2010 JAGUAR XFR rear entertainment
[x] Cancel search: rear entertainmentPage 22 of 3039

Operation and
Component DescriptionCellular PhoneComponent
Location
Overview
System Operation
and Component DescriptionNavigation SystemComponent Location
Overview
System Operation and Component DescriptionVideo SystemComponent
Location
Overview
System Operation
and Component DescriptionDiagnosis and TestingInformation and Entertainment SystemRemoval and InstallationAudio Unit
Audio Unit Antenna Amplifier
Audio and Climate Control Assembly
Front Door Speaker
Information and Entertainment Display
Information and Entertainment Module
Instrument Panel Speaker
Rear Door Speaker
Steering Wheel Audio Controls
Subwoofer Amplifier
Subwoofer Speaker
Satellite Radio Tuner415-01B: Information and Entertainment System - DTC: Audio Input Control Module
Diagnosis and TestingAudio Input Control Module417: Lighting
417-01: Exterior LightingSpecificationDescription and OperationComponent Location
Overview
System Operation and Component DescriptionDiagnosis and TestingHeadlampsGeneral ProceduresHeadlamp Adjustment (86.40.18)
Page 182 of 3039
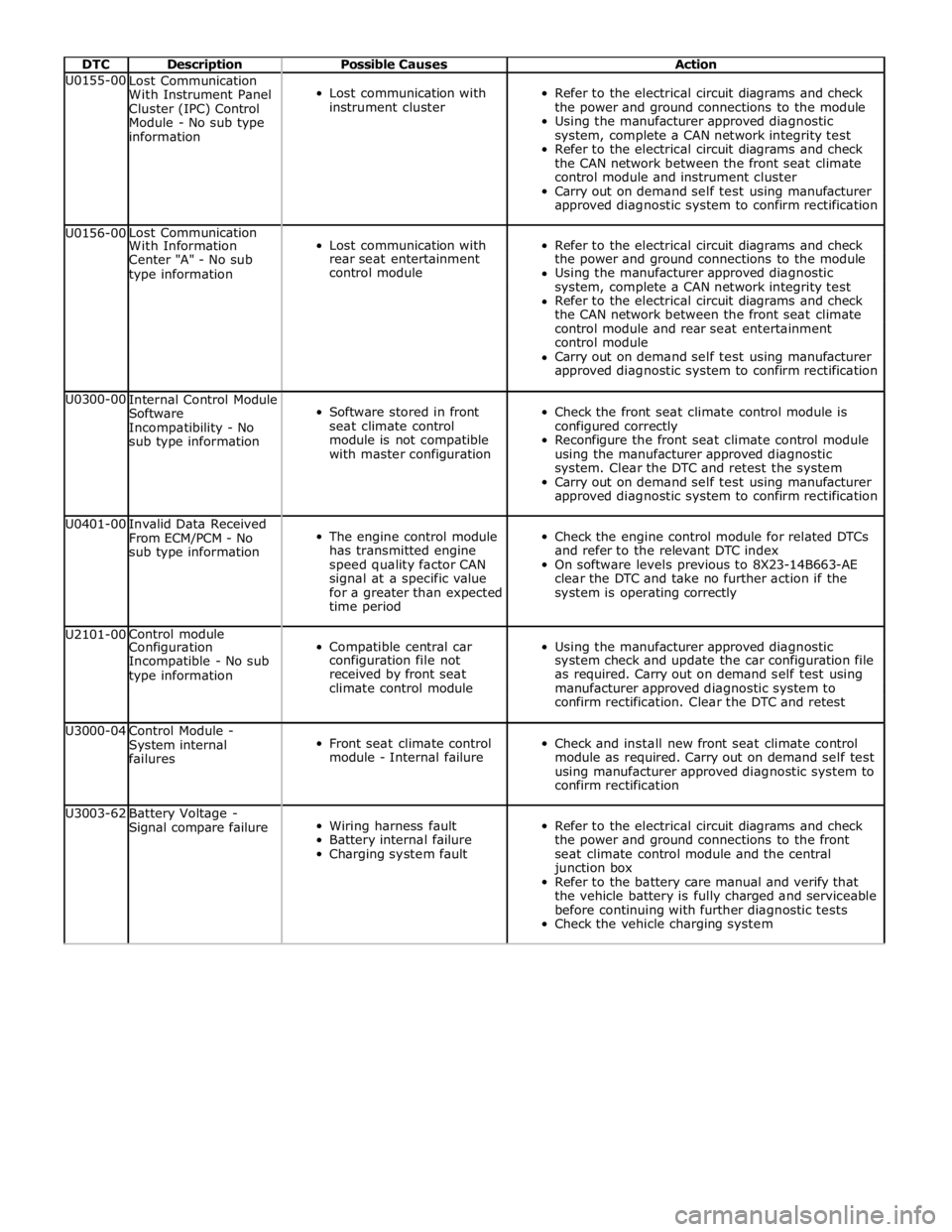
DTC Description Possible Causes Action U0155-00
Lost Communication
With Instrument Panel
Cluster (IPC) Control
Module - No sub type
information
Lost communication with
instrument cluster
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
the power and ground connections to the module
Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system, complete a CAN network integrity test
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
the CAN network between the front seat climate
control module and instrument cluster
Carry out on demand self test using manufacturer
approved diagnostic system to confirm rectification U0156-00 Lost Communication
Lost communication with
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check With Information Center "A" - No sub rear seat entertainment the power and ground connections to the module type information control module Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system, complete a CAN network integrity test Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check the CAN network between the front seat climate control module and rear seat entertainment control module Carry out on demand self test using manufacturer approved diagnostic system to confirm rectification U0300-00
Internal Control Module
Software
Incompatibility - No
sub type information
Software stored in front
seat climate control
module is not compatible
with master configuration
Check the front seat climate control module is
configured correctly
