1967 CHEVROLET CAMARO ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 333 of 659

ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-8
1
FIELD RELAY^I^p2
"LATCH"
^PFN?^
"P1
TERMINAL
JyJvJCTl^
NO. 2 TERMINAD^5^^^«
NO.
3 TERMINAL ^S5«£
NO.
4 TERMINAL ^^^
m
# / VOLTAGE
¥ REGULATOR
1
ACCESS PLUG TO
VOLTAGE ADJUSTMENT
No 4 TERMINAL
Double Contact
Fig.
2c—Voltage Regulator Assemblies
Transistor
regulator to handle the higher field current and enables it
to absorb the increased inductive voltages of the field
coil with satisfactory contact point life.
The double-contact regulator assembly (fig. 2c) con-
sists of a double contact voltage regulator unit and a field
relay unit. This unit uses two sets of contact points on
the voltage regulator unit to obtain desired field excita-
tion under variable conditions. Internal circuit wiring
diagrams of the double contact regulator are shown in
Figures 3c and 4c.
The transistor regulator (fig. 2c) is an assembly com-
posed principally of transistors, diodes, resistors, a
capacitor, and a thermistor to form a completely static
voltage regulating unit in combination with a conventional
vibrating type field relay.
The transistor is an electrical device which limits the
generator voltage to a preset value by controlling the
generator field current. The diodes, capacitor and re-
sistors act together to aid the transistors in controlling
the generator voltage. This is the only function that the
regulator performs in the charging circuit. The
thermistor provides a temperature-compensated voltage
setting. Wiring diagrams of the transistor regulator are
shown in Figures 3c and 4c.
The voltage at which the generator operates is deter-
mined by the regulator adjustment. The regulator voltage
setting can be adjusted externally by removing a pipe plug
in the cover (fig. 2c) and turning the adjusting arm inside
the regulator. This procedure is explained in the followr
ing section, and permits regulator adjustments without
removing the cover.
FUSIBLE
DOUBLE CONTACT
FUSIBLE LINK-^
JUNCTION HORN
BLOCK RELAY
RESISTOR
Q FIELD Q>
DELCOTRON TR-
TRANSISTOR
FUSIBLE LINK-
Fig.
3c-Circuity - Voltage Regulator Assemblies (Except Corvette)
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 334 of 659

ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-9
63 AMP 1
MODELS ONLY'
BATTERY FUSIBLE
LINK
HORN
FUSIBLE LINK'
TRANSISTOR
FUSIBLE LINK'
Fig.
4c— Circuitry - Voltage Regulator Assemblies (Corvette)
Engine compartment wiring harness incorporates sev-
eral fusible links. Each link is identified with its gage
size. A fusible link is a length of special wire (normally
four wire gages smaller than the circuit it is protecting)
used in wiring circuits that are not normally fused, such
as the ignition circuit. The same size wire with a hypalon
insulation must be used when replacing a fusible link.
The links are:
1.
The pigtail lead at the battery positive cable (except
Corvette) is a 14 gage, brown fusible link protecting
the 10 gage battery charging circuit. This wire is an
integral part of the battery cable assembly and serv-
icing requires replacing the complete battery cable
assembly. On Corvette models this link is installed
as a molded splice at the solenoid "Bat" terminal
and servicing requires splicing in a new link.
2.
A 16 gage black fusible link is located at the horn
4.
relay to protect all unfused wiring of 12 gage or
larger. It is installed as a molded splice and serv-
icing requires splicing in a new link.
The generator warning light and field circuitry (16
gage wire) is protected by a fusible link (20 gage
orange wire) used in the "battery feed to voltage
regulator #3 terminal" wire. The link is installed as
a molded splice in the generator and forward lamp
harness and is serviced by splicing in a new 20 gage
wire as required.
The ammeter circuit on all models is protected by
two orange, 20 gage wire fusible links installed as
molded splices in the circuit at the junction block or
the solenoid "Bat" terminal (Corvette only) and at
the horn relay. Each link is serviced by splicing in a
new 20 gage wire as required.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
At regular intervals, inspect the terminals for cor-
rosion an4 loose connections, and the wiring for frayed
insulation. Check mounting bolts for tightness. Check the
drive belt for alignment, proper tension and wear. Be-
cause of the higher inertia and load capacity of the rotor
used in A.C. generators, PROPER BELT TENSION is
more critical than on D.C. generators.
Since the Delcotron and its companion regulator are
designed for use on negative polarity systems only, the
following precautions must be observed. Failure to ob-
serve these precautions may result in serious damage to
the charging system.
1.
When installing a battery, always make absolutely
sure the ground polarity of the battery, generator and
regulator is the same.
2.
When connecting a booster battery, make certain to
connect the correct battery terminals together.
3.
When connecting a charger to the battery, connect the
correct charger leads to the battery
%
terminals.
4.
Never operate the generator on an uncontrolled open
TO SOLENOID
BAT ACC RES. WIRE
Fig.
5c—Typical Wiring Diagram Showing Lead Connections
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 335 of 659

ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-10
circuit. Make absolutely certain all connections in
the circuit are secure.
5.
Do not short across or ground any of the terminals
on the generator or regulator.
6. Do not attempt to polarize the generator.
7.
Do not disconnect lead at generator without first dis-
connecting battery ground cable.
Trouble in the A.C. charging system will usually be
indicated by one or more of the following conditions:
1.
Faulty indicator lamp or ammeter operation.
2.
An undercharged battery (usually evidenced by slow
cranking speeds).
3.
An overcharged battery (usually evidenced by exces-
sive battery water usage).
4.
Excessive generator noise or vibration.
Described below are a series of on-the-vehicle quick
checks which are designed to assist the service tech-
nician in locating troubles within the various components
of the engine electrical system. Additional checks, ad-
justments and overhaul procedures of these components
are also described in the "Charging Systems—Service
Operations Section" and should be referred to as
necessary.
STATIC CHECKS
Before making any electrical checks, perform the fol-
lowing static checks:
1.
Check for loose fan belt.
2.
Check for defective battery. (Refer to Battery).
3.
Inspect all connections, including the slip-on con-
nectors at the regulator and Delcotron.
NOTE: Do not short field to ground to check if
generator is charging since this will seriously
damage the charging system.
SYSTEM CONDITION TEST
This test is used .to indicate the overall condition of the
charging system (both good and defective) and to isolate
the malfunctioning unit if the system is defective.
NOTE: On Corvette models difficulty may be
encountered -when attempting to make the re-
quired test connections at the voltage regulator.
It is advisable to remove the regulator from its
mounting location to perform the necessary con-
nections at the regulator for the following tests
but make sure unit is grounded.
1.
With ignition off, perform the prescribed Static
Checks outlined in this section. Then set hand brake
and shift transmission
into
neutral.
2.
Connect a voltmeter from junction block relay to
ground at regulator base.
CAUTION: Be sure meter clip does not touch a
resistor or terminal extension under regulator,
3.
Connect a tachometer on engine.
4.
Models equipped with Indicator Lamp: Turn ignition
switch on "ON" position and check indicator lamp.
If lamp fails to glow, perform appropriate tests and
corrections (Indicator Lamp Circuit Tests) before
continuing.
Models equipped with Ammeter: Turn ignition
switch to "ACC" with an accessory on and check
ammeter. If ammeter fails to read discharge, check
ammeter circuit before continuing.
5.
Models equipped with Indicator Lamp: If lamp glows,
start the engine and run' it at 1500 rpm or above.
Check indicator lamp. If lamp fails to go out, per-
form appropriate test and corrections (Indicator
Lamp Circuit Test) before continuing.
Models equipped with Ammeter: If ammeter reads
discharge, start the engine and observe ammeter. If
meter fails to move toward charge (from original
position), perform appropriate test and corrections
(Field Circuit Tests) before continuing.
NOTE: At this point a field circuit has been
established and any other problem will lie in
generator or regulator.
6. Turn on high-beam headlights and heater blower
motor to high speed, run engine at or above 1500
rpm (for a few minutes, if necessary) and read the
voltage on meter.
AIR GAP
ADJUSTING NUT
ONLY
ADJUSTING SCREW
(Turn To Adjust
Voltage Setting)
Fig.
6c—Adjusting Voltage Setting
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 350 of 659

ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-25
1.
Remove the rotor.
2.
Remove both weight springs and advance weights.
3.
Remove roll pin retaining driven gear to distributor
shaft, slide the gear and spacers from the shaft.
Remove tachometer drive gear on Corvette models.
4.
Before sliding the distributor shaft from the hous-
ing, check for and remove any burrs on the shaft.
This will prevent damage to the seals and bushing
still positioned in the housing.
5. Slide the distributor mainshaft and cam-weight base
assembly from the housing.
6. Remove vacuum advance mechanism retaining
screws, remove the vacuum advance assembly.
7. Remove the spring retainer, remove the breaker
plate assembly from the distributor housing. Re-
move the contact point and condenser from the
breaker plate. Remove the felt washer and plastic
seal located beneath the breaker plate.
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
1.
Wash all parts in cleaning solvent except cap, rotor,
condenser, breaker plate assembly and vacuum con-
trol unit. Degreasing compounds may damage insula-
tion of these parts or saturate the lubricating felt in
the case of the breaker plate assembly.
2.
Inspect the breaker plate assembly for damage or
wear and replace if necessary.
3.
Inspect the shaft for wear and check its fit in the
bushings in the distributor body. If the shaft or bush-
ings are worn, the parts should be replaced.
4.
Mount the shaft in "V" blocks and check the shaft
alignment with a dial guage. The run-out should not
exceed .002".
5. Inspect the advance weights for wear or burrs and
free fit on their pivot pins.
6. Inspect the cam for wear or roughness. Then check
its fit on the end of the shaft. It should be absolutely
free without any roughness.
7. Inspect
the •
condition of the distributor points. Dirty
points should be cleaned and badly pitted points
should be replaced. (See Distributor Contact Points.)
8. Test the condenser for series resistance, micro-
farad capacity (.18 to .23) and leakage or breakdown,
following the instructions given by the manufacturer
of the test equipment used.
9. Inspect the distributor cap and sparkplug wires for
damage and replace if necessary.
ASSEMBLY
Four and Six Cylinder Engine
Refer to Figure 12i for Exploded View of Distributor.
1.
Replace cam assembly to mainshaft.
NOTE:
Lubricate top end of shaft with Delco
cam and ball bearing grease or equivalent prior
to replacing.
2.
Install governor weights on their pivot pins, replace
weight springs. Install weight cover and stop plate.
3.
Lubricate mainshaft and install it in distributor
housing.
4.
Install distributor driven gear to mainshaft and in-
sert attaching roll pin. Check to see that shaft turns
freely.
5. Install breaker plate assembly in the distributor body
and attach retaining screws.
6. Attach condenser and contact point set in proper lo-
cation with appropriate attaching screws.
NOTE:
Contact point set pilot must engage
matching hole in breaker plate. Connect primary
and condenser leads to contact set quick-
disconnect terminal.
7. Attach vacuum control assembly to distributor
housing.
8. Check and adjust contact point opening and align-
ment (See setting and alignment of points.)
9. Check breaker lever spring tension which should
be.
19-23 ounces. (See contact point replacement.)
V-8 Assembly-(Fig. 13i)
1.
Fill housing lubricating cavity with proper compound,
press in new plastic seal and install felt washer.
2.
Replace the vacuum advance unit, install the breaker
plate in housing and install the spring retainer on
the upper bushing.
3.
Lubricate and slide weight cam over mainshaft and
install weights and spring (fig. 14i).
4.
Insert mainshaft into housing, indexing it with drive
gear and washers. Install tachometer drive gear on
Corvette models.
5. Slide distributor drive gear shims and gear over
shaft and install new pin. Tap new pin through gear
and mainshaft. Check shaft for free rotation.
NOTE:
Mainshaft end clearance should be
.002"-.007". Add or remove shims as necessary.
6. Install contact point set and condenser to breaker
plate. Connect leads as shown in Figure 6i.
NOTE:
Contact point spring tension is factory-
set above specifications to assure ease of final
adjustment. Correct tension is 19-23 oz.
7. Install rotor to cam assembly, indexing round and
square pilot holes.
Flg.
Hi-Advance Weights Installed
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE
Page 391 of 659

CLUTCH AND TRANSMISSIONS 7-32
21.
Remove transmission output shaft slip yoke and in-
sert a plastic shipping plug in end of extension to
prevent spillage of transmission fluid.
NOTE:
The yoke is removed to avoid tearing
the heat reflecting pad on the underbbdy, when
the transmission is being removed.
22.
Remove bright metal ignition shielding from dis-
tributor area.
23.
Remove the transmission dip stick and tube
assembly.
24.
Disconnect transmission vacuum modulator line at
distributor advance line tee.
25.
Position transmission hoist under transmission and
attach safety chain to transmission.
26.
Remove transmission converter housing-to-engine
attaching foolts and slide transmission rearward.
NOTE:
Observe converter when moving trans-
mission rearward. If converter does not move
with the transmission, pry it free of flywheel
before proceeding.
27.
Install converter retaining strap.
28.
Lower and remove transmission from vehicle by
tilting the front down and to the right while inter-
mittently lowering the transmission to facilitate its
• removal.
29.
Reinstall transmission assembly by performing the
above steps in reverse order.
Bolt Torques
Transmission Case to Flywheel
Housing Bolts 35 ft. lbs.
Converter to Flywheel Bolts. . , . . 35 ft. lbs.
OTHER SERVICE OPERATIONS
Although certain operations, such as oil pan or gasket
replacement, valve body, governor, filler pipe "O" ring,
speedometer drive gear, case extension "0" ring and
rear oil seal, vacuum modulator, and servo cover or
gasket service may be performed from underneath the
vehicle without removing the Powerglide; their service
procedure is covered in the Passenger Overhaul Manual
and is not repeated here. Refer to the- Powerglide Sec-
tion of the Passenger Overhaul Manual for all other
service operations not covered here.
DIAGNOSIS
Proper operation of the Powerglide transmission may
be affected by a number of factors, all of which must be
considered when trouble in the unit is diagnosed.
Proper trouble diagnosis can only be accomplished
when performed in a thorough step by step procedure.
The following procedure has been devised and tested and
is recommended for all trouble diagnosis complaints and
if the service man will follow this checking procedure,
accurate and dependable diagnosis may be accomplished.
This will result in a savings of time, not only to the
service man, but to the customer as well.
WARMING UP TRANSMISSION
Before attempting to check and/or correct any com-
plaints on the Powerglide transmission it is absolutely
essential that the oil level be checked and corrected if
necessary. An oil level which is either too high or too
low can be the cause of a number of abnormal conditions
from excessive noise to slippage in all ranges.
It must be remembered that cold oil will slow up the
action of the hydraulic controls in the transmission. For
this reason a trouble or oil leak diagnosis should not be
attempted until the transmission has been warmed up by
either of the following procedures:
Shop Warm Up
1.
Connect tachometer to engine.
2.
Set parking brake tight and start engine.
3.
Place selector light in
"D"
(drive) range.
4.
Adjust carburetor idle speed adjusting screw to run
engine at approximately 750 rpm and operate in this
manner for two minutes. At the end of two minutes
of operation, the transmission will be sufficiently
warmed up for diagnosis purposes.
NOTE:
At this point, readjust the engine idle
speed to 450-475 rpm in
"D"
range.
Road Warm Up
Drive the car approximately 5 miles with frequent
starts and stops.
NOTE:
At this point, make sure the engine idle
speed is set to 450-475 rpm in
"D"
range.
CHECKING FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
After transmission has been warmed up, check the
fluid level with the engine idling, parking brake set and
control lever in "N" (neutral). If the fluid level is low,
add fluid to bring level up to the full mark on gauge rod,
CAUTION: If fluid level is too high, fluid may
be aerated by the planet carrier. Aerated fluid
will cause turbulence in the converter which will
result in lost power, lower stall speed and lower
pressures in control circuits. Lower fluid level
to full mark, then shut off engine to allow air
bubbles to work out of fluid.
When checking oil level, aburned smell and discolora-
tion indicate burned clutches or bands and the transmis-
sion will have to be removed.
MANUAL LINKAGE
Manual linkage adjustment and the associated neutral
safety switch are important from a safety standpoint.
The neutral safety switch should be adjusted so that the
engine will start in the Park and Neutral positions only.
With the selector lever in the Park position, the park-
ing pawl should freely engage and prevent the vehicle
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 408 of 659

FUEL TANK AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS 8-2
COMPONENT PART REPLACEMENT
FUEL TANK
Draining Tank
The absence of a drain plug in the gas tanks makes it
necessary to siphon fuel from the tank when draining is
needed. The following procedure is recommended.
1.
Obtain approximately 10 feet of 3/8" I.D. hose and
cut a flat-type slit 18" from one end. Make this cut
on the hose in the direction "toward the shorter end
(See Figure 2).
2.
Insert a small pipe nipple (slightly larger O.D. than
the hose I.D.) into the opposite end of hose.
3.
Insert the nipple end of the siphon hose into the fuel
tank filler neck with the natural curl of the hose
pointing down. Insert until the hose is heard to strike
bottom of the tank.
4.
With the opposite end of the hose in a suitable con-
taner insert an air hose in downward direction in the
flap-type slit and trigger the flow of fuel.
FUEL FLOW
-If*
APPROX.-1 >SUT «<>«
AS SHOWN
10 FEET APPROX.-
Fig. 2—Siphon Construction
FWD
V-8
VIEW B
Fig. 3-Fuel Lines
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 414 of 659

FUEL TANK AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS
8-8
CHEVELLE
FUEL TANKS
INDEX
Page
General Description.
g.g
Component Part Replacement
8-8
Fuel Tanks
. 8-8
Fuel Lines
8-8
Metering Units (Gauge, Sending Unit)
Fuel Tank Filler Neck Caps.
. .
Fuel Tank Vent Lines
Page
8-8
8-8
8-9
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
All models
use a 20
gallon capacity (approx.) fuel tank
mounted between
the
frame rails behind
the
rear axle.
The fuel tanks
are
basically
the
same
for
sedan, 2-seat
station wagon
and
pickup models except
for
filler neck
location
and
venting
(fig. 8).
All fuel tanks
are
vented
to the
atmosphere. Sedan
model tanks have
an
external vent hose and pipe assem-
bly
(fig. 11) and use a
non-vented fuel cap. Station wagon
and pickup model tanks
are
vented through
a
hose
and
vent pipe assembly
to the
filler neck
(fig. 8)
and
use a
vented, anti-surge type
gas cap. The
fuel caps
are two
different designs conforming
to SAE
standards
and are
not interchangeable.
The filler neck assembly
on
sedan models
is a
rear
fill design located behind
the
center
bar of the
bumper.
Station wagon
and
sedan pickup model filler neck assem-
blies
are
located
in
the left rear quarter panel.
The fuel pickup pipe
is
built integrally with
the
tank
gauge, located
at the
top-front center
of
the tank.
A
fine
mesh screen
is
located
at
the bottom-end
of the
fuel pick-
up pipe
to
prevent
the
entrance
of
foreign material into
the fuel system.
The sedan fuel tanks
are
held
in
place
by
two metal
straps attached individually
to the
underbody
at
each
end.
The straps hinge
at the
forward end and secure
the
tank
at
the
rear with
an
adjustable bolt
and nut
assembly.
The station wagon
and
pickup models have
a
frame
mounted fuel tank secured with straps
to
front and rear
supports.
COMPONENT PART REPLACEMENT
FUEL TANK
Draining Tank
The absence
of a
drain plug
in the gas
tanks makes
it
necessary
to
siphon fuel from
the
tank when draining
is
needed. Refer
to the
recommended draining procedures
previously outlined under Chevrolet Models
in
this
section.
Removal
and
Installation (Sedan Models)
1.
Raise vehicle.
2.
Drain fuel tank.
3.
Disconnect fuel pickup line
and
gauge wires from
tank unit.
4.
Disconnect vent hose from tank.
5. Remove tank support straps and lower tank carefully.
6.
To
install, reverse
the
removal procedure.
Removal
and
Installation
(Station Wagon
and
Pickup)
1.
Follow Steps
1
thru
3
outlined under sedan models.
2.
Remove tank support straps.
3.
Remove frame screw attachments from
the
front
support
(fig. 8).
4.
Guide tank forward
and
remove.
5.
To
install, reverse removal procedure.
FUEL LINES
The fuel lines, extending from fuel tank toiiuelpump,
are routed
on the
underside
of the
underbody along
the
right side
of the
vehicle opposite
the
single exhaust
sys-
tem.
The
fuel lines should occasionally
be
inspected
for
leaks,
kinks,
or
dents.
If
evidence
of
dirt
is
found
in the
carburetor
or
fuel pump
on
disassembly,
the
lines should
be disconnected
and
blown
out.
Check
the
fuel tank
strainer
for
damage
or
omission. Fuel lines
are of 5/16"
diameter tubing with beaded type ends
for
connections
of
hoses.
FUEL PIPE RETAINER
CUP
Removal
and
Installation
If fuel pipes
and
retainer clips
are
removed, Tool
J-7777 should
be
used
to
install
new
retainer clips
(fig.
10).
After removal
of the old
clip from
the
frame, position
the
new
clip
in the
location
of the old
clip. Index
the
"blind rivet"
and
press hard (hand pressure should
do)
to expand rivet.
GAUGE UNIT
AND
FUEL STRAINER
Removal
and
Installation
(Fig. 11)
1.
Drain tank
to a
level below
the
unit.
2.
Disconnect fuel pickup line
and
gauge unit wire.
3.
Use
special Tool J-8950
to
remove
cam
lock.
Re-
move unit
and
rubber gasket.
CAUTION: Carefully remove unit
so as not to
damage screen
on the end of
the pipe.
4.
Clean screen
by
blowing
out
with compressed
air.
5. Reverse procedure
to
install.
FUEL TANK FILLER NECK CAPS
The fuel tank filler neck caps
are
non-vented with
an
anti-surge feature. Station wagons have vented caps.
(Refer
to
"Fuel Tank Vent Lines").
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 419 of 659
FUEL TANK
AND
EXHAUST SYSTEMS
8-13
CHEVY II
FUEL TANKS
INDEX
Page
Page
General Description.
8-13
Component Part Replacement
8-13
Fuel Tanks
8-13
Fuel Lines
8-14
Metering Units (Gauge Sending Unit)
8-13
Fuel Tank Filler- Neck Caps.
. . 8-14
Fuel Tank Vent Lines .......
8-14
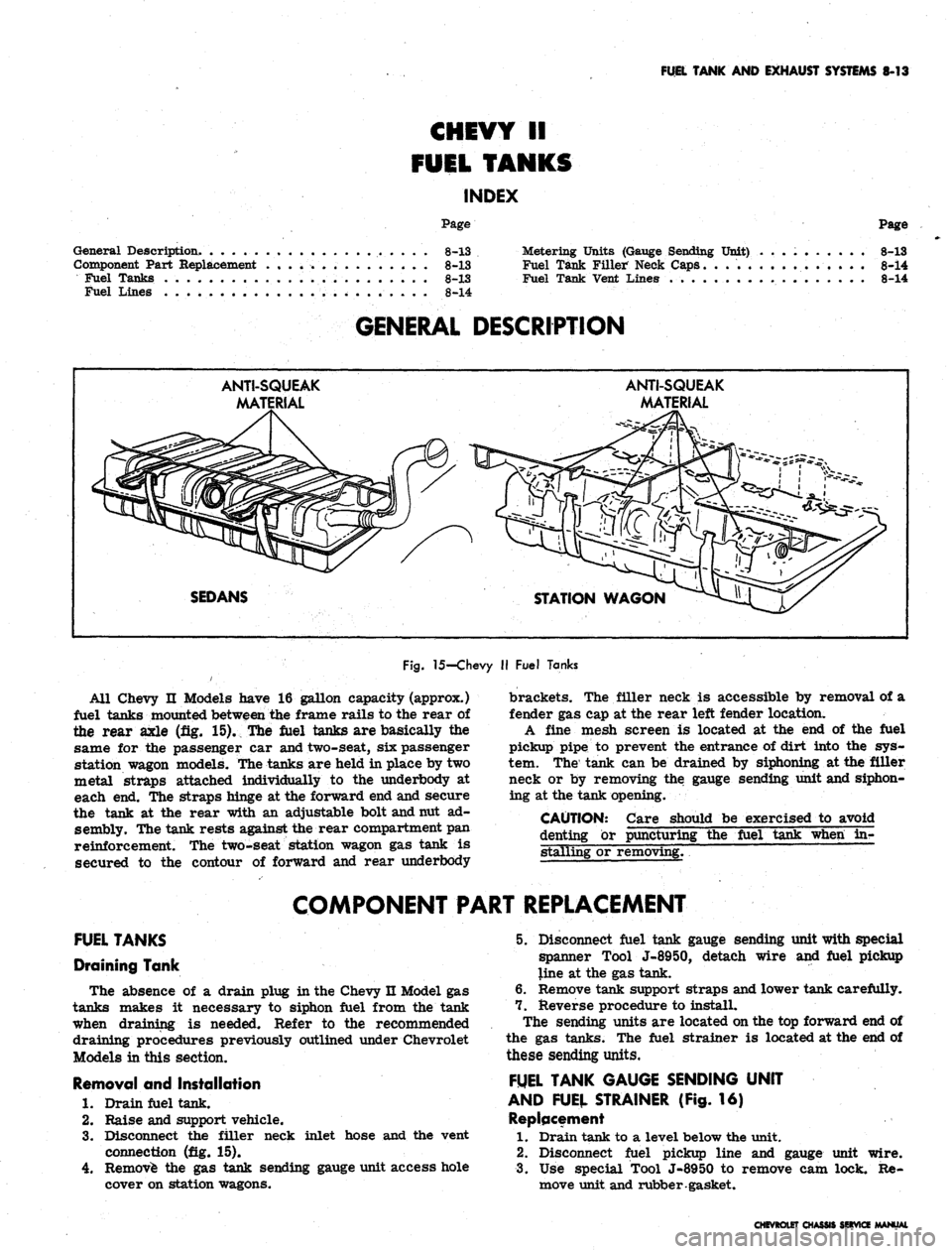
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
ANTI-SQUEAK
MA'
ANTI-SQUEAK
MATERIAL
SEDANS
STATION WAGON
Fig.
15-Chevy
II
Fuel Tanks
All Chevy
II
Models have
16
gallon capacity (approx.)
fuel tanks mounted between
the
frame rails
to the
rear
of
the rear axle
(fig. 15). The
fuel tanks
are
basically
the
same
for the
passenger
car
and two-seat,
six
passenger
station wagon models. The tanks
are
held
in
place
by two
metal straps attached individually
to the
underbody
at
each
end. The
straps hinge
at the
forward
end
and secure
the tank
at the
rear with
an
adjustable bolt and nut
ad-
sembly. The tank rests against the rear compartment
pan
reinforcement.
The
two-seat station wagon
gas
tank
is
secured
to the
contour
of
forward
and
rear underbody
brackets.
The
filler neck
is
accessible
by
removal
of a
fender
gas cap at the
rear left fender location.
A fine mesh screen
is
located
at the end of the
fuel
pickup pipe
to
prevent
the
entrance
of
dirt into
the sys-
tem.
The
tank
can be
drained
by
siphoning
at the
filler
neck
or by
removing
the
gauge sending unit and siphon-
ing
at the
tank opening.
CAUTION: Care should
be
exercised
to
avoid
denting
or
puncturing
the
fuel tank when
in-
stalling
or
removing.
~
COMPONENT PART REPLACEMENT
FUEL TANKS
Draining Tank
The absence
of a
drain plug
in
the Chevy
n
Model
gas
tanks makes
it
necessary
to
siphon fuel from
the
tank
when draining
is
needed. Refer
to the
recommended
draining procedures previously outlined under Chevrolet
Models
in
this section.
Removal
and
Installation
1.
Drain fuel tank.
2.
Raise
and
support vehicle.
3.
Disconnect
the
filler neck inlet hose
and the
vent
connection
(fig. 15).
4.
Remove
the gas
tank sending gauge unit access hole
cover
on
station wagons.
5. Disconnect fuel tank gauge sending unit with special
spanner Tool J-8950, detach wire
and
fuel pickup
line
at the gas
tank.
6. Remove tank support straps and lower tank carefully.
7. Reverse procedure
to
install.
The sending units
are
located on
the top
forward
end of
the
gas
tanks.
The
fuel strainer
is
located
at the end of
these sending units.
FUEL TANK GAUGE SENDING UNIT
AND FUEL STRAINER
(Fig. 16)
Replacement
1.
Drain tank
to a
level below
the
unit.
2.
Disconnect fuel pickup line
and
gauge unit wire.
3.
Use
special Tool J-8950
to
remove
cam
lock.
Re-
move unit and rubber gasket.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL