2011 FORD KUGA torque converter
[x] Cancel search: torque converterPage 82 of 2057

sometimes noticed in the steering wheel/column,
seats, front floor panel, front door trim panel or
front end sheet metal. It is a low frequency
vibration (around 9-15 cycles per second). It
may or may not be increased by applying the
brakes lightly. REFER to Idle
Boom/Shake/Vibration in the Driveline Noise
and Vibration Symptom Chart.
3. High Speed: A vibration is felt in the front floor panel or seats with no visible shake, but with
an accompanying sound or rumble, buzz, hum,
drone or booming noise. Coast with the clutch
pedal depressed (manual transmission) or shift
control selector lever in "N" (NEUTRAL)
(automatic transmission) and engine idling. If
vibration is still evident, it may be related to
wheels, tires, front brake discs, wheel hubs or
front wheel bearings. REFER to Shake and
Vibration While Driving in the Driveline Noise
and Vibration Symptom Chart.
4. Engine rpm Sensitive: A vibration is felt whenever the engine reaches a particular rpm.
It will disappear in neutral coasts. The vibration
can be duplicated by operating the engine at
the problem rpm while the vehicle is stationary.
It can be caused by any component, from the
accessory drive belt to the clutch or torque
converter which turns at engine speed when the
vehicle is stopped. REFER to Shake and
Vibration While Driving in the Driveline Noise
and Vibration Symptom Chart.
5. Noise and Vibration While Turning: Clicking, popping or grinding noises may be due to the
following:
• worn, damaged or incorrectly installed front wheel bearing.
• damaged powertrain/drivetrain mounts.
Road Conditions
An experienced technician will always establish a
route that will be used for all NVH diagnosis road
tests. The road selected should be reasonably
smooth, level and free of undulations (unless a
particular condition needs to be identified). A
smooth asphalt road that allows driving over a
range of speeds is best. Gravel or bumpy roads
are unsuitable because of the additional road noise
produced. Once the route is established and consistently used, the road noise variable is
eliminated from the test results.
NOTE:
Some concerns may be apparent only on
smooth asphalt roads.
If a customer complains of a noise or vibration on
a particular road and only on a particular road, the
source of the concern may be the road surface. If
possible, try to test the vehicle on the same type
of road.
Vehicle Preparation
Carry out a thorough visual inspection of the
vehicle before carrying out the road test. Note
anything which is unusual. Do not repair or adjust
any condition until the road test is carried out,
unless the vehicle is inoperative or the condition
could pose a hazard to the technician. After
verifying that the condition has been corrected,
make sure all components removed have been
installed.
Power Steering Conditions
Check for the noise in the following conditions to
verify the customer concern.
• Check for the noise in several temperature conditions.
• Is the noise from when the vehicle was new?
• Can the noise be repeated constantly or is it random?
• Check the condition of the vehicle age, mileage and service record.
• Interview the customer to find the operating condition in which the noise will occur. Test the
vehicle based on the detail(s) from the customer
interview.
• Follow the power steering operation noise condition tables below, to find which condition
the noise will occur.
Power Steering Operation Noise Check
Step 1: Check for NVH concerns from non-steering
components, which may sound like noises coming
from the steering system.
G37349en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
100-04- 4
Noise, Vibration and Harshness
100-04- 4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1549 of 2057

Engine – System Operation and Component Description
System Operation
The variable camshaft timing occurs
electro-hydraulically and individually for both
camshafts.
The camshaft adjusters work according to the vane
cell principle and have an adjustment range of 52°
crank angle on the intake side and 47° crank angle
on the exhaust side. On starting the engine and
during idling, both camshafts are mechanically
locked in their starting positions. The exhaust
camshaft is in the early position and the intake
camshaft is in the late position. The camshaftadjuster on the exhaust side has a torsion spring
which compensates the camshaft drive torque.
This ensures that the assembly can return to the
starting position under all operating conditions and
when the engine is turned off.
Internal exhaust gas recirculation can be realized
through continuous adjustment of the timings. This
results in better fuel consumption and more
favorable combustion temperatures which produce
less pollutants. This means that pollutant level IV
can be adhered to with a 3-way catalytic converter.
The variable timings also make it possible to
optimize performance with wide open throttle.
