1968 DATSUN 510 engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 102 of 252
ENGINE
ELECI
RlCAL
SYSTEM
97
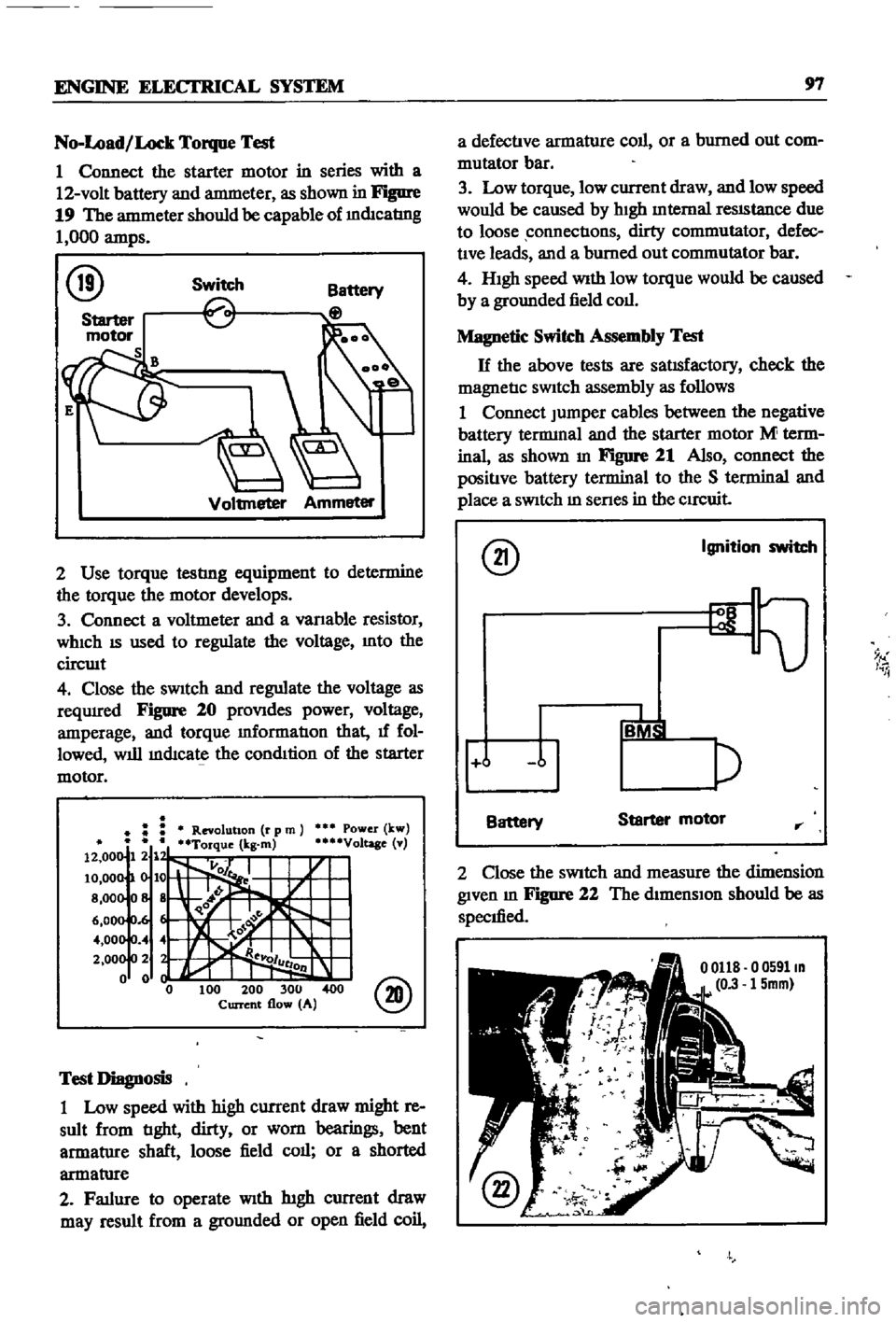
No
Load
Lock
Torque
Test
1
Connect
the
starter
motor
in
series
with
a
12
volt
battery
and
antmeter
as
shown
in
Figure
19
The
antmeter
should
be
capable
of
mdIcatIng
1
000
amps
@
Switch
Voltmeter
Ammeter
2
Use
torque
testlng
equipment
to
determine
the
torque
the
motor
develops
3
Connect
a
voltmeter
and
a
vanable
resistor
WhICh
IS
used
to
regulate
the
voltage
Into
the
circwt
4
Close
the
sWitch
and
regulate
the
voltage
as
reqUIred
Figure
20
proVIdes
power
voltage
amperage
and
torque
mformatIon
that
1f
fol
lowed
will
mdIcate
the
condItion
of
the
starter
motor
Power
kw
Voltage
v
@
Test
Diagnosis
1
Low
speed
with
high
current
draw
might
re
sult
from
tIght
dirty
or
worn
bearings
bent
armatlIre
shaft
loose
field
call
or
a
shorted
armatlIre
2
Fatlure
to
operate
With
htgh
current
draw
may
result
from
a
gromlded
or
open
field
coil
a
defectIve
armature
coll
or
a
burned
out
com
mutator
bar
3
Low
torque
low
current
draw
and
low
speed
would
be
caused
by
hIgh
Internal
reSIStance
due
to
loose
connectIons
dirty
commutator
defec
tIve
leads
and
a
burned
out
commutator
bar
4
HIgh
speed
With
low
torque
would
be
caused
by
a
grounded
field
coll
Magnetic
Switch
Assembly
