1983 FIAT UNO ECO mode
[x] Cancel search: ECO modePage 215 of 303

TDC sensor
48Insert the probes of the ohmmeter
between terminals 1 and 2 of the multipin
connector; 618 to 748 ohms (1301 cc) or 578
to 782 ohms (1372 cc) should be indicated.
49If necessary, carry out a check of the gap
between the sensor and the crankshaft pulley,
as described in Chapter 4, Section 10.
ECU supply
50Switch on the ignition, and then insert the
probes of a voltmeter between terminals 13
and 11 of the multipin connector. Battery
voltage should be indicated. If not, check the
battery earth, ignition switch or intermediate
connector plug for security.
Power module supply (1301 cc)
51Pull the multipin plug from the powermodule, and connect the probes of a
voltmeter between terminal 4 of the connector
and earth. If the reading is less than battery
voltage, check the security of all connections
between the ignition switch and terminal + 15
of the ignition coil.
52Reconnect the multipin connector to the
ECU, but have the one from the power
module disconnected, and then switch on the
ignition.
53Connect the voltmeter between terminals
4 and 2 of the power module multipin
connector. If the indicated voltage is less than
battery voltage, check the security of all
connections between the ignition switch and
terminal + 15 of the ignition coil, and the
battery earth. If all are satisfactory, check for
continuity between terminals 11 and 12. If
continuity is broken, renew the ECU.
Power module (1372 cc)
54Proceed as described in paragraph 53.
Anti-knock sensor
55If “pinking” occurs, or loss of power is
noticed, test the sensor by substitution of a
new one.
Ignition coil
56Disconnect the leads from terminals 1
and 15 on the coil before testing.
57Using the ohmmeter, check the resistance
of the primary winding. This should be
between 0.31 and 0.37 ohms (1301 cc) or
0.40 to 0.49 ohms (1372 cc), at an ambient
temperature of 20ºC (68ºF).
58The secondary winding resistance should
be between 3330 and 4070 ohms (1301 cc) or
4320 to 5280 ohms (1372 cc), at an ambient
temperature of 20ºC (68ºF).
Distributor
59Check the resistance of the rotor arm,
which should be between 800 and
1200 ohms.
60Where all the foregoing tests have proved
satisfactory, then any problem must be due to
a fault in either the power module or the ECU.
These components can only be checked by
the substitution of a new unit - power module
first, then the ECU.
Safety pressure switch
61The device protects the engine from
excessive turbocharging pressure, cutting off
the ignition by earthing the Microplex ECU.
Testing is not possible without a special
pressure pump, so the easiest way to check a
suspected fault is to fit a new unit.
Digiplex 2 ignition system -
description
62This system operates in a similar manner
to that of the earlier type described in Chap-
ter 4, but the circuit layout differs to suit the
Mono Jetronic fuel injection system. In
operation, the main difference is that the
Digiplex 2 system has a greater number of
13•90 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.81 Microplex ignition system
control unit connection (Sec 10)
For colour code, see main wiring diagramsFig. 13.80 Microplex ignition system ECU multipin connector (Sec 10)
For colour code, see main wiring diagrams
Fig. 13.79 Ignition advance curves - Microplex ignition system on the 1301 cc Turbo ie
(Sec 10)
Page 216 of 303

advance points than the earlier system.
Comparison of Fig. 13.82 with Fig. 4.2
illustrates the difference in layout. Note that
the distributor is mounted on the rear end of
the cylinder head and is driven by the
camshaft.
63When working on the Digiplex 2 ignition
system or associated components, the
precautionary notes outlined in Section 9 of
Chapter 4 must be adhered to.
64As with the earlier system, test
procedures possible on the Digiplex 2 system
are restricted due to the need for specialised
testing equipment. The following checks are
possible, however, using a conventional test
meter.
Ignition coil check
65To check the resistance of the coil’s
primary windings, connect the probes of an
ohmmeter between the positive terminal and
the negative terminal as shown in Fig. 13.83,
and check that the resistance reading at 18 to
28ºC is 0.45 ohms ± 10% (photo).66To check the resistance of the coil’s
secondary windings, connect the probes of an
ohmmeter between the positive terminal and
the HT lead terminal as shown in Fig. 13.84.
Check that the resistance reading at 18 to
28ºC (64 to 82ºF) is 4800 ohms ± 10%.
Ignition timing check
67Refer to paragraph 2 in this Section.
Engine speed and TDC sensor check
68To check the resistance between the
sensor and the ECU, detach the wiring
connector (photo). Connect the probes of an
ohmmeter to the connector terminals and
check that the resistance reading is between
600 and 760 ohms at 20ºC (68ºF). If the
reading is not as specified, the sensor must
be renewed.
69The gap between the sensor and the pins
on the rear face of the flywheel must be
between 0.2 and 0.8 mm. Any deviation
outside of this clearance will be due to
mechanical damage to the sensor andnecessitates its renewal. The sensor is
accurately positioned during manufacture and
secured with tamperproof screws; it does not
require any adjustment during servicing. If it is
necessary to renew the sensor, a special gap
setting tool is required and the task is
therefore best entrusted to a FIAT dealer.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•91
Fig. 13.82 Digiplex 2 ignition system wiring circuits and components (Sec 10)
10.68 ECU location on the 1372 cc ie
engine10.65 Ignition coil and connections on the
1372 cc ie engineFig. 13.84 Test connections for ignition
coil secondary windings check - Digiplex 2
ignition system (Sec 10)
Fig. 13.83 Test connections for ignition
coil primary windings check - Digiplex 2
ignition system (Sec 10)
13
1 Connection point (lines connected to
the intake manifold)
2 ECU
3 Ignition coil
4 Distributor
5 Engine flywheel (with
five pins)
6 On/off switch (if fitted)
for advance reduction
7 On/off switch 2 (if fitted)
for curves
8 Battery
9 Spark plugs
10 Tachometer
11 Diagnostic socket
12 Engine speed and TDC sensor
13 To check actuator idle speed
14 To terminal no. 1 of injection control unit
(rpm signal)
Page 217 of 303

11 Clutch
Clutch pedal - adjustment
(cable clutch)
Á
1The method of adjusting the clutch has
been revised.
2Fully depress the clutch pedal two or three
times.
3Using a suitable measuring stick placed in
contact with the floor panel (carpet peeled
back), measure dimension “X” in Fig. 13.87.
This dimension must be taken between the
centre of the pedal pad and the floor, first withthe pedal in the fully depressed position, and
then in the fully released position.
4The dimension measured should fall within
the range quoted in the Specifications for this
Supplement.
5Any adjustment which may be required
should be carried out by slackening the
locknut on the cable at the release lever (on
top of the gearbox) and turning the adjusting
nut. Tighten the locknut on completion.
Hydraulic clutch - description
6Some later models are fitted with an
hydraulically operated clutch in place of the
cable operated type. The main components of
the system are a master cylinder, with
separate hydraulic fluid reservoir, and the
operating cylinder. The master cylinder is
Distributor (Digiplex Z) -
removal and refitting#
70Proceed as described in paragraphs 14
to 21. When refitting the distributor, ensure that
the engine is still set at the TDC position. Engage
the rotor arm into position on the shaft so that its
lug engages in the slot in the top end of the drive
spindle. Align the rotor arm with the reference
slot on the edge of the distributor housing as
shown in Fig. 13.85, then fit the distributor into
position and secure with the retaining nuts
(photo). As previously mentioned, the fine timing
is made automatically through the ECU.
Spark plugs and HT leads -
general
71Copper-cored spark plugs are now fitted
to all models. The recommended types are
given in the Specifications Section of this
Supplement.72The HT lead connection sequence to the
distributor cap on the 999 and 1108 cc
engines is shown in Fig. 13.86. That for the
1301 cc Turbo ie is as shown (photo).
13•92 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.87 Clutch pedal adjustment
diagram - cable clutch (Sec 11)
For dimension “X” , refer to Specifications
Fig. 13.86 HT lead connections on distributor cap of the 999 and 1108 cc engines (Sec 10)
Fig. 13.85 Rotor arm must align with
slot (1) in distributor housing when refitting
distributor - Digiplex 2 ignition system
(Sec 10)
10.72 HT lead connecting sequence on the
1301 cc Turbo ie engine10.70 Ignition distributor and HT lead
connections on the 1372 cc ie engine
Fault finding - Microplex ignition system
Starter motor turns but engine will not start
m mExcessive TDC sensor gap
m mEngine speed or TDC sensors short-circuited
m mFaulty ECU
m mECU multipin contacts corroded
m mDefective ignition coil
m mDefective ignition switch
m mECU terminal 8 cable faulty
Engine firing on three cylinders
m
mFaulty spark plug
m mDistributor cap cracked
m mFaulty HT cable
Loss of power, excessive fuel consumption
m
mTDC sensor incorrectly located
m mFault in ECU advance angle facility
Page 218 of 303

mounted in-line with and just forward of the
clutch pedal. The operating cylinder is
mounted within a housing on top of the
transmission. The fluid reservoir is located in
the engine compartment and is mounted on
the left-hand side near the bulkhead. No
settings or specific procedures are given by
the manufacturer at the time of writing.
Maintenance
(hydraulic clutch)Á
7Periodically check the fluid level in the
reservoir. If the level has dropped, top it up
with the specified fluid. The fluid level must
not be allowed to drop below the MIN level
mark on the side of the reservoir (photos). If
the fluid level drops by a significant amount, it
is indicative of a leak in the hydraulic circuit
and this must therefore be traced and
repaired at the earliest opportunity.
8Inspect the fluid lines and connections for
security and any signs of leaks.
Clutch master cylinder -
removal, overhaul
and refitting
#
9If the cylinder is to be dismantled, it will first
be necessary to obtain a cylinder repair kit.
Start by detaching and removing the trim
panel from the underside of the facia on the
driver’s side.
10Place a suitable covering over the floor
carpet to prevent staining in the event of fluid
spillage. Clamp the fluid supply hose at the
master cylinder end, then unscrew the
retaining clip and detach the hose from the
cylinder. Position the hose out of the way and
with its end pointing up.
11Detach the operating rod clevis from the
brake pedal.
12Unscrew and detach the hydraulic pipe to
the operating cylinder from the master
cylinder (photo).
13Undo the two retaining nuts and withdraw
the master cylinder.
14To dismantle the cylinder, prise free and
pull back the dust boot, extract the retainer
and withdraw the operating rod.
15Invert the cylinder and shake free the
piston and seal assembly. If it is stuck inside
the cylinder, apply moderate air pressure
(from a foot pump) into the tail end and catchthe assembly in a clean cloth as it is ejected.
16Remove the seals noting their orientation.
Clean all components in methylated spirits or
new hydraulic fluid. If the cylinder is damaged,
scored or badly worn it must be renewed. The
seals must always be renewed once they are
removed.
17Assemble the new seals to the piston and
lubricate the cylinder, seals and piston
assembly with new hydraulic fluid (of the
specified type) before assembling them.
Ensure that the seals are fitted the correct
way round (as noted during removal).
18Renew the dust boot, fit and secure the
operating rod into position with the retainer,
then refit the dust boot over the cylinder.
19If the intake pipe connector was removed,
this must be refitted using a new seal.
20Refit the cylinder in the reverse order of
removal. Connect and hand tighten the
hydraulic pipe to the operating cylinder before
fully tightening the cylinder securing nuts. The
hydraulic pipe can then be fully tightened.21Reconnect the fluid supply hose to the
cylinder and tighten the retaining clip to
secure. Release the clamp.
22Top up the clutch fluid level in the
reservoir then bleed the system as described
later in this Section.
Clutch operating cylinder -
removal, overhaul
and refitting
¢
23If the cylinder is to be dismantled once it
is removed, it will first be necessary to obtain
a cylinder repair kit. Access is much improved
by first detaching the appropriate ducts and
hoses from the areas directly above the
cylinder, on top of the transmission/clutch
housing.
24To avoid excessive fluid loss when the
hydraulic line is detached from the operating
cylinder, remove the filler cap from the
reservoir, place a clean piece of polythene
sheet over the filler neck and refit the reservoir
cap.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•93
Fig. 13.88 Exploded view of the hydraulic clutch components (Sec 11)
1 Filler cap
2 Fluid reservoir
3 Hose
4 Master cylinder5 Cover
6 Clip
7 Bracket
8 Hose9 Operating cylinder
10 Bracket
11 Circlip
12 Operating lever
11.12 Clutch master cylinder and hydraulic
pipe connections11.7B Topping up the fluid level in the
clutch fluid reservoir11.7A Clutch hydraulic fluid reservoir
showing MIN and MAX markings
13
Page 219 of 303

25Unscrew the union nut and detach the
hydraulic fluid line from the operating cylinder
(photo).
26Undo the cylinder/mounting bracket
retaining bolts and lift clear the cylinder
together with the bracket (photo). Release the
retaining clip and separate the cylinder from
the bracket.
27To dismantle the cylinder, prise free and
pull back the dust boot, withdrawing it
together with the operating rod.
28Invert the cylinder and shake free the
piston and seal assembly. If it is stuck inside
the cylinder, remove the bleed screw then
apply moderate air pressure (from a foot
pump) into the bleed port and catch the
cylinder in a clean cloth as it is ejected.
29Remove the seals noting their orientation.
Clean all components in methylated spirits or
new hydraulic fluid. If the cylinder is damaged,
scored or badly worn it must be renewed. The
seals must always be renewed once they are
removed.
30Assemble the new seals to the piston and
lubricate the cylinder, seals and piston
assembly with new hydraulic fluid (of the
specified type) before assembling them.
Ensure that the seals are fitted the correct
way round (as noted during removal).
31Renew the dust boot, fit and secure the
operating rod into position then refit the dust
boot over the cylinder. If removed, refit the
bleed screw.
32Reconnect the cylinder to the mounting
bracket and refit the combined assembly to
the vehicle in the reverse order of removal.
Ensure the hydraulic union is clean and take
care not to damage the threads as it is
reconnected.
33Remove the polythene seal from the
hydraulic reservoir filler neck, top up the fluid
level and bleed the system as described
below.
Clutch hydraulic system -
bleeding#
34The clutch hydraulic circuit is bled in
much the same manner to that described for a
brake circuit. Refer to Section 12 in Chapter 8
and proceed as described, but note that the
bleed screw for the clutch circuit is located inthe end of the operating cylinder (see
photo 11.25). The clutch hydraulic circuit
reservoir is mounted in the engine
compartment on the left-hand side near the
bulkhead and is separate from the master
cylinder. As the system is being bled, ensure
that the fluid level in the reservoir is
maintained between the MIN and MAX level
marks. Do not allow the fluid level to drop
below the MIN level mark otherwise air will
enter the system and greatly lengthen the
operation. Wipe clean any fluid spillage from
the paintwork or adjacent components as it
has a corrosive effect if left.
12 Transmission
PART A:
1301 CC TURBO IE ENGINE
Description
1The transmission is of five-speed type,
based on that used in the Fiat Strada 105 TC.
2For all practical purposes, the operations
described in Chapter 6 apply, but observe the
following differences.
Gearchange linkage -
removal and refitting Á
3This is of two-rod type.
4Remove the gaiter and disconnect the rodsat the gear lever end as described in Chap-
ter 6, Section 3.
5Disconnect the rods at the transmission
end by unscrewing the nuts and bolts which
connect the linkage rods to the selector rods
(photo).
6Extract the spring clip which retains the end
of the short link rod (photo).
Gearchange linkage
(Antiskid models) - general
7The gearchange linkage and internal
selector arrangement has been modified, as
shown in Fig. 13.89.
Final drive output shafts -
description and
oil seal renewal
#
8The output shafts on this transmission
incorporate a flange on the left-hand side, to
which a coupling flange on the driveshaft is
bolted. On the right-hand side, an
intermediate shaft (see Section 13) is splined
directly into the differential side gear.
9A leaking oil seal may be renewed on the
left-hand side of the final drive casing after
first disconnecting the driveshaft. Then using
two levers, prise out the flange/stub shaft
against the tension of its retaining circlip.
10Unbolt and remove the bearing cover.
When refitting the cover, make sure that the
O-ring is in good condition.
11To renew the oil seal on the right-hand
side, first remove the intermediate driveshaft,
and then prise the defective seal out of the
final drive housing using a suitable tool.
12Apply grease to the new seal lips before
refitting the intermediate shaft or the stub
shaft. Tighten all bolts to the specified torque.
PART B:
1372 CC IE AND 1372 CC
TURBO IE ENGINES
Description
1The transmission is of five-speed type,
based on that used in the FIAT Tipo. The
transmission is mounted in-line with the
engine and is located in the left-hand side of
the engine compartment. Drive from the
clutch is transferred through the input shaft
and the mainshaft to the integrally-located
13•94 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
12A.6 Gearchange link rod spring clip
(arrowed) on the 1301 cc Turbo ie engine12A.5 Gearchange rod connections at
transmission (1301 cc Turbo ie engine)
11.26 Clutch operating lever (A) and
operating cylinder bracket-to-transmission
housing bolt (B)11.25 Clutch operating cylinder showing
hydraulic line connection and bleed nipple
(arrowed)
Page 222 of 303

27The engine must now be supported at its
left-hand end. If the engine/transmission lift
bracket is unbolted it can be attached at
another suitable position on the engine and
the lift sling/tool attached to it, but take care
not to attach it to a weak fixing point.
28The engine will need to be supported
using an engine lift beam/support bar of the
type shown in Fig. 13.93. A strong wood or
metal beam resting on blocks in the front wing
drain channels will suffice, or alternatively use
an engine lift hoist and sling.
29Refer to Section 13 in this Chapter and
Section 2 in Chapter 7 for details and remove
the front driveshaft each side.
30Prise back the tabs of the retaining
washers, then undo the retaining nuts and
detach the exhaust downpipe from the
manifold. Detach the exhaust mounting
bracket (where applicable) and lower the
exhaust to allow access to the gearchange
linkages.
31Disconnect the gearchange control and
selector link rod balljoints (photo). Do not alter
their lengths or the adjustment setting will be
affected.
32Using a small diameter pin punch, drive the
retaining pins from the retaining clips which
secure the left-hand side underwing shield.
Prise free the clips and detach the shield.
33Undo the retaining bolts and remove the
lower cover plate from the flywheel housing
(photo).
34Position a trolley jack under the
transmission with an interposed block ofwood to protect the casing and spread the
load. Raise the jack to support the weight of
the transmission.
35Check that the weight of the engine is
securely supported, then unbolt and detach
the front engine mounting unit, then the rear
engine mounting unit.
36Unscrew and remove the remaining bolts
securing the transmission to the engine. As
they are removed, note the position of any
brackets or additional fixings secured by
these bolts (photo).
37Check around the transmission to ensure
that all fixings are detached from it and out of
the way, then carefully pull the transmission
free from the engine dowel pins. If possible
engage the aid of an assistant to help in
guiding or lowering the unit as it is removed.
As the unit is withdrawn from the engine, take
care not to place any strain on the input shaft.
Once the input shaft is clear of the clutch, the
transmission can be lowered and manoeuvred
from underneath the car. If available, lower the
unit onto a suitable crawler board to ease its
withdrawal from under the front end of the car.
38Dismantling and overhaul of this
transmission is not recommended. If the
transmission has covered a high mileage it is
likely that several internal components are in
need of renewal. The cumulative cost of
renewing all worn and defective components
will almost certainly make overhaul
uneconomical when compared with the cost
of a new or service exchange transmission
from a FIAT dealer or transmission specialist.39Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure, but note the following special
points.
a) Ensure that the engine and transmission
mating surfaces and the dowel pins are
clean and that all clutch components are
in good condition.
b) Apply a thin smear of molybdenum
disulphide grease to the splines of the
input shaft. Do not over-lubricate though
or the grease may work its way onto the
clutch friction surfaces and cause clutch
slip.
c) Raise the transmission so that it is in-line
with the engine, engage the end of the
input shaft into the clutch driven plate hub
and align the splines of each to enable the
transmission to be pushed home. It may
well be necessary to turn the flywheel a
fraction so that the splines align for
re-engagement
d) Do not fully tighten the engine and
transmission retaining bolts until all are
attached.
e) Tighten all retaining bolts and nuts of the
specified torque wrench settings (where
given).
f) Refer to Section 13 in this Chapter for
details on refitting the driveshafts.
g) Refill the transmission with the specified
quantity and grade of oil before lowering
the car to the ground (see paragraph 11).
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•97
Fig. 13.93 FIAT lift beam/support bar in
place to support the weight of the engine.
Inset shows lift hook engagement point -
1372 cc models (Sec 12)
12B.24B . . . and retaining bolts (arrowed)
on the 1372 cc ie engine12B.24A Starter motor electrical
connection . . .
12B.36 Transmission upper retaining bolts.
Note bracket under the left-hand bolt12B.33 Lower cover plate and retaining
bolts (arrowed)12B.31 Gear control and selector link rod
joints
13
Page 223 of 303
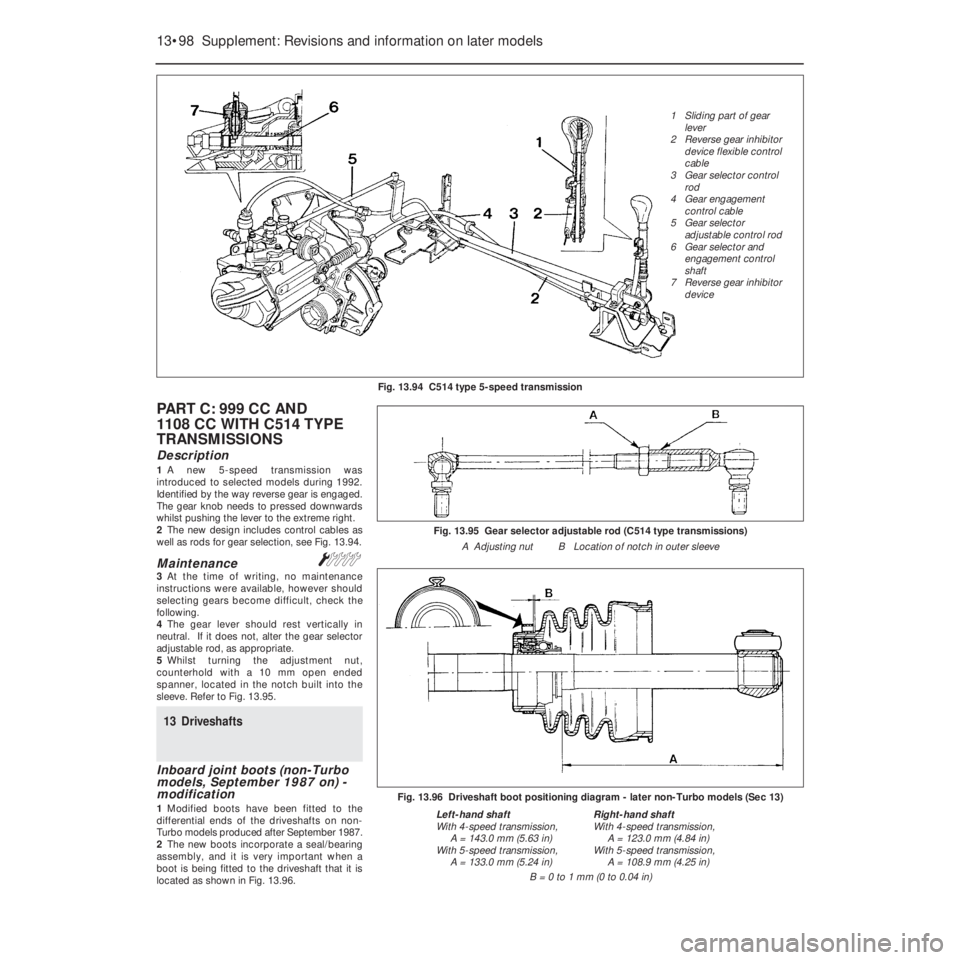
PART C: 999 CC AND
1108 CC WITH C514 TYPE
TRANSMISSIONS
Description
1A new 5-speed transmission was
introduced to selected models during 1992.
Identified by the way reverse gear is engaged.
The gear knob needs to pressed downwards
whilst pushing the lever to the extreme right.
2The new design includes control cables as
well as rods for gear selection, see Fig. 13.94.
MaintenanceÁ3At the time of writing, no maintenance
instructions were available, however should
selecting gears become difficult, check the
following.
4The gear lever should rest vertically in
neutral. If it does not, alter the gear selector
adjustable rod, as appropriate.
5Whilst turning the adjustment nut,
counterhold with a 10 mm open ended
spanner, located in the notch built into the
sleeve. Refer to Fig. 13.95.
13 Driveshafts
Inboard joint boots (non-Turbo
models, September 1987 on) -
modification
1Modified boots have been fitted to the
differential ends of the driveshafts on non-
Turbo models produced after September 1987.
2The new boots incorporate a seal/bearing
assembly, and it is very important when a
boot is being fitted to the driveshaft that it is
located as shown in Fig. 13.96.
13•98 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.96 Driveshaft boot positioning diagram - later non-Turbo models (Sec 13)
Left-hand shaft
With 4-speed transmission,
A = 143.0 mm (5.63 in)
With 5-speed transmission,
A = 133.0 mm (5.24 in)Right-hand shaft
With 4-speed transmission,
A = 123.0 mm (4.84 in)
With 5-speed transmission,
A = 108.9 mm (4.25 in)
Fig. 13.94 C514 type 5-speed transmission
1 Sliding part of gear
lever
2 Reverse gear inhibitor
device flexible control
cable
3 Gear selector control
rod
4 Gear engagement
control cable
5 Gear selector
adjustable control rod
6 Gear selector and
engagement control
shaft
7 Reverse gear inhibitor
device
B = 0 to 1 mm (0 to 0.04 in)
Fig. 13.95 Gear selector adjustable rod (C514 type transmissions)
A Adjusting nut B Location of notch in outer sleeve
Page 226 of 303

4Using a ring spanner and an open-ended
spanner, unscrew and remove the caliper
cylinder housing lower guide bolt (photo).
Release the upper bolt, but do not remove it.
5Swivel the cylinder housing upwards and tie
it up out of the way. There is no need to
disconnect the hydraulic hose. The sensor
wiring plug will have to be disconnected
(where fitted).
6Remove the pads, complete with anti-rattle
springs (photo).
7Clean away all dust and dirt, taking care not
to inhale it as it may be injurious to health.
8The caliper piston must now be fully
depressed to accommodate the new, thicker,
pads. Do this using a G-clamp or lever, but
anticipate a rise in the brake fluid reservoir
level by syphoning out some of the fluid using
a clean syringe.
9Fit the new pads, which must be of the
same type as the originals, complete with
anti-rattle springs.
10Locate the cylinder body. The fixing bolts
are of self-locking type, and should be
renewed whenever they are loosened or
removed. If new ones are not available, clean
the threads of the old ones thoroughly and
apply thread-locking fluid (photo). Tighten the
bolts to the specified torque. Check that the
rubber dust excluders are in good condition.
11Reconnect the sensor wiring plug.
12Renew the pads on the other front wheel.
13Refit the roadwheels, and then apply the
footbrake several times to position the pads
against the discs.14Top up the brake fluid reservoir if
necessary (photo).
Front disc caliper -
removal and refitting#
15Raise the front of the car and remove the
appropriate roadwheel.
16Using a ring spanner and an open-ended
spanner, unscrew and remove the cylinder
housing fixing bolts.
17Withdraw the cylinder housing, and then,
holding it firmly, release the flexible hydraulic
hose union. Unscrew the cylinder body from
the end of the flexible hose, and then cap the
end of the hose to prevent loss of fluid.
18If required, the disc pads can be removed
and the caliper support bracket unbolted and
removed.
19Refitting is a reversal of removal, but use
new fixing bolts.
20Bleed the front hydraulic circuit.
Front disc caliper - overhaul
21The operations are as described in
Chapter 8, Section 5, paragraphs 6 to 13.
Front brake disc - inspection,
renovation or renewal
22The operations are as described in
Chapter 8, Section 6, but the caliper fixing
bolts are secured with thread-locking fluid;
lockplates are not used.
Rear disc pads - renewal ª
23Any wear in the disc pads can be
observed through the aperture in the calipercylinder body, once the car has been jacked
up and the roadwheels removed (photo).
24If the thickness of the pad friction material
is less than 1.5 mm, renew the pads on both
sides in the following way.
25Using a ring spanner and an open-ended
spanner, unscrew the caliper cylinder body
fixing bolts.
26Withdraw the caliper and remove the disc
pads, complete with anti-rattle springs (photo).
27Clean away all dust and dirt, but avoid
inhaling it, as it may be injurious to health.
28Fully retract the caliper piston in order to
accommodate the new, thicker, pads. To do
this, rotate the piston clockwise, using a
suitable tool engaged in the handbrake
sectors (photo). Anticipate a rise in the brake
fluid reservoir level by syphoning out some
fluid, using a clean syringe.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•101
14B.10 Applying thread-locking fluid to the
bolt threads14B.6 Disc pad and anti-rattle spring
removal14B.4 Unscrewing the caliper cylinder
housing lower guide bolt
14B.28 Rotating a rear caliper piston14B.26 Withdrawing the rear brake caliper14B.23 Rear brake pad inspection aperture
14B.14 Topping up the brake fluid reservoir
(1301 cc Turbo ie model)
13