G1032416en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-01-
16
Engine— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-01-
16
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1823 of 2057

307-01-29
Automatic transmission, selector lever in position "D". ...................................................
307-01-29
Sport mode, selector lever in position "S" .......................................................................
307-01-29
Changing gear in select-shift mode........................................................................\
........
307-01-30
Selector lever from 'N' to 'R' position ........................................................................\
......
307-01-30
Self-test and Diagnosis ........................................................................\
...........................
307-01-30
Temperature controlled torque converter lockup ............................................................
307-01-30
Slip locking ........................................................................\
..............................................
307-01-30
Hill climbing ........................................................................\
.............................................
307-01-31
Downhill driving ........................................................................\
.......................................
307-01-31
Hill-hold function ........................................................................\
.....................................
307-01-31
Altitude correction ........................................................................\
...................................
307-01-31
Selector lever lock ........................................................................\
..................................
307-01-31
Shifting from P into another transmission range .............................................................
307-01-31
Shifting from N into another transmission range .............................................................
307-01-31
Power flow through the transmission ........................................................................\
......
307-01-31
Clutches and brakes ........................................................................\
...............................
307-01-33
Position P (park) ........................................................................\
.....................................
307-01-34
Position N (neutral) ........................................................................\
.................................
307-01-35
Position D, 1st gear........................................................................\
................................
307-01-36
Position D, 2nd gear ........................................................................\
...............................
307-01-37
Position D, 3rd gear ........................................................................\
................................
307-01-38
Position D, 4th gear ........................................................................\
................................
307-01-39
Position D, 5th gear ........................................................................\
................................
307-01-40
Position R (reverse) ........................................................................\
................................
307-01-41
Service instructions ........................................................................\
.................................
307-01-41
Towing procedure ........................................................................\
...................................
307-01-42
Reset adaptation data ........................................................................\
.............................
307-01-42
Limp home mode ........................................................................\
....................................
307-01-42
Component Description ........................................................................\
..............................
Tasks of the electronic components ........................................................................\
........
307-01-44
Input signals ........................................................................\
............................................
307-01-45
Output signals ........................................................................\
.........................................
Control valve assembly ........................................................................\
...........................
Shift solenoids S1 - S5 ........................................................................\
...........................
PWM-
solenoid valve – TCC (SLU) ........................................................................\
........
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS) ...................................................................
PWM solenoid valve for main line pressure (SLT) ..........................................................
307-01-52
Installation position ........................................................................\
.................................
Operation ........................................................................\
................................................
Selector lever with integrated select-shift switch module ...............................................
Oil pump ........................................................................\
..................................................
Torque converter with TCC ........................................................................\
.....................
The TSS sensor ........................................................................\
......................................
The OSS sensor ........................................................................\
.....................................
The TFT sensor ........................................................................\
......................................
The TR sensor ........................................................................\
........................................
GENERAL PROCEDURES
T ransmission Fluid Level Check ........................................................................\
.................
307-01-63
T ransmission Fluid Drain and Refill ........................................................................\
............
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION 307-01-67
Halfshaft Seal LH ........................................................................\
........................................
307-01-68
Halfshaft Seal RH........................................................................\
.......................................
307-01-69
Main Control Valve Body ........................................................................\
............................
307-01-2
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 2
.
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
307-01-42
307-01-49
307-01-52 307-01-47
307-01-45
307-01-50
307-01-51
307-01-53
307-01-55
307-01-54
307-01-56
307-01-57
307-01-58
307-01-61 307-01-60
PAGE 2 OF 3 FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1824 of 2057

307-01-72
Output Shaft Speed (OSS) Sensor ........................................................................\
.............
307-01-73
Torque Converter Seal ........................................................................\
................................
307-01-75
Transmission Fluid Pan ........................................................................\
..............................
307-01-77
Transmission Range (TR) Sensor ........................................................................\
..............
307-01-81
Turbine Shaft Speed (TSS) Sensor ........................................................................\
............
REMOVAL 307-01-82
Transmission ........................................................................\
..............................................
INSTALLATION 307-01-91
Transmission ........................................................................\
..............................................
307-01-3
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 3
.
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
PAGE 3 OF 3 FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1827 of 2057
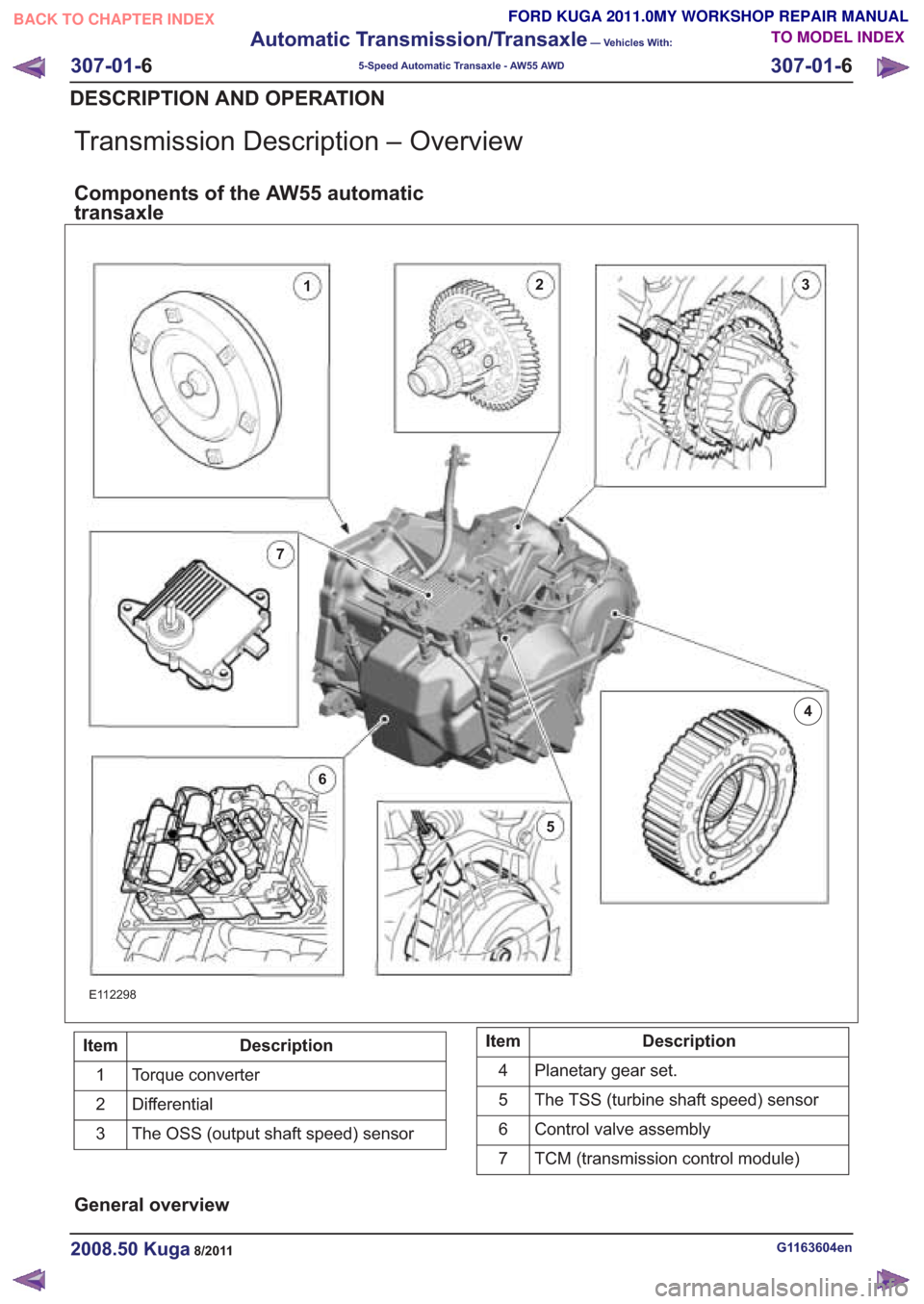
Transmission Description – Overview
Components of the AW55 automatic
transaxle
E112298
Description
Item
Torque converter
1
Differential
2
The OSS (output shaft speed) sensor
3Description
Item
Planetary gear set.
4
The TSS (turbine shaft speed) sensor
5
Control valve assembly
6
TCM (transmission control module)
7
General overview
G1163604en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 6
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
23
4
5
6
7
1
Page 1831 of 2057
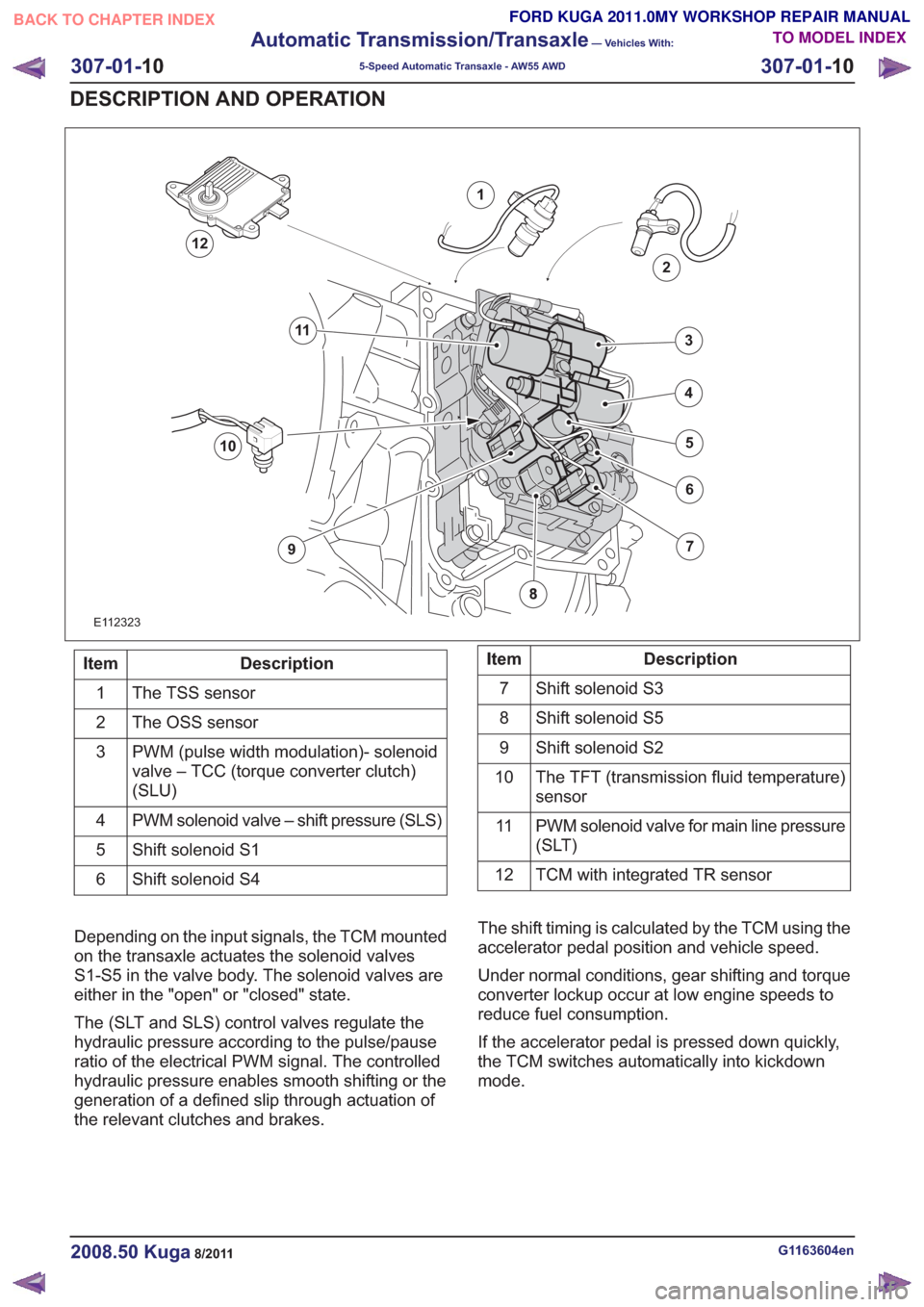
E112323
1
2
7
6
4
5
3
10
9
11
12
Description
Item
The TSS sensor
1
The OSS sensor
2
PWM (pulse width modulation)- solenoid
valve – TCC (torque converter clutch)
(SLU)
3
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
4
Shift solenoid S1
5
Shift solenoid S4
6Description
Item
Shift solenoid S3
7
Shift solenoid S5
8
Shift solenoid S2
9
The TFT (transmission fluid temperature)
sensor
10
PWM solenoid valve for main line pressure
(SLT)
11
TCM with integrated TR sensor
12
Depending on the input signals, the TCM mounted
on the transaxle actuates the solenoid valves
S1-S5 in the valve body. The solenoid valves are
either in the "open" or "closed" state.
The (SLT and SLS) control valves regulate the
hydraulic pressure according to the pulse/pause
ratio of the electrical PWM signal. The controlled
hydraulic pressure enables smooth shifting or the
generation of a defined slip through actuation of
the relevant clutches and brakes. The shift timing is calculated by the TCM using the
accelerator pedal position and vehicle speed.
Under normal conditions, gear shifting and torque
converter lockup occur at low engine speeds to
reduce fuel consumption.
If the accelerator pedal is pressed down quickly,
the TCM switches automatically into kickdown
mode.
G1163604en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
10
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 10
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1842 of 2057
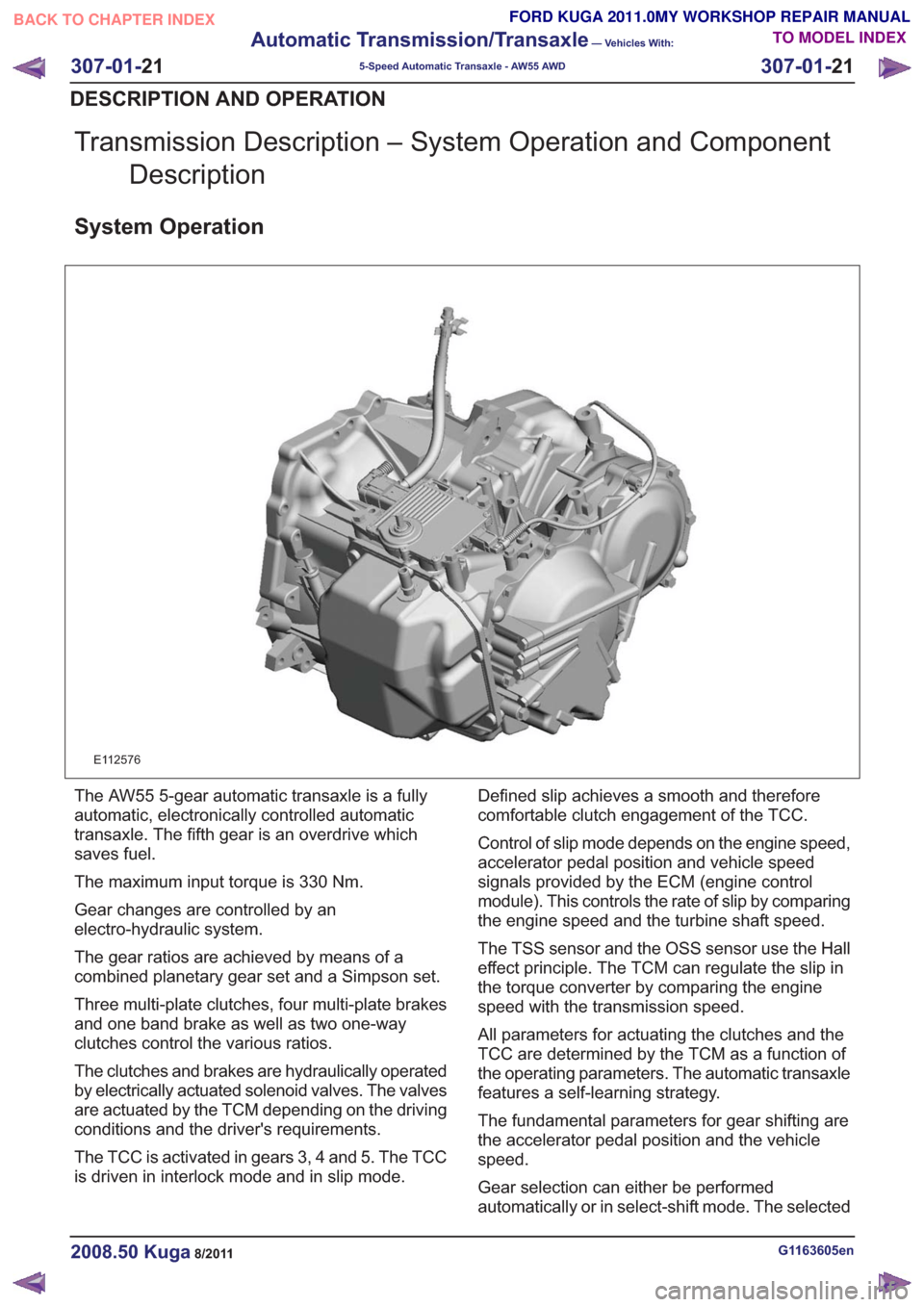
Transmission Description – System Operation and ComponentDescription
System Operation
E112576
The AW55 5-gear automatic transaxle is a fully
automatic, electronically controlled automatic
transaxle. The fifth gear is an overdrive which
saves fuel.
The maximum input torque is 330 Nm.
Gear changes are controlled by an
electro-hydraulic system.
The gear ratios are achieved by means of a
combined planetary gear set and a Simpson set.
Three multi-plate clutches, four multi-plate brakes
and one band brake as well as two one-way
clutches control the various ratios.
The clutches and brakes are hydraulically operated
by electrically actuated solenoid valves. The valves
are actuated by the TCM depending on the driving
conditions and the driver's requirements.
The TCC is activated in gears 3, 4 and 5. The TCC
is driven in interlock mode and in slip mode. Defined slip achieves a smooth and therefore
comfortable clutch engagement of the TCC.
Control of slip mode depends on the engine speed,
accelerator pedal position and vehicle speed
signals provided by the ECM (engine control
module). This controls the rate of slip by comparing
the engine speed and the turbine shaft speed.
The TSS sensor and the OSS sensor use the Hall
effect principle. The TCM can regulate the slip in
the torque converter by comparing the engine
speed with the transmission speed.
All parameters for actuating the clutches and the
TCC are determined by the TCM as a function of
the operating parameters. The automatic transaxle
features a self-learning strategy.
The fundamental parameters for gear shifting are
the accelerator pedal position and the vehicle
speed.
Gear selection can either be performed
automatically or in select-shift mode. The selected
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
21
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 21
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1847 of 2057

E112322
The TCM adapts the gear changing to ensure that
the correct gear is selected for the style of driving,
the engine load, driver requirements, vehicle speed
etc. This leads to lower fuel consumption together
with improved comfort through smoother gear
changes and lower noise levels.
The TCM receives information on the driver's
desired transmission range and type of driving
mode. In contrast to a transmission which is only
controlled hydraulically, the control module can
calculate the best times to shift gear and activate
torque converter lockup by using the signals from
the sensors in the transmission and the engine
management system.
The control module enables small changes in the
operating conditions to be made and adapts thevarious transmission functions to ensure that the
correct gear is always selected in relation to the
type of driving mode.
The TCM has adaptive capabilities. This ensures
smooth gear changes throughout the whole service
life of the transmission.
To exactly determine the activation points of the
gear shifts and torque converter lockup on the
basis of the type of driving mode chosen, the TCM
receives the following information:
• Transmission range chosen (TR sensor).
• Type of driving mode chosen
(normal/sport/select-shift).
• Transmission input shaft speed (TSS sensor).
• Transmission output shaft speed (OSS sensor).
• Transmission fluid temperature (TFT sensor).
• The engine speed and the torque as well as the throttle plate opening - from the PCM via the
CAN data bus.
• Actuation of the accelerator pedal - from the PCM via the CAN data bus.
• Coolant temperature - from the PCM via the CAN data bus.
• Vehicle speed - from the ABS via the CAN data bus.
• Actuation of the brake pedal - from the ABS via the CAN data bus.
Pin assignment for TCM connector 'A' (connection to vehicle)
11
E125669
Description
Item
Battery (+)
1
not assigned
2Description
Item
not assigned
3
not assigned
4
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 26
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 26
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL