2011 FORD KUGA Engine control
[x] Cancel search: Engine controlPage 1863 of 2057

Reset adaptation data
Adaptation values are stored in the software of the
TCM:
• Adaptation should be reset after an internalcomponent has been exchanged or the whole
transmission has been changed.
The adaptation of the transmission is reset via IDS.
Limp home mode
The TCM software contains functions which take
control of the transmission if serious faults occur.
The fault characteristic decides which strategies
are to be used.
The vehicle remains capable of restricted
operation.
The TCM strategy differentiates between four emergency modes adapted to the fault situation:
Gear
Position
Mode
4th
D, S+
Emergency 1
2nd
S-
Reverse
Reverse
3rd
D, S+
Emergency 2
2nd
S-
Reverse
Reverse
4th
D, S+
Emergency 3 (*)
2nd
S-
Reverse
Reverse
4th
D, S+, S-
Emergency 4
Reverse
Reverse
(*) As for Emergency 1 mode, the second gear will however be shifted using other solenoid valves.
Different measures are implemented, depending
on the current gear position and driving situation
when the fault occurs:
• When a fault occurs, the TCM makes it possible
for the vehicle to maintain restricted operation.
The distance travelled should be kept as short
as possible.
• Torque limitation is activated in order to protect the transaxle components.
• When the engine is restarted (ignition switched off for approx. 15 seconds), the transaxle is no
longer in limp home mode. There is no longer
a fault indication on the instrument cluster, and
the MIL (malfunction indicator lamp) is off.
However, the fault remains stored in the TCM.
If the fault is still present, limp home mode is
reactivated.
• If limp home mode is reactivated after the ignition is switched on, the option exists in select-shift mode to pull away in 2nd gear. This
is the case unless the transaxle is in emergency
mode 4. Only 4th gear and the reverse gear are
available in this mode.
Component Description
Tasks of the electronic components
The following overview summarizes the input and
output signals from the transmission control
module.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
42
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 42
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1865 of 2057

Description
Item
ABS5
Cruise control
6
Select-shift switch module
7
PCM
8
Selector lever lock
9
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
10
PWM solenoid valve for main line pressure
(SLT)
11
PWM- solenoid valve – TCC (SLU)
12Description
Item
Shift solenoid S1 (open when dormant)
13
Shift solenoid S2 (closed when dormant)
14
Shift solenoid S3 (closed when dormant)
15
Shift solenoid S4 (open when dormant)
16
Shift solenoid S5 (closed when dormant)
17
The TSS sensor
18
The OSS sensor
19
The TFT sensor
20
TR sensor in TCM
21
Input signals
Hard wired
• Item 18: ISS (input shaft speed) sensor
– Supplies information on the transmissioninput shaft speed. Used for calculations, for
instance the shift process, checking the
torque converter lockup and for diagnosis of
the hydraulic/mechanical operations in the
transmission.
• Item 19: OSS sensor – Supplies information on the transmissionoutput shaft speed. Used for calculations, for
instance the vehicle speed and for diagnosis
of the hydraulic/mechanical operations in the
transmission.
• Item 20: TFT sensor – Supplies information on the transmission fluidtemperature. This information is used to
adjust the shift times and the fluid pressure.
• Item 21: TR sensor – Supplies the TCM with the information on thechosen transmission range. Starting is only
possible when the selector lever is in the P
or N position. The sensor is a permanent
magnet which creates a magnetic field over
the different Hall sensors and in this way
creates a specific voltage for each shift
operation.
Via the LIN data bus
• Item 7: Selector lever module (select-shift module)
– Indicates that the selector lever is locked inposition P and supplies information on the
sport mode status. Also transmits a control
signal during select-shift gear changes and
supplies information on the fault status in the selector lever module, so that the fault codes
in the module can be stored as required.
Via the CAN data bus
• Item 4: PCM – Stop light switch ON/OFF, is used by theTCC.
– Coolant temperature, used for diagnosis of the transmission temperature sensor and for
activating the catalytic converter.
– Engine speed >400 rpm = engine running. Used for starting the transmission fluid
pressure and diagnosis functions.
– Engine rpm. Used for checking the torque converter slip and the pressure build-up,
which have an effect on the shift comfort.
