1983 FIAT UNO oil type
[x] Cancel search: oil typePage 79 of 303

this type is used and the engine is in good
condition, the spark plugs should not need
attention between scheduled replacement
intervals. Spark plug cleaning is rarely
necessary and should not be attempted unless
specialised equipment is available as damage
can easily be caused to the firing ends.
2At the specified intervals, the plugs should
be renewed. The condition of the spark plug
will also tell much about the overall condition
of the engine.
3If the insulator nose of the spark plug is
clean and white, with no deposits, this is
indicative of a weak mixture, or too hot a plug.
(A hot plug transfers heat away from the
electrode slowly - a cold plug transfers it away
quickly.)
4If the tip of the insulator nose is covered
with sooty black deposits, then this is
indicative that the mixture is too rich. Should
the plug be black and oily, then it is likely that
the engine is fairly worn, as well as the mixture
being too rich.
5The spark plug gap is of considerable
importance, as, if it is too large or too small
the size of the spark and its efficiency will be
seriously impaired. The spark plug gap should
be set to the gap shown in the Specifications
for the best results.
6To set it, measure the gap with a feeler
gauge, and then bend open, or close, the
outer plug electrode until the correct gap is
achieved. The centre electrode should never
be bent as this may crack the insulation and
cause plug failure, if nothing worse.
7When fitting new plugs, check that the plug
seats in the cylinder head are quite clean.
Refit the leads from the distributor in the
correct firing order, which is 1-3-4-2; No 1cylinder being the one nearest the flywheel
housing (903 cc) or timing belt (1116 or
1301 cc). The distributor cap is marked with
the HT lead numbers to avoid any confusion.
Simply connect the correctly numbered lead
to its respective spark plug terminal (photo).
12 Ignition switch-
removal and refitting
1
1Access to the steering column lock/ignition
switch is obtained after removing the steering
wheel and column shrouds (Chapter 10) and
the column switch unit (Chapter 9).
2In the interest of safety, disconnect the
battery negative lead and the ignition switch
wiring plug (photo).
3Insert the ignition key and turn to the STOP
position (photo).
4Pull the two leads from the switch.
5Turn the ignition key to MAR.
6Using a screwdriver depress the retaining
tabs (1) (Fig. 4.16) and release the ignition
switch.
7Set the switch cam (2) so that the notches
(3) are in alignment.
8Insert the switch into the steering lock and
engage the retaining tabs.
9Turn the ignition key to STOP and connect
the two leads.
10Reconnect the battery and refit the
steering wheel, switch and shrouds.
11Removal and refitting of the steeringcolumn lock is described in Chapter 10.
Note: The ignition key is removable when set
to the STOP position and all electrical circuits
will be off. If the interlock button is pressed,
the key can be turned to the PARK position in
order that the parking lamps can be left on
and the steering lock engaged, but the key
can be withdrawn.
4•8 Ignition system
Fig. 4.16 Typical ignition switch (Sec 12)
1 Retaining tabs 3 Alignment notches
2 Switch cam 4 Locating projection12.3 Ignition key positions
1 AVV (Start) 3 Stop (Lock)
2 Park (Parking lights on) 4 MAR (Ignition)12.2 Ignition switch and lock
11.7 Distributor cap HT lead markingsFig. 4.15 Spark plug connections on
1116 cc and 1301 cc engines (Sec 11)
Fig. 4.14 Spark plug connections on
903 cc engine (Sec 11)
It’s often difficult to insert spark plugs
into their holes without cross-threading
them. To avoid this possibility, fit a
short piece of rubber hose over the end
of the spark plug. The flexible hose
acts as a universal joint, to help align
the plug with the plug hole. Should the
plug begin to cross-thread, the hose
will slip on the spark plug, preventing
thread damage.
Page 83 of 303

into its cylinder to accommodate them. This
will cause the fluid level to rise in the reservoir.
Anticipate this by syphoning some out
beforehand, but take care not to let it drip
onto the paintwork - it acts as an effective
paint stripperl
8Refit the anti-rattle springs, the pads
(friction lining-to-disc), the cylinder body, the
locking blocks and their retaining clips
(photos).
9Refit the roadwheel and apply the footbrake
hard, several times, to bring the pads into
contact with the brake disc.
10Renew the pads on the opposite brake.
The pads should always be renewed in axle
sets.
11Top up the fluid reservoir.
4 Rear brake shoes-
inspection and renewal
2
1Jack up the rear of the car and remove the
roadwheels.
2Fully release the handbrake.
3Unscrew and remove the drum securing
bolts. One of these is a long locating spigot
for the roadwheel.
4Pull off the drum. lf it is tight, clean off the
rust at its joint with the hub flange, and apply
a little penetrating fluid. Two bolts may be
screwed into the drum securing bolt holes if
necessary and the drum thus eased off the
hub. The securing bolt holes are tapped for
this purpose.
5Brush away all the dust and dirt from the
shoes and operating mechanism, taking care
not to inhale it.
6The friction linings fitted as original
equipment are of the bonded type and the
rivet heads normally used as a guide to wear
are not, of course, fitted. However, if the
thickness of the friction linings is down to
1.5 mm (0.06 in) or less, the shoes must be
renewed. Always purchase new or factory
relined brake shoes.
7Before removing the brake shoes, note the
way in which the shoes are positioned, with
respect to leading and trailing ends (the end
of the shoe not covered by lining material).Note also into which holes in the shoe web
the return springs are connected. Sketch the
shoes or mark the holes on the new shoes
with quick drying paint if you are doubtful
about remembering (photo).
8Undo the steady springs by depressing and
rotating their caps a quarter turn to disengage
the slot from the pin. On later models a
U-shaped steady spring is used. Depress and
slide it out.
9Rotate the hub until the cut-outs in its rear
flange face are in alignment with the shoe
self-adjusters.
10Pivot the trailing shoe on the self-adjuster
post and disengage the ends of the shoe from
the slot in the wheel cylinder tappet and from
the lower anchor block.
11Work the shoe up the self-adjuster pivot
post until the self-adjuster boss enters the
cut-out in the hub flange. The shoe can now
be withdrawn (photo).
12Once off the self-adjuster post, the
pull-off spring tension is eased, as the shoe
can move towards the other, so the springs
can be unhooked.
13Remove the leading shoe in a similar way.
14The new shoes will already be fitted with
new self-adjusters.
15Fit the new shoes to their self-adjuster
posts, making sure that the handbrake shoe
lever is correctly located. Engage the ends of
the shoes.
16Using a wooden or plastic-faced mallet,
tap the shoes inwards against the friction of
their self-adjuster coil springs. This will havethe effect of reducing the overall diameter of
the shoes to facilitate fitting of the shoe return
springs and to allow the brake drum to slide
over them.
17Using pliers, reconnect the upper (longer)
and lower shoe return springs.
18Hold the steady pins in position from the
rear of the backplate. Fit the small coil springs
and the retaining cap, again using pliers to
grip the cap and to depress and turn it to
engage the pin. On later models fit the
U-shaped springs.
19Before refitting the drum, clean it out and
examine it for grooves or scoring (refer to
Section 8).
20Fit the drum and the roadwheel.
21Apply the brakes two or three times to
position the shoes close to the drum.
22Renew the shoes on the opposite brake in
a similar way.
23The handbrake should be automatically
adjusted by the action of the shoe adjuster. If
the handbrake control lever has excessive
travel, refer to Section 16 for separate
adjusting instructions.
5 Caliper- removal,
overhaul and refitting
4
Note: Purchase a repair kit in advance of
overhaul.
1Jack up the front roadwheel and remove it.
2Brush away all dirt from the caliper
Braking system 8•3
4.11 Rear hub showing cut-outs on rear
face for shoe self-adjuster bosses4.7 Rear brake assembly3.8B Cylinder body located on caliper
bracket
Fig. 8.2 Exploded view of caliper (Sec 5)
8
Page 84 of 303

assembly and the flexible pipe, particularly the
fixing bracket and union at the car end of the
flexible pipe.
3Have ready a container suitable to catch
the brake fluid, and sheets of clean
newspaper on which to put parts.
4Take out the spring clips and locking
blocks, and take the caliper off the support
bracket.
5Disconnect the hydraulic flexible pipe at the
under wing support bracket and cap both
pipe ends. It may help to prevent loss of fluid
if the vent in the reservoir cap is sealed with
adhesive tape, to create a vacuum.
6Remove the caliper to the bench or other
work surface, and clean it thoroughly with
hydraulic fluid or methylated spirit.
7Depress the piston until the dust excluding
boot can be removed.
8Now apply air pressure to the flexible hose
and eject the piston. Quite a low pressure is
required for this, such as can be generated
with a hand or foot operated pump.
9Pick out the piston seal from its groove in
the cylinder. Use a sharp probe, but take care
to avoid scratching the cylinder bore.
10Examine the surface of the piston and
cylinder bore. If either is corroded, scored or
shows metal-to-metal rubbed areas, the
complete assembly should be renewed.
11If the components are in good condition,
discard the oil seals, clean the piston and
cylinder and fit the new seal for the piston.
This is included in the repair kit. Use the
fingers only to manipulate it into its groove.
12Lubricate the piston with clean hydraulic
fluid and insert it partially into the cylinder.
13Fit the new dust excluding boot to its
projecting end, push the piston fully into the
cylinder and engage the dust excluder with
the rim of the cylinder.
14Refit the caliper, reconnect the flexible
hose, then bleed the front hydraulic circuit
(refer to Section 12).
6 Brake disc- inspection,
renovation or renewal
2
1Whenever the front disc pads are being
checked for wear, take the opportunity to
inspect the discs for deep scoring or
grooving. After a high mileage the disc may
become reduced in thickness away from the
extreme outer edge of the disc. lf this wear is
rapid, it is possible that the friction pads are of
too hard a type.
2If the disc has evidence of many tiny cracks,
these may be caused by overheating due to a
seized caliper piston in the “applied” position.
3The foregoing conditions may be corrected
by regrinding the disc provided that the
thickness of the disc is not reduced below
that specified by such action. Alternatively, fit
a new disc.
4To remove a disc, take off the caliper andpads as described in Sections 3 and 5. Tie the
caliper up, out of the way.
5Knock back the tabs of the lockplates and
unbolt the caliper support bracket from the
hub carrier.
6Unscrew and remove the two bolts which
hold the disc assembly to the hub. One of
these bolts is for wheel locating purposes.
7Pull the disc from the hub.
8Refitting is a reversal of the removal
process. If the disc has excessive run-out,
repositioning it in relation to the hub may
bring it within tolerance by cancelling out the
run-out characteristics in the hub and disc,
once the most suitable fitted position has
been found.
7 Rear wheel cylinder-
removal, overhaul and refitting
4
Note: Purchase a repair kit in advance of
overhaul.
1If fluid seepage is observed from the ends
of the rear wheel cylinder when the brake
drum has been removed, the seals are leaking
and immediate action must be taken.
2Although the cylinder can be dismantled
without taking it from the backplate, this is not
recommended due to the possibility of under
wing dirt and mud dropping onto the
components as work proceeds. 3Remove the brake shoes, as described in
Section 4.
4Disconnect the hydraulic line from the
wheel cylinder and cap the open end of the
pipe. lt may help to reduce the loss of fluid if
the vent hole in the reservoir cap is taped over
to create a vacuum.
5Unscrew and remove the setscrews which
hold the cylinder to the backplate and
withdraw the cylinder. Prise off the rubber
dust excluding boots.
6Apply gentle air pressure from a hand or
foot operated pump to eject the pistons and
spring. Alternatively, tap the end of the
cylinder on a piece of hardwood and the
pistons should move out.
7Inspect the piston and cylinder bore
surfaces for scoring, corrosion or evidence of
metal-to-metal rubbing areas. lf these are
found, discard the assembly and purchase a
new one.
8If the components are in good condition,
note which way round the lips are fitted, then
discard the seals and boots and wash the
pistons and cylinder bore in clean hydraulic
fluid or methylated spirit.
9Manipulate the new seals into position,
using the fingers only for this job.
10Dip the pistons in clean hydraulic fluid and
insert them with the coil spring and washers
into the cylinder.
11Fit the new dust excluding boots.
12Refit the wheel cylinder to the backplate,
reconnect the hydraulic pipe, then refit the
shoes, the drum and the roadwheel.
13Bleed the rear hydraulic circuit as
described in Section 12.
8 Brake drum- inspection,
renovation or renewal
2
1Whenever the rear brake linings are being
checked for wear, take the opportunity to
inspect the internal surfaces of the brake
drums.
2If the drums are grooved or deeply scored,
they may be reground, provided that their new
internal diameter will not then exceed the
specified dimension. If it will, or the drum is
cracked, it must be renewed.
3Removal and refitting of a brake drum is
described in Section 4.
8•4 Braking system
Fig. 8.4 Exploded view of a rear wheel cylinder (Sec 7)
1 Pads
2 Dust excluder
3 Piston seal4 Piston
5 Cylinder body
Fig. 8.3 Sectional view of caliper (Sec 5)
Page 108 of 303

11
Front suspension
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Independent with MacPherson struts and coil springs
Coil springs
Free height:
903 cc models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334 mm (13.16 in)
1116 and 1301 cc models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342 mm (13.5 in)
Number of coils . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.25
Rear suspension
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Beam axle, trailing arms, coil springs and double-acting gas-filled
shock absorbers
Coil springs
Free height . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246.5 mm (9.7 in)
Number of coils . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.75
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Front suspension
Driveshaft/hub nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272 200
Strut upper mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 18
Strut spindle nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60 44
Strut base clamp bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 36
Track control arm balljoint nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 36
Track control arm inboard mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90 66
Roadwheel bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86 63
Crossmember bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60 44
Rear suspension
Trailing arm bracket to body bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 15
Trailing arm pivot bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70 52
Shock absorber lower mounting bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 22
Shock absorber upper mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 9
Shock absorber spindle nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 22
Roadwheel bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86 63
Chapter 11 Suspension
For modifications, and information applicable to later models, see Supplement at end of manual
Fault finding - suspension . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See end of Chapter
Front coil spring - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Front crossmember - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Front hub carrier - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Front suspension strut - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Rear coil spring - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Rear shock absorber - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Rear suspension - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Track control arm - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Trailing arm rubber bush - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
11•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 109 of 303

1 General description
The front suspension is of independent
MacPherson strut type.
The rear suspension consists of a beam
axle with trailing arms, coil springs and double
acting gas-filled telescopic shock absorbers.
Operations covering the hubs, roadwheels
and tyres are described in Chapter 7.
2 Maintenance
4
1Periodically check the tightness of all
suspension nuts and bolts using a torque
wrench.
2At the intervals specified in “Routine
Maintenance” inspect all suspension rubber
bushes for deterioration or wear. Renew
where necessary.
3Check for wear in the track control arm to
hub carrier balljoint. Do this by raising the
roadwheel and prising the control arm down.
If the hub carrier is pulled outwards, any up
and down movement or slackness will
necessitate renewal of the track control arm,
although it may be possible to obtain a
balljoint repair kit from a motor factor.
4A defective strut or shock absorber can
usually be detected by the tendency of the car
to pitch badly when braking or cornering.
However the component can be tested more
thoroughly in the following way.
5Remove the strut and take off the coil
spring or withdraw the rear shock absorber as
described later in this Chapter.
6Grip the strut or shock absorber lower
mounting in the jaws of a vice and then fully
extend and contract the unit five or six times,
with the unit held in a vertical attitude. If there is
any lack of resistance, jerkiness or seizure, then
the unit will have to be renewed, no repair being
possible. It is recommended that struts orshock absorbers are renewed in pairs as axle
sets, in order to maintain similar suspension
characteristics on both sides of the car.
7Check for signs of hydraulic fluid leakage
from around the front strut spindle gland and
also the condition of the dust excluding boot.
Oil leakage will mean a new unit, a split boot
can be renewed after having withdrawn the
coil spring.
3 Front suspension strut-
removal and refitting
4
1Raise the front of the car, support it
securely and remove the roadwheel.2Release the brake hydraulic hose
from the strut by unscrewing the retaining clip
bolt.
3Unscrew and remove the two bolts from the
clamp at the bottom of the strut, push the hub
carrier down out of the clamp (photo).
4Open the bonnet. Unscrew and remove the
domed reinforcement cover. Then remove the
strut top mounting nuts from the turret. Do not
attempt to unscrew the centre spindle nut
(photos).
5Withdraw the strut downwards and out
from under the wing (photo).
6Coil spring clamps must now be fitted.
These are available from most motor stores or
can be hired (photo).
7Once the spring has been compressed to
11•2 Suspension
3.5 Withdrawing a front strut3.4B Strut upper mounting nuts
3.4A Strut reinforcement plate3.3 Strut clamp bolt
Fig. 11.1 Front suspension arrangement (Sec 1)Fig. 11.2 Rear suspension arrangement (Sec 1)
Page 110 of 303
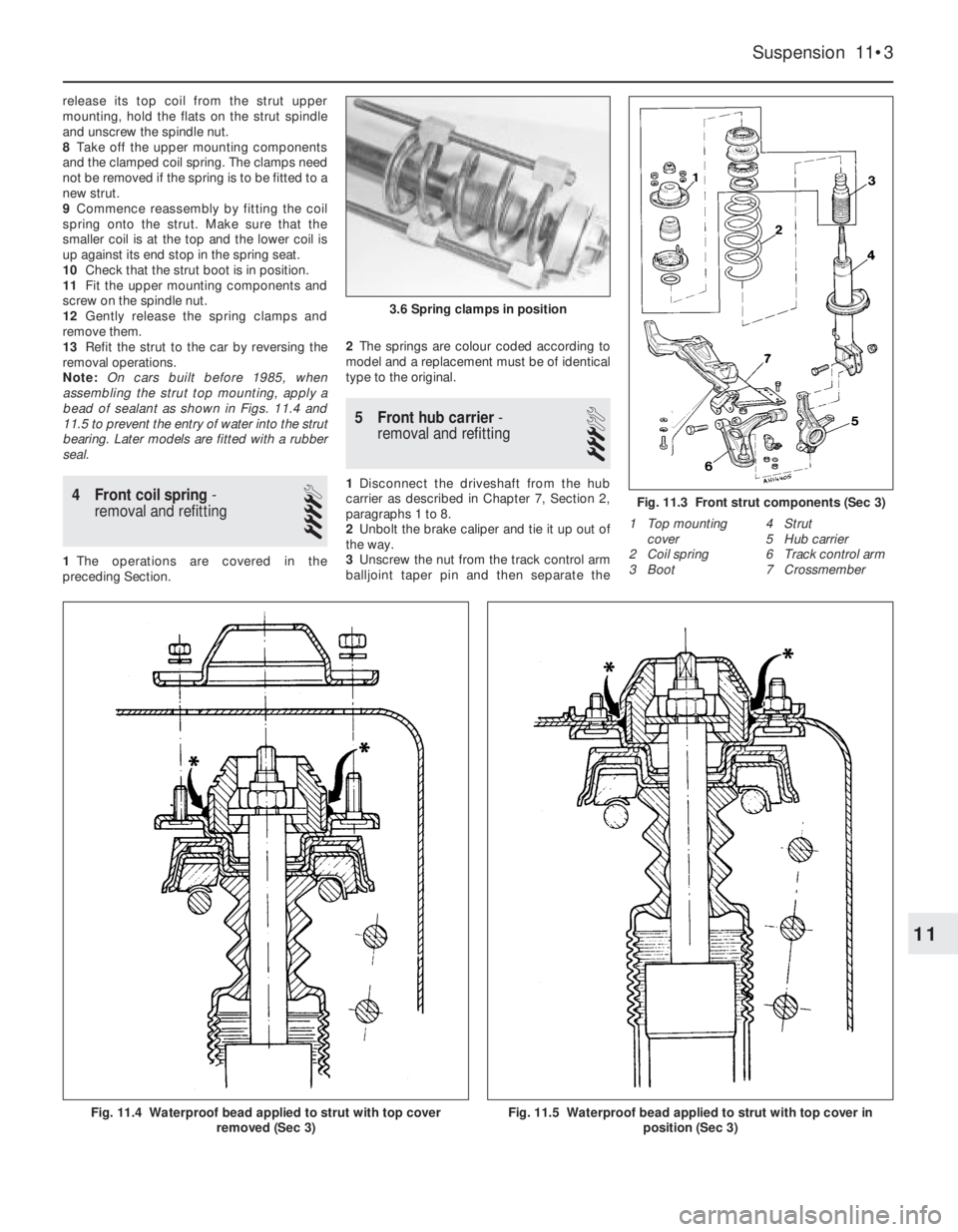
release its top coil from the strut upper
mounting, hold the flats on the strut spindle
and unscrew the spindle nut.
8Take off the upper mounting components
and the clamped coil spring. The clamps need
not be removed if the spring is to be fitted to a
new strut.
9Commence reassembly by fitting the coil
spring onto the strut. Make sure that the
smaller coil is at the top and the lower coil is
up against its end stop in the spring seat.
10Check that the strut boot is in position.
11Fit the upper mounting components and
screw on the spindle nut.
12Gently release the spring clamps and
remove them.
13Refit the strut to the car by reversing the
removal operations.
Note: On cars built before 1985, when
assembling the strut top mounting, apply a
bead of sealant as shown in Figs. 11.4 and
11.5 to prevent the entry of water into the strut
bearing. Later models are fitted with a rubber
seal.
4 Front coil spring-
removal and refitting
4
1The operations are covered in the
preceding Section.2The springs are colour coded according to
model and a replacement must be of identical
type to the original.
5 Front hub carrier-
removal and refitting
3
1Disconnect the driveshaft from the hub
carrier as described in Chapter 7, Section 2,
paragraphs 1 to 8.
2Unbolt the brake caliper and tie it up out of
the way.
3Unscrew the nut from the track control arm
balljoint taper pin and then separate the
Suspension 11•3
1 Top mounting
cover
2 Coil spring
3 Boot4 Strut
5 Hub carrier
6 Track control arm
7 Crossmember
Fig. 11.3 Front strut components (Sec 3)
3.6 Spring clamps in position
Fig. 11.4 Waterproof bead applied to strut with top cover
removed (Sec 3)Fig. 11.5 Waterproof bead applied to strut with top cover in
position (Sec 3)
11
Page 127 of 303

Cooling system................................................................................. 8
Part A: 999 cc engine
Description
Maintenance
Thermostat - removal and refitting
Coolant pump - removal and refitting
Part B: 1301 cc Turbo ie engine
Description
Part C: 1372 cc ie and 1372 cc Turbo ie engines
Description
Maintenance
Cooling system - draining, flushing and refilling
Radiator (and cooling fan) - removal and refitting
Thermostat - removal and refitting
Coolant pump - removal and refitting
Coolant pump/alternator drivebelt - checking, renewal and
tensioning
Part D: Heater unit later models
Heater unit - removal and refitting
Heater unit - dismantling and reassembly
Fuel and exhaust systems............................................................... 9
Part A: General
Unleaded fuel
Air cleaner modified types
Fuel pump (999 cc engine) - description, removal and
refitting
Fuel tank (999 cc engine)
Part B: Carburettor models
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) - description
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) - idle speed and mixture
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) - removal and refitting
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) - overhaul
Carburettor (Weber 30/32 DMTE) - general
Carburettor (Weber 30/32 DMTE) - overhaul
Carburettor (Weber 32 ICEV 61/250 and DMTE 30/32,
DMTE 30/150) - general
Carburettor (Solex C 30/32-CIC 8) - description
Part C: Bosch LE-2 Jetronic fuel injection system
Description
Maintenance
Fuel filter - renewal
Air cleaner element - renewal
Idle speed and mixture - adjustment
Fuel injection system - electrical tests
Fuel injection system - mechanical tests
Fuel injection system components - removal and
refitting
Throttle control linkage - general
Fuel tank - general
Part D: Bosch Mono-Jetronic fuel injection system
Description
Maintenance
Fuel filter - renewal
Air cleaner element - renewal
Idle speed and mixture adjustment
Accelerator control system - check and adjustment
Fuel system - depressurisation
Fuel pump and supply - system checks
Fuel pump - removal and refitting
Injector unit - removal and refitting
Intake air temperature sensor - removal and refitting
Fuel injector - removal and refitting
Electronic control unit (ECU) - removal and refitting
Inlet manifold - removal and refitting
Exhaust manifold - removal and refitting
Catalytic converter - general information
Fuel evaporation control system - generalPart E: Bosch L3.1/2 Jetronic fuel injection systems
Description
Fuel system - depressurisation
Maintenance
Fuel filter - renewal
Air cleaner element - renewal
Checks and adjustments
Injection system components - removal and refitting
Part G: Turbocharger system
Description
Precautions
Turbocharger (1301 cc ie engine) - removal and refitting
Turbocharger (1372 cc ie engine) - removal and refitting
Intercooler - removal and refitting
Injector cooling fan - removal and refitting
Fault finding - fuel injection system
