1953 JEEP DJ gas type
[x] Cancel search: gas typePage 64 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
FIG.
D-34—GAUGING
CRANKSHAFT
END
PLAY
FIG.
D-35
—
DRILLING FLYWHEEL
D-84.
Install
Crankshaft Timing
Gear
Install
the woodruff key in the longer of the two keyways on the front end of the crankshaft.
Install
the crankshaft timing gear on the front end of the crankshaft with the timing
mark
facing out, away from the cylinder block. Align the
keyway in the gear with the woodruff key and then
drive
or press the gear
onto
the crankshaft firmly against the thrust washer.
D-85.
Install
Crankshaft
Rear
Bearing Seal
When
installing the crankshaft
rear
bearing seal
around
the crankshaft, apply a thin coat of light cup grease to both halves of the seal except for the
ends which are already treated with sealing com pound. When installing the
rear
main bearing cap
in
the crankcase, place a small amount of plastic- type gasket cement on both sides and face of the
cap to prevent oil leakage. Insert the rubber
packings shown in
Fig. D-3
7
into the
holes
between
the bearing cap and the case. Do not trim
these
packings. The packings are of a predetermined
length that
will
cause them to protrude approxi mately 34* [6 mm.] from the case. When the oil
pan
is installed, it
will
force them tightly into the
holes
and effectively seal any opening
between
the bearing cap and the crankcase.
D-86.
Install
Front
End Plate
Assemble the gasket to the front end plate making
certain
that it is positioned properly down to the
bottom
of the crankcase.
Install
the front end plate
on the cylinder block and tighten in place.
D-87.
Install
Flywheel
Be
sure the crankshaft flange and flywheel mating
surfaces are clean to permit proper flywheel align ment. With the crankshaft in the cylinder block,
FIG.
D-36—
REAMING FLYWHEEL
FIG.
D-37—REAR
BEARING
CAP
PACKING
64
Page 69 of 376

'Jeep9
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
h.
Check
ignition (distributor) timing; reset if
necessary.
i.
Check
carburetor
adjustments; reset if necessary,
j.
With
engine
fully warmed up, tighten cylinder
head and manifold
bolts
and nuts to specified
torque.
Check
cylinder head gaskets and
bolts
for
air
or coolant leaks.
Note:
Tightness of cylinder head
bolts
should be
checked and corrected after 500 to 600 miles [800
a
960 km.] of normal operation.
k.
Check
fan belt tension; adjust if necessary.
I.
Check
for and correct any oil leak, fuel leak or
coolant leak.
D-107.
VALVE
ADJUSTMENT
Proper
valve adjustment is important to prevent
burning
of valves and poor
engine
performance.
This
adjustment consists of obtaining a specified
lash
in the valve mechanism. The exhaust valve
tappets and the intake valve rocker arms should be adjusted to the proper clearance with the
engine
cold (at room temperature). Valve clearance can
be properly adjusted only when the tappet is on the
heel or low portion of the cam.
INTAKE
OPENS
9°
BTC?
FIG.
D-43-
10270
-VALVE
TIMING
D-108. Valve Adjustment Procedure
The
exhaust valve tappets are adjusted by turning
the adjusting screw in or out of the tappet as neces
sary
to obtain the proper clearance. Where special
wrenches can be obtained, they should be used to facilitate the adjustment. The proper clearance is .016" [0,406 mm.]
between
the end of the adjusting
screw and the
bottom
of the exhaust valve.
Crank
the
engine
over to
close
a valve and check
the clearance with a feeler
gauge.
To adjust, hold
the tappet with one wrench and
turn
the adjusting
screw,
with the other.
Check
and adjust each of
the tappets in proper sequence.
Adjust
each intake valve by adjusting the rocker
arm
screw at the push rod to obtain .018" [0,457 mm.] clearance
between
the rocker arm and the
valve stem with tappet on the heel of the cam.
D-109.