Reconfigure the front seat climate control module
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Clear the DTC and retest the system
Carry out on demand self test using manufacturer
approved diagnostic system to confirm rectification U0401-00
Invalid Data Received
From ECM/PCM - No
sub type information
The engine control module
has transmitted engine
speed quality factor CAN
signal at a specific value
for a greater than expected
time period
Check the engine control module for related DTCs
and refer to the relevant DTC index
On software levels previous to 8X23-14B663-AE
clear the DTC and take no further action if the
system is operating correctly U2101-00 Control module
Compatible central car
Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic Configuration Incompatible - No sub configuration file not system check and update the car configuration file type information received by front seat as required. Carry out on demand self test using climate control module manufacturer approved diagnostic system to confirm rectification. Clear the DTC and retest U3000-04
Control Module -
System internal
failures
Front seat climate control
module - Internal failure
Check and install new front seat climate control
module as required. Carry out on demand self test
using manufacturer approved diagnostic system to
confirm rectification U3003-62
Battery Voltage -
Signal compare failure
Wiring harness fault
Battery internal failure
Charging system fault
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
the power and ground connections to the front
seat climate control module and the central
junction box
Refer to the battery care manual and verify that
the vehicle battery is fully charged and serviceable
before continuing with further diagnostic tests
Check the vehicle charging system
Page 200 of 3039

Published: 12-May-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Integrated
Control Panel (FCIMB)
Description and Operation
Integrated Control Panel (ICP)
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If a control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the Warranty
Policy and Procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation of a new
module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system).
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places, and with
an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required.
The table below lists all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the Integrated Control Panel (ICP). For
additional diagnosis and testing information, refer to the relevant Diagnosis and Testing section in the workshop manual.
