2011 FORD KUGA Throttle
[x] Cancel search: ThrottlePage 1722 of 2057

Description
Item
PWM (pulse width modulation) signal
Comments:from PCM (powertrain control module)
5
Atmospheric pressure
6
Turbocharger boost pressure.
7
from air filter
8
Intake air
9Description
Item
Recirculated air valveRefertoComponentDescription:(page
7)
10
Vacuum line, recirculated air valve
11
to intake manifold
12
Throttle plate
13
Compressor
14
Turbine
15
System Operation
Turbocharger(s)
The TC consists of a turbine and a compressor.
The turbine is driven by the exhaust gas flow. A
common shaft drives the compressor and this then
compresses the intake air.
Turbocharger boost pressure control
E98942
1
2
3
4
Description
Item
Atmospheric pressure
1
Turbocharger boost pressure.
2
Wastegate control valve
3
Pilot pressure
4
The size of the TC is designed to produce a charge
effect even at medium engine speeds and lower
exhaust gas flows. This means that, when the engine speed is high and there is a large amount
of exhaust gas, either the boost pressure of the
TC will become too high or its speed will be too
high. The TC must therefore be regulated. The
best regulation is achieved by an electronically
controlled wastegate control valve. The wastegate
control valve controls the pressure on the
membrane in the boost pressure regulator.
The wastegate control valve is actuated by the
PCM with a PWM signal according to a map. The
boost pressure is applied to the wastegate control
valve via the pressure line from the compressor.
This pressure is passed to the boost pressure
regulator via the wastegate control valve. This
opens the bypass valve using a linkage. This
channels a portion of the exhaust gases around
the turbine. If the wastegate control valve is
actuated by the PCM, a bypass is opened in the
wastegate control valve. This causes the pressure
which can act on the membrane in the boost
pressure regulator to be reduced. This occurs until
the boost pressure has reached a set value. By
actuation with a PWM signal, it is also possible to
partially open or close the wastegate control valve.
This results in a constant boost pressure and
therefore high torque over a wide range of engine
speeds.
Because the PCM calculates the boost pressure
using the signal from the boost pressure sensor
and the IAT (intake air temperature) sensor, the
atmospheric pressure and the temperature are
automatically compensated for. Because of this
compensation, the engine power is not noticeably
affected by variations in atmospheric temperature
or pressure.
G1032426en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04B-
6
Fuel Charging and Controls - Turbocharger
—
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-04B- 6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1723 of 2057
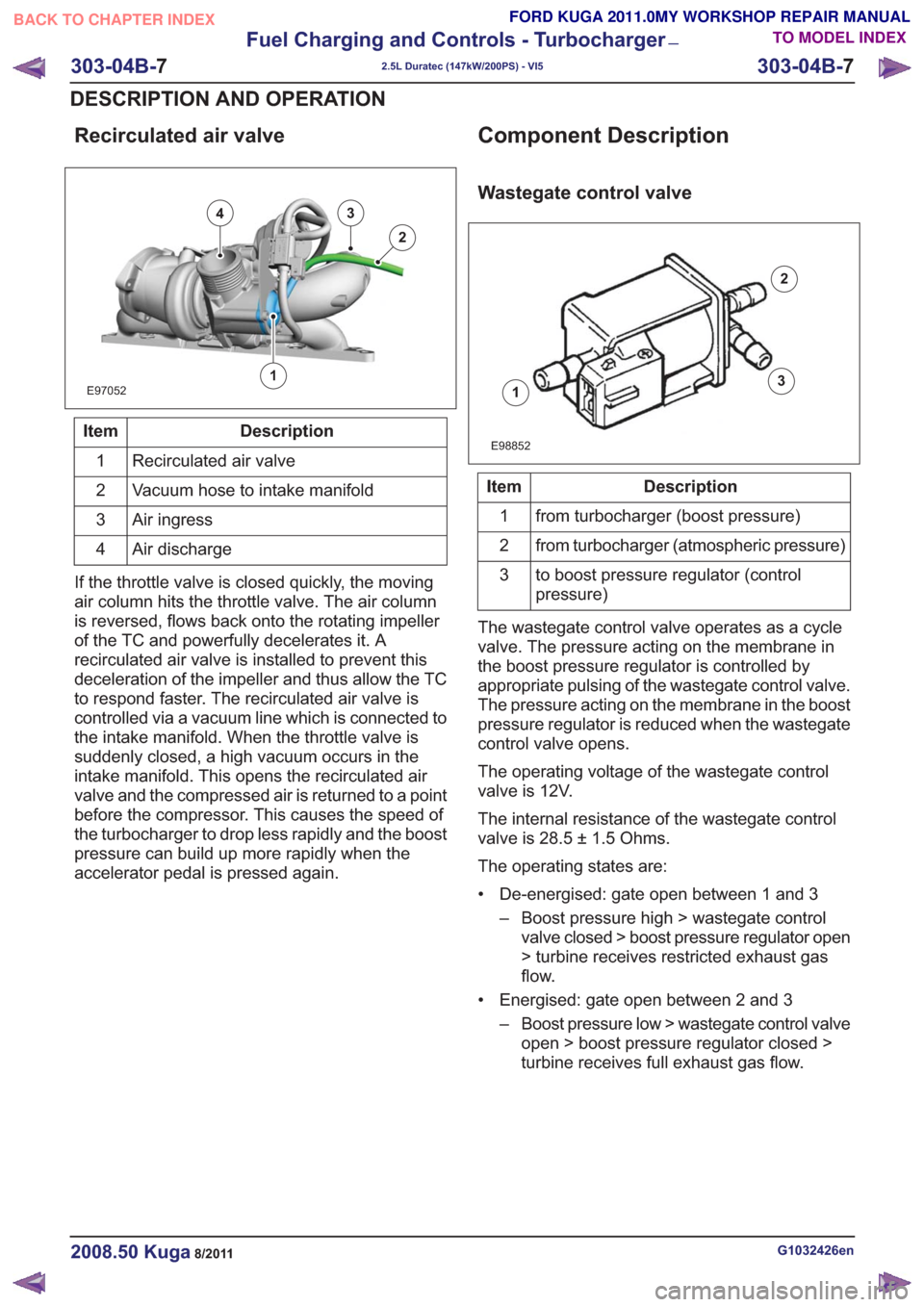
Recirculated air valve
E97052
43
2
1
Description
Item
Recirculated air valve
1
Vacuum hose to intake manifold
2
Air ingress
3
Air discharge
4
If the throttle valve is closed quickly, the moving
air column hits the throttle valve. The air column
is reversed, flows back onto the rotating impeller
of the TC and powerfully decelerates it. A
recirculated air valve is installed to prevent this
deceleration of the impeller and thus allow the TC
to respond faster. The recirculated air valve is
controlled via a vacuum line which is connected to
the intake manifold. When the throttle valve is
suddenly closed, a high vacuum occurs in the
intake manifold. This opens the recirculated air
valve and the compressed air is returned to a point
before the compressor. This causes the speed of
the turbocharger to drop less rapidly and the boost
pressure can build up more rapidly when the
accelerator pedal is pressed again.
Component Description
Wastegate control valve
1
2
3
E98852
Description
Item
from turbocharger (boost pressure)
1
from turbocharger (atmospheric pressure)
2
to boost pressure regulator (control
pressure)
3
The wastegate control valve operates as a cycle
valve. The pressure acting on the membrane in
the boost pressure regulator is controlled by
appropriate pulsing of the wastegate control valve.
The pressure acting on the membrane in the boost
pressure regulator is reduced when the wastegate
control valve opens.
The operating voltage of the wastegate control
valve is 12V.
The internal resistance of the wastegate control
valve is 28.5 ± 1.5 Ohms.
The operating states are:
• De-energised: gate open between 1 and 3 – Boost pressure high > wastegate controlvalve closed > boost pressure regulator open
> turbine receives restricted exhaust gas
flow.
• Energised: gate open between 2 and 3 – Boost pressure low > wastegate control valveopen > boost pressure regulator closed >
turbine receives full exhaust gas flow.
G1032426en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04B- 7
Fuel Charging and Controls - Turbocharger
—
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-04B- 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1767 of 2057
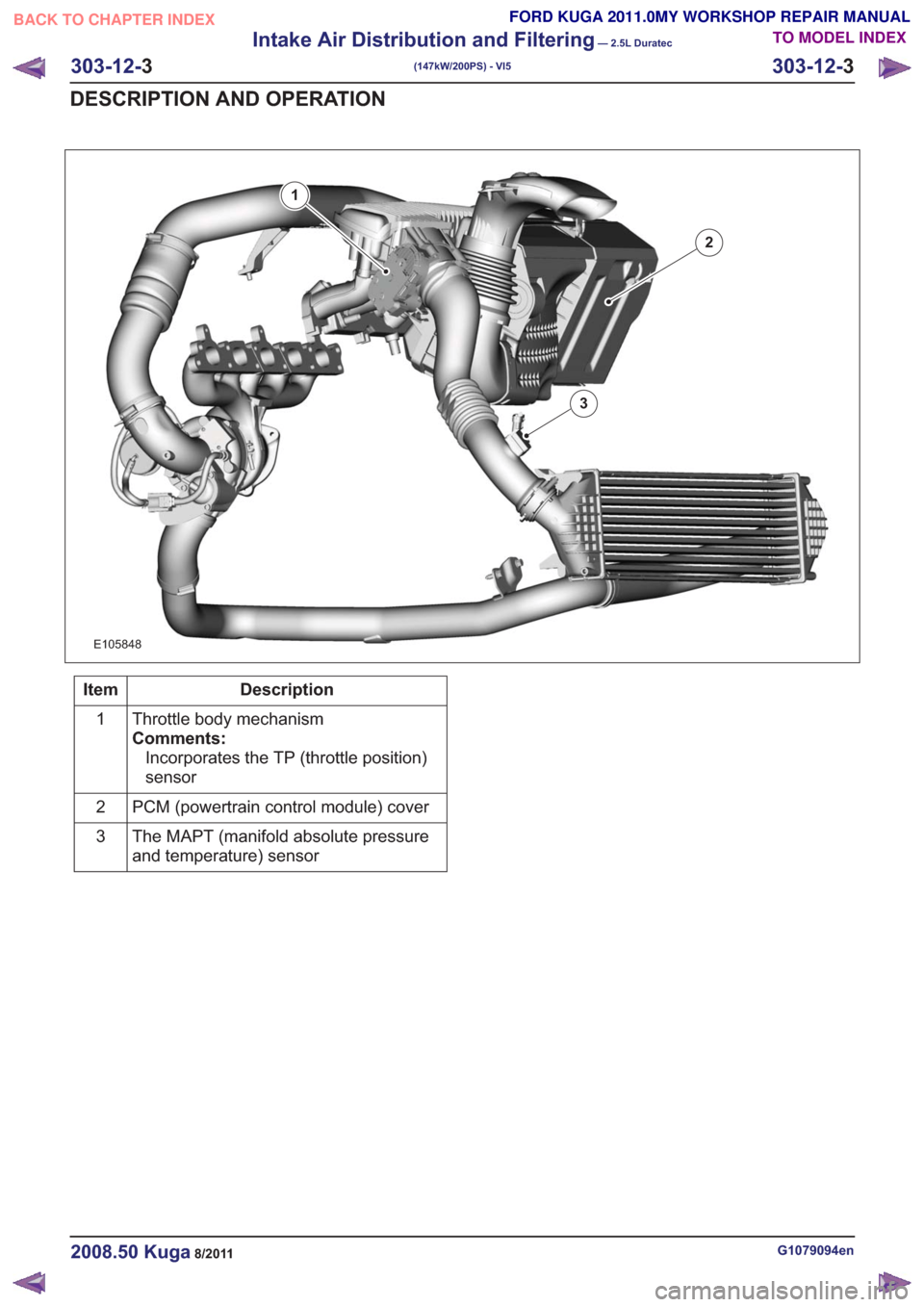
E105848
1
2
3
Description
Item
Throttle body mechanism
Comments:Incorporates the TP (throttle position)
sensor
1
PCM (powertrain control module) cover
2
The MAPT (manifold absolute pressure
and temperature) sensor
3
G1079094en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-12-
3
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering
— 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-12- 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1775 of 2057

SECTION 303-14 Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5
VEHICLE APPLICATION: 2008.50 Kuga
PA G E
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
303-14-3
Electronic Engine Controls (Component Location) .............................................................
303-14-7
Electronic Engine Controls (Overview) ........................................................................\
.......
303-14-7
General overview ........................................................................\
........................................
303-14-8
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) ........................................................................\
..............
303-14-8
Knock Sensor ........................................................................\
.............................................
303-14-8
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor ........................................................................\
...............
303-14-9
Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor ........................................................................\
..............
303-14-9
Camshaft adjuster solenoid valve........................................................................\
...............
303-14-9
Manifold absolute pressure and temperature sensor .........................................................
303-14-9
Accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor ........................................................................\
....
303-14-10
Throttle control unit ........................................................................\
.....................................
303-14-10
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.......................................................................
303-14-10
Ignition coil-on-plug ........................................................................\
....................................
303-14-12
Electronic Engine Controls (System Operation and Component Description) ...................
303-14-12
System Diagram ........................................................................\
.........................................
303-14-16
System Operation ........................................................................\
.......................................
303-14-18
Speed and TDC recording ........................................................................\
......................
303-14-19
Calculation of the ignition angle ........................................................................\
..............
303-14-20
Engine fueling ........................................................................\
.........................................
303-14-22
Engine speed control ........................................................................\
..............................
303-14-22
Oil monitoring ........................................................................\
..........................................
303-14-23
Calculation of valve timing adjustment angle..................................................................
303-14-23
Boost pressure control ........................................................................\
............................
303-14-24
Starting process ........................................................................\
......................................
303-14-24
Alternator control (Smart Charge) ........................................................................\
...........
303-14-24
Component Description ........................................................................\
..............................
303-14-24
CKP sensor ........................................................................\
.............................................
303-14-25
Broadband HO2S ........................................................................\
...................................
303-14-26
VCT (variable camshaft timing) solenoids ......................................................................
303-14-27
MAF sensor ........................................................................\
.............................................
303-14-28
APP sensor ........................................................................\
.............................................
303-14-29
CPP sensor ........................................................................\
.............................................
303-14-29
BPP switches ........................................................................\
..........................................
303-14-30
Air conditioning (A/C) pressure sensor ........................................................................\
...
303-14-30
Throttle
control unit ........................................................................\
.................................
303-14-31
ECT sensor ........................................................................\
.............................................
303-14-31
Cooling fan module ........................................................................\
.................................
303-14-32
injectors........................................................................\
...................................................
303-14-32
Ignition coil-on-plug ........................................................................\
.................................
303-14-33
Fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensor ........................................................................\
...
303-14-33
Wastegate control valve ........................................................................\
..........................
303-14-34
Engine oil level, temperature and quality sensor ............................................................
303-14-1
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
1
.
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
PAGE 1 OF 2
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1777 of 2057
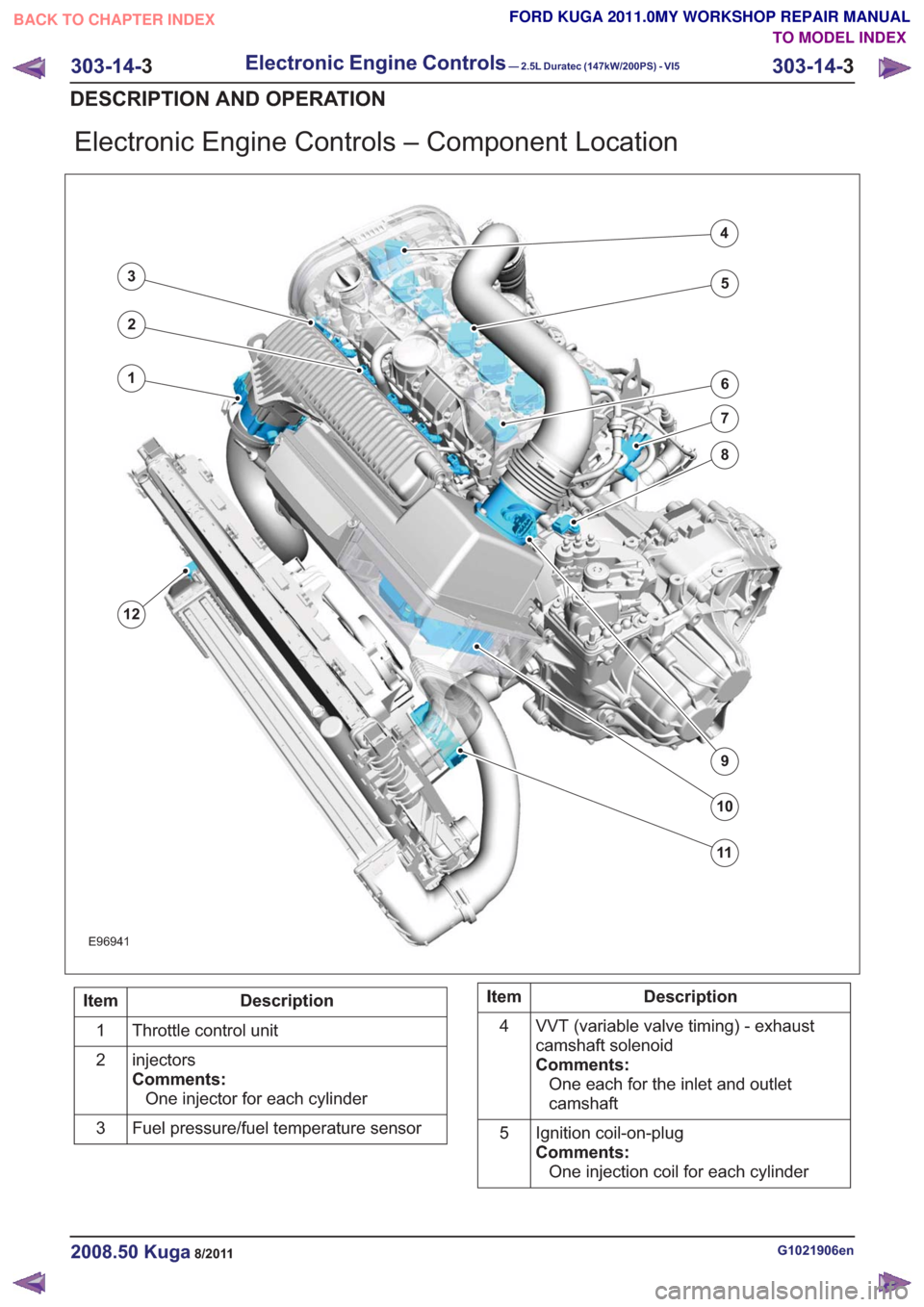
Electronic Engine Controls – Component Location
E96941
1
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Description
Item
Throttle control unit
1
injectors
Comments:One injector for each cylinder
2
Fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensor
3Description
Item
VVT (variable valve timing) - exhaust
camshaft solenoid
Comments:One each for the inlet and outlet
camshaft
4
Ignition coil-on-plug
Comments:One injection coil for each cylinder
5
G1021906en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-
3
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1779 of 2057
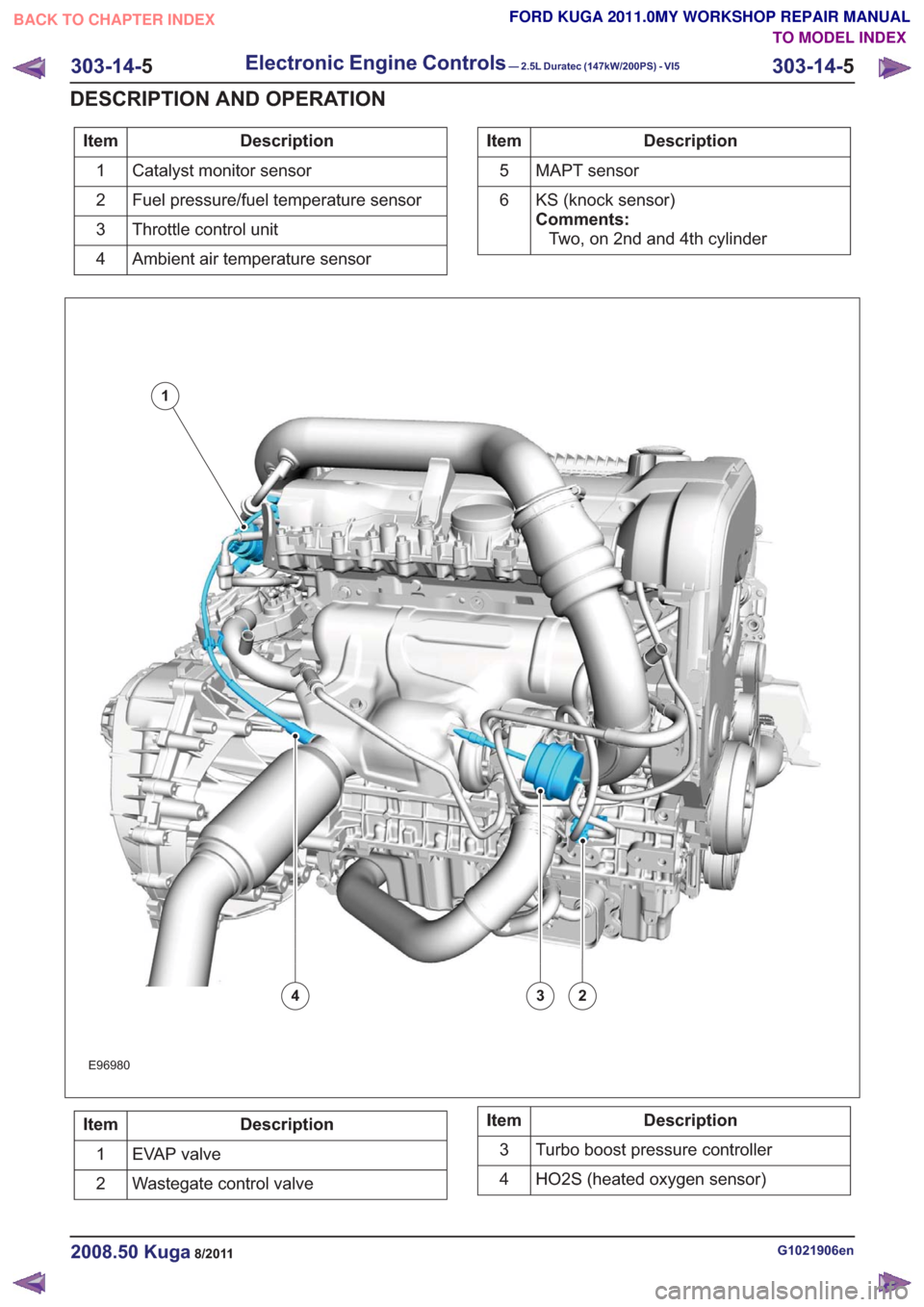
Description
Item
Catalyst monitor sensor
1
Fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensor
2
Throttle control unit
3
Ambient air temperature sensor
4Description
Item
MAPT sensor
5
KS (knock sensor)
Comments:Two, on 2nd and 4th cylinder
6
E96980
1
234
Description
Item
EVAP valve
1
Wastegate control valve
2Description
Item
Turbo boost pressure controller
3
HO2S (heated oxygen sensor)
4
G1021906en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 5
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1781 of 2057
Electronic Engine Controls – Overview
General overview
Engine Management System
• Bosch ME 9.0 engine management system
• Knock control with two knock sensors
• Electronic Throttle Control Unit.
• Electronic accelerator pedal
• Variable camshaft timing for intake and exhaustcamshafts • Fuel injection supply manifold with combined
fuel pressure and temperature sensor
• Sequential multi-port fuel injection
• Camshaft position (CMP) sensors for intake and exhaust camshafts.
• satisfies the European exhaust emissions standard IV
• EOBD (European On-board Diagnostic) for the monitoring of emissions-related components.
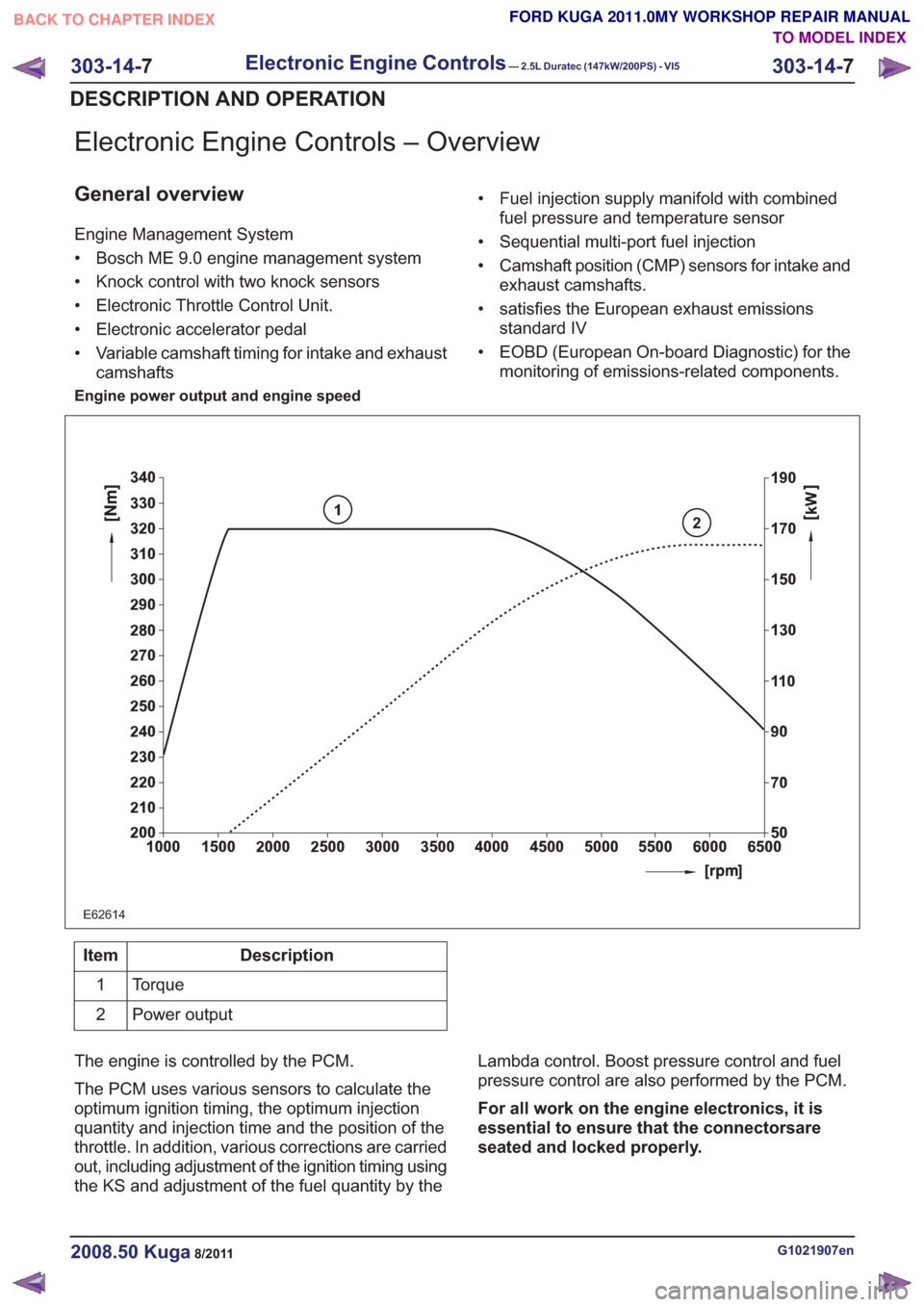
Engine power output and engine speed
2
E62614
1
Description
Item
Torque
1
Power output
2
The engine is controlled by the PCM.
The PCM uses various sensors to calculate the
optimum ignition timing, the optimum injection
quantity and injection time and the position of the
throttle. In addition, various corrections are carried
out, including adjustment of the ignition timing using
the KS and adjustment of the fuel quantity by the Lambda control. Boost pressure control and fuel
pressure control are also performed by the PCM.
For all work on the engine electronics, it is
essential to ensure that the connectorsare
seated and locked properly.
G1021907en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-
7
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1782 of 2057
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
E65160
The PCM communicates with all engine sensors
and the other modules. Communication of the PCM
with the other modules and the system diagnostics
takes place via the CAN (controller area network)
data bus.
The following functions are regulated or controlled
by the PCM:
• Fuel supply to the engine including lambdacontrol
• Ignition setting including knock control
• Idle speed control
• Control of optimum valve timing via the camshaft adjustment for intake and exhaust camshafts
• The refrigerant compressor is controlled by the air conditioning clutch relay and the delivery of
the refrigerant compressor is controlled by a
PWM (pulse width modulation) signal.
• Control of EVAP purge valve
• Boost pressure control
• Control of the cooling fan
• Charging system (Smart Charge)
• Starting system (Smart Start)
If the PCM is isolated from the vehicle electrical
system or the battery is disconnected, the throttle
control unit mustbe initialized.
The PCM is fitted in the engine compartment in the
air filter housing. On right hand drive vehicles a
protective metal plate is also installed to prevent
the plug connector from being pulled off, or make
it harder to pull off, in case of theft. The protective
plate is secured with a shear bolt. The shear bolt
needs to be drilled out in order to remove the
protective plate.
Knock Sensor
E96986
Two KSs are fitted. They are on the cylinder block,
one close to the 2nd cylinder and one close to the
4th cylinder.
When fitting, adhere strictly to the specified
tightening torque, otherwise the KS will not work
properly.
If the signal from one or both KS is implausible or
absent, knock control is deactivated. The PCM
switches to an ignition map that is further away
from the knock limit. As a result, engine damage
caused by combustion knock is avoided. If a fault
occurs, a fault code is stored in the error memory
of the PCM.
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
E89993
If one or both CMP sensors fail, a fault is saved in
the error memory of the PCM and the camshaft
adjustment and knock control are deactivated.
G1021907en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 8
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL