1982 CHEVROLET CAMARO oil type
[x] Cancel search: oil typePage 411 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 411
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Relieve the fuel system pressure
and drain the engine coolant from the
radiator into a suitable container.
3. Remove the intake manifold and the spark plugs.
4. Remove the dipstick tube and bra cket. Raise and support the vehicle
safely. Drain the oil and remove the oil filter. Lower the vehicle.
5. Remove the exhaust manifolds.
6. Remove the drive belt(s).
7. Remove the air conditioning compresso r and bracket, reposition it aside.
Do not disconnect the lines.
8. Remove the power steering pump and bracket, reposition it aside.
9. Remove the alternator and br acket, reposition it aside.
10. Remove the ground cable from the rear of the cylinder head and remove
the engine lift bracket.
11. Remove the rocker arm covers.
12. Loosen the rocker arms until the pushrods can be removed.
13. Remove the cylinder head bolts and remove the cylinder heads.
To install: 14. Clean the gasket mating surfaces of all components. Be careful not to
nick or scratch any surfaces as this will allow leak paths. Clean the bolt
threads in the cylinder bl ock and on the head bolts. Dirt will affect bolt
torque.
15. Place the head gaskets in pos ition over the dowel pins.
16. Install the cylinder heads.
17. Coat the cylinder head bolts th reads with GM sealer 1052080 or
equivalent, and install the bolts. Tight en the bolts in the proper sequence
to:
• 1982-1987 engines: 70 ft lbs. (90 Nm)
• 1988-1992 engines: 1st step: 40 ft lbs. (55 Nm); 2nd step: tighten
an additional 1/4 (90 degree) turn
18. Install the pushrods a nd loosely retain them wit h the rocker arms. Make
sure the lower ends of the pushrods ar e in the lifter seats. Refer to the
rocker arm procedures outlined ea rlier in this section.
19. Install the power steering pump br acket and pump. Do the same for the
air conditioning compressor bracket and compressor.
20. Install the ground cable to t he rear of the cylinder head.
21. Install the exhaust manifolds.
22. Install the dipstick tube and bracket.
23. Install the intake manifold.
24. Install the alternator bracket and alternator.
25. Install the drive belt(s).
26. Install the spark plugs.
27. Fill the cooling system with the proper type and quantity of coolant. Install
a new oil filter and fill the crankca se with the proper type and quantity of
oil.
28. Connect the negative battery cable, star t the vehicle and check for leaks.
Page 417 of 875
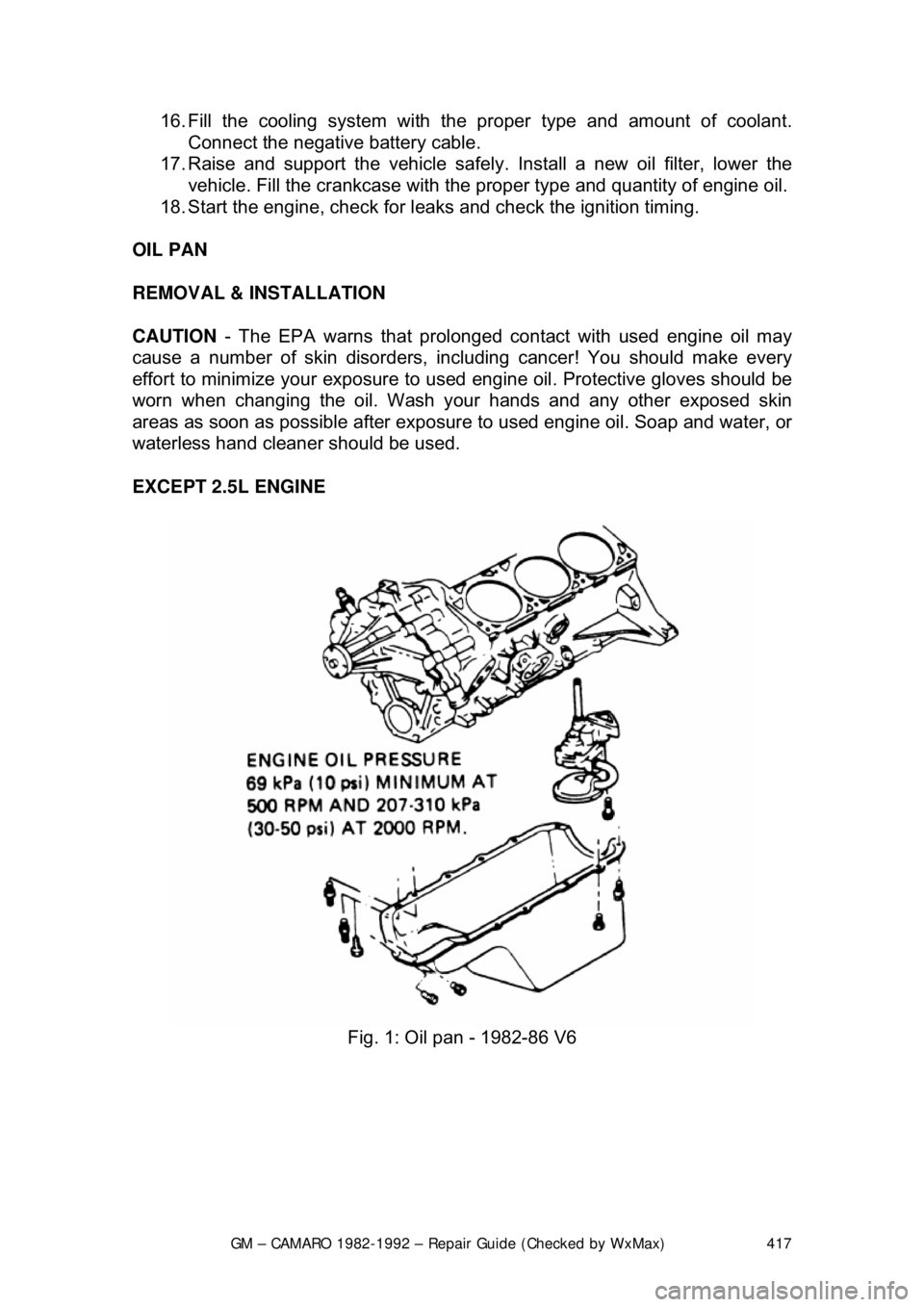
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 417
16. Fill the cooling syst
em with the proper type and amount of coolant.
Connect the negative battery cable.
17. Raise and support the vehicle safely . Install a new oil filter, lower the
vehicle. Fill the crankcase with the proper type and quantity of engine oil.
18. Start the engine, check for lea ks and check the ignition timing.
OIL PAN
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
CAUTION - The EPA warns that prolonged contact with used engine oil may
cause a number of skin disorders, incl uding cancer! You should make every
effort to minimize your exposure to used engine oil. Pr otective gloves should be
worn when changing the oil. Wash y our hands and any other exposed skin
areas as soon as possible after exposure to used engine oil. Soap and water, or
waterless hand cleaner should be used.
EXCEPT 2.5L ENGINE
Fig. 1: Oil pan - 1982-86 V6
Page 462 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 462
REPLACEMENT
There are basically two types of exhaust sy
stems. One is the flange type where
the component ends are attached with bolts and a gasket in-between. The other
exhaust system is the slip joint type. These components slip into one another
using clamps to retain them together.
CAUTION - Allow the exhaust system to c ool sufficiently before spraying a
solvent exhaust fasteners. Some solvents are highly flammable and could ignite
when sprayed on hot exhaust components.
Before removing any component of the ex haust system, ALWAYS squirt a liquid
rust dissolving agent onto the fasteners fo r ease of removal. A lot of knuckle
skin will be saved by following this rule. It may even be wise to spray the
fasteners and allow them to sit overnight.
Fig. 8: Nuts and bolts will be extremely difficult to remove when deteriorated
with rust
FLANGE TYPE
CAUTION - Do NOT perform exhaust repairs or inspection with the engine or
exhaust hot. Allow the system to cool completely before attempting any work.
Exhaust systems are noted for sharp edges , flaking metal and rusted bolts.
Gloves and eye protection ar e required. A healthy supply of penetrating oil and
rags is highly recommended. Never spra y liquid rust dissolving agent onto a hot
exhaust component.
Page 466 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 466
wear. Worn piston rings, scored or wo
rn cylinder bores, blown head gaskets,
sticking or burnt valves, and worn valve seats are all possible culprits. A check
of each cylinder's compression will help locate the problem.
A screw-in type compression gauge is more accurate than the type you simply
hold against the spark plug hole. Although it takes slightly longer to use, it's
worth the effort to obtain a more accurate reading.
1. Make sure that the proper amount and viscosity of engine oil is in the
crankcase, then ensure the battery is fully charged.
2. Warm-up the engine to normal operat ing temperature, then shut the
engine OFF.
3. Disable the ignition system.
4. Label and disconnect all of the spark plug wires from the plugs.
5. Thoroughly clean the cylinder h ead area around the spark plug ports,
then remove the spark plugs.
6. Set the throttle plate to the fully open (wide-open throttle) position. You
can block the accelerator linkage open for this, or you can have an
assistant fully depress the accelerator pedal.
Fig. 1: A screw-in type compression gauge is more accurate and easier to use
without an assistant
7. Install a screw-in type compression gauge into the No. 1 spark plug hole
until the fitting is snug.
WARNING - Be careful not to crossthread the spark plug hole.
Page 471 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 471
Most of the cleaning process can
be carried out with common hand tools and
readily available solvents or soluti ons. Carbon deposits can be chipped away
using a hammer and a hard wooden chisel. Old gasket material and varnish or
sludge can usually be re moved using a scraper and/ or cleaning solvent.
Extremely stubborn deposits may require the use of a power drill with a wire
brush. If using a wire brush, use extrem e care around any critical machined
surfaces (such as the gasket surfaces, bearing saddles, cylinder bores, etc.).
Use of a wire brush is NOT RECO MMENDED on any aluminum components.
Always follow any safety recommendations given by the manufacturer of the
tool and/or solvent. You s hould always wear eye prot ection during any cleaning
process involving scraping, chipping or spraying of solvents.
An alternative to the mess and hassle of cl eaning the parts yourself is to drop
them off at a local garage or machine shop. They will, more than likely, have the
necessary equipment to properly clean all of the parts for a nominal fee.
CAUTION - Always wear eye protection duri ng any cleaning process involving
scraping, chipping or spraying of solvents.
Fig. 2: Use a ring expander tool to remove the piston rings
Remove any oil galley plugs, freeze pl ugs and/or pressed-in bearings and
carefully wash and degrease all of the engine components including the
fasteners and bolts. Small par ts such as the valves, springs, etc., should be
placed in a metal basket and allowed to soak. Use pipe cleaner type brushes,
and clean all passageways in the co mponents. Use a ring expander and
remove the rings from the pistons. Cl ean the piston ring grooves with a special
tool or a piece of broken ri ng. Scrape the carbon off of the top of the piston. You
should never use a wire brush on the pist ons. After preparing all of the piston
assemblies in this manner, wash and degrease them again.
Page 475 of 875
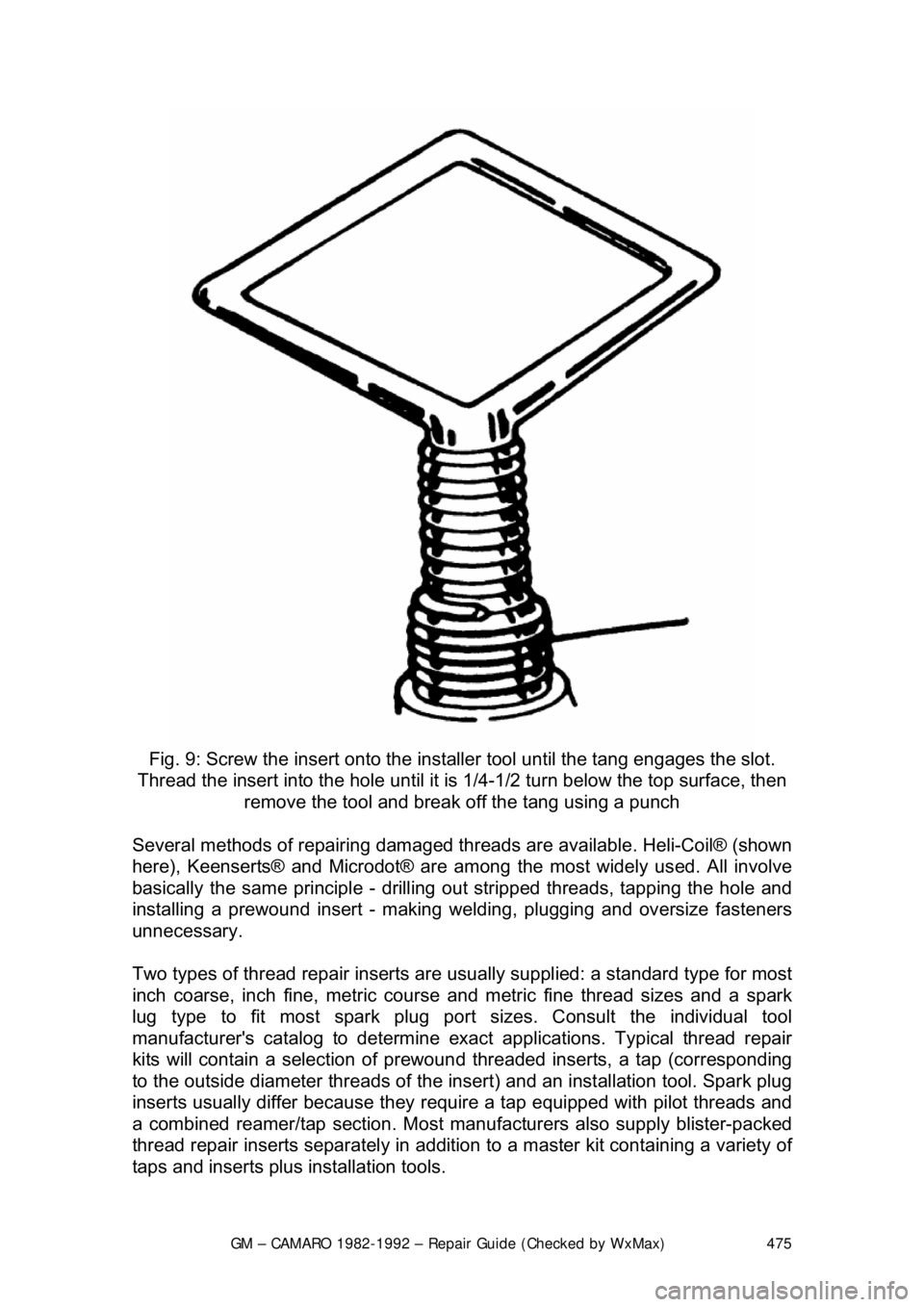
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 475
Fig. 9: Screw the insert onto the inst aller tool until the tang engages the slot.
Thread the insert into the hole until it is 1/4-1/2 turn below the top surface, then
remove the tool and break off the tang using a punch
Several methods of repairi ng damaged threads are availa ble. Heli-Coil® (shown
here), Keenserts® and Microdot® are among the most widely used. All involve
basically the same principl e - drilling out stripped thread s, tapping the hole and
installing a prewound insert - making we lding, plugging and oversize fasteners
unnecessary.
Two types of thread repair inserts are us ually supplied: a standard type for most
inch coarse, inch fine, metric course and metric fine thread sizes and a spark
lug type to fit most spark plug port si zes. Consult the individual tool
manufacturer's catalog to determine exac t applications. Typical thread repair
kits will contain a selection of prewoun d threaded inserts, a tap (corresponding
to the outside diameter thr eads of the insert) and an installation tool. Spark plug
inserts usually differ because they requi re a tap equipped with pilot threads and
a combined reamer/tap section. Most ma nufacturers also supply blister-packed
thread repair inserts separately in addition to a master kit containing a variety of
taps and inserts plus installation tools.
Page 476 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 476
Before attempting to repair a threaded
hole, remove any snapped, broken or
damaged bolts or studs. Penetrating oil ca n be used to free frozen threads. The
offending item can usually be removed with locking pliers or using a screw/stud
extractor. After the hole is clear, the thread can be repaired, as shown in the
series of accompanying illustrations and in the kit manufacturer's instructions.
ENGINE PREPARATION
To properly rebuild an engine, you must fi rst remove it from the vehicle, then
disassemble and diagnose it. Ideally you should place your engine on an engine
stand. This affords you the best access to the engine components. Follow the
manufacturer's directions for using the stand with your particular engine.
Remove the flywheel or fl explate before installing the engine to the stand.
Now that you have the engine on a stand, and assuming that you have drained
the oil and coolant from the engine, it's ti me to strip it of all but the necessary
components. Before you start disassembli ng the engine, you may want to take
a moment to draw some pictures, or fabr icate some labels or containers to mark
the locations of various components and the bolts and/or studs which fasten
them. Modern day engines use a lot of littl e brackets and clips which hold wiring
harnesses and such, and these holders are often mounted on studs and/or bolts
that can be easily mixed up. The manufacturer spent a lot of time and money
designing your vehicle, and they wouldn't have wasted any of it by haphazardly
placing brackets, clips or fasteners on t he vehicle. If it's present when you
disassemble it, put it back when you asse mble, you will regret not remembering
that little bracket which holds a wire har ness out of the path of a rotating part.
You should begin by unbolting any accessories still attached to the engine, such
as the water pump, power steering pump, alternator, etc. Then, unfasten any
manifolds (intake or exhaust) which were not removed during the engine
removal procedure. Finally, remove any covers remaining on the engine such
as the rocker arm, front or timing cove r and oil pan. Some front covers may
require the vibration dam per and/or crank pulley to be removed beforehand.
The idea is to reduce the engine to the bar e necessities (cylinder head(s), valve
train, engine block, crankshaft, pistons and connecting rods), plus any other 'in
block' components such as oil pumps, balance shafts and auxiliary shafts.
Finally, remove the cylinder head(s) from the engine block and carefully place
on a bench. Disassembly instructions fo r each component follow later in this
section.
CYLINDER HEAD
There are two basic types of cylinder heads used on today’s automobiles:
the Overhead Valve (OHV) and the Over head Camshaft (OHC). The latter can
also be broken down into two subgr oups: the Single Overhead Camshaft
(SOHC) and the Dual Overhead Camshaft (DO HC). Generally, if there is only a
single camshaft on a head, it is just referred to as an OHC head. Also, an
engine with a OHV cylinder head is also known as a pushrod engine.
Page 489 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 489
There is no repair or refinishing possi
ble with the springs, retainers and valve
locks. If they are found to be worn or defective, they must be replaced with new
(or known good) parts.
CYLINDER HEAD
Most refinishing procedures dealing wit h the cylinder head must be performed
by a machine shop. Read the informati on below and review your inspection
data to determine whether or not machining is necessary.
VALVE GUIDE
If any machining or replacements are made to the valve guides, the seats must
be machined.
Unless the valve guides need machining or replacing, the only service to\
perform is to thoroughly clean them of any dirt or oil residue.
There are only two types of valve gu ides used on automobile engines: the
replaceable-type (all alumi num heads) and the cast-in in tegral-type (most cast
iron heads). There are four recommended methods for repairing worn guides.
• Knurling
• Inserts
• Reaming oversize
• Replacing
Knurling is a process in which metal is displaced and raised, thereby reducing
clearance, giving a true center, and providing oil control. It is the least
expensive way of repairing the valve guides . However, it is not necessarily the
best, and in some cases, a knurled valve guide will not stand up for more than a
short time. It requires a special knurle r and precision reaming tools to obtain
proper clearances. It would not be cost effective to purchase these tools, unless
you plan on rebuilding several of the same cylinder head.
Installing a guide insert involves machin ing the guide to accept a bronze insert.
One style is the coil-type wh ich is installed into a threaded guide. Another is the
thin-walled insert where the guide is ream ed oversize to accept a split-sleeve
insert. After the insert is installed, a s pecial tool is then run through the guide to
expand the insert, locking it to the guide. The insert is then reamed to the
standard size for proper valve clearance.
Reaming for oversize valves restores normal clearances and provides a true
valve seat. Most cast-in type guides can be reamed to accept an valve wi\
th an
oversize stem. The cost factor for this can become quite high as you will need
to purchase the reamer and new, oversize stem valves for all guides which
were reamed. Oversizes ar e generally 0.003 to 0.030 in. (0.076 to 0.762mm),
with 0.015 in. (0.381mm) being the most common.