Page 541 of 751
08-4
3. SYSTEM LAYOUT AND TIGHTENING TORQUE OF
FRONT SUSPENSION
Upper arm assembly
Coil spring
Shock absorber
Front axle shaft assembly
Steering gear
box assembly Lower arm assembly
Shock absorber yoke
Knuckle assembly
Stabilizer bar assembly
Front View ▶
Upper arm (on knuckle) nut
Tightening torque: 140 ~ 160 Nm
Lower arm (on knuckle) nut
Tightening torque: 140 ~ 160 Nm
Shock absorber (to yoke) bolt
Tightening torque: 125 ~ 145 Nm
Page 542 of 751
08-54411-01
Stabilizer bar link lower nut
Tightening torque: 110 ~ 130 Nm
Coil spring mounting nut
Tightening torque: 60 ~ 80 Nm
Stabilizer bar link upper nut
Tightening torque: 30 ~ 50 NmUpper arm (frame side) bolt/nut
Tightening torque: 110 ~ 130 Nm
Stabilizer bar clamp bolt
Tightening torque: 40 ~ 60 Nm
Lower arm (end yoke) bolt
Tightening torque: 70 ~ 80 Nm
Lower arm (shock absorber yoke side) nut
Tightening torque: 150 ~ 170 Nm
Lower arm (frame side) bolt/nut
Tightening torque: 210 ~ 230 Nm Top View ▶
Page 543 of 751
08-6
4. SYSTEM LAYOUT AND TIGHTENING TORQUE OF REAR
SUSPENSION
Lower arm (link)
Stabilizer bar link
Stabilizer bar
Shock absorber
Coil spring seat (upper side)Lateral rod
Axle housing Upper arm (link)Top View ▶
Page 545 of 751
08-8
5. TROUBLESHOOTING
Problem Cause Action
Vehicle rollingBroken stabilizer bar Replace
Faulty shock absorber Replace
Abnormal noise.Loosening mounting Retighten
Damaged or worn wheel bearing Replace
Damaged shock absorber Replace
Damaged tire Replace
Poor ridingOver inflated tire Adjust pressure
Faulty shock absorber Replace
Loosened wheel nut Tighten as specified torque
Bent or broken coil spring Replace
Damaged tire Replace
Worn bushing Replace
Vehicle pulls to one sideDeformed arm assembly Replace
Worn bushing Replace
Bent or broken coil spring Replace
Hard steeringExcessive resistance of lower arm ball
jointReplace
Insufficient tire pressure Replace
Faulty power steering Replace
Unstable steering
Worn or loosened lower arm bushing Retighten or replace
Vehicle bottoming
Worn or broken coil spring Replace
Vehicle height loweredOver loaded on the vehicle -
Defective shock absorber Replace
Defective coil spring Replace
Page 547 of 751
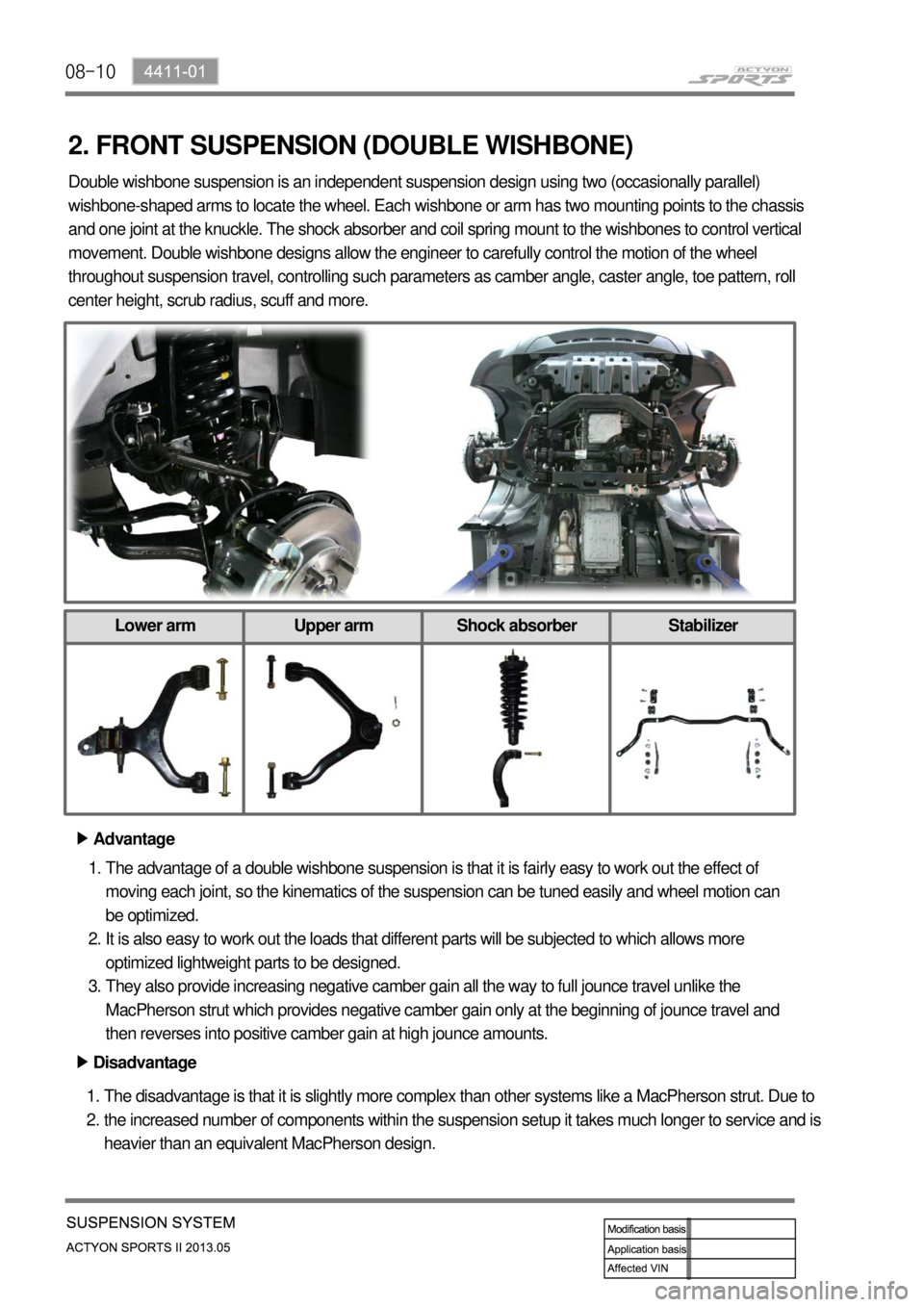
08-10
2. FRONT SUSPENSION (DOUBLE WISHBONE)
Advantage ▶
The advantage of a double wishbone suspension is that it is fairly easy to work out the effect of
moving each joint, so the kinematics of the suspension can be tuned easily and wheel motion can
be optimized.