Check
Valve
Timing
To
check the valve timing, carefully set the intake
valve rocker arm adjustment for No. 1 cylinder to .026"
[0,6604
mm.]
between
the rocker arm and the
valve stem. Rotate the crankshaft clockwise until
the piston in No. 1 cylinder is ready for the intake stroke. The intake valve
opens
9° before top center
(BTC).
Note
the distance
between
the
"TC"
and
"5°"
marks on the indicator on the timing gear
cover and estimate the 9° before top center position.
See
Fig.
D-43.
With
the crankshaft in this position, timing is correct if the rocker arm is just tight
against the intake valve stem. Do not overlook resetting the rocker arm adjustment to the correct
running
clearance.
D-110. Positive
Crankcase
Ventilation
Be
sure there are no air leaks at the tube connec
tions
between
the air cleaner and the oil filler tube,
and
that the oil filler tube cap gasket is in
good
condition. Always keep the cap locked securely in
place. When tuning the
engine
or grinding valves, remove the control valve and clean it thoroughly.
If
the valve is blocked with carbon, the ventilating
system
will
not operate and, should the valve
fail
to seat, it
will
be impossible to make the
engine
idle satisfactorily. Refer to Par. C-6 for servicing.
D-111. Oil
Filter
The
engine
is equipped with a throw-away type
oil
filter.
This
oil filter must be serviced periodi
cally
as outlined in the
Lubrication
Section. 69
Page 76 of 376
Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
DM.
GENERAL
This
section describes service and repair of the
Dauntless V-6 engine. The
engine
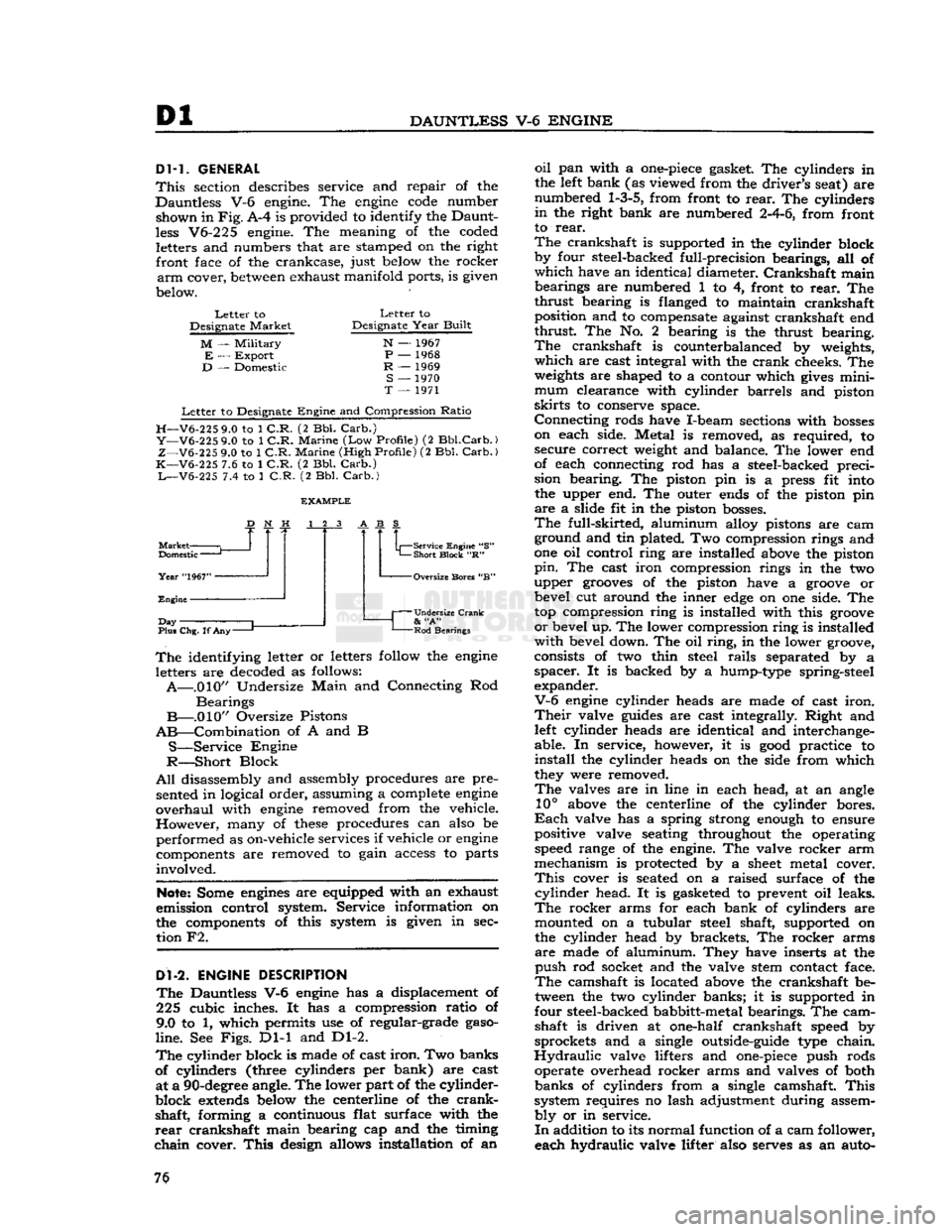
code
number shown in
Fig.
A-4 is provided to identify the Daunt
less
V6-225 engine. The meaning of the coded letters and numbers that are stamped on the right front face of the crankcase, just below the rocker
arm
cover,
between
exhaust manifold ports, is given
below.
Letter
to
Designate
Market
M
—
Military
E
—
Export
D
— Domestic
Letter
to
Designate
Year
Built
N
— 1967
P
— 1968
R
— 1969
S
— 1970
T
— 1971
Letter
to Designate
Engine
and Compression
Ratio
H—V6-225
9.0 to 1
C.R.
(2 Bbl.
Carb.)
Y—V6-225
9.0 to 1
C.R.
Marine
(Low
Profile)
(2
Bbl.Carb.)
Z—V6-225
9.0 to 1
C.R.
Marine
(High
Profile)
(2 Bbl.
Carb.)
K—V6-225
7.6 to 1
C.R.
(2 Bbl.
Carb.)
L—V6-225
7.4 to 1
C.R.
(2 Bbl.
Carb.)
Market
Domestic
—
Year
"1967"
Engine
J
Day
Plus Chg. If
Any-
Service Engine "S"
Short
Block
"R" -Oversize Bores "B"
Undersize Crank
&
"A"
Rod
Bearings
The
identifying letter or letters follow the
engine
letters are decoded as follows:
A—.010"
Undersize
Main
and Connecting Rod
Bearings
B—.010"
Oversize Pistons
AB—Combination
of A and B
S—Service
Engine
R—Short
Block
All
disassembly and assembly procedures are pre sented in logical order, assuming a complete
engine
overhaul
with
engine
removed from the vehicle.
However,
many of
these
procedures can also be
performed as on-vehicle services if vehicle or
engine
components are removed to gain access to parts
involved.
Note:
Some
engines
are equipped with an exhaust
emission control system. Service information on
the components of this system is given in sec tion F2.
Dl-2.
ENGINE
DESCRIPTION
The
Dauntless V-6
engine
has a displacement of
225 cubic inches. It has a compression ratio of
9.0 to 1, which permits use of regular-grade
gaso
line.
See
Figs.
Dl-1 and Dl-2.
The
cylinder block is made of cast
iron.
Two banks
of cylinders (three cylinders per bank) are cast at a
90-degree
angle. The lower part of the cylinder-
block
extends
below the centerline of the
crank
shaft, forming a continuous flat surface with the
rear
crankshaft main bearing cap and the timing
chain
cover.
This
design allows installation of an
oil
pan with a
one-piece
gasket. The cylinders in
the left bank (as viewed from the driver's seat) are
numbered
1-3-5,
from front to
rear.
The cylinders
in
the right bank are numbered
2-4-6,
from front
to
rear.
The
crankshaft is supported in the cylinder block
by four steel-backed full-precision bearings, all of
which
have an identical diameter.
Crankshaft
main bearings are numbered 1 to 4, front to
rear.
The
thrust
bearing is flanged to maintain crankshaft position and to compensate against crankshaft end
thrust
The No. 2 bearing is the thrust bearing.
The
crankshaft is counterbalanced by weights,
which
are cast integral with the
crank
cheeks. The
weights
are shaped to a contour which
gives
mini
mum
clearance with cylinder barrels and piston
skirts
to conserve space.
Connecting
rods have I-beam sections with
bosses
on each side. Metal is removed, as required, to secure correct weight and balance. The lower end
of each connecting rod has a steel-backed preci
sion bearing. The piston pin is a press fit into the upper end. The outer ends of the piston pin
are
a slide fit in the piston
bosses.
The
full-skirted, aluminum alloy pistons are cam ground and tin plated. Two compression rings and
one oil control ring are installed above the piston
pin.
The cast iron compression rings in the two
upper
grooves
of the piston have a
groove
or bevel cut around the inner
edge
on one side. The
top compression ring is installed with this
groove
or
bevel up. The lower compression ring is installed
with
bevel down. The oil
ring,
in the lower groove,
consists of two thin steel
rails
separated by a
spacer.
It is backed by a hump-type spring-steel
expander.
V-6
engine
cylinder heads are made of cast
iron.
Their
valve
guides
are cast integrally. Right and left cylinder heads are identical and interchange
able. In service, however, it is
good
practice to
install
the cylinder heads on the side from which
they were removed.
The
valves are in line in each head, at an angle
10°
above the centerline of the cylinder bores.
Each
valve has a spring strong enough to ensure
positive valve seating throughout the operating speed range of the engine. The valve rocker arm
mechanism is protected by a
sheet
metal cover.
This
cover is seated on a raised surface of the
cylinder
head. It is gasketed to prevent oil leaks.
The
rocker arms for each bank of cylinders are mounted on a tubular steel shaft, supported on
the cylinder head by brackets. The rocker arms
are
made of aluminum. They have inserts at the
push
rod socket and the valve stem contact face.
The
camshaft is located above the crankshaft be
tween the two cylinder banks; it is supported in
four steel-backed babbitt-metal bearings. The cam shaft is driven at one-half crankshaft speed by
sprockets and a single outside-guide type chain.
Hydraulic
valve lifters and
one-piece
push rods operate overhead rocker arms and valves of both
banks
of cylinders from a single camshaft.
This
system requires no lash adjustment during assem
bly
or in service.
In
addition to its normal function of a cam follower,
each hydraulic valve lifter also serves as an auto- 76
Page 112 of 376

E
FUEL
SYSTEM
9
©
FIG.
E-4—FUEL
EVAPORATIVE
EMISSION
CONTROL
SYSTEM-
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
A—Side
View
1—
Charcoal
Canister
2—
P.C.V.
Crankcase
Valve
3—
Purge
Line
4—
Fuel
Tank
5—
Fuel
Filler
Hose
B—Plan
View
6—
Non-Vented
Gas Cap 7—
Vapor
Separator or Expansion
Tank
g—Fuei
Gauge
9—Fuel
Line-to-Fuel
Pump
10—Fuei
Return
Line
during
normal temperature vehicle operation, thus
minimizing
driveability problems. An additional
feature of this valve is a built-in vacuum relief
which
allows inward air flow under negative fuel
tank
pressure conditions. The valve housing con
tains the normal tank vent and purge connections.
E-5.
Fuel Tank
The
fuel tank is external expansion type.
Fuel
tank
venting is accomplished by several vapor
lines which lead to the vapor separator or expan
sion tank. The vapor lines which lead from the
fuel tank are located at the front and
rear
so that
during
any inclination of the vehicle, at least one
line
will
be open to vent at all times.
E-6.
Vapor Separator
or
Expansion Tank
The
vapor separator is chambered so that the
rear
fuel tank vent lines lead into a separate chamber
with
a fuel shutofl valve.
This
prevents solid fuel
from
flowing from the fuel tank to the vapor can
ister during uphill operation or parking of the
vehicle. A single vapor vent line leads from the fuel
vapor separator to the vapor collection canister
where fuel vapors are stored until they can be drawn into the
engine
and burned.
The
expansion tank allows expansion of the fuel as
required
during temperature changes and simul taneously
becomes
a liquid trap that only allows
vapors to pass.
E-7.
Sealed
Gas Cap
The
sealed gas cap is designed to allow no vapors to
discharge into the atmosphere under normal
operation of the system. If the system
becomes
plugged or a failure of the demand valve occurs 112
Page 113 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
E
there is a relief valve that
opens
to reduce high
(dangerous) pressures in the fuel tank. In con
junction
with the pressure relief valve there is a
vacuum
relief valve to
stop
collapse of the fuel
tank
in case of a plugged system or failure of the demand valve. When replacing the gas cap, the
same type must be used as originally installed.
E-8.
System Inspection Test
The
fuel emission vent system should be checked
carefully
to ensure the absence of any leaks to the
atmosphere of either liquid or vapor which might
affect the accuracy, safety, or performance of the control system.
To
assure that the sealed system has been properly
installed,
the following
test
procedure has been
developed.
Disconnect the vent line from the fuel tank system
to the activated charcoal canister, induce l/i p.s.i.
air
pressure. If this pressure can be maintained for
a
few seconds the vent system is assured to be sealed. DO NOT add air pressure to the canister
because damage can occur to the demand valve if
care
is not taken.
E-9.
Servicing the System
Periodic
Maintenance — Replace carbon canister filter at
12,000
miles
[19,200
km.] or 12 month intervals (more
often
for operation in dusty areas).
This
is the only regular maintenance service
required.
Canister
Filter
Replacement — Disconnect
hoses
from
top of canister, remove canister from mount
-
t
FIG.
E-5—CARBURETOR—
F4 ENGINE,
EARLY
MODEL
1—
Choke
Clamp
Bracket
2—
Choke
Shaft and
Lever
Assembly
3—
Fuel
Inlet
Elbow
4—
Bowl
Vent Tube 5—
Idle
Air Adjusting
Needle
6—
Throttle
Lever
and Shaft Assembly
7—
Idle
Speed Adjusting Screw
8—
Fast
Idle Connector Rod ing bracket. Remove cover from
bottom
of canister
by pulling it down to
disengage
clips. Remove and
discard
polyurethane filter element
(squeeze
ele
ment out from under retainer bar).
Install
new
filter by squeezing element under retainer bar and positioning it evenly around entire
bottom
of
canister with
edges
tucked under canister lip, snap
bottom
cover in place, reinstall canister on bracket
and
reconnect
hoses.
Vapor
line
hoses
used in this system are made of
special
rubber material.
Bulk
hoses
are available for
parts
service.
Ordinary
rubber
hose
should not be
used to service vapor lines as they are subject to deterioration and may clog the system.
Liquid
vapor separators or expansion tanks and canisters
are
serviced as complete units only.
Canister
air filters, however, are serviced separately.
E-10.
CARBURETOR
—
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
A
single-barrel manual choke, down-draft carbure
tor (Fig. E-6) is used on the
Hurricane
F4 engine.
The
carburetor is internally vented by a tube
opening located in the air horn body of the
car
buretor.
This
opening is connected by a rubber
tube to the air
outlet
horn of the air cleaner thus
allowing only filtered atmospheric pressure air
to enter the float chamber for balance pressure
of the carburetor fuel.
Note:
A carburetor with a specific flow character
istic
is used for exhaust emission control. The
carburetor
is identified by a number, and the correct
carburetor
must be used, when replacement is
necessary.
Early
production models
CJ-3B,
CJ-5,
CJ-5A,
CJ-6,
and
CJ-6A
have a
Carter
YF-938SD
carbure
tor superseding the earlier
YF-938SC,
YF-938SA,
or
YF-938S
models.
Note."
Conversion kits for changing earlier models
to SD models are available. See Par E-23. It is recommended that when a carburetor is converted
that a tag be fashioned stamped with the new model number and installed under one of the air
horn
screws.
Look
for such a tag to determine if
the carburetor has previously been converted.
Carburetors
listed above are all in the same YF
series and have only minor differences. Descriptions
and
repair procedures given in the following
para
graphs apply equally to all
YF-series
carburetors.
YF-series
carburetors employ manual and vacuum
control of the metering rod and accelerator pump.
The
carburetor controls and vaporizes the fuel
through five separate systems: float system, low-
speed system, high-speed system, choke system,
and
accelerating-pump system. A description of the function and operation of each system provides an over all description of the carburetor.
For
identification, the series designation is stamped
on the body under the name
Carter
and the model
designation is stamped on a flange protruding
from
the body.
Note:
When checking for carburetor icing causes,
also check the vacuum-pump-to-manifold vacuum
line connector. 113
Page 118 of 376

E
FUEL
SYSTEM
Note:
Do not remove pressed-in parts such as
nozzle, pump jet, or antipercolator air bleed.
j.
Remove body flange attaching screws, body flange assembly, and gasket.
k.
Remove idle-adjustment screw, spring, idle
port
rivet, throttle lever assembly, washer, fast
idle arm, throttle plate screws, throttle plate, and throttle shaft.
1. Remove throttle shaft seal by prying out seal
retainer.
Note:
Do not remove pressed-in vacuum passage
orifice.
m.
Remove choke valve screws and choke valve.
Unhook
choke spring and slide shaft from housing,
n.
Wash all parts in carburetor cleaning solution
and
blow out passages with compressed air. Do not immerse diaphragm or seals in cleaning solution.
Inspect
all parts for wear or damage. Always use
new gaskets when reassembling.
E-22.
Carburetor
Reassembly
•
Refer to Fig. E-13.
To
expedite
reassembly, it is advisable to group all
related
parts by the circuit to which they belong.
a.
Install
throttle shaft seal and retainer in flange casting.
b.
Install
fast-idle
arm,
washer, and lever assembly
on throttle shaft. Slide shaft into place and install throttle valve.
c.
Install
idle port rivet plug and idle adjusting
screw
and spring.
d.
Attach flange assembly to body casting. Use new gasket.
e.
Install
low-speed jet assembly.
f.
Early
production models install pump intake
strainer
in pump diaphragm housing and carefully
press into recess.
Note:
If strainer is even slightly damaged, a new
one must be installed.
g.
Install
pump diaphragm assembly in diaphragm housing.
Then,
install pump diaphragm spring
(lower)
and retainer.
h.
Install
pump lifter
link,
metering rod
arm,
upper
pump spring, and retainer.
I.
Install
metering rod jet.
Note:
No gasket is used with this jet.
j.
Install
diaphragm housing attaching screws in
the diaphragm housing, making sure that the
edges
of the diaphragm are not wrinkled.
Lower
into place and tighten screws evenly and securely,
k.
Install
throttle shaft seal, dust seal washer, and
shaft seal spring.
I.
Install
pump connector
link
in the throttle arm
assembly.
Install
throttle shaft arm assembly on
throttle shaft guiding connector
link
in pump lifter
link
hole.
CAUTION:
Linkage
must not bind in any throttle
position. If binding occurs,
loosen
clamp screw in
throttle arm, adjust slightly, then retighten screw.
m.
Install
pump check disc, disc retainer, and lock
ring.
n.
Install
metering rod and pin spring. Connect
metering rod spring.
o.
Check
and if necessary correct meter ing rod adjustment. Follow procedure of
Par.
E-16.
p.
Install
needle
seat and gasket assembly, needle,
float
and
float pin. The
stop
shoulder on the float
pin
must be on the side away from the bore of
the carburetor.
q.
Set float level to specifications. Follow pro cedure of
Par.
E-12.
r.
Install
air horn gasket and air horn assembly.
Install
attaching screws, lock washers, and choke
tube clamp assembly. Tighten center screws first,
s. Slide choke shaft and lever assembly into place
and
connect choke lever
spring.
Install
choke valve.
Center
the valve by tapping lightly, then hold in
place with fingers when tightening screws,
t.
Install
fast-idle connector rod with
offset
portion
of rod on top and pin spring on outside.
Install
fast-idle connecting rod spring.
E-23.
Correcting Acceleration
Flat
Spot
Early
production
Carburetor
Models 938-S, 938-
SA,
938-SC
Inasmuch
as a flat
spot
on acceleration or low speed
stumble can
come
from causes other than
car
buretor
malfunction, it is recommended that
engine
tuning be thoroughly checked before attempting
any
actual carburetor work. Make sure that
ignition, compression, and timing are correct and
that fuel pump is supplying enough gas. Also, the F-head
engine
employs a water-heated intake
manifold.
Proper vaporization of the fuel depends
on correct intake manifold temperature. Since this
temperature is controlled by the cooling system
thermostat, include an operational check of the
thermostat when diagnosing the stumble. Operating
temperatures consistently below
155°F.
can cause stumble.
If
the stumble persists, a
YF-938-S,
YF-938-SA,
or
YF-938-SC
carburetor can be converted to a
YF-938-SD
carburetor by installing Special Kit
924161, consisting of a pump discharge check
needle, a metering rod, and a metering rod jet. If this kit is installed, the pump discharge check
needle
replaces the original
ball,
weight, and re
tainer
and the small wire-type retainer used with
the
ball
check assembly must not be reinstalled.
When
installing the kit, check the size of the pump discharge jet, No. 2, Fig. E-14.
Early
production
YF-938S
and
YF-938SA
carburetors have a .025" [0,635 mm.] jet installed. If the carburetor being
converted has a .025" jet it must be opened up to .031" [0,787 mm.] by running a No. 68
drill
through
the jet as shown in
Fig.
E-14.
The jet must be drilled
as it is a pressed in part and cannot be replaced.
Upon
completing the installation of the conversion
kit,
mark
or tag the carburetor to indicate that it
is a
YF-938SD.
118
Page 131 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
E
possibility of vapor lock by keeping cool fuel from
the tank constantly circulating through the fuel
pump.
Fuel
pump pressure at carburetor (inlet) on Daunt
less
V6-225
engine
should be 3% lbs.
[0,264
kgm-cm2] minimum at idle with the vapor return
hose
squeezed off. With the vapor return
hose
open
pump pressure should be 2j^ lbs. [0,176 kg-cm2]
minimum.
The
Dauntless V-6
engine
is equipped with a sealed
unit,
non-repairable, single-action fuel pump (Fig.
E-33).
Note:
All Dauntless V-6
engines
are equipped with
a
throw-away can-type gasoline filter installed in
the fuel line
between
the fuel pump and the
car
buretor.
This
unit must be replaced every
12,000
miles
[19.200
km.] of vehicle operation.
E-68.
Fuel
Pump Removal
To
remove the fuel pump from the Dauntless V-6
engine, disconnect the fuel inlet, fuel
outlet
and fuel return lines from the pump. Remove the two
fuel pump body attaching cap screws and lock
washers.
Pull
the fuel filter bracket free and remove the pump and gasket. Discard pump and gasket.
Install
new pump in reverse procedure of removal.
E-69.
AIR
CLEANER
Servicing
of the air cleaner is properly taken care of as part of the periodic lubrication and servicing of the vehicle. For this reason, air cleaner servicing
information is given in the Lubrication Section.
Refer
to and follow the instructions given there.
E-70. ACCELERATOR LINKAGE
The
accelerator linkage is properly adjusted when
the vehicle leaves the factory. However, in time
components parts
will
become
worn and require re
adjustment to maintain a smooth even control of
engine
speed. On Models equipped with F4
engines
the adjustment is made at the adjusting block,
Fig.
E-34. Loosen the lock nuts, and adjust the length of the accelerator rod so that when the
car
buretor throttle valve is wide open the accelerator
treadle
will
just strike the toe board. After correct
adjustment is made tighten both lock nuts firmly.
To
adjust the accelerator linkage on V6
engines
loosen
the lock nuts securing the accelerator rod
housing to its securing bracket and adjust the length
of the accelerator rod so that when the carburetor throttle valve is wide open the accelerator treadle
will
just strike the toe board. After correct adjust
ment is made, tighten lock nut firmly, see Fig. E-35 for Dauntless V-6 engine.
E-71. FUEL
TANK
AND
FUEL LINES
The
following paragraphs (E-70 through E-73) describe the removal, installation and services to
be performed when replacing the fuel tank or
servicing
the fuel system.
FIG.
E-34—ACCELERATOR LINKAGE,
F4
ENGINE
1—
Grommet
2— Nut and Lockwasher
3—
Throttle
Control
4—
Choke
Control 5—
Treadle
Rod Seal
6—
Accelerator
Treadle
7—
Treadle
Hinge Pin
8—
Treadle
Hinge 9— Nut and Lockwasher
10—
Screw
11—
Accelerator
Rod
12— Nut
13—
Adjusting
Block
14—
Retracting
Spring
15—
Cotter
Pin
16—
Lower
Beilcrank
17—
Washer
18—
Beilcrank
Link
Rod
19—
Bracket
20—
Throttle
Wire
Stop
21—
Beilcrank
Spring
22—
Rod
23—
Upper
Beilcrank
24—
Wesher
10731
131
Page 133 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
E
portant that
these
lines are not accidentally re
versed.
When
installing the fuel tank on late model vehicles, position the tank
between
the frame
rail
to allow space to connect the fuel line(s), vent
hose
and
sending unit wire. After connecting
these
items, align and secure tank to frame brackets.
Position filler
hose
on tank filler neck and tighten
hose
clamp.
Fill
tank with fuel and check for leaks.
When
installing the fuel tank on early model vehicles, reverse the order of removal as given in
Par.
E-73.
E-75.
Fuel
Tank
Cap
A
surge pressure type fuel tank filler cap is used on
all
models.
This
is necessary to prevent fuel leakage
from
the cap vent opening when the vehicle is on a
side slope. Two spring loaded relief valves which
open when venting is required are built into the
cap.
Should the pressure valve
fail
to open, pressure
in
the tank may force fuel by the carburetor inlet
valve causing flooding.
Failure
of the vacuum valve may prevent flow of fuel to the carburetor. Should
the valves
fail
to vent install a new cap.
Note:
Vehicles having a
Fuel
Evaporative
Emis
sion System are equipped with a non-vent sealed gas cap. The sealed cap is designed to allow no
vapors to discharge to the atmosphere. No other type of cap is to be used on vehicles having this
type system.
E-76.
Fuel
Gauge Float Unit
The
fuel tank
gauge
float unit is mounted in the top
of the fuel tank and consists of a housing enclosing
a
rheostat that is actuated by the float arm, and a
float
which
moves
with the fuel level in the tank.
On
V-6 and current production F4
engine
equipped vehicles, the fuel
outlet
pipe is integral with the
float
unit.
The fuel
outlet
pipe has a mesh filter on the inner end.
Note:
Under no circumstances should a fuel tank
gauge
be installed without a mesh filter element.
The
filter,
outlet
pipe, and float unit are locked as
an
assembly to the top of the fuel tank. To remove,
turn
the lock plate that secures the float unit
assembly.
E-77.
Fuel
Lines
Check
lines and connections occasionally for leaks,
and
for severe kinks that might restrict the flow of
fuel. If an excessive amount of
dirt
is found in the
carburetor
or fuel pump, the fuel tank should be
drained
and the fuel lines blown out with com
pressed air.
All
rubber fuel lines and their respective clamps should be checked occasionally to be certain they
are
correctly positioned and not leaking. 133