Test
H
the
above
tests
are
satIsfactory
check
the
magnetIc
SWitch
assembly
as
follows
1
Connect
Jumper
cables
between
the
negative
battery
tennmal
and
the
starter
motor
M
term
inal
as
shown
In
Figure
21
Also
connect
the
positIve
battery
terminal
to
the
S
terminal
and
place
a
SWitch
m
senes
in
the
CIrCuit
@
Ignition
switch
9
I
i
j
Battery
Starter
motor
rr
2
Close
the
SWitch
and
measure
the
dimension
given
m
Figure
22
The
dimensIon
should
be
as
specIfied
o
0591m
15mm
Page 104 of 252
ENGINE
ELECfRlCAL
SYSTEM
99
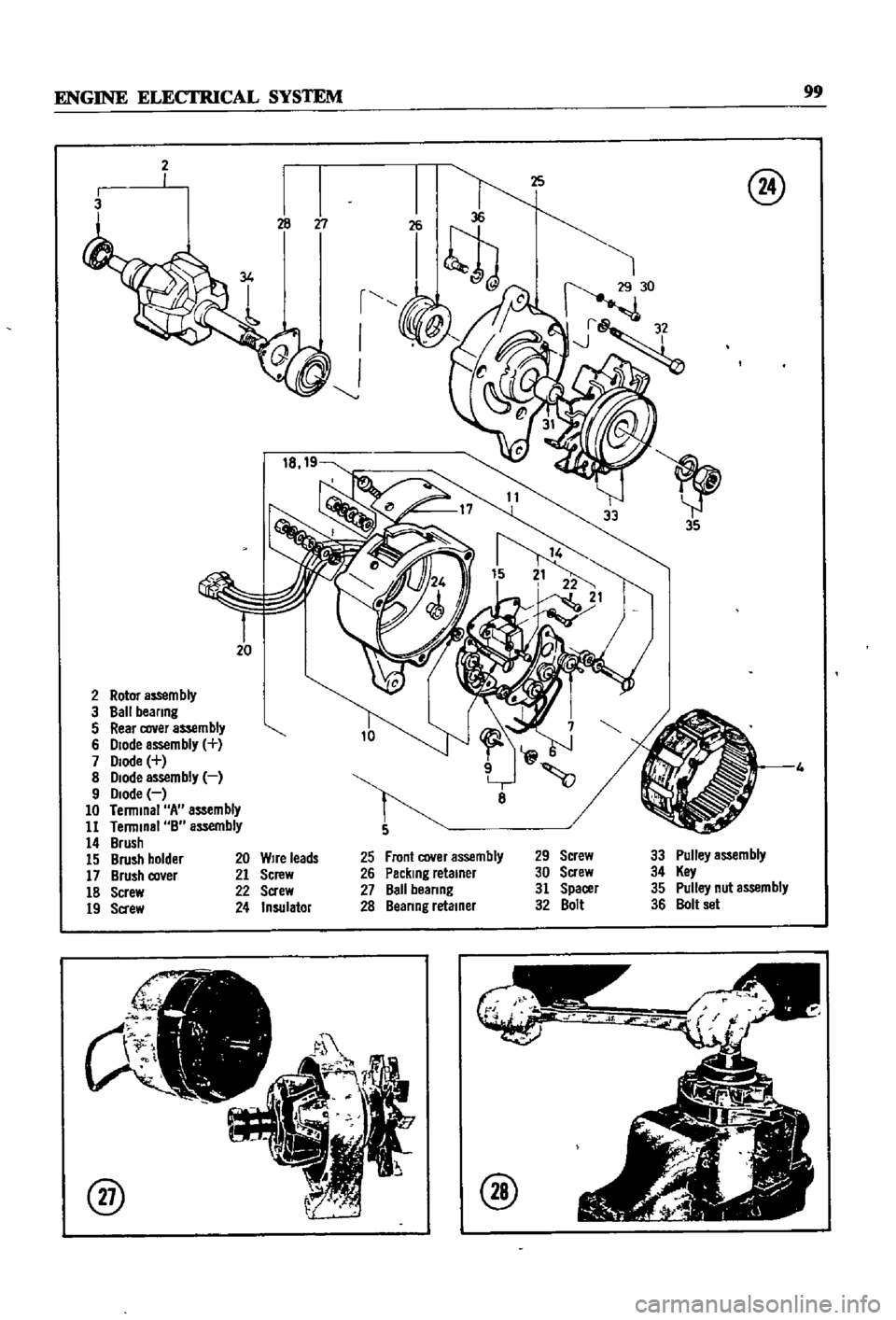
2
3
r
I
J
20
2
Rotor
aS5em
bly
3
Ball
beanng
5
Rear
cover
assembly
6
Diode
assembly
7
Diode
8
Diode
assembly
9
Diode
10
Terminal
A
assembly
11
Terminal
B
assembly
14
Brush
15
Brush
holder
17
Brush
co
er
18
Screw
19
Sa
ew
@
8
Front
cover
assembly
Packing
retainer
Ball
beanng
Beanng
retainer
29
Screw
30
Screw
31
Spacer
32
Bolt
33
Pulley
assembly
34
Key
35
Pulley
nut
assembly
36
Bolt
set
20
Wire
leads
21
Screw
22
Screw
24
Insulator
@
@
Page 106 of 252

ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
101
8
To
separate
the
stator
from
the
dIode
end
housmg
assembly
unsolder
the
three
negatIve
dIodes
from
the
three
co1l1ead
WIres
The
nega
tIve
dIodes
are
marked
WIth
black
figures
and
the
posItIve
ones
With
red
figures
CAUTION
Use
extreme
care
when
unsoldenng
the
diodes
to
prevent
excessive
heat
from
damagmg
thi
m
Use
a
100
to
200
watt
soldermg
Iron
for
no
more
than
two
seconds
at
the
dIOde
Junction
9
Remove
the
brush
cover
by
unscreWIng
the
two
set
screws
10
Unsolder
the
negatIve
terminal
lead
wire
Separate
dIOde
end
from
stator
Figure
33
@
11
Remove
the
heat
smk
and
the
brush
holder
from
the
rear
cover
by
unscrewmg
the
setscrews
as
shown
m
Figure
34
@
12
DIsassemble
the
brush
holder
by
unsolder
ing
the
F
lead
WIre
black
whIte
E
lead
WIre
black
and
the
negatIve
and
pOSItIve
brush
holder
Wires
Figure
35
shows
the
brush
holder
dIsassembled
O
tlII
I
@
13
To
remove
a
dIode
from
the
heat
smk
sup
port
the
heat
SInk
WIth
a
swtable
stand
Figure
36
and
push
out
the
dIode
With
an
arbor
press
Do
not
attempt
removal
WIth
a
hammer
as
the
shock
may
damage
all
the
dIodes
ill
the
heat
SInk
Press
out
so
as
not
to
Injure
the
mounting
bore
01
the
frame
or
the
heat
Sink
14
To
replace
a
dIode
m
the
heat
smk
support
the
heat
SInk
With
a
SUItable
stand
and
press
the
dIode
mto
place
as
shown
m
Figure
37
Inspection
and
Repair
I
InspectIon
of
the
alternator
Includes
electncal
testmg
and
mechanIcal
InspectIon
of
all
parts
for
damage
or
exceSSIve
wear
An
electrIcal
tester
proVIdmg
reSIstance
anI
contmUlty
testlng
IS
requIred
Before
dIsassembly
of
the
alternator
Page 108 of 252
ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
103
2
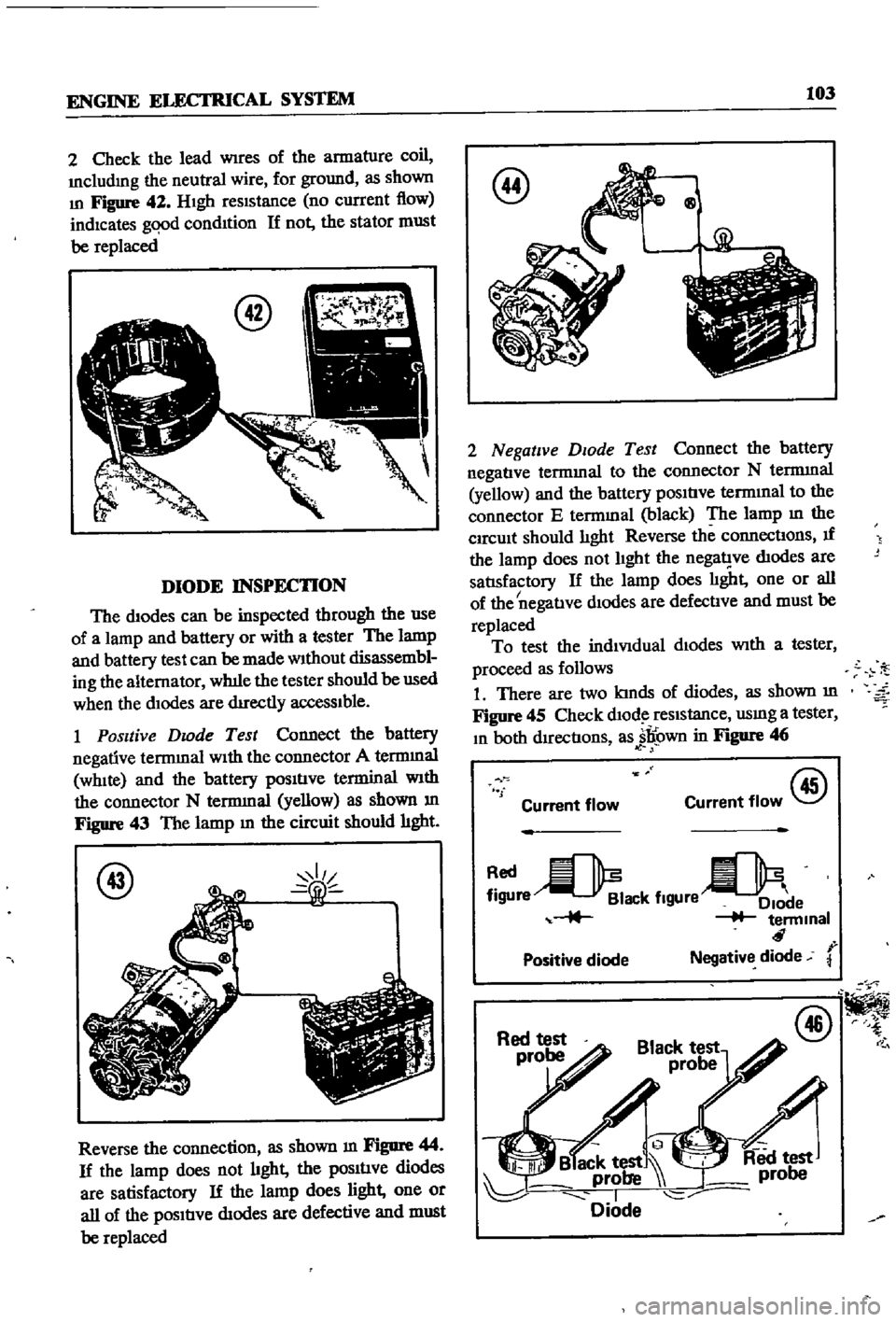
Check
the
lead
Wires
of
the
armature
coil
Includmg
the
neutral
wire
for
ground
as
shown
In
Figure
42
HIgh
reSIStance
no
current
flow
indicates
gqod
condItion
If
not
the
stator
must
be
replaced
DIODE
INSPECTION
The
diodes
can
be
inspected
through
the
use
of
a
lamp
and
battery
or
with
a
tester
The
lamp
and
battery
test
can
be
made
Without
disassembl
ing
the
alternator
wh1le
the
tester
should
be
used
when
the
dIodes
are
dIrectly
acceSSIble
1
Positive
Dwde
Test
Connect
the
battery
negative
terrmnal
WIth
the
connector
A
terrmnal
WhIte
and
the
battery
pOSItIve
terminal
With
the
connector
N
terrmnal
yellow
as
shown
m
Figure
43
The
lamp
m
the
circuit
should
hght
@
Reverse
the
connection
as
shown
m
Figure
44
If
the
lamp
does
not
hght
the
pOSItIve
diodes
are
satisfactory
If
the
lamp
does
light
one
or
all
of
the
pOSItIve
dIodes
are
defective
and
must
be
replaced
@
Qg
2
Negative
DIOde
Test
Connect
the
battery
negatIve
termmal
to
the
connector
N
terrmnal
yellow
and
the
battery
pOSItIve
termInal
to
the
connector
E
termmal
black
The
lamp
m
the
CIrcUit
should
lIght
Reverse
the
connectIons
If
the
lamp
does
not
lIght
the
nega1
ve
dIodes
are
satlsfactory
If
the
lamp
does
lIght
one
or
all
I
of
the
negatIve
dIodes
are
defectIve
and
must
be
replaced
To
test
the
indiVIdual
dIodes
With
a
tester
proceed
as
follows
1
There
are
two
kInds
of
diodes
as
shown
m
Figure
45
Check
dlOd
reSIstance
usmg
a
tester
In
both
dIrectIons
as
jl
own
in
Figure
46
f
Current
flow
@
Current
flow
re
ack
flgUre
e
terminal
r
Positive
diode
Negative
diode
@
Page 110 of 252
ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
105
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
REMOVAL
To
remove
the
voltage
regulator
dISconnect
the
6
way
multIple
electrIcal
COlInector
and
the
screws
holdmg
the
regulator
to
the
SIde
wall
lJ
R
ftl5
C
Wt
Str
Ii
DISTRIBUTOR
W
I
vE
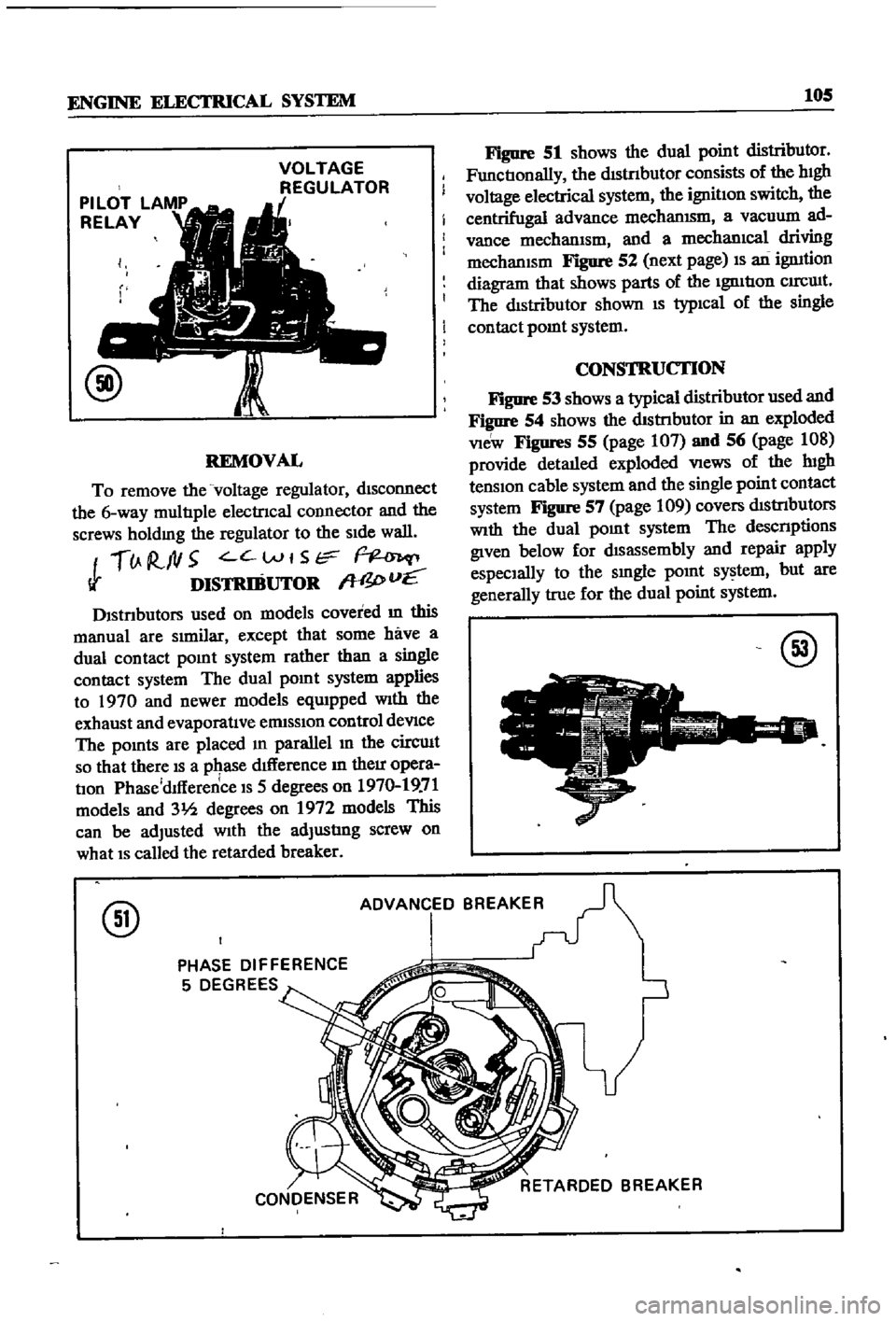
Dlstnbutors
used
on
models
covered
m
this
manual
are
SImilar
except
that
some
have
a
dual
contact
pomt
system
rather
than
a
single
contact
system
The
dual
pomt
system
applies
to
1970
and
newer
models
eqUIpped
With
the
exhaust
and
evaporatIve
ermsslOn
control
deVIce
The
pomts
are
placed
m
parallel
In
the
circuIt
so
that
there
IS
a
pqase
dIfference
In
their
opera
tIon
Phase
dlfference
IS
5
degrees
on
1970
19
71
models
and
31h
degrees
on
1972
models
This
can
be
adjusted
With
the
adjustIng
screw
on
what
IS
called
the
retarded
breaker
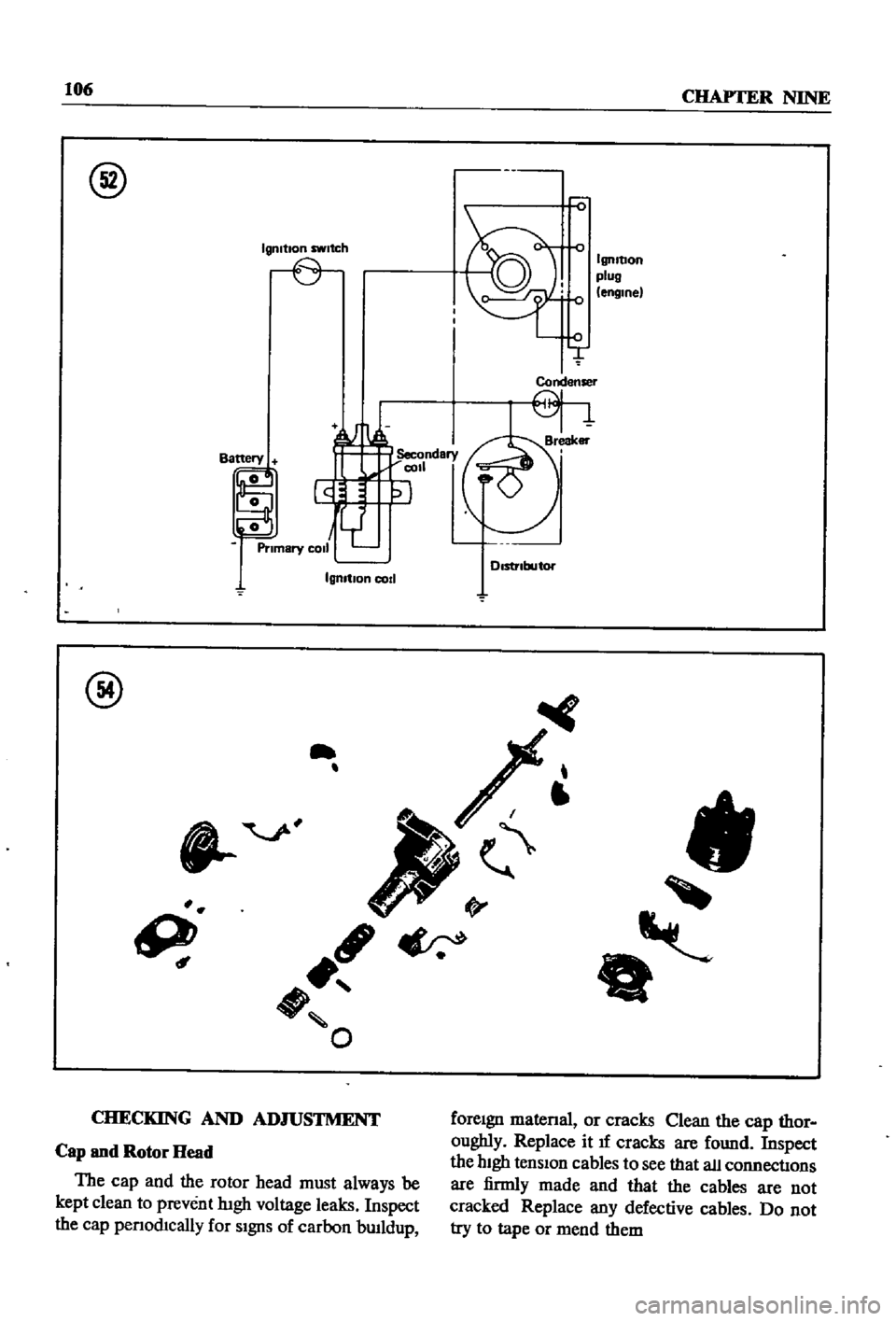
Figure
51
shows
the
dual
point
distributor
FunctIonally
the
dIStnbutor
consists
of
the
hIgh
voltage
electrical
system
the
ignitIon
switch
the
centrifugal
advance
mechanISm
a
vacuum
ad
vance
mechanIsm
and
a
mechanIcal
driving
mechanISm
Figure
52
next
page
IS
an
ignItion
diagram
that
shows
parts
of
the
IgnItIon
CIrCUIt
The
dIstributor
shown
IS
typIcal
of
the
single
contact
pomt
system
CONSTRUCTION
Figure
53
shows
a
typical
distributor
used
and
Figure
54
shows
the
dIStnbutor
in
an
exploded
VIeW
Figures
55
page
107
and
56
page
108
provide
detaIled
exploded
VIews
of
the
lugh
tenSIon
cable
system
and
the
single
point
contact
system
Figure
57
page
109
covers
dIStrIbutors
With
the
dual
pOInt
system
The
descnptions
given
below
for
dIsassembly
and
repair
apply
espeCIally
to
the
smgle
pOInt
system
but
are
generally
true
for
the
dual
point
system
@
@
ADVANCED
BREAKER
PHASE
DIFFERENCE
5
DEGREES
Page 111 of 252
106
CHAPTER
NINE
@
Igmtlon
switch
IgnItion
plug
engine
Condenser
IgnItIon
cod
@
II
9
ft
O
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTMENT
foreIgn
matenal
or
cracks
Qean
the
cap
thor
oughly
Replace
it
If
cracks
are
found
Inspect
the
hIgh
tensIon
cables
to
see
that
all
connectIons
are
firmly
made
and
that
the
cables
are
not
cracked
Replace
any
defective
cables
Do
not
try
to
tape
or
mend
them
Cap
and
Rotor
Head
The
cap
and
the
rotor
head
must
always
be
kept
clean
to
prevent
lugh
voltage
leaks
Inspect
the
cap
penod1cally
for
SIgnS
of
carbon
bwldup
Page 116 of 252
ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
111
@
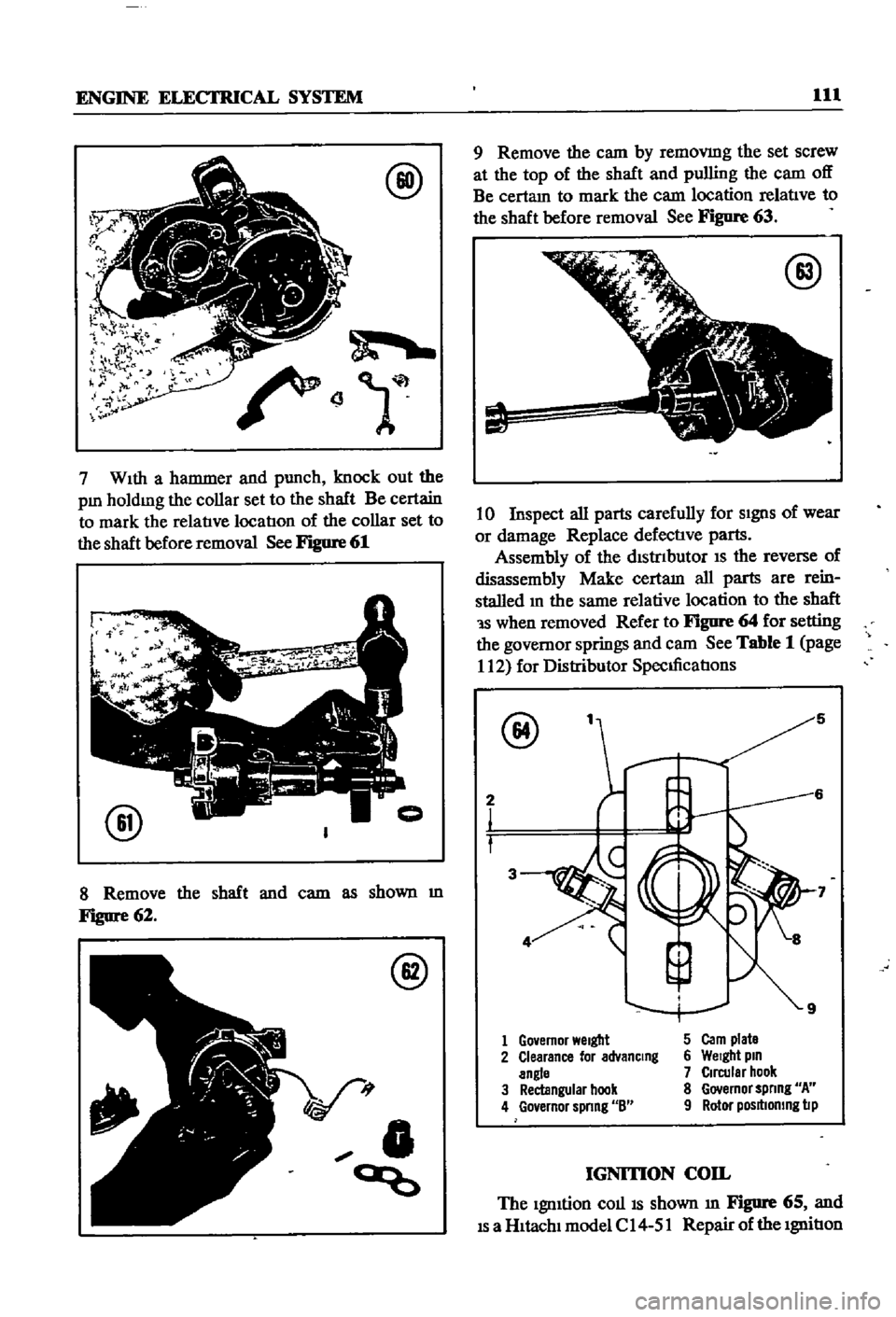
7
WIth
a
hammer
and
punch
knock
out
the
pm
holdmg
the
collar
set
to
the
shaft
Be
certain
to
mark
the
relatIve
locatIon
of
the
collar
set
to
the
shaft
before
removal
See
Figure
61
@
8
Remove
the
shaft
and
cam
as
shown
m
Figure
62
@
V
t
0
ao
9
Remove
the
cam
by
removmg
the
set
screw
at
the
top
of
the
shaft
and
pulling
the
cam
off
Be
certam
to
mark
the
cam
location
relatIve
to
the
shaft
before
removal
See
Figure
63
@
10
Inspect
all
parts
carefully
for
SIgnS
of
wear
or
damage
Replace
defectIve
parts
Assembly
of
the
dIStrIbutor
IS
the
reverse
of
disassembly
Make
certam
all
parts
are
rein
stalled
m
the
same
relative
location
to
the
shaft
1S
when
removed
Refer
to
Figure
64
for
setting
the
governor
springs
and
cam
See
Table
1
page
112
for
Distributor
SpecIficatIons
@
5
2
3
1
Go
emor
Welgbt
5
Carn
plate
2
Clearance
lor
advanCing
6
Welgbt
pin
angle
7
Circular
hook
3
Rectangular
hook
8
Governor
spnng
A
4
Go
ernor
spnng
8
9
Rotor
posltlomng
lip
IGNITION
COIL
The
IgnItion
COllIS
shown
m
Figure
65
and
IS
a
HItachI
model
C
14
51
Repair
of
the
IgnitIon
Page 118 of 252

ENGINE
ELECI
RICAL
SYSTEM
113
i
Normal
plug
appearance
noted
by
the
brown
to
graYlsll
lan
depOSits
and
slight
eleclrode
wear
This
plug
indicates
the
correct
plug
heal
range
and
proper
air
fuel
ratio
jI
Jo
t
Ql
i
Carbon
fouhng
distinguished
by
dry
fluffy
black
carbon
depOSits
which
may
be
caused
by
an
over
rich
alr
lue
mixture
excessive
hand
choking
clogged
air
filler
or
excessl
e
Idling
t
I
j
if
r
l
1
tfc
ji
0
1
fouling
indicated
by
wet
o
ly
depOSits
caused
by
011
pumping
past
worn
rings
or
down
the
Intake
valve
gUIdes
A
hotter
plug
temporanly
reduces
011
depOSits
but
a
plug
that
IS
too
hot
leads
to
pre
Ignition
end
possible
engine
damage
@
Red
brown
yellow
and
white
coatings
caused
by
luel
and
011
addltl
es
These
depOSits
are
not
harm
ful
If
they
remain
In
a
powdery
lorm
pr
11
L
J
J
S
C
ShinY
yellow
glaze
on
Insulalor
cone
IS
caused
when
the
powdery
depOSits
from
fuel
and
011
addltl
es
melt
Melting
occurs
during
hard
acceleration
alter
prolonged
Idling
This
glaze
conducts
electnclty
and
shorts
out
the
plug
e
1
A
I
A
I
7
Overheated
plug
indIcated
by
burned
or
blistered
Insulator
tiP
and
badly
worn
electrodes
ThiS
condl
J
tlon
may
be
caused
by
pre
Ignition
cooling
system
defects
lean
alr
luel
ratiOS
low
octane
luel
or
o
er
advanced
Ignition
timing
Spark
plUI
condition
photos
courtesy
of
AC
SPIr1l
Plug
Olv
s
on
Gene
MolDrs
Corporlllon