2011 FORD KUGA 414-02
[x] Cancel search: 414-02Page 263 of 2057

Charging System
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Section 414-02, for
schematic and connector information.
General Equipment
Midtronics EXP-1050 battery tester
Midtronics GR590-2
Ford diagnostic equipment
Inspection and Verification
WARNINGS: Batteries contain sulphuric acid. Avoid
contact with skin, eyes, or clothing. Also,
shield your eyes when working near
batteries to protect against possible
splashing of the acid solution. In case of
acid contact with skin or eyes, flush
immediately with water for a minimum of
15 minutes and get prompt medical
attention. If acid is swallowed, call a
physician immediately. Failure to follow
these instructions may result in personal
injury.
Batteries normally produce explosive
gases which can cause personal injury.
Therefore, do not allow flames, sparks or
lighted substances to come near the
battery. When charging or working near a
battery, always shield your face and
protect your eyes. Always provide
ventilation. Failure to follow these
instructions may result in personal injury.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical
or electrical damage.
Visual Inspection Chart Electrical
Mechanical
– Fuse(s)
– Wiring harness(es)
– Generator
– Electricalconnector(s)
– Battery junction box (BJB)
– Battery
– Battery cables
– Battery monitoring sensor (BMS)
– Charging system warning indicator
–
Accessory drive belt
– Generator
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible)
before proceeding to the next step.
4. Check the operation of the charging system warning indicator lamp, located in the instrument
cluster. Normal operation is as follows:
Normal Charging System Voltages Charging System
Warning Indicator Operation
Engine to
battery ground
Battery
Gener-
ator B+ Circuit
I Circuit
Ignition Switch
Position
OFF
0V
10-12V
10-12V
0V
Position 0
Illuminated
0V
10-12V
10-12V
0V
Position II
OFF
0V
13-15V
13-15V
13-15V
Position II with
the engine
running
5. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Component Tests. Component Tests
Generator On-Vehicle Tests - No-Load Test
1. Turn off all electrical loads and the ignition
switch. G1055063en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 414-00-2
Charging System - General Information
414-00-2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 273 of 2057

SECTION 414-02 Generator and Regulator
VEHICLE APPLICATION:
2008.50 Kuga
PAGE
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
414-02-2
Generator ............................................................................................................................
414-02-2
Smart Charge system.........................................................................................................
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION 414-02-3
(31 414 0)
Generator — 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5.......................................... 414-02-1
Generator and Regulator
414-02-1
.TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 274 of 2057

Generator
General information
The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the
alternator charging voltage. The connection
between the PCM and the generator is made via
the control module subnetwork (LIN) bus.
If the load on the alternator is high, the PCM can
increase the idle speed.
The alternator is temporarily deactivated during
engine starting so that the engine drag moment is
minimized and it is reactivated again after the
starting procedure.
The PCM controls the charge control lamp in the
instrument cluster via the controller area network
(CAN) bus.
Smart Charge system
In addition to the familiar functions, the Smart
Charge system also performs the following
functions:
•
Automatic deactivation of non-critical high power
electrical consumers when the battery voltage
is low in order to reduce the level of current
drawn.
• Automatic activation of non-critical high power electrical consumers when the battery voltage
is excessively high in order to protect
components which are sensitive to increased
voltages.
The battery charging current is optimized through
continuous calculation of the battery temperature
and monitoring of the alternator output voltage.
By receiving the forwarded alternator load signal,
the PCM is given early warning whenever an
electric consumer is switched on or off. This means
that the PCM receives information about imminent
changes in the torque drawn by the alternator. By
evaluating this information the PCM can provide a
higher level of idling stability.
The two remaining functions of the Smart Charge
System are controlled by the GEM.
Electrical consumers are switched off due to low
voltage when the GEM determines (on the basis
of the message received from the PCM on the CAN
bus via the instrument cluster) that the battery
voltage has dropped below the threshold.
When the threshold for low battery voltage is
reached the GEM automatically deactivates the following consumers - in this order and with a gap
of 5 seconds between each:
• Electric booster heater (vehicles with diesel
engines)
• Heated exterior mirrors
• Heated rear window
• Heated windscreen
If the battery voltage rises back above the lower
threshold then the GEM re-enables all of the
electrical consumers which were previously
disabled. They then have switched off status and
must be switched back on by the driver.
Electrical consumers are switched on due to
excessively high voltage if the GEM determines
that the battery voltage is above the threshold for
overvoltage and the charge control lamp has been
switched on.
When the threshold is reached the GEM
automatically activates the following consumers -
in this order and with a gap of 5 seconds between
each:
• Heated rear window
• Heated exterior mirrors
• Electric booster heater (vehicles with diesel engines)
• Blower motor
If the battery voltage drops back below the
threshold then the GEM automatically deactivates
any consumers that were switched on. However,
if they were switched on by the driver before the
automatic activation, they will then be switched on
again in turn with a 5-second time interval. G964174en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 414-02-2
Generator and Regulator
414-02-2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 276 of 2057

7. NOTE:
Install all the bolts finger tight before
final tightening.
1. Torque: 15 Nm
2. Torque: 25 Nm
Installation
1.
To install, reverse the removal procedure.
2. Refer to: Door Window Motor Initialization
(501-11 Glass, Frames and Mechanisms,
General Procedures). G1202465en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 414-02-4
Generator and Regulator
414-02-4
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUALE6359021
Page 1798 of 2057
Starting process
The PCM enables the starting process when a key
providing a valid code is read via the PATS.
Refer to:Starting System (303-06 Starting System
- 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5, Description
and Operation).
Alternator control (Smart Charge)
The vehicle is fitted with a Smart Charging charge
system.
In this system, the charge voltage is regulated by
the PCM.
Refer to: Generator (414-02 Generator and
Regulator, Description and Operation).
Component Description
PCM
E73522
A voltage transformer integrated into the PCM
provides various components of the PCM and
sensors on the engine with a 5 volt supply.
Functions which work at battery voltage, such as
the injectors, are controlled via internal power end
stages or, like the ignition coils, via external power
end stages in the ignition coils themselves.
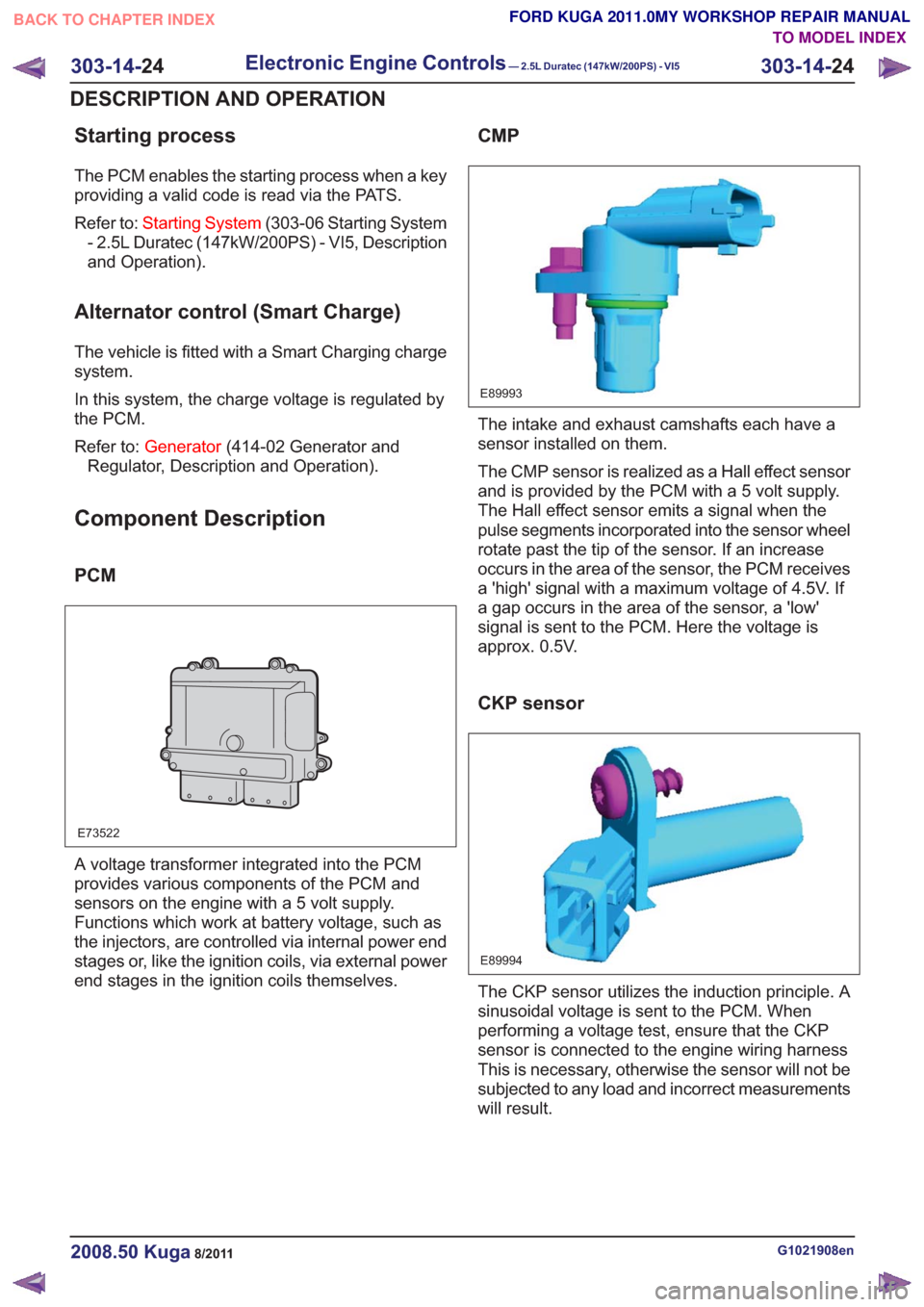
CMP
E89993
The intake and exhaust camshafts each have a
sensor installed on them.
The CMP sensor is realized as a Hall effect sensor
and is provided by the PCM with a 5 volt supply.
The Hall effect sensor emits a signal when the
pulse segments incorporated into the sensor wheel
rotate past the tip of the sensor. If an increase
occurs in the area of the sensor, the PCM receives
a 'high' signal with a maximum voltage of 4.5V. If
a gap occurs in the area of the sensor, a 'low'
signal is sent to the PCM. Here the voltage is
approx. 0.5V.
CKP sensor
E89994
The CKP sensor utilizes the induction principle. A
sinusoidal voltage is sent to the PCM. When
performing a voltage test, ensure that the CKP
sensor is connected to the engine wiring harness
This is necessary, otherwise the sensor will not be
subjected to any load and incorrect measurements
will result.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 24
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
24
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL