Page 285 of 1336

0000-00
1. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION OF E-VGT
(Electric-Variable Geometry Turbine)
A turbocharger is a centrifugal compressor powered by a high speed turbine that is driven by an engine's
exhaust gases. Its benefit lies with the compressor increasing the mass of air entering the engine (forced
induction), thereby resulting in greater performance (for either, or both, power and efficiency). As the
turbine, at exhaust end, is rotated by exhaust gas pressure the impeller, at intake end, gets rotated to
send air around center of the impeller, being circumferentially accelerated by the centrifugal force, into
the diffuser. The air, which has been introduced to the diffuser having a passage with big surface,
transforms its speed energy into the pressure energy while being supplied to the cylinder improving the
volume efficiency. Also, the exhaust efficiency improves as the exhaust turbine rotates. The
turbocharger is often referred to as the exhaust turbine turbocharger.
The E-VGT system installed to the D20DTF engine variably controls the passages of the turbine
housing to regulate the flow rate of the exhaust gas. The actuator of E-VGT is a DC motor actuator (E-
Actuator) which controls more quickly and precisely than the previous vacuum type actuator.
The engine ECU controls the E-Actuator electronically as follows:
Diffuser: With the meaning of spreading out it is a device that transforms fluid's speed energy into the
pressure energy by enlarging the fluid's passage to slow down the flow.
At low speed: Narrows the flow passage for the exhaust gas, resulting in increasing the flow speed
of the exhaust gas and running the turbine quickly and powerfully.
At high speed: Expands the flow passage for the exhaust gas, resulting in increasing the mass flow
of the exhaust gas and running the turbine more powerfully. -
-
Page 287 of 1336
0000-00
E-VGT turbocharger
Improves engine power
T-MAP sensor
Boost pressure and
temperature
2. COMPONENTS
Engine ECU (D20DTF)
E-VGT duty controlAccelerator pedal position
sensor
Transfers accelerating demand
to ECU
Atmospheric pressure, RPM
signal
HFM sensor
Improves the engine powerCoolant temperature sensor
Operates the VGT according to
engine warm-up
For more information about control logic, refer to Chapter "Engine Control".
Page 297 of 1336
0000-00
3. LUBRICATION
1)Anti-friction
The oil makes a thin film on the surface of sliding components to reduce the wear due to friction.
2)Cooling
The friction makes the heat on the components. The oil absorbs the heat and radiates it or cools it down.
3) Sealing
The piston ring on the piston seals the cylinder. The oil gets into the clearance in piston ring to secure
the sealing for compression pressure and combustion gas.
4) Anti-corrosion
The oil generates the thin film on the surface of components to prevent the material from contacting with
air, water and corrosive gas.
5) Cleaning
The oil transfers the residue of material due to friction, oxidized substance, and carbonized substance
while circulating in the engine by oil pump.
Page 304 of 1336
0000-00
Electric fan
Circulates the fresh air forcibly to exchange heat
with the radiator core fin.
Coolant temperature sensor
Measures the coolant
temperature and sends the
result to the engine ECU.
Radiator
Releases heat through fins and cools down the hot coolant as the
coolant passes through the tube of the radiator core.
Page 322 of 1336
1413-00
1. OVERVIEW
The pre-heating system for D20DTF engine has the glow plug to the cylinder head (combustion
chamber), and improves the cold start performance and reduces the emission level.
The pre-heating resistor (air heater) is used to heat the intake air.
This enables the diesel fuel to be ignited in low temperature condition.
The ECU receives the information such as, engine rpm, coolant temperature, engine torque, etc.,
through CAN communication during pre-heating process; and the pre-heating control unit controls the
pre-heating, heating during cranking and post-heating by the PWM control.
Glow plugGlow plug control unit
(GCU)
Glow indicatorEngine ECU (D20DTF)
Page 327 of 1336
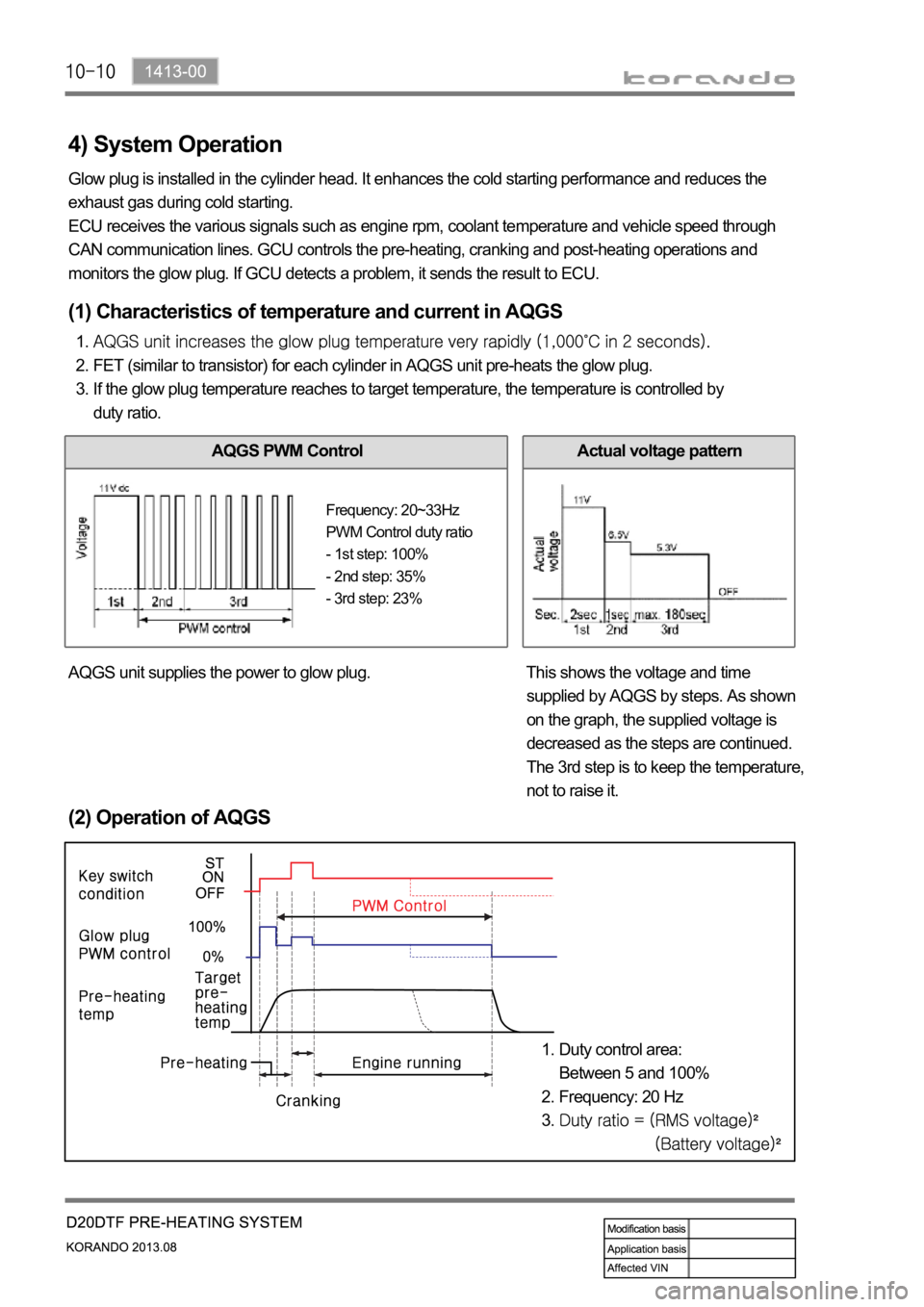
4) System Operation
Glow plug is installed in the cylinder head. It enhances the cold starting performance and reduces the
exhaust gas during cold starting.
ECU receives the various signals such as engine rpm, coolant temperature and vehicle speed through
CAN communication lines. GCU controls the pre-heating, cranking and post-heating operations and
monitors the glow plug. If GCU detects a problem, it sends the result to ECU.
(2) Operation of AQGS
Duty control area:
Between 5 and 100%
Frequency: 20 Hz1.
2.
3.
(1) Characteristics of temperature and current in AQGS
FET (similar to transistor) for each cylinder in AQGS unit pre-heats the glow plug.
If the glow plug temperature reaches to target temperature, the temperature is controlled by
duty ratio. 1.
2.
3.
AQGS PWM ControlActual voltage pattern
AQGS unit supplies the power to glow plug. This shows the voltage and time
supplied by AQGS by steps. As shown
on the graph, the supplied voltage is
decreased as the steps are continued.
The 3rd step is to keep the temperature,
not to raise it.
Frequency: 20~33Hz
PWM Control duty ratio
- 1st step: 100%
- 2nd step: 35%
- 3rd step: 23%
Page 328 of 1336
1413-00
(3) Operating Steps
Pre-Glow: Step 1
If normal communication with the ECU is established 2 seconds after the power is supplied to the IGN
terminal from the battery, the GCU supplies the battery power to raise the temperature of the glow plug
- The time for pre-heating is controlled by the ECU.
If the input voltage (VB) is 11.5 V or less, GCU supplies the battery voltage for preheating time (T1).
If the input voltage (VB) is greater than 11.5 V, GCU supplies the voltage of 11.5 V for preheating time
(T1). -
-
The preheating time may vary according to the conditions.
Input voltage
VB (V)Pre-heating time T1
(sec)
6 8.27
7 5.8
8 4.1
9 3.15
10 2.4
11 1.95
1.9
Page 329 of 1336
During cranking: Step 2 and step 3
Step 2: If the ECU receives the cranking signal after pre-heating (step 1), the GCU supplies the 1.
2.
Under fixed temperature: The AQGS unit supplies power for 30 seconds (Step 1 + Step 3) if no
cranking signal is received after the step 1.
During cranking: The step 3 is started after the step 2. *
*
Post-glow: Step 4:
The post-heating is for reducing HC/CO after the engine is started. If the time for post-heating exceeds
180 sec., the GCU unit cuts off the power to each glow plug even if there is preheating request from the
engine ECU.
Emergency glow
If no CAN signal is received for 4 seconds from the engine ECU after the IGN ON signal is input, the
GCU performs emergency preheating (Step 3) for 30 seconds.