For additional information, refer to: Information and Entertainment System (415-00 Information and Entertainment System - General Information, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B1012-23 Heated Windshield Switch
- Signal stuck low
Button stuck
down/jammed
Integrated control
panel failure
Check for stuck down/jammed button. Check and
install a new integrated control panel as required B1013-23 Heater Rear Defog Switch
- Signal stuck low
Button stuck
down/jammed
Integrated control
panel failure
Check for stuck down/jammed button. Check and
install a new integrated control panel as required B1014-23
Recirculation Switch -
Signal stuck low
Button stuck
down/jammed
Integrated control
panel failure
Check for stuck down/jammed button. Check and
install a new integrated control panel as required B1015-23
Screen On/Off Switch -
Signal stuck low
Button stuck
down/jammed
Integrated control
panel failure
Check for stuck down/jammed button. Check and
install a new integrated control panel as required
Page 801 of 3039

battery power supply to be passed via the slip ring assembly in the steering wheel to the heated steering wheel control
module. The steering wheel module supplies power to the steering wheel heater element and also monitors the temperature
via a NTC (negative temperature coefficient) temperature sensor incorporated into the heater element. The control module
varies the power supply to the element to maintain the steering wheel rim at the optimum temperature.
Component Description STEERING COLUMN MULTIFUNCTION SWITCHES
The steering column multifunction switches are situated on the steering column and consists of the wiper switch, the turn
signal indicator/lighting switch and the trip computer switch.
The steering column adjustment switch is located in the steering column lower shroud on the LH side. The switch is a 4 position 'joystick' which controls reach and rake adjustment.
Steering wheel mounted switches on the LH side of the driver's airbag, control the audio and telephone functions. Switches on the RH side of the driver's airbag, control the speed control functions. For additional information, refer to:
Audio System (415-01A Information and Entertainment System, Description and Operation), Speed Control (310-03A, Description and Operation),
Speed Control (310-03B, Description and Operation),
Speed Control (310-03C, Description and Operation).
Two transmission paddle switches are located at the rear of the steering wheel.
Refer to: External Controls (307-05, Description and Operation).
LH Multifunction Switch
Item Description 1 High beam 2 Lighting control rotary switch 3 RH turn signal indicator 4 Headlamp flash 5 LH turn signal indicator 6 Trip computer function button The LH multifunction switch controls the following windshield wiper functions:
Page 1687 of 3039
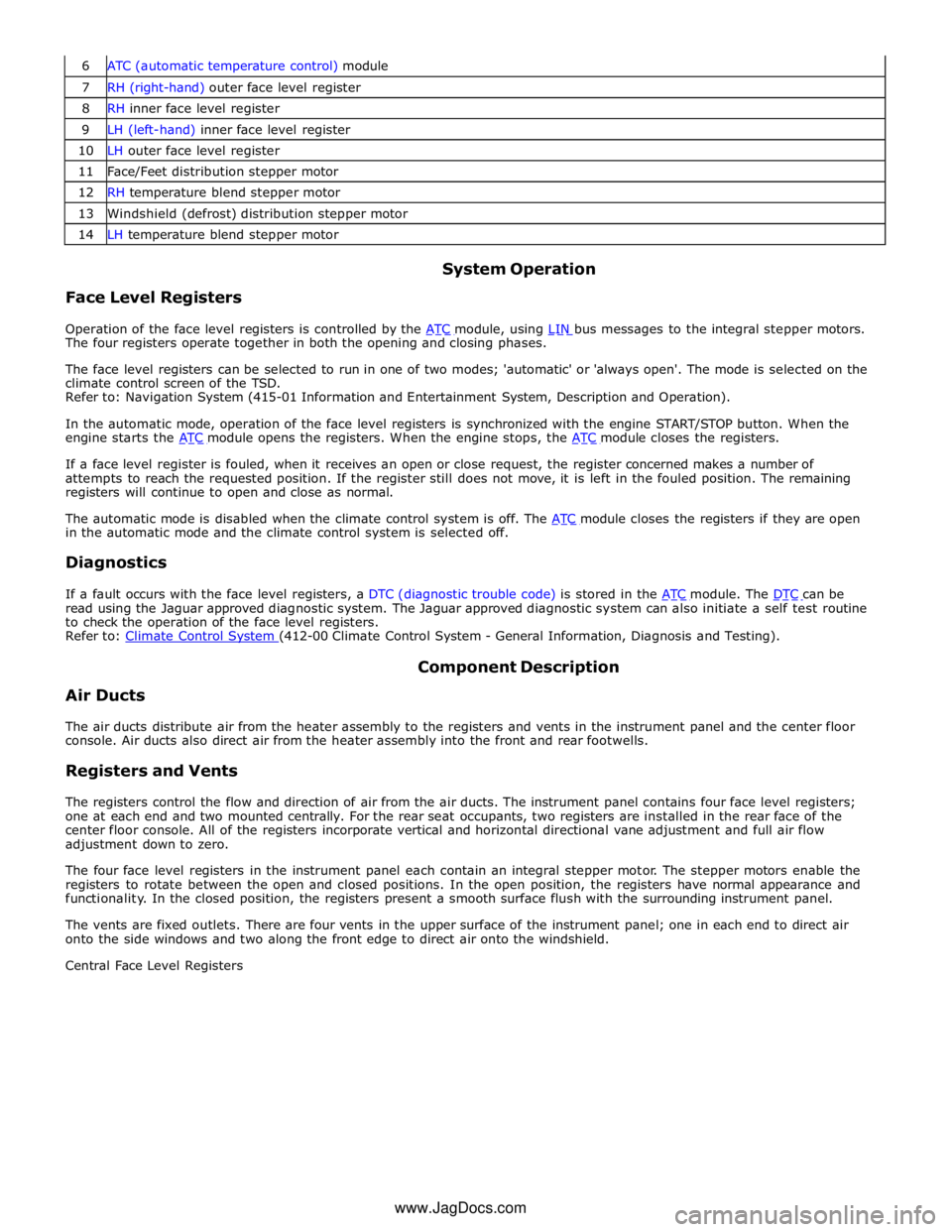
7 RH (right-hand) outer face level register 8 RH inner face level register 9 LH (left-hand) inner face level register 10 LH outer face level register 11 Face/Feet distribution stepper motor 12 RH temperature blend stepper motor 13 Windshield (defrost) distribution stepper motor 14 LH temperature blend stepper motor
Face Level Registers System Operation
Operation of the face level registers is controlled by the ATC module, using LIN bus messages to the integral stepper motors. The four registers operate together in both the opening and closing phases.
The face level registers can be selected to run in one of two modes; 'automatic' or 'always open'. The mode is selected on the
climate control screen of the TSD.
Refer to: Navigation System (415-01 Information and Entertainment System, Description and Operation).
In the automatic mode, operation of the face level registers is synchronized with the engine START/STOP button. When the
engine starts the ATC module opens the registers. When the engine stops, the ATC module closes the registers.
If a face level register is fouled, when it receives an open or close request, the register concerned makes a number of
attempts to reach the requested position. If the register still does not move, it is left in the fouled position. The remaining
registers will continue to open and close as normal.
The automatic mode is disabled when the climate control system is off. The ATC module closes the registers if they are open in the automatic mode and the climate control system is selected off.
Diagnostics
If a fault occurs with the face level registers, a DTC (diagnostic trouble code) is stored in the ATC module. The DTC can be read using the Jaguar approved diagnostic system. The Jaguar approved diagnostic system can also initiate a self test routine
to check the operation of the face level registers.
Refer to: Climate Control System (412-00 Climate Control System - General Information, Diagnosis and Testing).
Air Ducts Component Description
The air ducts distribute air from the heater assembly to the registers and vents in the instrument panel and the center floor
console. Air ducts also direct air from the heater assembly into the front and rear footwells.
Registers and Vents
The registers control the flow and direction of air from the air ducts. The instrument panel contains four face level registers;
one at each end and two mounted centrally. For the rear seat occupants, two registers are installed in the rear face of the
center floor console. All of the registers incorporate vertical and horizontal directional vane adjustment and full air flow
adjustment down to zero.
The four face level registers in the instrument panel each contain an integral stepper motor. The stepper motors enable the
registers to rotate between the open and closed positions. In the open position, the registers have normal appearance and
functionality. In the closed position, the registers present a smooth surface flush with the surrounding instrument panel.
The vents are fixed outlets. There are four vents in the upper surface of the instrument panel; one in each end to direct air
onto the side windows and two along the front edge to direct air onto the windshield.
Central Face Level Registers
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1838 of 3039
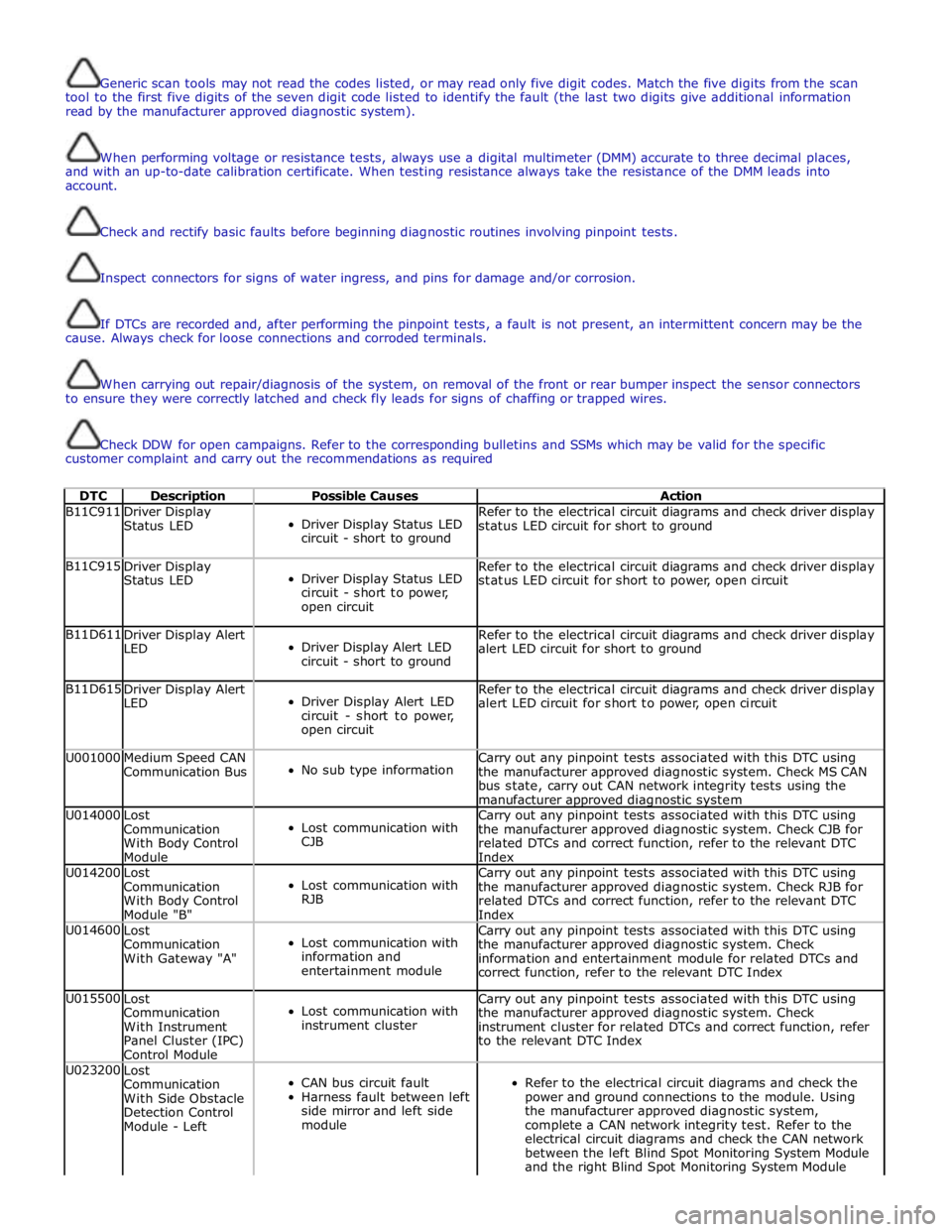
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only five digit codes. Match the five digits from the scan
tool to the first five digits of the seven digit code listed to identify the fault (the last two digits give additional information
read by the manufacturer approved diagnostic system).
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter (DMM) accurate to three decimal places,
and with an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance always take the resistance of the DMM leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
When carrying out repair/diagnosis of the system, on removal of the front or rear bumper inspect the sensor connectors
to ensure they were correctly latched and check fly leads for signs of chaffing or trapped wires.
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B11C911
Driver Display
Status LED
Driver Display Status LED
circuit - short to ground Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check driver display
status LED circuit for short to ground B11C915
Driver Display
Status LED
Driver Display Status LED
circuit - short to power,
open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check driver display
status LED circuit for short to power, open circuit B11D611
Driver Display Alert
LED
Driver Display Alert LED
circuit - short to ground Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check driver display
alert LED circuit for short to ground B11D615
Driver Display Alert
LED
Driver Display Alert LED
circuit - short to power,
open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check driver display
alert LED circuit for short to power, open circuit U001000
Medium Speed CAN
Communication Bus
No sub type information Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using
the manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Check MS CAN
bus state, carry out CAN network integrity tests using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system U014000
Lost
Communication
With Body Control
Module
Lost communication with
CJB Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using
the manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Check CJB for
related DTCs and correct function, refer to the relevant DTC
Index U014200
Lost
Communication
With Body Control
Module "B"
Lost communication with
RJB Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using
the manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Check RJB for
related DTCs and correct function, refer to the relevant DTC
Index U014600
Lost
Communication
With Gateway "A"
Lost communication with
information and
entertainment module Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using
the manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Check
information and entertainment module for related DTCs and
correct function, refer to the relevant DTC Index U015500
Lost
Communication
With Instrument
Panel Cluster (IPC)
Control Module
Lost communication with
instrument cluster Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using
the manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Check
instrument cluster for related DTCs and correct function, refer
to the relevant DTC Index U023200
Lost
Communication
With Side Obstacle
Detection Control
Module - Left
CAN bus circuit fault
Harness fault between left
side mirror and left side
module
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check the
power and ground connections to the module. Using
the manufacturer approved diagnostic system,
complete a CAN network integrity test. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check the CAN network
between the left Blind Spot Monitoring System Module
and the right Blind Spot Monitoring System Module
Page 1843 of 3039
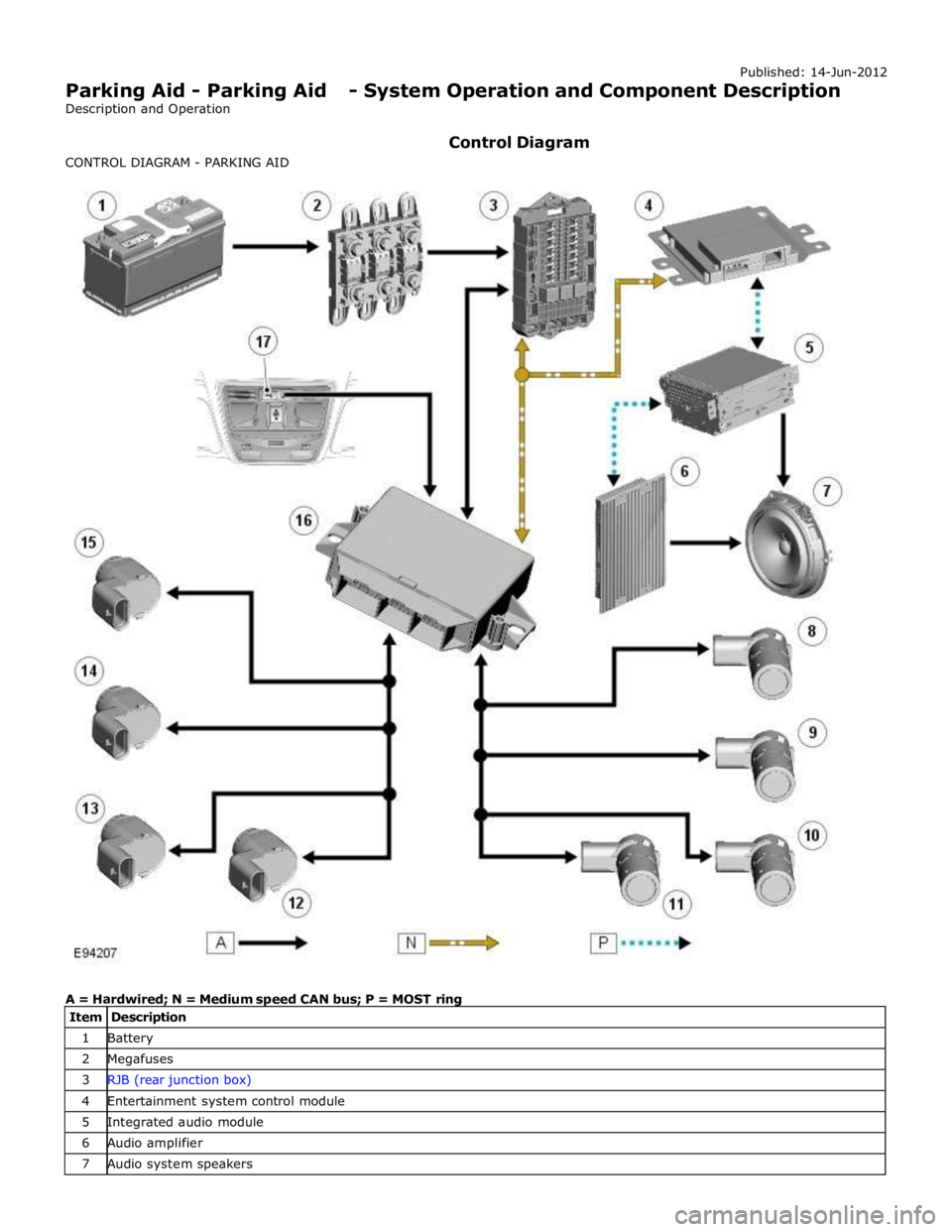
1 Battery 2 Megafuses 3 RJB (rear junction box) 4 Entertainment system control module 5 Integrated audio module 6 Audio amplifier 7 Audio system speakers
Page 1845 of 3039
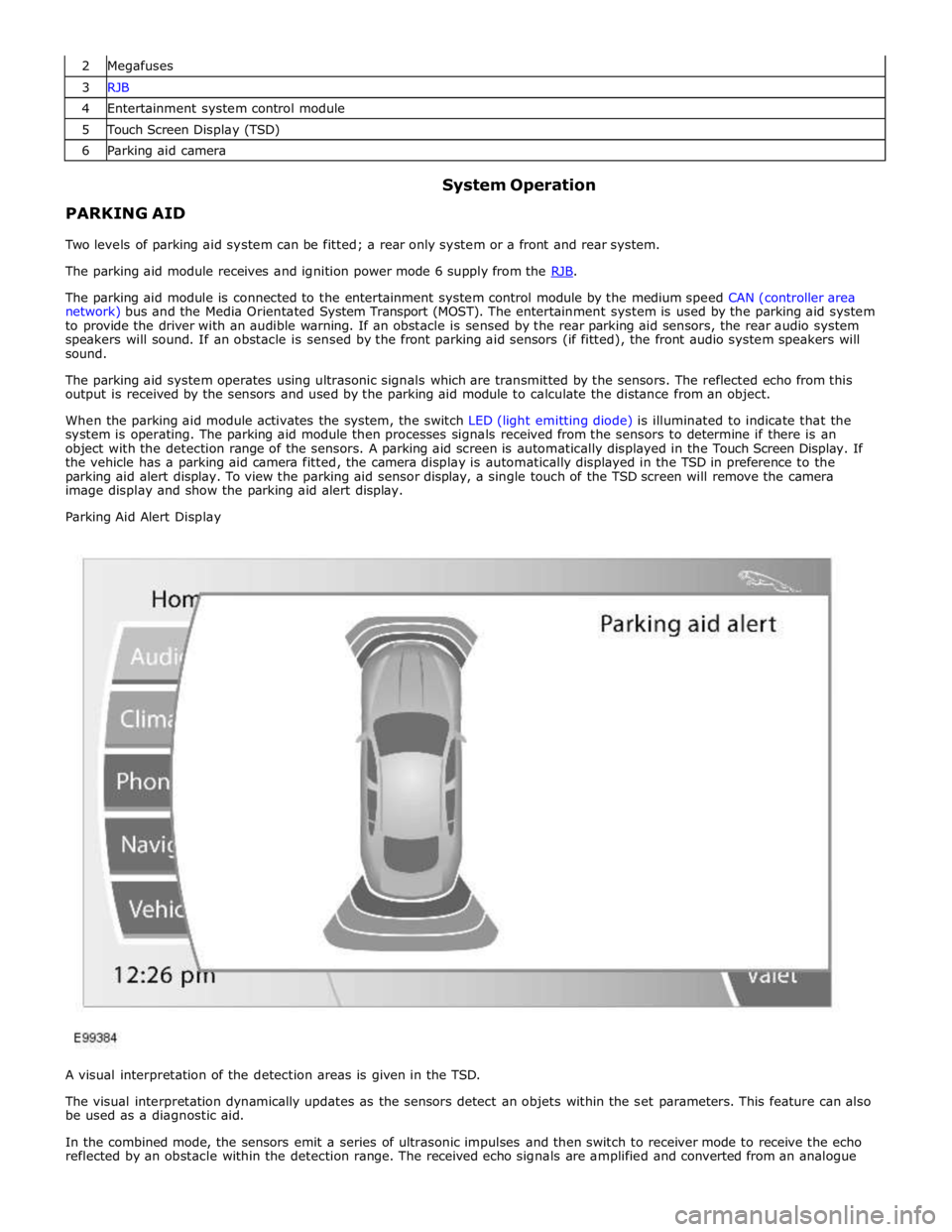
3 RJB 4 Entertainment system control module 5 Touch Screen Display (TSD) 6 Parking aid camera
PARKING AID System Operation
Two levels of parking aid system can be fitted; a rear only system or a front and rear system.
The parking aid module receives and ignition power mode 6 supply from the RJB. The parking aid module is connected to the entertainment system control module by the medium speed CAN (controller area
network) bus and the Media Orientated System Transport (MOST). The entertainment system is used by the parking aid system
to provide the driver with an audible warning. If an obstacle is sensed by the rear parking aid sensors, the rear audio system
speakers will sound. If an obstacle is sensed by the front parking aid sensors (if fitted), the front audio system speakers will
sound.
The parking aid system operates using ultrasonic signals which are transmitted by the sensors. The reflected echo from this
output is received by the sensors and used by the parking aid module to calculate the distance from an object.
When the parking aid module activates the system, the switch LED (light emitting diode) is illuminated to indicate that the
system is operating. The parking aid module then processes signals received from the sensors to determine if there is an
object with the detection range of the sensors. A parking aid screen is automatically displayed in the Touch Screen Display. If
the vehicle has a parking aid camera fitted, the camera display is automatically displayed in the TSD in preference to the
parking aid alert display. To view the parking aid sensor display, a single touch of the TSD screen will remove the camera
image display and show the parking aid alert display.
Parking Aid Alert Display
A visual interpretation of the detection areas is given in the TSD.
The visual interpretation dynamically updates as the sensors detect an objets within the set parameters. This feature can also
be used as a diagnostic aid.
In the combined mode, the sensors emit a series of ultrasonic impulses and then switch to receiver mode to receive the echo
reflected by an obstacle within the detection range. The received echo signals are amplified and converted from an analogue