Page 1004 of 1336
The shiftable gear can be adjusted by pressing the
"UP (D+)" or "DOWN(D-)" switch when the gear
Shift lock release button
If the selector lever cannot be moved from
while pushing down this button with finger. For
safety, turn off the engine and depress the
brake pedal before the attempt.Shift up Shift down Tip switches on steering wheel
Meter cluster
This indicator shows the current position of
the gear.
Gear selector lever
Lever positions
P : Park
R : reverse
N : Neutral
D : Drive
Mode switch
W: Winter mode (pressed "OUT")
S: Standard mode (pressed "IN")
Toggle the mode between winter mode
and standard mode by pressing this
switch.Tip switch (manual shift switch)
The shiftable gear can be adjusted by
moving this switch to forward and rearward
position.
Selection of Manual/Automatic Shift Function
D: Automatic shift according to the driving condition
M: Manual shift
Page 1031 of 1336
3660-01
The shiftable gear can be adjusted by pressing the
"UP (D+)" or "DOWN(D-)" switch when the gear
Shift lock release button
If the selector lever cannot be moved from
while pushing down this button with finger. For
safety, turn off the engine and depress the
brake pedal before the attempt.Shift up Shift down Tip switches on steering wheel
Meter cluster
This indicator shows the current position of
the gear.
Gear selector lever
Lever positions
P : Park
R : reverse
N : Neutral
D : DriveTip switch (manual shift switch)
The shiftable gear can be adjusted by
moving this switch to forward and rearward
position.
Selection of Manual/Automatic Shift Function
D: Automatic shift according to the driving condition
M: Manual shift
Page 1076 of 1336
4110-01
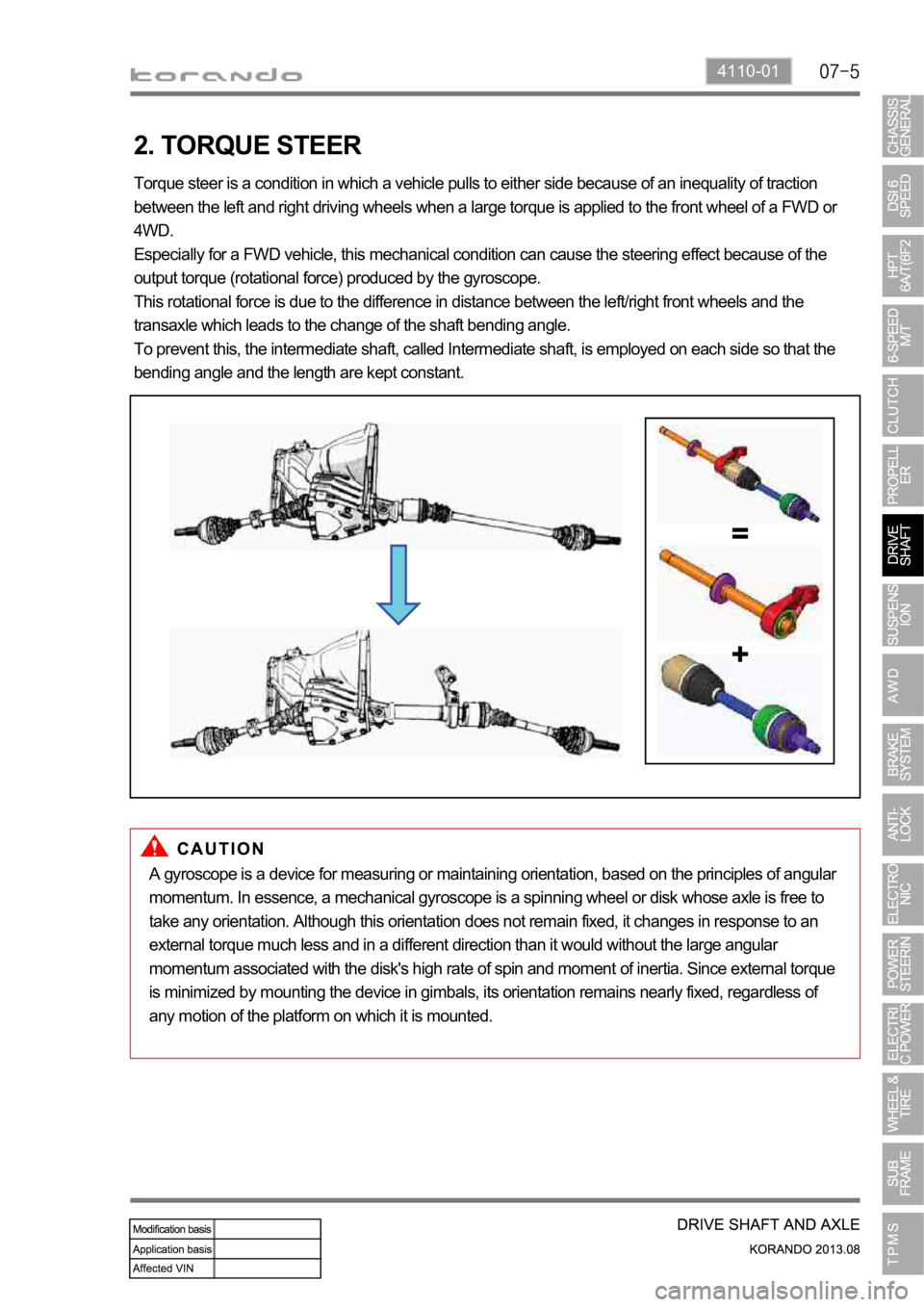
2. TORQUE STEER
Torque steer is a condition in which a vehicle pulls to either side because of an inequality of traction
between the left and right driving wheels when a large torque is applied to the front wheel of a FWD or
4WD.
Especially for a FWD vehicle, this mechanical condition can cause the steering effect because of the
output torque (rotational force) produced by the gyroscope.
This rotational force is due to the difference in distance between the left/right front wheels and the
transaxle which leads to the change of the shaft bending angle.
To prevent this, the intermediate shaft, called Intermediate shaft, is employed on each side so that the
bending angle and the length are kept constant.
A gyroscope is a device for measuring or maintaining orientation, based on the principles of angular
momentum. In essence, a mechanical gyroscope is a spinning wheel or disk whose axle is free to
take any orientation. Although this orientation does not remain fixed, it changes in response to an
external torque much less and in a different direction than it would without the large angular
momentum associated with the disk's high rate of spin and moment of inertia. Since external torque
is minimized by mounting the device in gimbals, its orientation remains nearly fixed, regardless of
any motion of the platform on which it is mounted.
Page 1083 of 1336
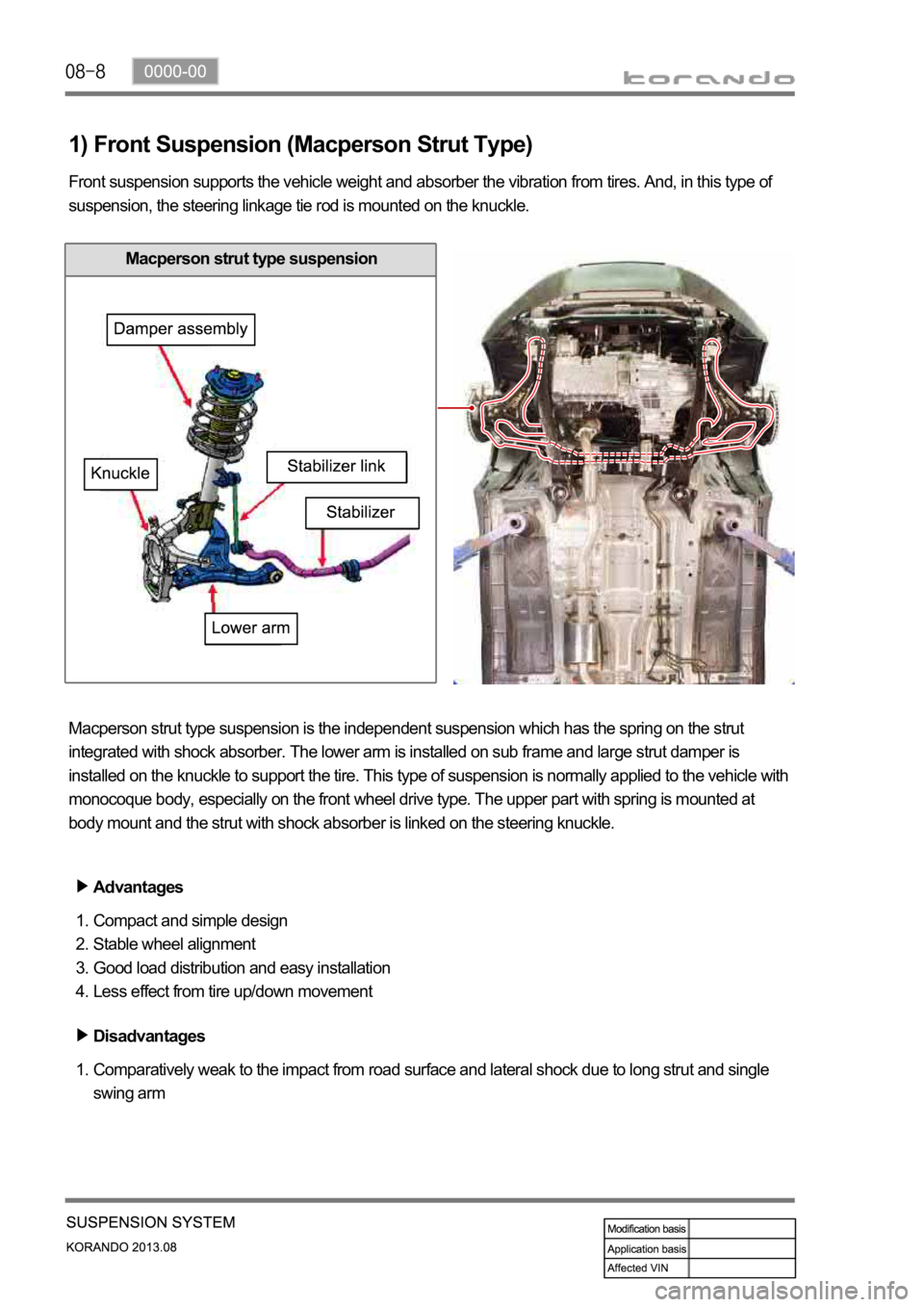
1) Front Suspension (Macperson Strut Type)
Front suspension supports the vehicle weight and absorber the vibration from tires. And, in this type of
suspension, the steering linkage tie rod is mounted on the knuckle.
Macperson strut type suspension is the independent suspension which has the spring on the strut
integrated with shock absorber. The lower arm is installed on sub frame and large strut damper is
installed on the knuckle to support the tire. This type of suspension is normally applied to the vehicle with
monocoque body, especially on the front wheel drive type. The upper part with spring is mounted at
body mount and the strut with shock absorber is linked on the steering knuckle.
Advantages
Compact and simple design
Stable wheel alignment
Good load distribution and easy installation
Less effect from tire up/down movement 1.
2.
3.
4.
Disadvantages
Comparatively weak to the impact from road surface and lateral shock due to long strut and single
swing arm 1.
Macperson strut type suspension
Page 1089 of 1336
3) Parts Arrangement
Part nameVehicle with
CBSVehicle with ABS/EBDVehicle with
ESP
HECU
Not appliedAppliedApplied Front wheel speed sensor
Rear wheel speed sensor
ABS warning lamp
EBD indicator
Longitudinal G sensor 2WD: N/A, 4WD: Applied Not applied
Sensor cluster
(Yaw rate sensor,
lateral/longitudinal G sensor)
Not applied Applied
ESP indicator
ESP OFF switch and warning
lamp
Steering wheel angle sensor
Page 1101 of 1336

4890-00
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
1) What is ABS?
When braking suddenly or braking on slippery roads, the vehicle keeps moving forward but the wheels
are locking and not rotating. If these happen, the vehicle may lose stability or rotate resulting in an
accident. ABS helps to maintain directional stability and control of the vehicle. ABS is designed to
secure more safety and increase the control of steering wheel during emergency braking situation. But,
ABS does not guarantee perfect safety beyond its physical limit. ABS in this vehicle contains EBD
function. In normal driving conditions, the brake system operates without ABS function.
2) What is EBD (Electronic Brake-force Distribution)?
EBD is an automobile brake technology that automatically varies the amount of force applied to each of a
vehicle's brakes, based on road conditions, speed, loading, etc. Always coupled with anti-lock braking
systems, EBD can apply more or less braking pressure to each wheel in order to maximize stopping
power whilst maintaining vehicular control. EBD does not operate when ABS is working. ABS effect according to braking conditions
Braking on split road Maneuvering while braking
Page 1102 of 1336
3. G-sensor (for 4WD)
Located on the floor under
parking brake bracket in center
console.4. Rear wheel speed sensor
(for 2WD)
Located on knuckle. The
appearance is different from that
for 4WD.4. Wheel speed sensor
(for 4WD)
Located on knuckle. The
appearance of front sensor is
same with rear sensor.
2. ABS warning lamp
EBD warning lamp (ABS warning lamp +
Brake warning lamp)1. ABS hydraulic device and control unit
Located under the power steering fluid reservoir and
contains the pressure sensor.
2. COMPONENT
Page 1120 of 1336
0000-00
1. SPECIFICATION
1) Specification of Active Wheel Sensor
Description Specification
Supplying voltage DC 12 V
Output current (at 2.75 km/h of vehicle speed) 7 mA (Lo) ~ 14 mA (Hi) +20%/-16%
Tightening torque Front: 7.8 to 11.8 Nm
Rear: 7.8 to 11.8 Nm
Operating temperature
Operating frequency 1 ~ 2,500 Hz
UnitDescription
ABS ESP
HECU Clock frequency: 32 MHz Clock frequency: 50 MHz
Memory: 128 KB Memory: 512 KB
Switch orifice Switch orifice
Wheel speed sensor Active type Active type
Steering wheel angle
sensorNone Max. detection angle speed:
Operating voltage: 9 to 12 V
Sensor cluster None Yaw rate sensor + lateral G sensor +
longitudinal G sensor (4WD)
Longitudinal G sensor 4WD only None
Pressure sensor None HECU integrated