Fault finding - turbocharger system
Ignition system................................................................................. 10
General
Ignition timing (all later models)
Breakerless ignition system - description
Distributor (breakerless type) - removal and refitting
Distributor (breakerless type) - overhaul
Breakerless ignition system components - testing
Microplex ignition system - description
Distributor (Microplex) - removal and refitting
Microplex ignition system components - testing
Digiplex 2 ignition system - description
Distributor (Digiplex 2) - removal and refitting
Spark plugs and HT leads - general
Fault finding - Microplex ignition system
Clutch................................................................................................ 11
Clutch pedal adjustment (cable clutch)
Hydraulic clutch - description
Maintenance (hydraulic clutch)
Clutch master cylinder - removal, overhaul and
refitting
Clutch operating cylinder - removal, overhaul and
refitting
Clutch hydraulic system - bleeding
Transmission.................................................................................... 12
Part A: 1301 cc Turbo ie engine
Description
Gearchange linkage - removal and refitting
Gearchange linkage (Antiskid models) - general
Final drive output shafts - description and oil seal
renewal
Part B: 1372 cc ie and 1372 cc Turbo ie engines
Description
Maintenance
Oil level - checking
Oil - renewal
Gearlever and linkages - general
Transmission - removal and refitting
Part C: 999 and 1108 cc with C514 type transmission
Description
Maintenance
Driveshafts........................................................................................ 13
Inboard joint boots (non-Turbo models, September 1987 on) -
modification
Intermediate driveshaft (Turbo ie models)
Inboard CV joints (Turbo ie models - overhaul
Right-hand driveshaft damper weight (1108 and 1372 cc
models) - removal and refitting
13•2 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Page 133 of 303

Lubrication system
Oil pump type:
999/1108 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Gear driven from front of crankshaft.
1372 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pump operated from front of crankshaft. Oil pressure relief valve in
front cover.
Tooth tip-to-body clearance (999/1108 cc) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.080 to 0.186 mm
Gear endfloat:
999/1108 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.025 to 0.056 mm
1372 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.040 to 0.106 mm
Oil pressure (at normal operating temperature) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.4 to 4.9 bars
Oil filter:
999/1108 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion F107
1372 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion C106
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Auxiliary shaft sprocket bolt (1372 cc) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83 62
Big-end cap bolts:
999/1108 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41 30
1372 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51 38
Camshaft bearing cap bolts:
M8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 14
M6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Camshaft cover screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 6
Camshaft housing to lower cylinder head securing bolt (1372 cc) . . . . . 20 15
Camshaft housing to inlet manifold bracket bolt (1372 cc) . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Camshaft sprocket bolt
999/1108 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68 50
1372 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83 62
Centre mounting to final drive casing bracket (1201/1301 cc) . . . . . . . . 23 17
Coolant temperature switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Crankshaft pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Crankshaft pulley nut (1372 cc) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197 145
Crankshaft rear oil seal retainer bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Crankshaft sprocket bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79 58
13•8 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
View of front end from below on
the 1372 cc ie engine model
1 Oil filter
2 Engine oil drain plug
3 Starter motor
4 Horns
5 Transmission front mounting
6 Front fog lamp and adjuster
7 Driveshaft
8 Transmission rear mounting
9 Gearchange linkage
10 Exhaust downpipe and system
joint
11 Anti-roll bar
12 Track control arm
13 Tie-rod balljoint
14 Brake unit
15 Driveshaft damper
16 Underwing shield