It is also easy to work out the loads that different parts will be subjected to which allows more
optimized lightweight parts to be designed.
They also provide increasing negative camber gain all the way to full jounce travel unlike the
MacPherson strut which provides negative camber gain only at the beginning of jounce travel and
then reverses into positive camber gain at high jounce amounts. 1.
2.
3.
Disadvantage ▶
The disadvantage is that it is slightly more complex than other systems like a MacPherson strut. Due to
the increased number of components within the suspension setup it takes much longer to service and is
heavier than an equivalent MacPherson design. 1.
2. Double wishbone suspension is an independent suspension design using two (occasionally parallel)
wishbone-shaped arms to locate the wheel. Each wishbone or arm has two mounting points to the chassis
and one joint at the knuckle. The shock absorber and coil spring mount to the wishbones to control vertical
movement. Double wishbone designs allow the engineer to carefully control the motion of the wheel
throughout suspension travel, controlling such parameters as camber angle, caster angle, toe pattern, roll
center height, scrub radius, scuff and more.
Lower arm Upper arm Shock absorber Stabilizer
Page 548 of 751
08-114411-01
3. REAR SUSPENSION (MULTI LINK TYPE)
Multi-link (5-Link) type suspension is the independent suspension. It provides good ride comfort and
drivability by reducing the coil spring weight. Also, it increases the space for passenger compartment by
lowering the floor. This type of suspension consists of multiple links such as coil spring, shock absorber,
upper and lower arms, lateral rod and stabilizer bar.
Shock absorber Stabilizer bar Rear coil spring
Lower arm Upper arm Lateral rod
Page 552 of 751

09-34850-01
1. SPECIFICATION
Unit Description Specification
Front brake Type Ventilated disc
Outer diameter of discØ294 mm
Inner diameter of caliper cylinderØ43.0 x 2 mm
Thickness of disc 28 mm (wear limit: 25.4 mm)
Area of brake pad Above 60 cm2
Pad wear indicator Mechanical type
Rear brake Type Solid disc
Outer diameter of discØ299 m
Thickness of disc 10.4 mm (wear limit: 8.5 mm)
Area of brake pad Above 28.8 cm2
Pad wear indicator Mechanical type
Brake booster Type Vacuum assist type
Size8” + 9” (Tandem)
Master cylinder Type Tandem type(integrated level sensor)
Inner diameter of cylinderØ26.99 mm
Brake pedal Maximum operating stroke 150 mm
Pedal ratio 4 : 1
Free play 3 to 10 mm
Parking brake Type Mechanically expanded rear lining
Operating type Hand operated type
Inner diameter of drumØ190 mm
Brake oil Specification DOT 4
Capacity As required
Service Interval: Change the brake oil at every 2 years
DOT?
It is the quality grade of brake fluid established by US Department of Transportation.
Page 556 of 751

09-74850-01
Problem Possible Cause Action
Noise or vehicle
vibration when appliedIncorrectly mounted back plate or caliper Repair
Loosened bolt of back plate or caliper Retighten
Uneven wear of brake disc Replace
Brake pad contamination Clean or replace
Sticking brake pad on contact surface Replace
Wear or hardening of brake pad Replace
Excessive clearance between caliper and pad Repair
Uneven contact of pad Repair
Lack of lubrication in sliding parts Lubricate
Improper operation of caliper Replace
Dust cover missing Repair
Loosened suspension mounting bolt Retighten
Pulls to one side when
brakingUnbalanced tire pressure between left and right Adjust
Poor contact of brake pad Repair
Oil or grease on brake pad Replace
Scratch, uneven wear, distortion of brake disc Replace
Improperly installed brake caliper Repair
Improper operation of auto adjuster Repair
Crack or distortion of brake pad Replace
Poor braking Oil leak or contamination Repair or replace
Air in brake line Bleed air
Improper operation of brake booster Repair
Poor contact of brake pad Repair
Oil or grease on brake pad Replace
Improper operation of auto adjuster Repair
Clogged brake line Repair
Improper operation of proportioning valve Repair
3. TROUBLESHOOTING