Page 654 of 828
09-6
5) Indicators and Warning Lamps for ABS/ESP
LampIndicator/Warning Lamp
Description
EBD warning lamp ON when EBD function is failed
ABS warning lamp ON when ABS function is failed
ESP indicator Blinking when ESP function is operating
ESP OFF indicator ON when the ESP OFF switch is pressed
ESP warning lamp ON when ESP function is failed
ESP buzzer Sound when ESP function is operating
Page 682 of 828
10-34892-01
1. SPECIFICATION
Unit DescriptionSpecification
Remark
ABS ESP
HECU Clock frequency 32MHz 50MHz
Memory 128KB 256KB
S-sensor Operating voltage 4.75~5.25V
None (functions
in sensor cluster)Installed in IP
panel behind
audio (only for
4WD) Operating temperature-30 ~ 85℃
Operating range -1.5 ~ 1.5g
Output voltage 0.5 ~ 4.5V
Wheel
speed
sensorSupplying voltage 4.5 ~ 16V←
Output current (approx. 2.7
km/h of vehicle speed)7mA(Lo) ~ 14mA
+20%←
Operating temperature-40 ~ 150℃ ←
Operating frequency 1~2500Hz←
Page 698 of 828
10-194892-01
5) EBD (Electronic Brake Force Distribution) System
System description ▶
As an add-on logic to the ABS base algorithm, EBD works in a range in which the intervention
thresholds for ABS control are not reached yet.
EBD ensures that the rear wheels are sensitively monitored for slip with respect to the front axle. If
slip is detected, the inlet valves for the rear wheels are switched to pressure hold to prevent a
further increase in pressure at the rear-wheel breaks, thus electronically reproducing
a pressure-reduction function at the rear-wheel brakes.
ABS features an enhanced algorithm which includes control of the brake force distribution
between the front and rear axles. This is called Electronic Brake Distribution. In an unloading car
condition the brake efficiency is comparable to the conventional system but for a fully loaded
vehicle the efficiency of the EBD system is higher due to the better use of rear axle braking
capability.
Advantages ▶
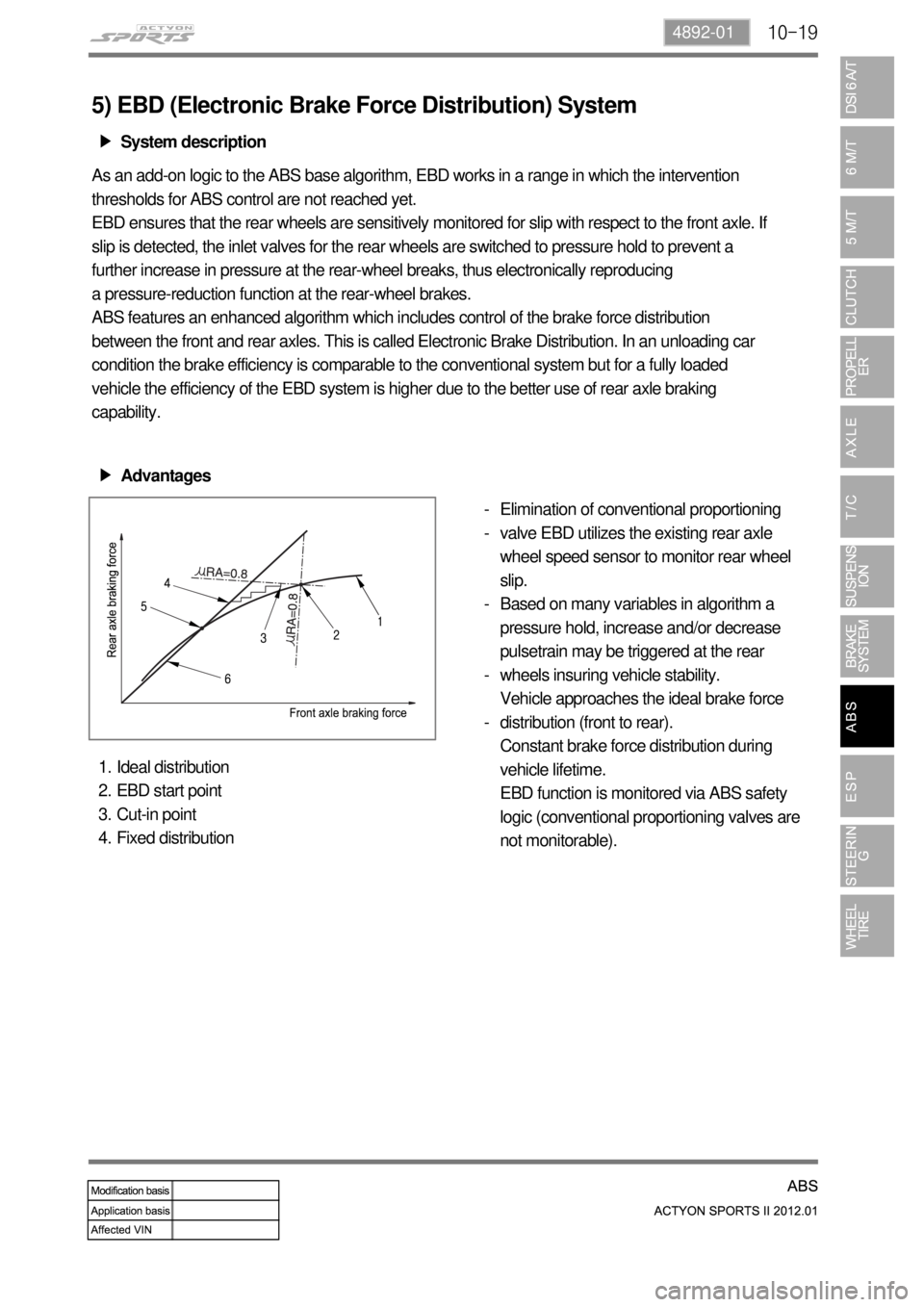
Elimination of conventional proportioning
valve EBD utilizes the existing rear axle
wheel speed sensor to monitor rear wheel
slip.
Based on many variables in algorithm a
pressure hold, increase and/or decrease
pulsetrain may be triggered at the rear
wheels insuring vehicle stability.
Vehicle approaches the ideal brake force
distribution (front to rear).
Constant brake force distribution during
vehicle lifetime.
EBD function is monitored via ABS safety
logic (conventional proportioning valves are
not monitorable). -
-
-
-
-
Ideal distribution
EBD start point
Cut-in point
Fixed distribution 1.
2.
3.
4.
Page 704 of 828
11-34890-10
1. SPECIFICATION
1) Specification of Active Wheel Sensor
Description Specification Remark
Supplying voltage 4.5 ~ 16.0V
Output current (at 2.75 km/h of
vehicle speed)7mA(Lo) ~ 14mA(Hi)
Tightening torqueFront: 7.8 to 11.8 Nm
Rear: 7.8 to 11.8 Nm
Operating temperature-40 ~ 150℃
Operating frequency 1 ~ 2,500Hz
UnitDescription
Specification
ABS ESP
HECU Clock frequency: 32 MHz Clock frequency: 50 MHz
Memory: 128 KB Memory: 256 KB
Wheel speed
sensorActive type Active type Output: 7~14
mA
Steering wheel
angle sensorNone Max. detection angle speed:
1500 °/SecPulse duty:
50±10%
Operating voltage: 9 to 12 V
Sensor cluster None Yaw rate sensor + lateral G
sensor + longitudinal G sensor
(4WD)Mounting
direction should
be kept (CAN
communcation)
Longitudinal G
sensor4WD only None
Pressure
sensorNone HECU integrated
Page 706 of 828
11-54890-10
2. SYSTEM LAYOUT
ESP System ▶
Sensor - front wheel speed
Sensor - rear wheel speed
Screw (7.8~11.8 Nm)
Clip - cable holder
Clip - sensor cable mounting rear
Plug - blind
HECU
Sensor - cluster
Nut (9.8~10.8 Nm)
ESP OFF switch
Steering wheel sensor 1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
Page 708 of 828
11-74890-10
1. OVERVIEW
The ESP (Electronic Stability Program) has been developed to help a driver avoid danger of losing
control of the vehicle stability due to understeer or oversteer during cornering. The yaw rate
sensor, lateral sensor and longitudinal sensor in the sensor cluster and the steering wheel angle
sensor under the steering column detect the vehicle conditions when the inner or outer wheels are
spinning during oversteer, understeer or cornering. The ESP ECU controls against oversteer or
understeer during cornering by controlling the vehicle stability using input values from these
sensors and applying the braking force to the corresponding wheels independently. The system
also controls the engine power right before the wheel spin synchronized to decelerate the vehicle
automatically in order to maintain the vehicle stable during cornering.
Page 709 of 828
11-8
ESP OFF switch
Located on the left side of
instrument panel.
Rear wheel speed sensor
Located on the both ends of
rear axle.Front wheel speed sensor
Located on the hub
assembly.Sensor cluster
Located at the bottom of
center fascia panel.
Steering wheel angle sensor
Located on column shaft with
contact coil.HECU assembly
Located near the brake
booster in engine
compartment and contains
the pressure sensor.
2. COMPONENTS
Page 710 of 828

11-94890-10
3. PRECAUTIONS
The warning lamp flashes and warning beep sounds when the ESP is operating
When the ESP operates during vehicle movement, the ESP warning lamp on the instrument
panel flashes and beep comes on every 0.1 second. The ESP system is only a
supplementary device for comfortable driving. When the vehicle exceeds its physical limits, it
cannot be controlled.
Do not rely on the system. Keep on the safe driving.
Feeling when ESP is working
When the ESP system activates, the feeling can be different depending on vehicle driving
conditions.
For example, you will feel differently when the ESP system is activated during the ABS is
operating with the brakes applied and when the brakes are not applied on a curve.
If the ESP system operates when the brake is applied, the brake pressure will be increased on
the corresponding wheel which already has braking pressure for the ESP controls.
ARP Operation
During the ARP operation, vehicle safety (rollover prevention) takes the first priority and thus,
stronger engine control is in effect. Consequently, the vehicle speed decreases rapidly, so the
driver must take caution for the vehicle may drift away from the lane.
Noise and vibration that driver feels when ESP system is operating
The ESP system may transfer noise and vibration to the driver due to the pressure changes
caused by the motor and valve operations in a very short period of time. And, keep in mind
that the output and vehicle speed could be decreased without rpm increase due to the ASR
function that controls the engine power.