1983 FIAT UNO length
[x] Cancel search: lengthPage 6 of 303

0•6General dimensions, weights and capacities
Dimensions
Overall length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3644 mm (143.6 in)
Overall width . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1555 mm (61.3 in)
Height . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1432 mm (56.4 in)
Wheelbase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2362 mm (93.1 in)
Front track . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1340 mm (52.8 in)
Rear track . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1300 mm (51.2 in)
Weights (kerb)
Uno 45:
Three-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 700 kg (1543 lb)
Five-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 710 kg (1566 lb)
Uno 55:
Three-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 730 kg (1610 lb)
Five-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 740 kg (1632 lb)
Uno 70:
Three-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 740 kg (1632 lb)
Five-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 750 kg (1654 lb)
Uno SX:
Three-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 770 kg (1698 lb)
Five-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 780 kg (1720 lb)
Capacities
Fuel tank . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42.0 litre (9.25 gal)
Engine oil (with filter change):
903 cc engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.42 litre (6.0 pint)
1116 and 1301 cc engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.10 Iitre (7.2 pint)
Transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.40 litre (4.2 pint)
Steering box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140.0 cc
Driveshaft CV joints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125.0 cc
Cooling system:
903 cc engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.6 litre (8.1 pint)
1116 cc engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.0 litre (10.6 pint)
1301 cc engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.2 litre (10.9 pint)
For information applicable to later models, see Supplement at end of manual
Page 14 of 303

0•14Conversion Factors
Length (distance)
Inches (in) x 25.4 = Millimetres (mm) x 0.0394 = Inches (in)
Feet (ft) x 0.305 = Metres (m) x 3.281 = Feet (ft)
Miles x 1.609 = Kilometres (km) x 0.621 = Miles
Volume (capacity)
Cubic inches (cu in; in3) x 16.387 = Cubic centimetres (cc; cm3) x 0.061 = Cubic inches (cu in; in3)
Imperial pints (Imp pt) x 0.568 = Litres (l) x 1.76 = Imperial pints (Imp pt)
Imperial quarts (Imp qt) x 1.137 = Litres (l) x 0.88 = Imperial quarts (Imp qt)
Imperial quarts (Imp qt) x 1.201 = US quarts (US qt) x 0.833 = Imperial quarts (Imp qt)
US quarts (US qt) x 0.946 = Litres (l) x 1.057 = US quarts (US qt)
Imperial gallons (Imp gal) x 4.546 = Litres (l) x 0.22 = Imperial gallons (Imp gal)
Imperial gallons (Imp gal) x 1.201 = US gallons (US gal) x 0.833 = Imperial gallons (Imp gal)
US gallons (US gal) x 3.785 = Litres (l) x 0.264 = US gallons (US gal)
Mass (weight)
Ounces (oz) x 28.35 = Grams (g) x 0.035 = Ounces (oz)
Pounds (lb) x 0.454 = Kilograms (kg) x 2.205 = Pounds (lb)
Force
Ounces-force (ozf; oz) x 0.278 = Newtons (N) x 3.6 = Ounces-force (ozf; oz)
Pounds-force (lbf; lb) x 4.448 = Newtons (N) x 0.225 = Pounds-force (lbf; lb)
Newtons (N) x 0.1 = Kilograms-force (kgf; kg) x 9.81 = Newtons (N)
Pressure
Pounds-force per square inch x 0.070 = Kilograms-force per square x 14.223 = Pounds-force per square inch
(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2) centimetre (kgf/cm2; kg/cm2) (psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Pounds-force per square inch x 0.068 = Atmospheres (atm) x 14.696 = Pounds-force per square inch
(psi; lbf/in
2; lb/in2)(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Pounds-force per square inch x 0.069 = Bars x 14.5 = Pounds-force per square inch
(psi; lbf/in
2; lb/in2)(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Pounds-force per square inch x 6.895 = Kilopascals (kPa) x 0.145 = Pounds-force per square inch
(psi; lbf/in
2; lb/in2)(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Kilopascals (kPa) x 0.01 = Kilograms-force per square x 98.1 = Kilopascals (kPa)
centimetre (kgf/cm
2; kg/cm2)
Millibar (mbar) x 100 = Pascals (Pa) x 0.01 = Millibar (mbar)
Millibar (mbar) x 0.0145 = Pounds-force per square inch x 68.947 = Millibar (mbar)
(psi; lbf/in
2; lb/in2)
Millibar (mbar) x 0.75 = Millimetres of mercury (mmHg) x 1.333 = Millibar (mbar)
Millibar (mbar) x 0.401 = Inches of water (inH
2O) x 2.491 = Millibar (mbar)
Millimetres of mercury (mmHg) x 0.535 = Inches of water (inH
2O) x 1.868 = Millimetres of mercury (mmHg)
Inches of water (inH
2O) x 0.036 = Pounds-force per square inch x 27.68 = Inches of water (inH2O)
(psi; lbf/in2; lb/in2)
Torque (moment of force)
Pounds-force inches x 1.152 = Kilograms-force centimetre x 0.868 = Pounds-force inches
(lbf in; lb in) (kgf cm; kg cm) (lbf in; lb in)
Pounds-force inches x 0.113 = Newton metres (Nm) x 8.85 = Pounds-force inches
(lbf in; lb in)(lbf in; lb in)
Pounds-force inches x 0.083 = Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft) x 12 = Pounds-force inches
(lbf in; lb in)(lbf in; lb in)
Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft) x 0.138 = Kilograms-force metres x 7.233 = Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft)
(kgf m; kg m)
Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft) x 1.356 = Newton metres (Nm) x 0.738 = Pounds-force feet (lbf ft; lb ft)
Newton metres (Nm) x 0.102 = Kilograms-force metres x 9.804 = Newton metres (Nm)
(kgf m; kg m)
Power
Horsepower (hp) x 745.7 = Watts (W) x 0.0013 = Horsepower (hp)
Velocity (speed)
Miles per hour (miles/hr; mph) x 1.609 = Kilometres per hour (km/hr; kph) x 0.621 = Miles per hour (miles/hr; mph)
Fuel consumption*
Miles per gallon (mpg) x 0.354 = Kilometres per litre (km/l) x 2.825 = Miles per gallon (mpg)
Temperature
Degrees Fahrenheit = (°C x 1.8) + 32 Degrees Celsius (Degrees Centigrade; °C) = (°F - 32) x 0.56
* It is common practice to convert from miles per gallon (mpg) to litres/100 kilometres (l/100km), where mpg x l/100 km = 282
Page 28 of 303
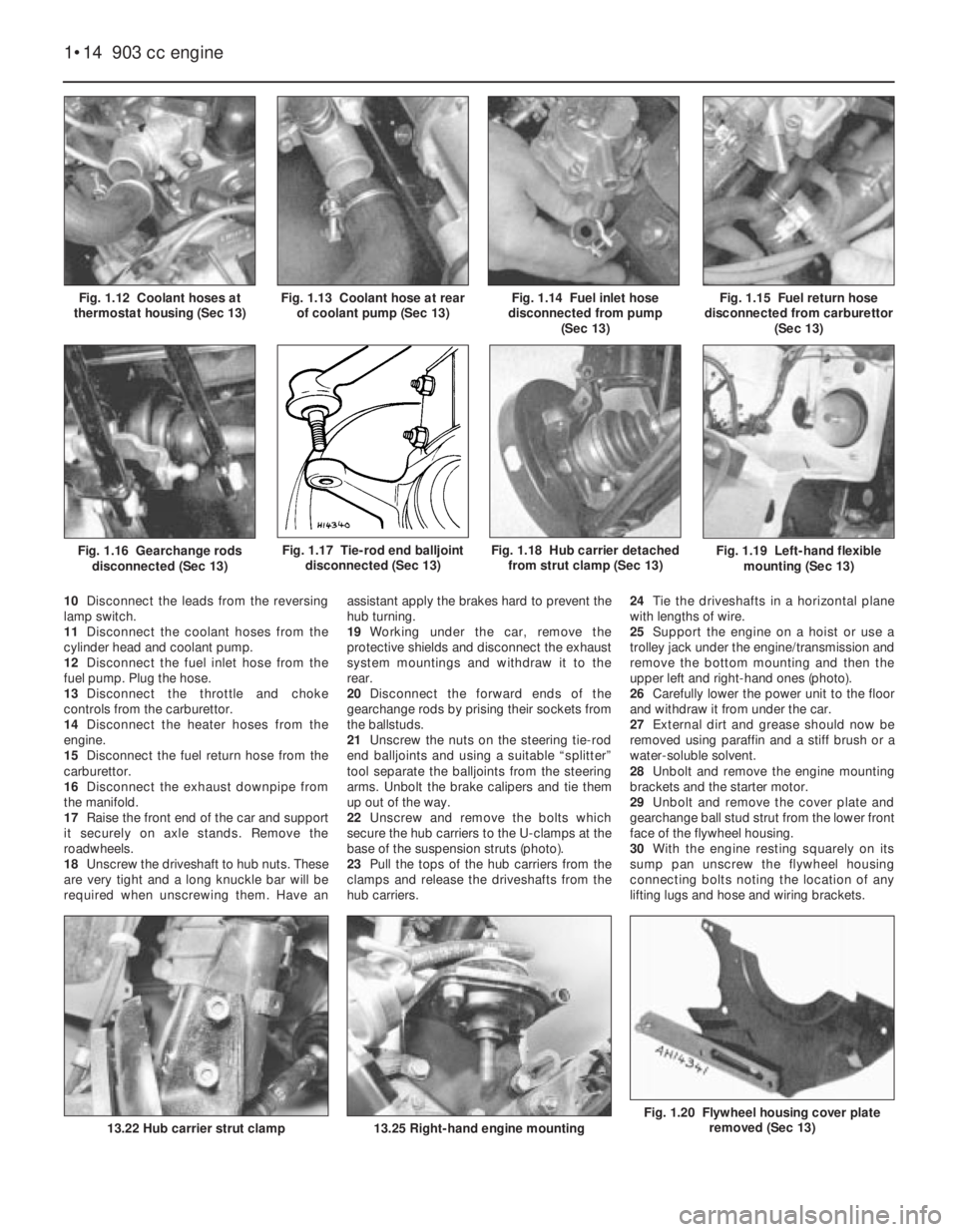
Fig. 1.20 Flywheel housing cover plate
removed (Sec 13)
Fig. 1.19 Left-hand flexible
mounting (Sec 13)
10Disconnect the leads from the reversing
lamp switch.
11Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
cylinder head and coolant pump.
12Disconnect the fuel inlet hose from the
fuel pump. Plug the hose.
13Disconnect the throttle and choke
controls from the carburettor.
14Disconnect the heater hoses from the
engine.
15Disconnect the fuel return hose from the
carburettor.
16Disconnect the exhaust downpipe from
the manifold.
17Raise the front end of the car and support
it securely on axle stands. Remove the
roadwheels.
18Unscrew the driveshaft to hub nuts. These
are very tight and a long knuckle bar will be
required when unscrewing them. Have anassistant apply the brakes hard to prevent the
hub turning.
19Working under the car, remove the
protective shields and disconnect the exhaust
system mountings and withdraw it to the
rear.
20Disconnect the forward ends of the
gearchange rods by prising their sockets from
the ballstuds.
21Unscrew the nuts on the steering tie-rod
end balljoints and using a suitable “splitter”
tool separate the balljoints from the steering
arms. Unbolt the brake calipers and tie them
up out of the way.
22Unscrew and remove the bolts which
secure the hub carriers to the U-clamps at the
base of the suspension struts (photo).
23Pull the tops of the hub carriers from the
clamps and release the driveshafts from the
hub carriers.24Tie the driveshafts in a horizontal plane
with lengths of wire.
25Support the engine on a hoist or use a
trolley jack under the engine/transmission and
remove the bottom mounting and then the
upper left and right-hand ones (photo).
26Carefully lower the power unit to the floor
and withdraw it from under the car.
27External dirt and grease should now be
removed using paraffin and a stiff brush or a
water-soluble solvent.
28Unbolt and remove the engine mounting
brackets and the starter motor.
29Unbolt and remove the cover plate and
gearchange ball stud strut from the lower front
face of the flywheel housing.
30With the engine resting squarely on its
sump pan unscrew the flywheel housing
connecting bolts noting the location of any
lifting lugs and hose and wiring brackets.
1•14 903 cc engine
13.25 Right-hand engine mounting
Fig. 1.18 Hub carrier detached
from strut clamp (Sec 13)
13.22 Hub carrier strut clamp
Fig. 1.17 Tie-rod end balljoint
disconnected (Sec 13)Fig. 1.16 Gearchange rods
disconnected (Sec 13)
Fig. 1.15 Fuel return hose
disconnected from carburettor
(Sec 13)Fig. 1.14 Fuel inlet hose
disconnected from pump
(Sec 13)Fig. 1.13 Coolant hose at rear
of coolant pump (Sec 13)Fig. 1.12 Coolant hoses at
thermostat housing (Sec 13)
Page 38 of 303

5In practice, if several shims have to be
changed, they can often be interchanged, so
avoiding the necessity of having to buy more
new shims than is necessary.
6If more than two or three valve clearances
are found to be incorrect, it will be more
convenient to remove the camshaft carrier for
easier removal of the shims.
7Where no clearance can be measured, even
with the thinnest available shim in position,
the valve will have to be removed and the end
of its stem ground off squarely. This will
reduce its overall length by the minimum
amount to provide a clearance. This job
should be entrusted to your dealer as it is
important to keep the end of the valve stem
square.
8On completion, refit the camshaft cover and
gasket.
27 Camshaft and camshaft
carrier- removal and refitting
3
1Disconnect the battery.
2Remove the air cleaner (see Chapter 3).
3Disconnect the fuel filter hose from the fuel
pump and tie it back, out of the way.
4Identify and then disconnect any electrical
leads which must be moved away to enable
the camshaft cover to be withdrawn.
5Identify and disconnect any vacuum gases
which must be moved away to enable the
camshaft cover to be withdrawn.
6Unscrew the securing nuts and remove the
camshaft cover.
7Turn the crankshaft pulley nut until No. 4
piston is at TDC. This can be established as
described in Section 28.
8Unbolt and remove the timing belt cover.
9Check that the timing mark on the camshaft
sprocket is aligned with, and adjacent to the
pointer on the timing belt cover backplate.
10Restrain the timing belt with the hand and
release but do not remove the camshaft
sprocket bolt. Release the belt tensioner
pulley by slackening the pulley centre nut.
Push the timing belt evenly from the
sprockets, noting which way round the belt isfitted if it is to be completely removed. The
lettering on the belt is normally legible from
the crankshaft pulley end of the engine when
the belt is as originally fitted.
11Unbolt the camshaft carrier and lift it
sufficiently from the cylinder head to break the
seal of the mating faces. Note: It is important
not to allow the cam followers to pull out; they
must be retained in their original locations.
This can be done if the carrier is raised very
slowly, until the fingers can be inserted to
prise the cam followers onto their respective
valve spring retainers. It is unlikely that the
valve clearance adjusting shims will be
displaced from their recesses in the cam
followers because of the suction of the
lubricating oil, but watch that this does not
happen; the shims must also be retained in
their originally fitted sequence.
12Remove the previously loosened
camshaft sprocket bolt and take the sprocket
from the camshaft.
13Unbolt and remove the camshaft end
cover with its gasket. Withdraw the camshaft
(photos).
14Refitting is a reversal of the removal
process, but observe the following points.
15Use new gaskets.
16Retain the cam followers and shims in
their bores in the camshaft carrier with thick
grease; they must not be allowed to drop out
when the carrier is lowered onto the cylinder
head.
17If the crankshaft or camshaft have been
moved from their set positions, re-align the
sprocket timing mark with the pointer on the
belt cover and the crankshaft pulley or
flywheel with the TDC mark. This must be
observed otherwise the valves may impinge
upon the piston crowns when the camshaft
lobes compress any of the valve springs
during bolting down of the carrier.
18Screw in the carrier bolts and tighten
them to the specified torque (photo).
19Refit and tension the timing belt as
described in Section 28.
20Refit the camshaft cover and gasket.
21Refit the hose and air cleaner.
22Reconnect the battery.
28 Timing belt- renewal
3
1Set No. 4 piston at TDC. Do this by turning
the crankshaft pulley nut or by jacking up a
front roadwheel, engaging a gear and turning
the wheel until the mark on the flywheel is
opposite to the TDC mark on the flywheel
bellhousing aperture. Remove No. 4 spark
plug, place a finger over the plug hole and feel
the compression being generated as the
crankshaft is rotated and the piston rises up
the cylinder bore.
2On some models the TDC marks on the
crankshaft pulley and belt cover may be
visible and can be used instead.
3Remove the alternator drivebelt (Chapter 2,
Section 8). Unbolt and remove the timing belt
cover.
4Check that the timing mark on the camshaft
sprocket is aligned with the pointer on the belt
cover backing plate (photo).
5Slacken the nut in the centre of the
tensioner pulley and push in on the support to
release the tension on the belt, then retighten
the nut. Slide the drivebelt off the pulleys.
6Check that the crankshaft and camshaft
pulleys have not been moved from their
previously aligned positions.
7To check that the auxiliary shaft sprocket
has not moved, take off the distributor cap
and check that the contact end of the rotor
arm is aligned with No. 4 HT lead contact in
the cap.
1•24 1116 cc and 1301 cc engine
28.4 Camshaft sprocket alignment marks
27.18 Tightening a camshaft carrier bolt27.13B Withdrawing camshaft from carrier27.13A Removing camshaft end cover
Page 43 of 303

6Remove the spring seat (photo).
7Discard the valve stem oil seal and fit a new
one (photo).
8Remove the remaining valves in a similar
way and keep the components in their
originally fitted sequence.
9Reassembly is a reversal of removal. Refit
the components to their original positions, but
renew the valve springs if their free length is
less than that of a new spring or if the
springs have been in operation for more than
80 000 km (50 000 miles).
10The original valve clearance adjusting
shims will no longer provide the correct
clearances if the valves have been ground in
or the seats recut. Only where dismantling of
a valve was carried out to renew a spring is
there any purpose in returning the shims to
their original locations. Try to obtain the loan
of eight thin shims from your dealer and insert
them into the tappets (cam followers) before
assembling the cam followers to the carrier,
where they should be retained with thick
grease (photo).
11Fit the camshaft carrier, complete with
cam followers and shims to the cylinder head.
12Adjust the valve clearances as described
in Section 26.
40 Examination and renovation
4
1The procedures are similar to those
described in Section 18 covering the
following:
Cylinder block and crankcase
Crankshaft and bearings
Pistons and piston rings
Flywheel
2The following additional items must also be
examined.
Oil pump
3Carefully, clamp the pump housing in a
vice, shaft downwards.
4Take off the pump cover, with the suction
pipe. This will release the oil pressure relief
valve inside. Also inside is a filter.
5Remove the internal cover plate.6Take out the driveshaft and the gears.
7Clean and examine all the parts. Measure
the clearances against the Specifications. The
end clearance is measured by putting a
straight-edge across the cover face.
8The oil pump should only need
replacements after very long mileage, when
the rest of the engine is showing great signs
of wear.
9The length of a new gear can be measured
against the old gear to see if a new gear will
restore the end clearance to the Specifica-
tions. Otherwise the housing must be
changed.
10The driven gear shaft is mounted in the
housing with an interference fit. If there is any
slackness, a new housing (which will come
with shaft fitted) must be used.
11The oil pump shares its drive with the
distributor.
Camshaft, cam followers and
shims
12The camshaft journals and cams should
be smooth, without grooves or scores.
13Wear in the camshaft carrier bearings can
only be rectified by renewal of the carrier.
14Cam follower wear is usually very small
and when they show slackness in their bores,
it is probably the light alloy of the camshaft
carrier which has worn.
15Always measure the thickness of the valve
clearance shims using a metric micrometer.
Any grooving or wear marks in the shims
should be rectified by renewal with ones of
similar thickness.
Auxiliary shaft
16The shaft journals, the fuel pump
eccentric, and the drivegear for the distributor
and oil pump should be smooth and shiny. If
not, the shaft will have to be renewed.
17The bushes should still be tight in the
cylinder block, their oil holes lined up with
those in the block.
18Measure the bearing clearance. If
excessive, the bushes will have to be
renewed. They are a press fit, and require
reaming with a special reamer after fitting.
This is a job best done by a Fiat agent with the
special tools.
19Ensure the new bushes are fitted with the
oil holes lined up.
20Also check the driven gear and its bush.
21It is recommended a new oil seal is fitted
in the endplate. Hold the shaft in a vice, and
remove the pulley. Fit the new oil seal in the
endplate, lips inwards.
Timing belt tensioner
22Check the bearing revolves smoothly and
freely, and has no play. Do not immerse it in
cleaning fluid, as it is partially sealed. Wipe
the outside, and then smear in some new
general purpose grease.
23The action of the spring will have been felt
when the belt was taken off. It should be
cleaned, and oiled, to prevent seizure through
dirt and rust.
24Note the circlip on the engine right-hand
mounting bracket. This retains the timing belt
tensioner plunger.
1116 cc and 1301 cc engine 1•29
39.6 Valve spring seat39.5 Removing a valve39.4B Double valve springs
39.10 Cam followers fitted to camshaft
carrier39.7 Valve stem oil seal
1
Page 87 of 303

The hose ends can then be unclipped from
the brackets. The mounting brackets,
particularly on the body frame, are not very
heavy gauge and care must be taken not to
wrench them off (photo).
4With the flexible hose removed, examine
the internal bore. If it is blown through first, it
should be possible to see through it. Any
specks of rubber which come out, or signs of
restriction in the bore, mean that the inner
lining is breaking up and the pipe must be
renewed.
5When refitting the flexible hoses check they
cannot be under tension, or rub, when the
wheels are at the full range of suspension or
steering movement.
6Bleed the system (see Section 12) on
completion.
Rigid pipes
7Inspect the condition of the braking system
rigid pipelines at frequent intervals. They must
be cleaned off and examined for any signs of
dents (or other percussive damage) and rust
and corrosion. Rust and corrosion should be
scraped off and, if the depth of pitting in the
pipes is significant, they will need renewal.
This is particularly likely in those areas
underneath the car body and along the rear
axle where the pipes are exposed to the full
force of road and weather conditions.
8Rigid pipe removal is usually straight-
forward. The unions at each end are undone,
the pipe and union pulled out, and the centre
sections of the pipe removed from the body
clips where necessary. Underneath the car,
exposed unions can sometimes be very tight.
As one can use only an open-ended spanner
and the unions are not large, burring of the
flats is not uncommon when attempting to
undo them. For this reason, a self-locking grip
wrench (Mole) is often the only way to remove
a stubborn union.
9Rigid pipes which need renewal can usually
be purchased at any garage where they have
the pipe, unions and special tools to make
them up. All they need to know is the total
length of the pipe, the type of flare used at
each end with the union, and the length and
thread of the union. Fiat is metric, remember.
10Fitting your new pipes is a straightforwardreversal of the removal procedure. If the rigid
pipes have been made up, it is best to get all
the sets bends in them before trying to fit
them. Also, if there are any acute bends ask
your supplier to put these in for you on a tube
bender. Otherwise, you may kink the pipe and
thereby restrict the bore area and fluid flow.
11Bleed the system (see Section 12) on
completion.
12 Hydraulic system-
bleeding
3
1If the master cylinder or the pressure
regulating valve has been disconnected and
reconnected then the complete system (both
circuits) must be bled.
2If a component of one circuit has been
disturbed then only that particular circuit need
be bled.
3The two disc brakes comprise the front
circuit and the two rear brakes the rear circuit.
4Unless the pressure bleeding method is
being used, do not forget to keep the fluid
level in the master cylinder reservoir topped
up to prevent air from being drawn into the
system which would make any work done
worthless.
5Before commencing operations, check that
all system hoses and pipes are in good
condition with all unions tight and free from
leaks.
6Take great care not to allow hydraulic fluid
to come into contact with the vehicle
paintwork as it is an effective paint stripper.
Wash off any spilled fluid immediately with
cold water.
7As the system on 55 and 70 models
incorporates a vacuum servo, destroy the
vacuum by giving several applications of the
brake pedal in quick succession. The car
should be loaded with enough weight to
actuate the pressure regulating valve before
bleeding commences.
Bleeding - two man method
8Gather together a clean glass jar and a
length of rubber or plastic tubing which will be
a tight fit on the brake bleed screws (photo).9Engage the help of an assistant.
10Push one end of the bleed tube onto the
flrst bleed screw and immerse the other end
of the glass jar which should contain enough
hydraulic fluid to cover the end of the tube.
11Open the bleed screw one half a turn and
have your assistant depress the brake pedal
fully then slowly release it. Tighten the bleed
screw at the end of each pedal downstroke to
obviate any chance of air or fluid being drawn
back into the system.
12Repeat this operation until clean hydraulic
fluid, free from air bubbles, can be seen
coming through into the jar.
13Tighten the bleed screw at the end of a
pedal downstroke and remove the bleed tube.
Bleed the remaining screws in a similar way.
Bleeding - using a one way
valve kit
14There are a number of one-man, one-way
brake bleeding kits available from motor
accessory shops. It is recommended that one
of these kits is used wherever possible as it will
greatly simplify the bleeding operation and also
reduce the risk of air or fluid being drawn back
into the system quite apart from being able to
do the work without the help of an assistant.
15To use the kit, connect the tube to the
bleedscrew and open the screw one half a
turn.
16Depress the brake pedal fully and slowly
release it. The one-way valve in the kit will
prevent expelled air from returning at the end
of each pedal downstroke. Repeat this
operation several times to be sure of ejecting
all air from the system. Some kits include a
translucent container which can be positioned
so that the air bubbles can actually be seen
being ejected from the system.
17Tighten the bleed screw, remove the tube
and repeat the operations on the remaining
brakes.
18On completion, depress the brake pedal. If it
still feels spongy repeat the bleeding operations
as air must still be trapped in the system.
Bleeding - using a pressure
bleeding kit
19These kits too are available from motor
accessory shops and are usually operated by
air pressure from the spare tyre.
Braking system 8•7
12.8 Caliper bleed screw with dust cap
fittedFig. 8.12 Bleeding a rear wheel cylinder
(Sec 12)11.3 Front hydraulic hose bracket
8
Page 90 of 303

9System type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 negative earth, battery alternator and pre-engaged starter
Battery
Except 70S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 Ah
70S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 Ah
Alternator
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Marelli, Valeo or Bosch 45A, 55A or 65A, with integral voltage
regulator
Nominal voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 V
Minimum brush (wear) length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.0 mm (0.236 in)
Starter motor
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Marelli, Bosch or Femsa pre-engaged
Nominal power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.8 kW or 1.0 kW
Armature shaft endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.1 to 0.5 mm (0.0039 to 0.0197 in)
Minimum brush (wear) length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.0 mm (0.39 in)
Wiper blades
Front . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion X-4801 (19 in) or X-4503 (18 in)
Rear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion X-3303
Chapter 9 Electrical system
For modifications, and information applicable to later models, see Supplement at end of manual
Alternator - maintenance and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Alternator - overhaul . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Alternator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Battery - inspection, charging, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Central door locking system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Check control (warning module) system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Cigar lighter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Clocks - setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Courtesy lamp switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Economy gauge (Econometer) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Electrically-operated front door windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Exterior lamps - bulb renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Fault finding - electrical system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See end of Chapter
Fuses and relays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Headlamp - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Headlamp beam - alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Headlamp bulb - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Heated tailgate window - precautions and repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29Horns . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Instrument panel - dismantling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Instrument panel - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Interior lamps - bulb renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Radio/cassette - fitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Rocker and push-button switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Speedometer drive cable - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Starter motor - description and testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Starter motor - overhaul . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Starter motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Steering column combination switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Tailgate contacts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Tailgate wiper blade and arm - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Tailgate wiper motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Voltage regulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Washer system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Windscreen wiper blade and arm - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . 24
Windscreen wiper motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
9•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 93 of 303

ease the holder out of the alternator. Inspect
the brushes and if worn below the specified
minimum length, they must be renewed.
7Disconnect the brush leads by unsoldering
or carefully cutting them.
8When soldering the new brush leads, do
not allow solder to run down them or their
flexibility will be ruined.
9When inspecting or renewing brushes,
check the surface of the slip rings. Clean them
with solvent or if they are very discoloured,
use very fine glasspaper.
6 Voltage regulator
1This is of integral type and is part of the
brushholder assembly.
2No provision is made for adjustment or
overhaul.
7 Starter motor-
description and testing
2
1The starter motor may be one of two
different makes. Both are of pre-engaged
type.
2This type of starter motor incorporates a
solenoid mounted on top of the starter motor
body. When the ignition switch is operated,
the solenoid moves the starter drive pinion,
through the medium of the shift lever, into
engagement with the flywheel starter ring
gear. As the solenoid reaches the end of its
stroke, and with the pinion by now partially
engaged with the flywheel ring gear, the main
fixed and moving contacts close and engage
the starter motor to rotate the engine.
3This pre-engagement of the starter drive
does much to reduce the wear on the flywheel
ring gear associated with inertia type starter
motors.
4If the starter fails, some fault-finding can be
done with it still on the car. Check the ignition
warning light comes on, and does not go out
when the starter is switched on. If it goes out,
the fault is probably in the battery. If it stays
bright, get an assistant to work the switch,whilst listening to the starter. Listen to find out
if the solenoid clicks into position. If it does
not, pull off the solenoid wire, and check it
with a test bulb. If the wire is live when the key
is turned, but the solenoid does not move,
take off the starter and remove it to the bench
for overhaul.
8 Starter motor-
removal and refitting
1
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the lead from the starter motor
(photo).
3Unscrew the fixing bolts and withdraw the
starter motor, downwards on 1116 cc and
1301 cc models (photo).
4Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure.
9 Starter motor- overhaul
3
1As with the alternator, the operations
should normally be limited to renewal of the
brushes. If the unit has covered a high
mileage it will usually be more economical to
purchase a new or factory-reconditioned one
rather than renew several components of the
original unit.
2Owing to the possibility that a fault can
develop in the starter motor solenoid or drive
assembly, full dismantling procedures are
given later in this Section.
Brush - renewal
3Slide off the cover band.
4Using a hooked piece of wire, pull up the
springs so that the brushes can be withdrawn
and their lengths checked for wear. If they
have worn below the specified minimum
length, renew them by extracting the brush
lead connecting screws (photo).
Solenoid
5Disconnect the field connecting wire from
the solenoid.
6Unscrew the bolts which hold the solenoid
to the end-frame.
7Unscrew the yoke tie-rod nuts.
9•4 Electrical system
9.4 Starter motor brush partly withdrawn
8.2 Starter motor connections8.3 Removing starter motor
Fig. 9.2 Exploded view of typical starter motor (Sec 9)
1 Armature
2 Drive pinion/clutch3 Drive end bracket
4 Shift lever5 Solenoid
6 Brush endplate7 Brush
8 Field windings
Gripping the brush leads with
a pair of pliers to act as a
heat sink will prevent heat
transfer to the internal
components of the alternator.