating systems
Fig. 2.10 Withdrawing heater matrix
(Sec 13)Fig. 2.9 Control lever platform screw
(Sec 13)12.10 Heater lower mounting bolt
12.9 Heater upper fixing screw
12.8A Heater coolant valve and control
cable
Fig. 2.8 Extracting heater upper fixing
screw (Sec 12)12.8B Heater flap valve cables
12.6B Removing heater control panel
escutcheon12.6A Heater control panel screw12.5 Pulling off heater control lever knob