1983 FIAT UNO coolant
[x] Cancel search: coolantPage 184 of 303

the trim cover, undo the retaining screw at the
rear of the console. Prise free and release the
gear lever gaiter and lift clear the central
console.
7Undo the retaining screws and remove the
steering column upper and lower shroud.
8Detach and remove the lower facia trim on
the side of the central facia.
9Referring to Fig. 13.32, unscrew and
remove the four heater facia to main facia
retaining screws from the points indicated.
10Undo the two retaining nuts securing the
heater to the body on the driver’s side.
11Undo the retaining screws and remove
the pipe shield from the side of the heater
unit, then disconnect the coolant supply and
return hoses from the heater. As the hoses are
detached, be prepared to catch any remainingcoolant as it flows from the hoses and heater
connections.
12Undo the remaining two heater unit
securing nuts and withdraw the heater unit
from the car. As the unit is removed, detach
the wiring and position the hoses with their
ends pointing upwards to avoid further
coolant spillage.
13Refit in the reverse order of removal.
Ensure that the hoses are securely
reconnected. Top up the cooling system on
completion.
Heater unit - dismantling
and reassemblyÁ
14Remove the heater unit as described
previously.
15Pull free the heater/fresh air and blower
control knobs (photo).
16Undo the two retaining screws and
withdraw the control panel from the facia.
Detach the wiring connectors from the panel
illumination lights and remove the panel.17Unscrew the retaining bolts and remove
the centre panel from the heater unit.
18Undo the retaining screws and remove
the control lever mounting.
19Loosen off the grub screws and detach
the cables from the control levers.
20Undo the retaining screws and remove
the control valve.
21Undo the two retaining screws and
withdraw the heater matrix from the heater
housing.
22To separate the casing halves, drill out the
pop rivet securing the mounting bracket,
release the retaining clips and unscrew the
securing bolts.
23Reassemble in the reverse order of
dismantling. Check that the control cables are
correctly adjusted and that the controls
operate in a satisfactory manner before
refitting the heater unit to the car.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•59
8D.15 Pull free the heater/fresh air and
blower control knobs
Fig. 13.33 Heater pipe shield securing
screw positions on later models (Sec 8D)
Fig. 13.32 Heater unit facia to main facia
retaining screw locations (arrowed)
(Sec 8D)
Fig. 13.34 Heater unit components on later models (Sec 8D)
1 Coolant inlet tap 2 Centre panel 3 Side casings 4 Heater matrix 5 Blower fan
13
Page 187 of 303
PART B:
CARBURETTOR MODELS
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) -
description
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of this Section before starting
any work.
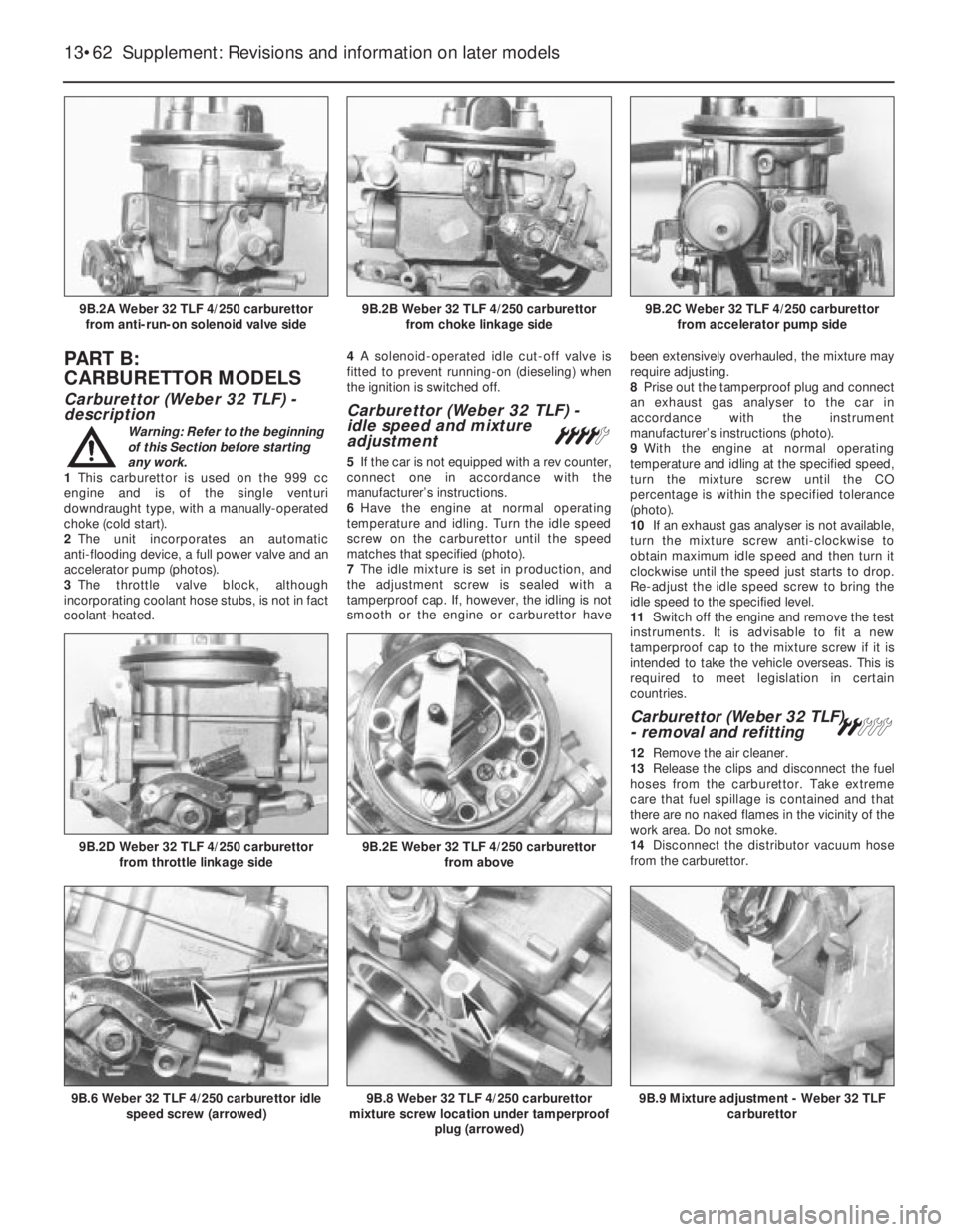
1This carburettor is used on the 999 cc
engine and is of the single venturi
downdraught type, with a manually-operated
choke (cold start).
2The unit incorporates an automatic
anti-flooding device, a full power valve and an
accelerator pump (photos).
3The throttle valve block, although
incorporating coolant hose stubs, is not in fact
coolant-heated.4A solenoid-operated idle cut-off valve is
fitted to prevent running-on (dieseling) when
the ignition is switched off.
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) -
idle speed and mixture
adjustment
¢
5If the car is not equipped with a rev counter,
connect one in accordance with the
manufacturer’s instructions.
6Have the engine at normal operating
temperature and idling. Turn the idle speed
screw on the carburettor until the speed
matches that specified (photo).
7The idle mixture is set in production, and
the adjustment screw is sealed with a
tamperproof cap. If, however, the idling is not
smooth or the engine or carburettor havebeen extensively overhauled, the mixture may
require adjusting.
8Prise out the tamperproof plug and connect
an exhaust gas analyser to the car in
accordance with the instrument
manufacturer’s instructions (photo).
9With the engine at normal operating
temperature and idling at the specified speed,
turn the mixture screw until the CO
percentage is within the specified tolerance
(photo).
10If an exhaust gas analyser is not available,
turn the mixture screw anti-clockwise to
obtain maximum idle speed and then turn it
clockwise until the speed just starts to drop.
Re-adjust the idle speed screw to bring the
idle speed to the specified level.
11Switch off the engine and remove the test
instruments. It is advisable to fit a new
tamperproof cap to the mixture screw if it is
intended to take the vehicle overseas. This is
required to meet legislation in certain
countries.
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF)
- removal and refitting ª
12Remove the air cleaner.
13Release the clips and disconnect the fuel
hoses from the carburettor. Take extreme
care that fuel spillage is contained and that
there are no naked flames in the vicinity of the
work area. Do not smoke.
14Disconnect the distributor vacuum hose
from the carburettor.
13•62 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
9B.9 Mixture adjustment - Weber 32 TLF
carburettor9B.8 Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor
mixture screw location under tamperproof
plug (arrowed)9B.6 Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor idle
speed screw (arrowed)
9B.2E Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor
from above9B.2D Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor
from throttle linkage side
9B.2C Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor
from accelerator pump side9B.2B Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor
from choke linkage side9B.2A Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor
from anti-run-on solenoid valve side
Page 191 of 303

adjustments described in this sub-Section,
however, will require removal of the
carburettor.
39Disconnect the short, curved diaphragm
hose from the top cover.
40Extract the top cover screws, lift the cover
from the carburettor body, and rotate it in
order to release the cranked choke control
rod from its key hole (photo). Mop out the fuel
and clean the jets.
41Check the jet sizes and other components
against those listed in the Specifications, in
case a previous owner has substituted
incorrect components (photo).
42Overhaul procedures are generally as
given in Chapter 3, Section 14 for the Weber
30/32 DMTR, but use the Specifications listed
in this Chapter. Additional overhaul
procedures are given here.
Fuel inlet needle valve
43If a high float level causing flooding of the
carburettor has been evident, first check that
the inlet valve housing is tight, and its washer
is sealing satisfactorily. A leak here will cause
fuel to bypass the inlet valve.
44If the needle valve is to be renewed,
remove it in the following way.
45Access to the fuel inlet needle valve is
obtained by carefully tapping out the float arm
pivot pin. Take care, the pivot pin pillars are
very brittle (photo).
46Unscrew the fuel inlet valve body and
remove the valve and washer.47When refitting the new valve, always use a
new sealing washer.
Float stroke (travel) - see Fig. 3.10
48The float stroke should be between 42.5
and 43.5 mm when measured from the top
cover gasket. Adjust if necessary by bending
the tab on the end of the arm.
Accelerator pump
49Adjustment of the accelerator pump is
very rarely required, but if performance is
suspect, carry out the following operations.
50Fill the carburettor float chamber and then
operate the throttle valve plate lever several
times to prime the pump.
51Position a test tube under the accelerator
pump jet and give ten full strokes of the
throttle lever, pausing between each stroke to
allow fuel to finish dripping.
52The total volume of fuel collected should
be as specified. Adjust the nut on the pump
control if necessary to increase or decrease
the volume of fuel ejected.
General
53When the stage is reached where the
valve plate spindle bushes have worn, then
the carburettor should be renewed complete.
54When reassembling the carburettor, use
new gaskets which can be obtained in a repair
pack.
Carburettor (Weber 32 ICEV
61/250 and DMTE 30/32,
DMTE 30/150) - general
55These carburettor types are fitted to later
models according to engine type. They are
similar in structure and operation to their
equivalents described in Chapter 3. Reference
can therefore be made to that Chapter for the
description and any operations concerning
them, but refer to Section 2 of this Chapter for
their specifications.
Carburettor (Solex
C 30/32-CIC 8) - description
56This carburettor is fitted as an alternative
to the Weber unit on 1116 cc models
produced for certain markets. The removal,
refitting and overhaul procedures are
essentially the same as described earlier for
the Weber carburettors.
PART C:
BOSCH LE2-JETRONIC
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
Description
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of this Section before starting
any work.
1The Bosch LE2-Jetronic fuel injection
system, fitted to the 1301 cc Turbo ie model,
is an electronically controlled multi-point
injection (MPi) system.
2The fuel injectors are fed at constant
pressure in relation to inlet manifold vacuum
pressure.
3The system electronic control unit (ECU)
actuates the injectors for variable duration,
and so supplies the precise volume of fuel
required for any given engine speed and load
condition.
4The ECU also monitors the air induction, air
temperature, coolant temperature and throttle
opening as additional parameters to compute
the required opening of the fuel injectors,
giving maximum power with fuel economy.
Fuel supply system
5The fuel supply system consists of an
electric pump and primary filter, located
adjacent to the fuel tank. A fuel pressure peak
damper is located next to the pump (photo).
6Fuel is then pumped through a filter to the
fuel rail and injectors. The injectors are of the
13•66 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
9C.5 Electric fuel pump/filter/pressure
damper assembly location on a 1301 cc
Turbo ie model
9B.41 Jets on the Weber 30/32 DMTE
carburettor (top cover removed)
9B.45 Float pivot arrangement and needle
valve on the Weber 30/32 DMTE
carburettor
9B.40 Unscrewing a top cover screw from
the Weber 30/32 DMTE carburettor9B.37F Unscrewing a carburettor fixing nut
Page 192 of 303

solenoid-operated type, actuated from the
ECU.
7Fuel pressure is regulated according to inlet
manifold vacuum pressure by a fuel pressure
regulator. Excess unpressurised fuel is
returned to the fuel tank.
Airflow meter
8This component measures the quantity of
air drawn into the engine, and converts this
into an electric signal which is transmitted to
the ECU.
9The intake air exerts a force on the floating
plate (1) (Fig. 13.39) which is connected to a
potentiometer (2).
10A compensating butterfly valve (3)
compensates for any reflex pressure which
may occur, and is subject to the braking effect
of the damper chamber (4).
11The idle mixture (air/fuel ratio) is altered by
means of the screw (8), which alters the
cross-section of the bypass channel (7).
12An integral-type temperature sensor is
fitted, the resistance value of which decreases
as the temperature of the intake air increases.
This facility is used to correct the mixture
strength within a pre-determined air
temperature range.
Throttle valve housing
13The housing incorporates a conventional
butterfly-type throttle valve, actuated by
cables and rods from the accelerator pedal.
14The idle bypass channel (2) (Fig. 13.40) is
fitted with an adjustment screw (3) to vary the
idle speed.
15The other screw (4) and locknut are usedto set the closing position of the throttle valve
plate.
Supplementary air valve
16This controls the air volume requirement
during cold starting. Essentially, the valve is an
electrically-heated bi-metallic strip, which rotates
the plate (4) (Fig. 13.41) to vary the volume of air
being drawn in through the aperture (1),
according to the temperature of the engine.
17The requirement for additional air during
cold starting is to dilute the additional fuel,
which is injected and controlled by the ECU
as a result of monitoring the engine coolant
temperature sensor.
Electrical control circuit
18The main components of the system are
the ECU and the system control relay. The
relay incorporates a fuel cut-off facility, which
cuts off the fuel supply in the event of engine
failure, the vehicle turning over, or a fuel line
breaking. The relay energises the following
electrical components.
19Coolant temperature sensor, which
signals the coolant temperature to the ECU.
20Throttle position switch, which signals the
ECU when the throttle valve plate is closed, in
order to actuate the deceleration fuel cut-off
device at speeds above 2500 rpm.21The switch also signals the ECU at full
throttle, so that the mixture can be enriched to
cope with full-power requirements.
22The system control relay also monitors the
engine speed directly from the ignition coil
primary winding.
MaintenanceÁ
23Regularly check the security of all system
hoses, wiring connections and plugs.
24At the intervals specified in Section 3,
renew the fuel filter and the air cleaner element.
Fuel filter - renewalÁ
25This is located within the engine
compartment just above the timing belt cover.
Disconnect the fuel hoses, but be prepared
for loss of fuel (photo).
26When fitting the new filter, make sure that
the arrow stamped on it is pointing towards
the fuel injector rail.
Air cleaner element -
renewal
Á
27Prise back the toggle-type clips and take
off the air cleaner lid. Remove and discard the
element, and wipe any dirt from the inside of
the casing (photos).
28Fit the new element and replace the lid.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•67
Fig. 13.41 Supplementary air valve -
1301 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 9C)
1 Aperture
2 Bi-metallic strip
3 Passage
4 Rotating plate (closed position)Fig. 13.40 Sectional view of throttle valve
housing - 1301 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 9C)
1 Butterfly-type throttle valve
2 Idle bypass channel
3 Idle speed adjusting screw
4 Throttle valve plate setting screwFig. 13.39 Sectional view of airflow meter -
1301 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 9C)
1 Floating plate
2 Potentiometer
3 Compensating butterfly valve
4 Damper chamber
6 Spring
7 Bypass channel
8 CO adjusting screw
9 Tamperproof plug
Terminals
5, 7, 8, Potentiometer
9 Air temperature sensor
E Sealed (not to be touched)
9C.27A Removing the air cleaner lid9C.25 Secondary fuel filter
13
Page 193 of 303

Idle speed and mixture
adjustment¢
29Before carrying out any adjustments, the
engine must be at operating temperature, the
fan having cut in at second speed and then
switched off.
30Release the locknut and turn the main idle
speed screw in the throttle valve housing until
the engine idles at the specified speed. This
should be all that is necessary to obtain the
correct idle speed, as the throttle valve plate
base setting is set during production.
However, if wear has taken place, or incorrect
adjustment has been carried out previously,
proceed in the following way.
31Disconnect the intake duct from the
throttle valve housing. Release the locknut on
the base (small) adjusting screw, and turn thescrew until there is a clearance between the
lower edge of the throttle valve plate and the
throat wall of between 0.05 and 0.1 mm
(photos).
32With the engine still at operating
temperature, start the engine, and having
released the locknut, turn the main (large) idle
speed screw fully clockwise to close the
bypass passage.
33Now turn the base (small) screw until the
engine idles at between 700 and 800 rpm.
Tighten the locknut.
34Finally, turn the main (large) adjusting
screw to give an idle speed of between 800
and 900 rpm.
35It is unlikely that the mixture will require
alteration, but if it does, connect an exhaust
gas analyser to the car in accordance with the
equipment manufacturer’s instructions.
36With the engine at operating temperature,
prise out the tamperproof cap, and turn the
mixture screw, which is located in the airflow
meter, until the CO level is as given in the
Specifications. Turning the screw clockwise
richens the mixture, turning it anti-clockwise
weakens the mixture. Use a close-fitting Allen
key for the adjustment (photo).
Fuel injection system -
electrical testsª
37When carrying out checks to trace a fault
in the system, an ohmmeter should be used
for the following tests.
38Disconnect the multipin connector from
the ECU, and also the one from the system
control relay, and apply the probes of the
ohmmeter in accordance with the following
sequence to check for continuity in thecables. The component wiring plug will of
course be disconnected for the test.
ECU connector Component connector
plug terminal plug terminal
1 1 of ignition coil
2 2 of throttle position
switch
3 3 of throttle position
switch
4 50 of ignition switch
5 Earth
5 5 of airflow meter
7 7 of airflow meter
8 8 of airflow meter
9 9 of airflow meter
9 9 of throttle position
switch
9 18 of supplementary air
valve
9 87 main relay socket
10 10 of coolant temperature
sensor
12 Injector terminals
13 Earth
System control Component connector
relay connector plug terminal
plug terminal
1 1 of ignition coil
15 15 of ignition switch
30 Battery positive
31 Earth
50 50 of ignition switch
87 Injector terminals
87 18 of throttle position
switch
87 9 of ECU multipin socket
87b Fuel pump (fused)
13•68 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.42 ECU and component connector plug terminals - 1301 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 9C)
For colour code see main wiring diagrams
9C.31C Checking throttle valve plate
opening with a feeler blade
9C.36 Using an Allen key to adjust the
mixture (CO level)
9C.31B Idle speed base setting screw (1)
and main adjustment screw (2)9C.31A Disconnecting the throttle valve
housing intake duct9C.27B Removing the air cleaner element
Page 194 of 303

39Now use the ohmmeter to check the
resistance of the following components.
Supplementary air valve
40Resistance between the terminals should
be between 40 and 60 ohms at 20ºC (68ºF).
Airflow meter
41Resistance between terminals 5 and 8 of
the potentiometer should be between 330 and
360 ohms at 20ºC (68ºF).
42Resistance between terminals 8 and 9 of
the internal circuit should be between 190 and
210 ohms at 20ºC (68ºF) and between 170
and 190 ohms at 60ºC (140ºF).
Coolant temperature sensor
43At 20ºC (68ºF) the resistance should be
between 2 and 4 k ohms. At 50ºC (122ºF) the
resistance should be between 600 and
900 ohms. At 90ºC (194ºF) the resistance
should be between 100 and 300 ohms.
Fuel injectors
44The winding resistance should be
between 15 and 17 ohms at 20ºC (68ºF).
Throttle position switch
45With the throttle butterfly valve closed,
there should be continuity between ter-
minals 18 and 2, and with the valve fully open,
there should be no continuity between
terminals 18 and 3.
46The throttle position switch should not be
disturbed unless absolutely necessary. If it
has to be removed, then refit it so that themicroswitch is heard to click immediately the
throttle butterfly is opened.
Fuel injection system -
mechanical tests ª
Fuel pump
47To test the pressure of the fuel pump, a
pressure gauge will be required, connected
into the fuel delivery hose.
48Remove the multipin plug from the system
control relay and bridge terminals 87b and 30.
49Turn the ignition switch on. The pump
should operate and indicate a pressure of
between 2.8 and 3.0 bars (40 and 44 lbf/in
2).
50To check the operation of the peak
pressure regulator, pinch the fuel return hose.
If the fuel pressure increases, the regulator
must be faulty, and should be renewed.
51Check that the fuel pressure increases
when, with the engine idling, the accelerator is
depressed sharply.
Supplementary air valve
52With the engine at normal operating
temperature and idling, pinch the
supplementary air valve hose using a pair of
pliers. The engine speed should not drop by
more than 50 rpm. If it does, renew the valve.
Fuel injection system
components -
removal and refitting
ª
53Disconnect the battery before carrying out
any of the following operations.
Air cleaner
54Remove the cover and filter element as
previously described.
55Disconnect the duct from the air cleaner
casing, and then unbolt and remove the
casing. Note that the lower bracket bolt need
not be completely removed, only unscrewed,
due to the design of the bracket. The air
cleaner metal duct is routed over the top of
the radiator (photos).
Airflow meter
56Release the securing clip and disconnect
the air intake duct (photo).
57Release the securing clip and disconnect
the air outlet duct (photo).
58Disconnect the wiring plug.
59Unscrew the fixing screws and remove
the airflow meter from its mounting bracket.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•69
9C.55B Removing the air cleaner casing
upper bracket9C.55A Disconnecting the duct from the air
cleanerFig. 13.43 System control relay connector
plug terminals 1301 cc Turbo ie engine
(Sec 9C)
9C.57 Air outlet duct securing clip removal
from airflow meter
9C.55C Air cleaner casing lower bracket
and bolt (arrowed)
9C.56 Air intake duct at airflow meter
(securing clip arrowed)9C.55D Air cleaner metal duct over
radiator
13
Page 195 of 303

Fuel pressure regulator
60Disconnect the vacuum hose from the
regulator (photo).
61Anticipate some loss of pressurised fuel,
and then disconnect the fuel hose from the
regulator. Unbolt and remove the unit.
Excessive air pressure switch
62This is screwed into the end of the inlet
manifold. Disconnect the electrical leads and
unscrew the switch.
Coolant temperature sensor
63This is screwed into the cylinder head and
has wires connected to it. Drain the cooling
system before commencing operations.
64Disconnect the wiring plug and unscrew
the sensor.
Throttle valve housing and inlet
manifold
65Disconnect the air inlet hose from the
throttle valve housing, and also the
supplementary air valve hose.
66Disconnect the throttle control cable by
swivelling the grooved sector and slipping the
cable nipple from its recess.
67Disconnect the wiring plug from the
throttle position (potentiometer) switch.
68Unbolt the fuel pressure regulator/wiring
loom bracket, and also the wiring loom
bracket at the other end of the inlet manifold.
Move the wiring loom aside.
69Unbolt and remove the throttle housing
support bracket.
70Disconnect the vacuum servo hose and
the fuel pressure regulator vacuum hosesfrom the inlet manifold (photos).
71Disconnect the leads from the excessive
air pressure switch.
72Unscrew the inlet manifold fixing nuts.
Note that double nuts are used at the ends of
the manifold in order to secure the exhaust
heat shield (photo). The shield should be
released and lowered to rest on the exhaust
manifold.
73Unscrew and remove the remaining two
nuts now exposed by lowering the heat shield
and lifting the inlet manifold away (photo).
74If necessary, the injectors and cooling
tube can be withdrawn, and the two twin inlet
pipe stubs removed. These are retained with
the exhaust manifolds using nuts and washers
(photo).
Fuel rail and injectors
75Disconnect the fuel delivery hose from the
fuel rail by unscrewing the union nut (photo).
Be prepared for some loss of pressurised fuel.
76Disconnect the fuel return hose.
77Unbolt the fuel pressure regulator and the
wiring loom brackets (photo).
78Disconnect the air intake hose from the
throttle valve housing, and then unbolt and
remove the throttle valve housing support
bracket (photo).
79Disconnect the hose from the injector
cooling fan, and also disconnect the fan
thermo-switch on the underside of the injector
cooling air duct (photo). Disconnect the
injector wiring plugs, and then slide out the
injector cooling air duct.
13•70 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
9C.77 Wiring loom clip and bracket9C.75 Disconnecting the fuel delivery hose
union9C.74 Removing an inlet manifold twin
pipe stub
9C.73 Removing the inlet manifold9C.72 Double nuts at the end of the inlet
manifold
9C.70B Fuel pressure regulator vacuum
hose connection at the inlet manifold9C.70A Brake servo vacuum hose
connection to inlet manifold9C.60 Fuel pressure regulator
Page 197 of 303

Throttle position switch
(potentiometer)
90This is located on the left side of the
throttle valve housing (photo).
91Disconnect the wiring plug, unscrew the
two fixing screws and withdraw the switch.
Fuel filter
92Unscrew the fuel line banjo unions from
the filter, which is located in the right-hand
rear corner of the engine compartment. Be
prepared for some loss of pressurised fuel,
and mop it up with rags.
Fuel pump
93The fuel pump can be removed from its
location beside the fuel tank afterdisconnecting the fuel hoses and wiring plug,
and then releasing the mounting clamp.
Refitting all components
94Refitting of all components is a reversal of
removal, but observe the following points.
95Use new seals and gaskets as applicable,
noting that three rubber seals are used on
each fuel injector and insulator (photos).
96Adjust the throttle position switch as
described in paragraph 46 of this Section.
97When refitting a new fuel filter, make sure
that the arrow marked on it is in the direction
of the fuel flow.
98Apply gasket cement to the threads of the
coolant temperature sensor.
Throttle control linkage -
general
99This is of the cable and rod type. Adjust the
cable by means of the end fitting and nut, to give
the slightest play in the cable when the plastic
socket is engaged with the ball on the link rod
which runs across the camshaft cover (photos).
100Keep the cross-shaft pivots and return
springs lubricated.
Fuel tank - general
101The fuel tank is of metal construction, but
note the plastic anti-blow-back compartment
between the filler cap and the tank. This is
accessible from under the right-hand wheel
arch (photo).
13•72 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
9C.99B Throttle cable (secondary section)
and cross-shaft9C.99A Throttle cable and end fitting
(primary section)9C.95D Inlet pipe stub gasket
9C.95C Fuel injector insulator seal9C.95B Fuel injector small seal9C.95A Fuel injector large seal
9C.90 Throttle position switch (wiring plug
arrowed)9C.88B Supplementary air valve (arrowed)9C.88A Disconnecting the supplementary
air valve hose from the inlet manifold