– Kickdown. If the accelerator pedal is pressed down and the throttle plate is wide open, the
PCM transmits a kickdown signal to the TCM.
– Current engine speed, used to check the line pressure of the transmission.
– Throttle plate opening, used to calculate the gear changes. During sport mode and
kickdown.
– Accelerator pedal position, used to calculate the shift threshold timings.
• Item 5: ABS module – Supplies information on the vehicle speedand also on the difference in speed between
the left-hand and right-hand wheels. Prevents
changing up if the speed difference is greater
than 40 km/h, to protect the differential in the
transmission.
• Item 6: Vehicle speed control system – Is used to calculate the acceleration,depending on the position of the resume and
set buttons.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 44
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 44
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1866 of 2057

Output signals
Hard wired
• Item 8: PCM– Start inhibitor. Supplies the PCM with a signalthat indicates whether the engine can be
started or not.
• Item 9: Selector lever module (select-shift module)
– Controls the solenoid switch in the selectorlever unit.
• Position 10: PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
– Matches the line pressure to a shift pressureand is activated for certain gears.
• Position 11: PWM solenoid valve – main line pressure (SLT)
– Adjusts the linear line pressure for gearchanges without jolts.
• Position 12: PWM- solenoid valve – TCC (SLU) – Matches the line pressure to a torqueconverter lock-up pressure. Is also used for
certain gearshifts.
• Items 13 - 17: Shift solenoids S1 – S5 – The TCM checks which gear is engaged asthe solenoids become active in different
patterns.
Via the LIN data bus
• Item 7: Selector lever module (select-shift module)
– The TCM transmits a signal to the selectorlever module which activates the LED (light
emitting diode) in the selector mechanism
assembly according to the selector lever
position. Via the CAN data bus
• Item 2: GEM
– The selector lever module transmits a signalvia the TCM, which indicates that the selector
lever is locked in position P. The GEM uses
this information to control the ignition switch
key inhibit function.
– The TCM transmits a signal via the GEM to activate the back-up lamps.
• Item 3: Instrument Cluster – Current selector lever position. Used toindicate the selector lever position in the
instrument cluster.
– Check the warning lamps via the GEM. In the event of a fault, the general warning lamp
lights.
– Text messages in the instrument cluster via the GEM. The driver receives various
malfunction messages from the TCM.
– The TCM transmits signals on the CAN data bus to the PCM so that the MIL lights up in
the event of emissions-related faults.
• Item 4: PCM – Transmission fluid temperature, used tocompensate for increased loads at low fluid
temperatures.
– Gear selected, used by the engine so that it can compensate for different loads.
– Torque converter lockup, used by the engine so that it can compensate for different loads.
– Next gear planned by the TCM, used by the engine to compensate for different loads.
– Requirement for a reduced engine torque during gear shifts, the engine reduces the
engine torque during gear shifts.
– Torque limiting requirement, the engine limits the engine torque according to the gear
engaged.
• Item 5: ABS module – Current gear, used to transmit a signal, notfor shift control.
– Vehicle speed, used as reserve.
Control valve assembly
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 45
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 45
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1867 of 2057
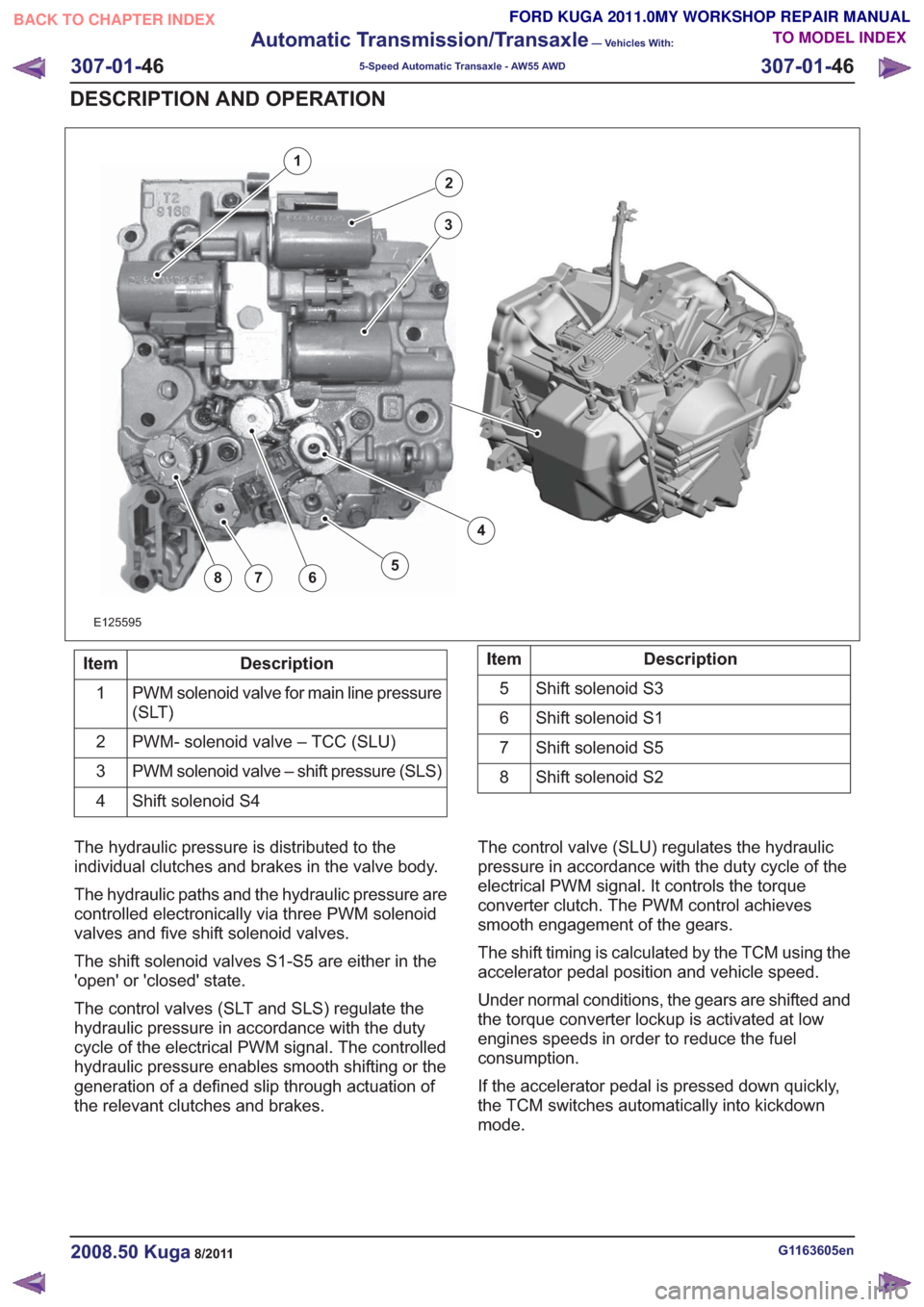
E125595
2
3
4
5678
1
Description
Item
PWM solenoid valve for main line pressure
(SLT)
1
PWM- solenoid valve – TCC (SLU)
2
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
3
Shift solenoid S4
4Description
Item
Shift solenoid S3
5
Shift solenoid S1
6
Shift solenoid S5
7
Shift solenoid S2
8
The hydraulic pressure is distributed to the
individual clutches and brakes in the valve body.
The hydraulic paths and the hydraulic pressure are
controlled electronically via three PWM solenoid
valves and five shift solenoid valves.
The shift solenoid valves S1-S5 are either in the
'open' or 'closed' state.
The control valves (SLT and SLS) regulate the
hydraulic pressure in accordance with the duty
cycle of the electrical PWM signal. The controlled
hydraulic pressure enables smooth shifting or the
generation of a defined slip through actuation of
the relevant clutches and brakes. The control valve (SLU) regulates the hydraulic
pressure in accordance with the duty cycle of the
electrical PWM signal. It controls the torque
converter clutch. The PWM control achieves
smooth engagement of the gears.
The shift timing is calculated by the TCM using the
accelerator pedal position and vehicle speed.
Under normal conditions, the gears are shifted and
the torque converter lockup is activated at low
engines speeds in order to reduce the fuel
consumption.
If the accelerator pedal is pressed down quickly,
the TCM switches automatically into kickdown
mode.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
46
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 46
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1870 of 2057
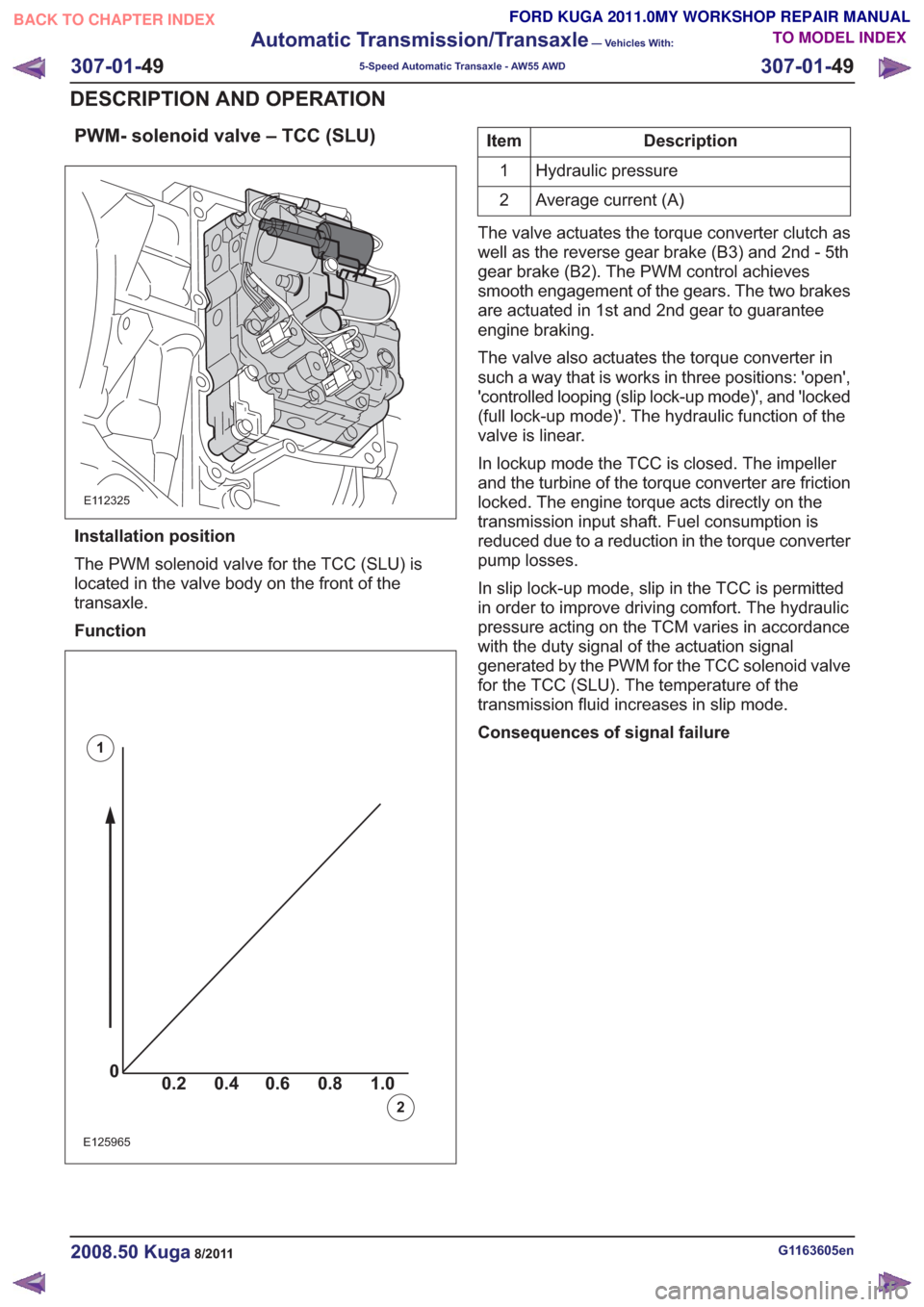
PWM- solenoid valve – TCC (SLU)
E112325
Installation position
The PWM solenoid valve for the TCC (SLU) is
located in the valve body on the front of the
transaxle.
Function
00.2 1.0 0.80.60.4
0
0.2 1.0
0.80.60.4
0
0.2 1.0
0.80.60.40
0.2 1.0 0.80.60.4
E125965
1
2
Description
Item
Hydraulic pressure
1
Average current (A)
2
The valve actuates the torque converter clutch as
well as the reverse gear brake (B3) and 2nd - 5th
gear brake (B2). The PWM control achieves
smooth engagement of the gears. The two brakes
are actuated in 1st and 2nd gear to guarantee
engine braking.
The valve also actuates the torque converter in
such a way that is works in three positions: 'open',
'controlled looping (slip lock-up mode)', and 'locked
(full lock-up mode)'. The hydraulic function of the
valve is linear.
In lockup mode the TCC is closed. The impeller
and the turbine of the torque converter are friction
locked. The engine torque acts directly on the
transmission input shaft. Fuel consumption is
reduced due to a reduction in the torque converter
pump losses.
In slip lock-up mode, slip in the TCC is permitted
in order to improve driving comfort. The hydraulic
pressure acting on the TCM varies in accordance
with the duty signal of the actuation signal
generated by the PWM for the TCC solenoid valve
for the TCC (SLU). The temperature of the
transmission fluid increases in slip mode.
Consequences of signal failure
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 49
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 49
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1873 of 2057
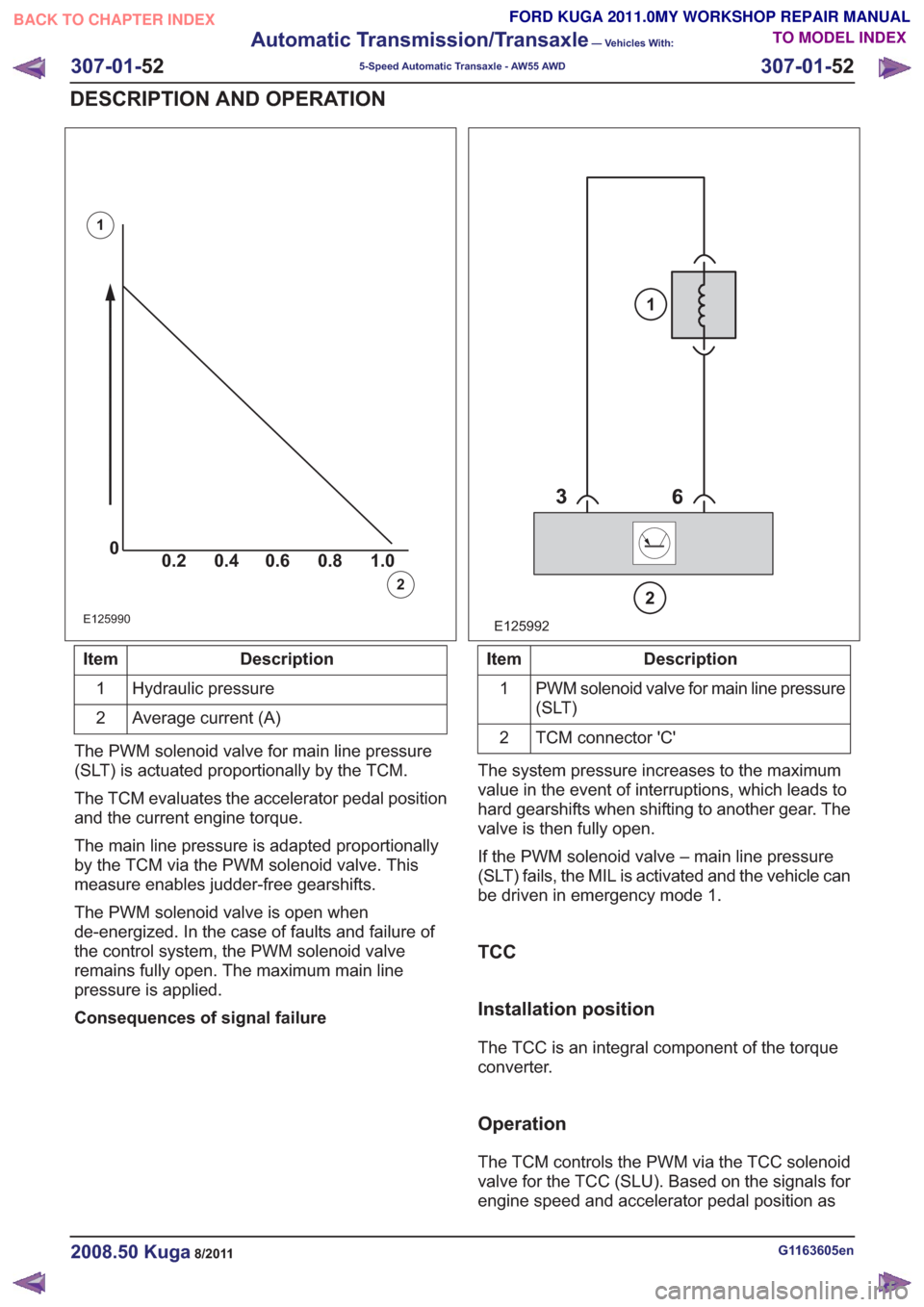
00.2 1.0 0.80.60.4
0
0.2 1.0
0.80.60.40
0.2 1.0 0.80.60.40
0.2 1.0 0.80.60.4
E125990
1
2
Description
Item
Hydraulic pressure
1
Average current (A)
2
The PWM solenoid valve for main line pressure
(SLT) is actuated proportionally by the TCM.
The TCM evaluates the accelerator pedal position
and the current engine torque.
The main line pressure is adapted proportionally
by the TCM via the PWM solenoid valve. This
measure enables judder-free gearshifts.
The PWM solenoid valve is open when
de-energized. In the case of faults and failure of
the control system, the PWM solenoid valve
remains fully open. The maximum main line
pressure is applied.
Consequences of signal failure
E125992
2
1
Description
Item
PWM solenoid valve for main line pressure
(SLT)
1
TCM connector 'C'
2
The system pressure increases to the maximum
value in the event of interruptions, which leads to
hard gearshifts when shifting to another gear. The
valve is then fully open.
If the PWM solenoid valve – main line pressure
(SLT) fails, the MIL is activated and the vehicle can
be driven in emergency mode 1.
TCC
Installation position
The TCC is an integral component of the torque
converter.
Operation
The TCM controls the PWM via the TCC solenoid
valve for the TCC (SLU). Based on the signals for
engine speed and accelerator pedal position as
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 52
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 52
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1876 of 2057
Description
Item
Drive
3
Intake side
4
Delivery side
5
The fluid pump operates on the principle of a
G-rotor fluid pump.
The fluid pump draws transmission fluid from the
fluid pan, builds up fluid pressure and then supplies
it to the valve body.
The fluid pump is driven by the crankshaft via the
torque converter housing.
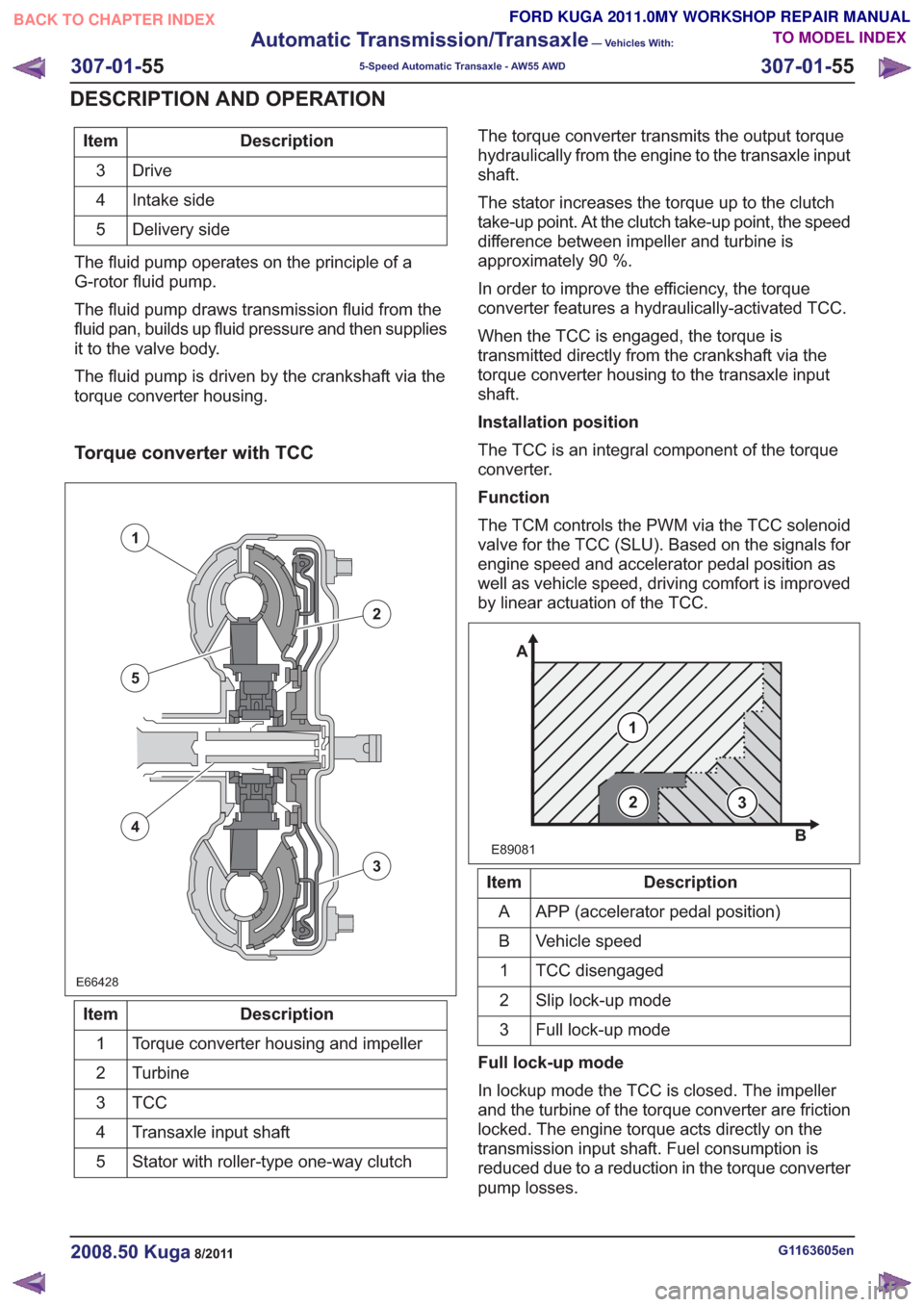
Torque converter with TCC
E66428E66428
1
2
3
5
4
Description
Item
Torque converter housing and impeller
1
Turbine
2
TCC3
Transaxle input shaft
4
Stator with roller-type one-way clutch
5 The torque converter transmits the output torque
hydraulically from the engine to the transaxle input
shaft.
The stator increases the torque up to the clutch
take-up point. At the clutch take-up point, the speed
difference between impeller and turbine is
approximately 90 %.
In order to improve the efficiency, the torque
converter features a hydraulically-activated TCC.
When the TCC is engaged, the torque is
transmitted directly from the crankshaft via the
torque converter housing to the transaxle input
shaft.
Installation position
The TCC is an integral component of the torque
converter.
Function
The TCM controls the PWM via the TCC solenoid
valve for the TCC (SLU). Based on the signals for
engine speed and accelerator pedal position as
well as vehicle speed, driving comfort is improved
by linear actuation of the TCC.
E89081
1
A
B
23
Description
Item
APP (accelerator pedal position)
A
Vehicle speed
B
TCC disengaged
1
Slip lock-up mode
2
Full lock-up mode
3
Full lock-up mode
In lockup mode the TCC is closed. The impeller
and the turbine of the torque converter are friction
locked. The engine torque acts directly on the
transmission input shaft. Fuel consumption is
reduced due to a reduction in the torque converter
pump losses.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 55
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 55
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1934 of 2057
External Controls – Overview
Transmission range selector
E112313
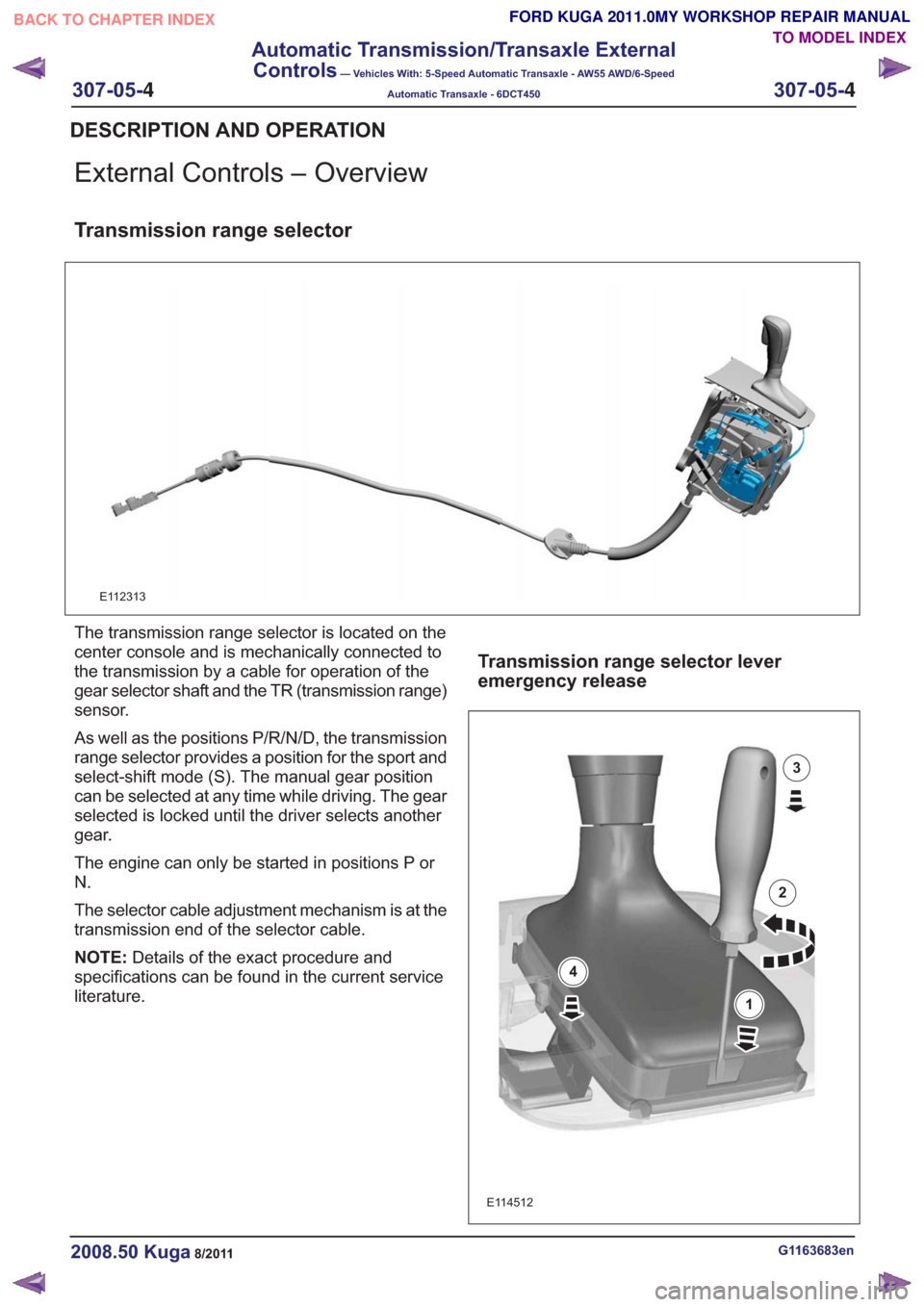
The transmission range selector is located on the
center console and is mechanically connected to
the transmission by a cable for operation of the
gear selector shaft and the TR (transmission range)
sensor.
As well as the positions P/R/N/D, the transmission
range selector provides a position for the sport and
select-shift mode (S). The manual gear position
can be selected at any time while driving. The gear
selected is locked until the driver selects another
gear.
The engine can only be started in positions P or
N.
The selector cable adjustment mechanism is at the
transmission end of the selector cable.
NOTE:Details of the exact procedure and
specifications can be found in the current service
literature.
Transmission range selector lever
emergency release
E114512
1
2
3
4
G1163683en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
307-05-
4
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle External
Controls
— Vehicles With: 5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD/6-Speed
Automatic Transaxle - 6DCT450
307-05-4
.