2011 FORD KUGA Starting system
[x] Cancel search: Starting systemPage 7 of 2057

100-00-48
Lubricants and Greases ........................................................................\
.............................
100-00-48
Transmission Fluids ........................................................................\
....................................
100-00-49
Noise ........................................................................\
..........................................................
100-00-49
Noise Insulation Materials ........................................................................\
..........................
100-00-49
O-Rings (Fluoroelastomer) ........................................................................\
.........................
100-00-49
Paints ........................................................................\
..........................................................
100-00-50
Pressurized Equipment ........................................................................\
..............................
100-00-50
Solder ........................................................................\
.........................................................
100-00-50
Solvents ........................................................................\
......................................................
100-00-50
Sound Insulation ........................................................................\
.........................................
100-00-50
Suspended Loads ........................................................................\
.......................................
100-00-50
Transmission Brake Bands ........................................................................\
.........................
100-00-50
Underseal ........................................................................\
...................................................
100-00-50
Viton ........................................................................\
............................................................
100-00-51
Welding ........................................................................\
.......................................................
100-00-52
Warning Symbols on Vehicles ........................................................................\
....................
100-00-53
White Spirit ........................................................................\
.................................................
100-00-54
Standard Workshop Practices ........................................................................\
....................
100-00-54
Vehicle in Workshop ........................................................................\
...................................
100-00-54
Towing the Vehicle ........................................................................\
......................................
100-00-54
Connecting a Slave Battery Using Jumper Cables ............................................................
100-00-55
Component Cleaning ........................................................................\
..................................
100-00-55
Calibration of Essential Measuring Equipment ...................................................................
100-00-57
Solvents, Sealants and Adhesives ........................................................................\
.............
100-00-57
Introduction ........................................................................\
.................................................
100-00-58
Road/Roller Testing ........................................................................\
....................................
100-00-58
Pre-Test Checks ........................................................................\
.........................................
100-00-58
Starting the Engine ........................................................................\
.....................................
100-00-58
Road or Roller Testing ........................................................................\
................................
100-00-59
Brake Testing ........................................................................\
..............................................
100-00-60
Air Conditioning (A/C) System Health and Safety Precautions ..........................................
100-00-61
Battery and Battery Charging Health and Safety Precautions ............................................
100-00-62
Brake System Health and Safety Precautions
....................................................................
100-00-63
Engine
Cooling System Health and Safety Precautions .....................................................
100-00-64
Petrol and Petrol-Ethanol Fuel Systems Health and Safety Precautions ...........................
100-00-65
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) Health and Safety Precautions .............................
100-00-66
Window Glass Health and Safety Precautions ...................................................................
100-00-67
Body Repair Health and Safety and General Precautions .................................................
100-00-67
General ........................................................................\
.......................................................
100-00-68
Personal protection ........................................................................\
.....................................
100-00-69
Protection of the vehicle ........................................................................\
.............................
100-00-2
General Information
100-00- 2
.
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
PAGE 2 OF 2 FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 63 of 2057

Road/Roller Testing
Road or roller testing may be carried out for various
reasons and a procedure detailing pre-test checks,
engine starting and stopping, pre-driving checks,
on-test checks and final checks to be completed
on completion of the test is given below.
Unless complete vehicle performance is being
checked, the full road test procedure need not be
carried out. Instead, those items particularly
relevant to the system(s) being checked can be
extracted.
Pre-Test Checks
WARNING: If the brake system hydraulic
fluid level is low, pedal travel is excessive
or a hydraulic leak is found, do not attempt
to road test the vehicle until the reason for
the low fluid level, excessive pedal travel
or hydraulic leak is found and rectified.
It is suggested that pre-test checks and functional
tests of those systems and circuits which affect the
safe and legal operations of the vehicle, such as
brakes, lights and steering, should always be
carried out before the road or roller test.
With the ignition switched off, check:
– the engine oil level.
– the engine coolant level.
– the tires, for correct pressure, compatible types and tread patterns, and wear within limits.
– that there is sufficient fuel in the tank to complete the test.
– all around the engine, transmission and under the vehicle for oil, coolant, hydraulic and fuel
leaks. Make a note of any apparent leaks and
wipe off the surrounding areas to make it easier
to identify the extent of the leak on completion
of the test.
Starting the Engine
NOTE: On initial drive away from cold and within
the first 1.5 km (1 mile), do not depress the
accelerator pedal beyond half travel until the
vehicle has attained a minimum speed of 25 km/h
(15 miles/h). Never operate at high engine speed
or with the accelerator pedal at full travel whilst the
engine is cold.
With the ignition switched off, check: – that the parking brake is applied.
– that the gear lever is in the neutral position.
– that all instrument gauges (except fuel gauge)
read zero.
With the ignition switched on, check:
– that the ignition controlled warning lamps are illuminated.
– that the engine temperature gauge registers a reading compatible with the engine temperature.
– that the fuel gauge registers a reading appropriate to the fuel level in the tank.
– the operation of the parking brake warning lamp and fluid level warning indicator.
Road or Roller Testing
CAUTION: If road testing, check the brake
operation while still traveling at low speed
before continuing with the test. If the
brakes pull to one side, or appear to be
otherwise faulty, do not continue with the
road test until the fault has been found and
rectified.
During the road or roller test, check:
– that the clutch pedal operation is not stiff or heavy.
– that the initial gear engagement is smooth and there is no evidence of clutch drag.
– that the parking brake control operates smoothly and releases quickly and completely.
– that the clutch takes up the drive smoothly, without slip or judder.
– that gear changing is smooth with no abnormal noises or vibrations from the transmission.
– the engine power output is satisfactory, full power is achieved, acceleration is smooth and
pedal operation is not stiff or heavy, and engine
speed returns to idle correctly.
– there is no excessive or abnormally colored smoke from the engine under normal driving,
heavy load or overrun conditions.
– that steering operation, including power steering (if equipped), is smooth, accurate, not
excessively heavy or with excessive free play
or vibration.
– that the steering does not pull to one side and self centers smoothly after cornering.
G17375en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
100-00- 58
General Information
100-00- 58
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 80 of 2057

Noise Conditions
• Gear noise is typically a howling or whining dueto gear damage or incorrect bearing preload. It
can occur at various speeds and driving
conditions, or it can be continuous.
• Chuckle is a particular rattling noise that sounds like a stick against the spokes of a spinning
bicycle wheel. It occurs while decelerating from
64 km/h (40 mph) and can usually be heard all
the way to a stop. The frequency varies with
vehicle speed.
• Knock is very similar to chuckle, though it may be louder and occurs on acceleration or
deceleration. The teardown will disclose what
has to be corrected.
Clicking, popping or grinding noises may be caused
by the following:
• worn, damaged or incorrectly installed wheel bearing, suspension or brake component.
Check and rule out tires, exhaust and trim items
before disassembling the transmission to diagnose
and correct gear noise.
The noises described under Road Test usually
have specific causes that can be diagnosed by
observation as the unit is disassembled. The initial
clues are the type of noise heard on the road test
and driving conditions.
Vibration Conditions
Vibration at highway speeds may be caused by
the following:
• out-of-balance front or rear wheels.
• out-of-round tires.
Shudder or vibration during acceleration may be
caused by the following:
• damaged powertrain/drivetrain mounts.
• excessively high constant velocity (CV) joint operating angles caused by incorrect ride height.
Check ride height, verify correct spring rate and
check items under inoperative conditions.
Road Test
A gear-driven unit will produce a certain amount
of noise. Some noise is acceptable and may be
audible at certain speeds or under various driving
conditions, as on a newly paved asphalt road. The slight noise is in no way detrimental and must be
considered normal.
The road test and customer interview (if available)
provide information needed to identify the condition
and give direction to the correct starting point for
diagnosis.
1. Make notes throughout the diagnosis routine.
Make sure to write down even the smallest bit
of information, because it may turn out to be the
most important.
2. Do not touch anything until a road test and a thorough visual inspection of the vehicle have
been carried out. Leave the tire pressures and
vehicle load just where they were when the
condition was first observed. Adjusting tire
pressures, vehicle load or making other
adjustments may reduce the condition(s)
intensity to a point where it cannot be identified
clearly. It may also inject something new into
the system, preventing correct diagnosis.
3. Make a visual inspection as part of the preliminary diagnosis routine, writing down
anything that does not look right. Note tire
pressures, but do not adjust them yet. Note
leaking fluids, loose nuts and bolts, or bright
spots where components may be rubbing
against each other. Check the load space for
unusual loads.
4. Road test the vehicle and define the condition by reproducing it several times during the road
test.
5. Carry out the Road Test Quick Checks as soon as the condition is reproduced. This will identify
the correct diagnostic procedure. Carry out the
Road Test Quick Checks more than once to
verify they are providing a valid result.
Remember, the Road Test Quick Checks may
not tell where the concern is, but they will tell
where it is not.
Road Test Quick Checks
1. 24-80 km/h (15-50 mph): with light acceleration,a moaning noise is heard and possibly a
vibration felt in the front floor panel. It is usually
worse at a particular engine speed and at a
particular throttle setting during acceleration at
that speed. It may also produce a moaning
sound, depending on what component is
causing it. REFER to Tip-in Moan in the
Driveline Noise and Vibration Symptom Chart.
2. Acceleration/Deceleration: With slow acceleration and deceleration, a shake is
G37349en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
100-04- 3
Noise, Vibration and Harshness
100-04- 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 166 of 2057
Description
Item
Glow plug
1
Combustion Air Blower
2
Fuel pump
3
Fuel-fired heater on
4
Fuel-fired heater - large regulating step
5
Fuel-fired heater - small regulating step
6 Description
Item
Fuel-fired heater off
7
Blower motor on
8
Flame detection
9
Blower motor off
10
Large regulating step
11
Small regulating step
12
Boost heat mode
When the engine is running, the booster heater
helps the engine to heat the passenger
compartment at low ambient temperatures.
When the coolant temperature reaches 30 °C, the
control unit transmits a switch-on signal for the
passenger compartment blower via the CAN bus.
When the coolant temperature drops, the blower
remains on until the temperature reaches 20 °C
whereupon it is deactivated.
The fuel tank must be filled to at least 14% for the
system to be switched on. If the fuel level drops
below 8% then the system is switched off.
In boost mode, the fuel fired booster heater is only
switched on if all of the following criteria are met:
• Engine speed above 500 rpm. The fuel fired booster heater is not allowed to start up while
the engine is being cranked; this prevents a
shut-down due to low voltage if the battery
charge is low.
• Ambient temperature below 5 °C.
• Fuel level above 14% of total capacity.
• Function is active on the trip computer menu.
One of the following conditions is sufficient to
switch off the booster heater in boost heat mode:
• Engine speed below 500 rpm.
• Ambient temperature above 11 °C.
• Function is active on the trip computer menu.
• Fuel level below 8% of total capacity.
Programmable fuel fired booster heater
The programmable fuel fired booster heater has
two operating modes:
• Instant start
• Programmed start
The heater status is displayed on the instrument
cluster display. The parking heater mode is controlled via a menu in the message centre. The
fuel fired booster heater can be activated and
deactivated via the message centre. (If set to 'Auto'
the system is activated, if set to 'Off' the system is
completely deactivated)
Immediate start-up of the booster
heater
This function enables the fuel-fired booster heater
to be switched on manually when the engine is not
running. This function is activated via the menu on
the driver information system.
The ignition key must be in the II" position before
this menu can be accessed. The timer function of
the booster heater remains active when the ignition
key is in position "0".
After an immediate start-up of the booster heater
it is switched off again after 30 minutes (or if the
fuel level in the fuel tank drops below 8%). The
booster heater stops within 2 minutes of the engine
starting. This leaves enough time to check whether
the switch-on conditions for boost heat mode have
been met, thus preventing the booster heater from
having to switch off and switch back on again. The
heater can be switched off manually at any time
from the menu.
Programmed start-up of the booster
heater
The driver can use a menu to adjust the time at
which the vehicle is to be pre-heated. The following
options are available:
• Time setting. One or two times can be
programmed for each day of the week. It is
possible to program days either individually or
together in groups (Mon-Sun/Mon-Sat/Mon-Fri).
• Time and data setting
With the first option, the fuel-fired booster heater
will start repeatedly without needing to be G1066982en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 412-02-13
Auxiliary Climate Control
412-02-13
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 167 of 2057

reprogrammed. However, if the engine hasn't been
run since the last programmed start, the fuel-fired
booster heater will not start up the second time so
as to prevent the battery from being discharged.
The length of time required to pre-heat the vehicle
is calculated in the control unit of the fuel-fired
booster heater and is based on two temperature
values:
• Ambient air temperature: this message is taken
from the GEM via the CAN bus.
• Coolant temperature: this is determined via an internal sensor in the fuel-fired booster heater.
The maximum heating time is 30 minutes at an
outside air temperature of -10 °C or lower. The
heating time decreases proportionally with
increasing ambient temperature until the ambient
temperature is between +15 °C and +20 °C. Then
the minimum heating time is 10 minutes. The
parking heater is deactivated at temperatures
above +20 °C.
The sequence for a programmed start of the
booster heater is as follows:
• Two minutes before the start of the maximum heating time the driver information
system/instrument cluster sends an activation
message to the fuel-fired booster heater via the
CAN bus.
• The fuel-fired booster heater calculates the required heating time and, if necessary, sends
a delay request on the CAN bus.
• At the calculated time, the fuel-fired booster heater starts up. The conditions for start-up are:
engine not running and amount of fuel in the
fuel tank is above 14% of maximum.
• When the coolant temperature reaches +30 °C, the control unit of the fuel-fired booster heater
sends a request to switch on the passenger
compartment blower.
• Eight minutes after the programmed switch-off time, the booster heater stops heating mode
and starts a run-on operation to clean the
system's spark plugs.
• Ten minutes after the switch-off time, the post-cleaning operation is complete. The
additional ten minutes run-on time provides
some leeway in case the driver is late arriving.
After a programmed start-up of the booster heater
it is switched off again after the heating time has
elapsed (or if the fuel level in the fuel tank drops
below 8%). The booster heater stops within 2 minutes of the engine starting. This leaves enough
time to check whether the switch-on conditions for
boost heat mode have been met, thus preventing
the booster heater from having to switch off and
switch back on again. The heater can be switched
off manually at any time from the menu.
Whilst the fuel-fired booster heater is in additional
heating mode and/or parking heating mode, the
instrument cluster receives a fuel consumption
signal; this is used to re-calculate the vehicle's
remaining range and fuel consumption data.
Emergency shutoff
In the event of an accident in which the airbags
are deployed, the control unit of the fuel-fired
booster heater receives a message on the CAN
bus from the restraints control module (RCM).
When this message is received, the booster heater
system switches off immediately.
The booster heater control module deactivates the
system and does not respond to further messages
on the CAN bus. The booster heater control module
needs to be activated with WDS.
Component Description
Electric Booster Heater
The electric booster heater consists of three
individual heating elements, which are incorporated
into a single housing. It is controlled by the generic
electronic module (GEM), taking into account the
following factors:
Detailed illustration of fuel-fired heater
G1066982en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 412-02-14
Auxiliary Climate Control
412-02-14
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUALE97621
Page 169 of 2057
Description
Item
Combustion chamber
16
'O' Ring
17 Description
Item
Combustion blower motor cover
18
Glow plug wiring harness
19
Flame sensor
If the flame goes out independently during
operation of the booster heater, a restart is carried
out. If the booster heater does not ignite within 90
seconds of fuel delivery or if the flame goes out
within 15 minutes of starting, a lockout will be
implemented by the flame sensor.
Lockout can be cancelled by switching the booster
heater off then on again, although this may only
be repeated at most 2 times.
Overheat Sensor
The overheating sensor enables the fuel-fired
booster heater module to determine the coolant
temperature, protecting the heater from
overheating. The overheating sensor is installed
next to the coolant temperature sensor under a
cover on the top of the fuel-fired heater.
In the event of overheating (lack of water, poorly
ventilated coolant circuit), the fuel supply to the
heater is interrupted and a lockout occurs. After
the cause of the overheating has been eliminated,
the heater can be restarted by switching it off and
on again, if the coolant temperature is below 70°C.
If the heater overheats ten times in a row, the
control unit is locked.
ECT
The fuel-fired booster heater module uses the
temperature sensor to determine the coolant
temperature, which it then uses to set the starting
and stopping time. The coolant temperature sensor
is installed next to the overheating sensor under a
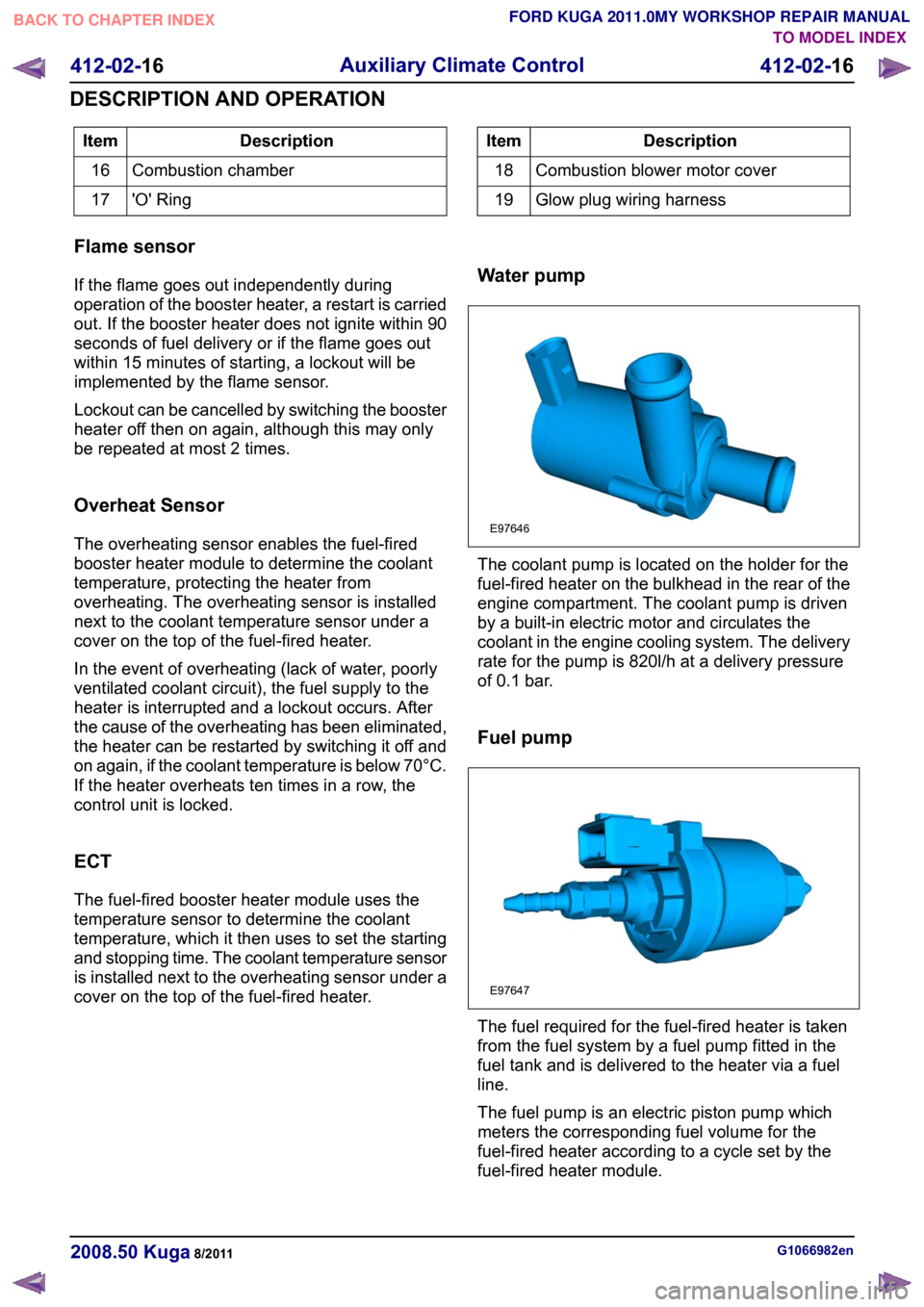
cover on the top of the fuel-fired heater. Water pump The coolant pump is located on the holder for the
fuel-fired heater on the bulkhead in the rear of the
engine compartment. The coolant pump is driven
by a built-in electric motor and circulates the
coolant in the engine cooling system. The delivery
rate for the pump is 820l/h at a delivery pressure
of 0.1 bar.
Fuel pump
The fuel required for the fuel-fired heater is taken
from the fuel system by a fuel pump fitted in the
fuel tank and is delivered to the heater via a fuel
line.
The fuel pump is an electric piston pump which
meters the corresponding fuel volume for the
fuel-fired heater according to a cycle set by the
fuel-fired heater module.
G1066982en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 412-02-16
Auxiliary Climate Control
412-02-16
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUALE97646 E97647
Page 274 of 2057

Generator
General information
The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the
alternator charging voltage. The connection
between the PCM and the generator is made via
the control module subnetwork (LIN) bus.
If the load on the alternator is high, the PCM can
increase the idle speed.
The alternator is temporarily deactivated during
engine starting so that the engine drag moment is
minimized and it is reactivated again after the
starting procedure.
The PCM controls the charge control lamp in the
instrument cluster via the controller area network
(CAN) bus.
Smart Charge system
In addition to the familiar functions, the Smart
Charge system also performs the following
functions:
•
Automatic deactivation of non-critical high power
electrical consumers when the battery voltage
is low in order to reduce the level of current
drawn.
• Automatic activation of non-critical high power electrical consumers when the battery voltage
is excessively high in order to protect
components which are sensitive to increased
voltages.
The battery charging current is optimized through
continuous calculation of the battery temperature
and monitoring of the alternator output voltage.
By receiving the forwarded alternator load signal,
the PCM is given early warning whenever an
electric consumer is switched on or off. This means
that the PCM receives information about imminent
changes in the torque drawn by the alternator. By
evaluating this information the PCM can provide a
higher level of idling stability.
The two remaining functions of the Smart Charge
System are controlled by the GEM.
Electrical consumers are switched off due to low
voltage when the GEM determines (on the basis
of the message received from the PCM on the CAN
bus via the instrument cluster) that the battery
voltage has dropped below the threshold.
When the threshold for low battery voltage is
reached the GEM automatically deactivates the following consumers - in this order and with a gap
of 5 seconds between each:
• Electric booster heater (vehicles with diesel
engines)
• Heated exterior mirrors
• Heated rear window
• Heated windscreen
If the battery voltage rises back above the lower
threshold then the GEM re-enables all of the
electrical consumers which were previously
disabled. They then have switched off status and
must be switched back on by the driver.
Electrical consumers are switched on due to
excessively high voltage if the GEM determines
that the battery voltage is above the threshold for
overvoltage and the charge control lamp has been
switched on.
When the threshold is reached the GEM
automatically activates the following consumers -
in this order and with a gap of 5 seconds between
each:
• Heated rear window
• Heated exterior mirrors
• Electric booster heater (vehicles with diesel engines)
• Blower motor
If the battery voltage drops back below the
threshold then the GEM automatically deactivates
any consumers that were switched on. However,
if they were switched on by the driver before the
automatic activation, they will then be switched on
again in turn with a 5-second time interval. G964174en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 414-02-2
Generator and Regulator
414-02-2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATIONTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 290 of 2057

Cellular Phone
Refer to
Wiring Diagrams Section 415-00, for
schematic and connector information. General Equipment
Ford diagnostic equipment
Principles of Operation
NOTE: Voice control will only operate with the
audio unit and components required switched ON.
Voice Control
The portable support electronics (PSE) module
has a voice control system. The customer will be
able to push the VOICE button on the audio control
switch located on the steering column lower
shroud, this will activate the PSE module and allow
voice control. An audible tone will be heard through
the audio unit speakers after which, a voice
command can then be spoken into the microphone
located in the overhead console.
The incoming calls and voice confirmation can be
heard through the audio system speakers.
When a voice command is spoken into the
microphone it will be sent as a signal to the PSE
module. The signal is then sent from the PSE
module to the relevant components on the
medium-speed controller area network (CAN) bus
network. The component will then convert the
signal back into the original voice command.
The components that the PSE module interacts
with are as follows:
• audio unit
• navigation system display module
• cellular phone
For additional information on the cellular phone
system, REFER to the cellular phone Owner's
Guide.
Bluetooth
An input can be given through the cellular phone
with or without the cellular phone connected to the
handset holder. Providing that the cellular phone
is one of the recommended cellular phones for the
system, is supplied with the Bluetooth technology
and the cellular phone is programmed to the PSE
module.
When selected as active the Bluetooth technology
is a wireless system that interacts with the relevant component modules through the PSE module. The
general operation of the Bluetooth is similar to the
voice control.
Bluetooth technology cannot transfer the cellular
phone's PHONEBOOK or recent outgoing and
incoming call details to the audio unit or navigation
system display module. If the cellular phone is
placed into the handset holder the PHONEBOOK
data and recent outgoing and incoming call
information will be transferred to the audio unit or
navigation system display module.
For additional information, REFER to the cellular
phone Owner's Guide.
Inspection and Verification
NOTE: Make sure that the cellular phone is
featured on the list of recommended cellular
phones for the system.
Make sure that the PSE module and cellular
phone are configured to each other before
starting a system diagnosis. ENTER the
following PIN number on the cellular phone to
configure the cellular phone to the PSE module:
0000.
Make sure that the MUTE symbol is not
displayed on the audio unit when trying to
operate the cellular phone system. If the MUTE
symbol is displayed, this indicates that the PSE
module requires configuring to the vehicle and
the cellular phone requires programming to the
PSE module. GO to
Pinpoint Test C.
1. Verify the customer concern by operating the system using the customers cellular phone.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of electrical damage.
Visual Inspection Chart Electrical
• Fuse(s)
• Wiring harness
• Electrical connector(s)
• Cellular phone
• Microphone
• PSE module
• Audio unit
• Instrument cluster
• Navigation system display module G1189085en
2008.50 Kuga 8/2011 415-00-4
Information and Entertainment System -
General Information
415-00-4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGTO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL