Page 1288 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Intake Air Distribution and Filtering - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Intake Air
Distribution and Filtering - System Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
Control Diagram
NOTE: A = Hardwired
Item Description 1 Battery 2 BJB (battery junction box) (250 A megafuse) 3 EJB (engine junction box) (EMS high current relay) 4 Tuning valve 5 ECM (engine control module)
Page 1289 of 3039

SUPERCHARGER System Operation
At closed or partially open throttle positions, the bypass valve is fully open, allowing a flow of air from the SC (supercharger)
outlet back to the inlet side. This results in little or no pressure increase across the SC. Progressive opening of the throttle reduces the depression downstream of the electric throttle. This is sensed by the pneumatic actuator, which moves to close
the bypass valve. As the bypass valve closes there is a corresponding increase in the outlet pressure from the SC, which increases engine power output.
NOISE FEEDBACK SYSTEM
Sound waves from the RH (right-hand) intake manifold are filtered by the calibrated orifice in the inlet pipe connection on the
symposer. The sound waves make the paddle oscillate and generate pulsations in the outlet chambers. When the pneumatic
valve is open, the pulsations are transmitted through the outlet pipe and feedback tube to the resonator in the passenger
compartment.
The tuning valve of the noise feedback system receives a power feed from the power distribution box and is connected to
ground through the ECM (engine control module). At lower engine loads and speeds the ECM keeps the ground open circuit and the tuning valve is de-energized closed. Atmospheric pressure is sensed at the pneumatic valve through the vent cap on the
tuning valve, which keeps the pneumatic valve closed and prevents sound from the symposer entering the feedback system.
At higher engine loads and speeds the ECM connects the tuning valve to ground. The tuning valve energizes, blanks off the atmospheric vent and opens the vacuum line between the brake vacuum system and the pneumatic valve. The depression in
the brake vacuum system is sensed at the pneumatic valve, which opens and allows sound from the symposer into the
feedback system.
The status of the pneumatic valve at various engine loads and speeds is given below:
Pneumatic Valve Status
NOTE: Values are for valve opening with increasing engine load and speed. Deduct 0.05 g/rev and 50 rev/min for valve
closing with decreasing engine load and speed.
Engine Load: g/rev Engine Speed: rev/min 0 500 1000 2500 3000 4000 5800 6500 1.30 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed 1.35 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed 1.40 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Open 1.60 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Open 1.80 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Open 2.50 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Open Open Open 3.00 Closed Closed Closed Closed Closed Open Open Open 3.50 Closed Closed Closed Open Open Open Open Open
Page 1290 of 3039
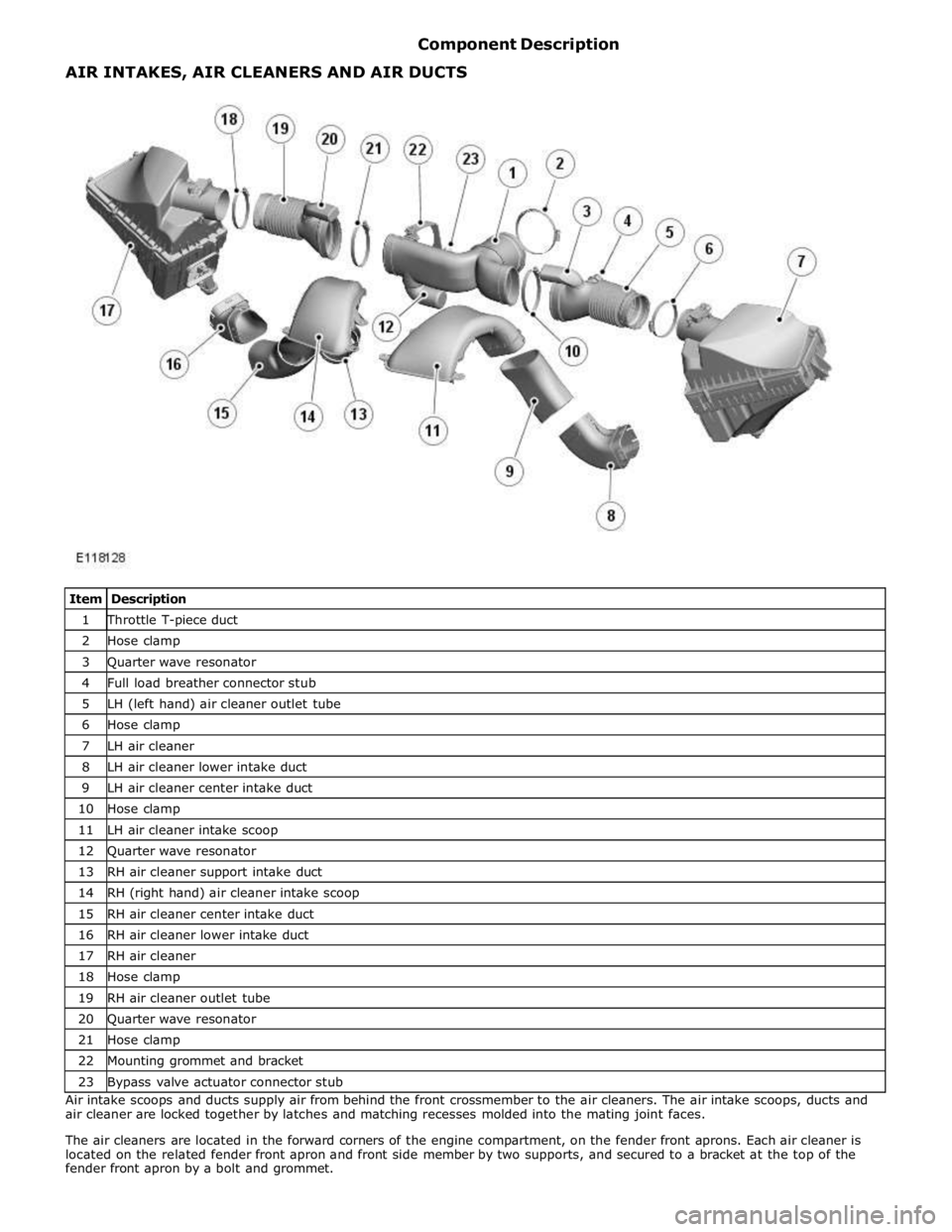
1 Throttle T-piece duct 2 Hose clamp 3 Quarter wave resonator 4 Full load breather connector stub 5 LH (left hand) air cleaner outlet tube 6 Hose clamp 7 LH air cleaner 8 LH air cleaner lower intake duct 9 LH air cleaner center intake duct 10 Hose clamp 11 LH air cleaner intake scoop 12 Quarter wave resonator 13 RH air cleaner support intake duct 14 RH (right hand) air cleaner intake scoop 15 RH air cleaner center intake duct 16 RH air cleaner lower intake duct 17 RH air cleaner 18 Hose clamp 19 RH air cleaner outlet tube 20 Quarter wave resonator 21 Hose clamp 22 Mounting grommet and bracket 23 Bypass valve actuator connector stub Air intake scoops and ducts supply air from behind the front crossmember to the air cleaners. The air intake scoops, ducts and
air cleaner are locked together by latches and matching recesses molded into the mating joint faces.
The air cleaners are located in the forward corners of the engine compartment, on the fender front aprons. Each air cleaner is
located on the related fender front apron and front side member by two supports, and secured to a bracket at the top of the
fender front apron by a bolt and grommet. AIR INTAKES, AIR CLEANERS AND AIR DUCTS
Page 1292 of 3039

9 Support 10 Inlet connection 11 Outlet connection 12 MAFT sensor The outlet tubes and T-piece duct direct the air from the air cleaners to the electric throttle. Hose clamps connect the outlet
tubes and T-piece duct together, and to the air cleaners and the electric throttle. A grommet and bracket attached the T-piece
duct to a bracket on the RH cylinder head. The two outlet tubes and the T-piece duct each incorporate a quarter wave resonator to reduce air induction noise.
The LH (left-hand) outlet tube incorporates a connector stub for the engine full load breather pipe.
The T-piece duct incorporates a connector stub for the vacuum tube of the bypass valve actuator on the supercharger.
SUPERCHARGER AND INTAKE MANIFOLDS
The SC increases the pressure, and thus mass, of the air supplied to the engine, to increase the engine's power output. Two separate intake manifolds direct air from the SC to the cylinder inlet ports.
The intake manifolds are attached to their related cylinder heads and the sides of the SC. Two dowels locate the SC in position on the cylinder block. A charge air cooler tank top is installed on top of the SC and intake manifolds to form the air duct from the SC outlet to the intake manifolds. A charge air cooler is installed in each intake manifold.
The charge air cooler tank top incorporates four studs for the attachment of the engine cover. A NVH (noise, vibration and
harshness) pad is attached to the side of each intake manifold.
Page 1293 of 3039
1 Engine cover rear attachment points 2 Vacuum connector stub 3 MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor 4 SC filler/level plug 5 Symposer inlet pipe connection 6 Dowels 7 Engine cover front attachment points 8 EVAP (evaporative emissions) connector stub 9 Part load breather connector stub 10 MAP (manifold absolute pressure ) sensor 11 Bypass valve pneumatic actuator 12 Outlet ports 13 Inlet port 14 Pulley 15 Coolant inlet and outlet connections Supercharger and Intake Manifolds - Assembled
Page 1294 of 3039
1 M08 x 35 mm screw (19 off) 2 M08 x 65 mm screw (4 off) 3 Charge air cooler tank top 4 Gasket 5 LH charge air cooler 6 M6 x 15 mm screw (4 off) 7 M08 x 45 mm screw (4 off) 8 M08 x 30 mm crew (3 off) 9 LH intake manifold 10 Gasket 11 N.H. (noise vibration and harshness) pad
Page 1295 of 3039
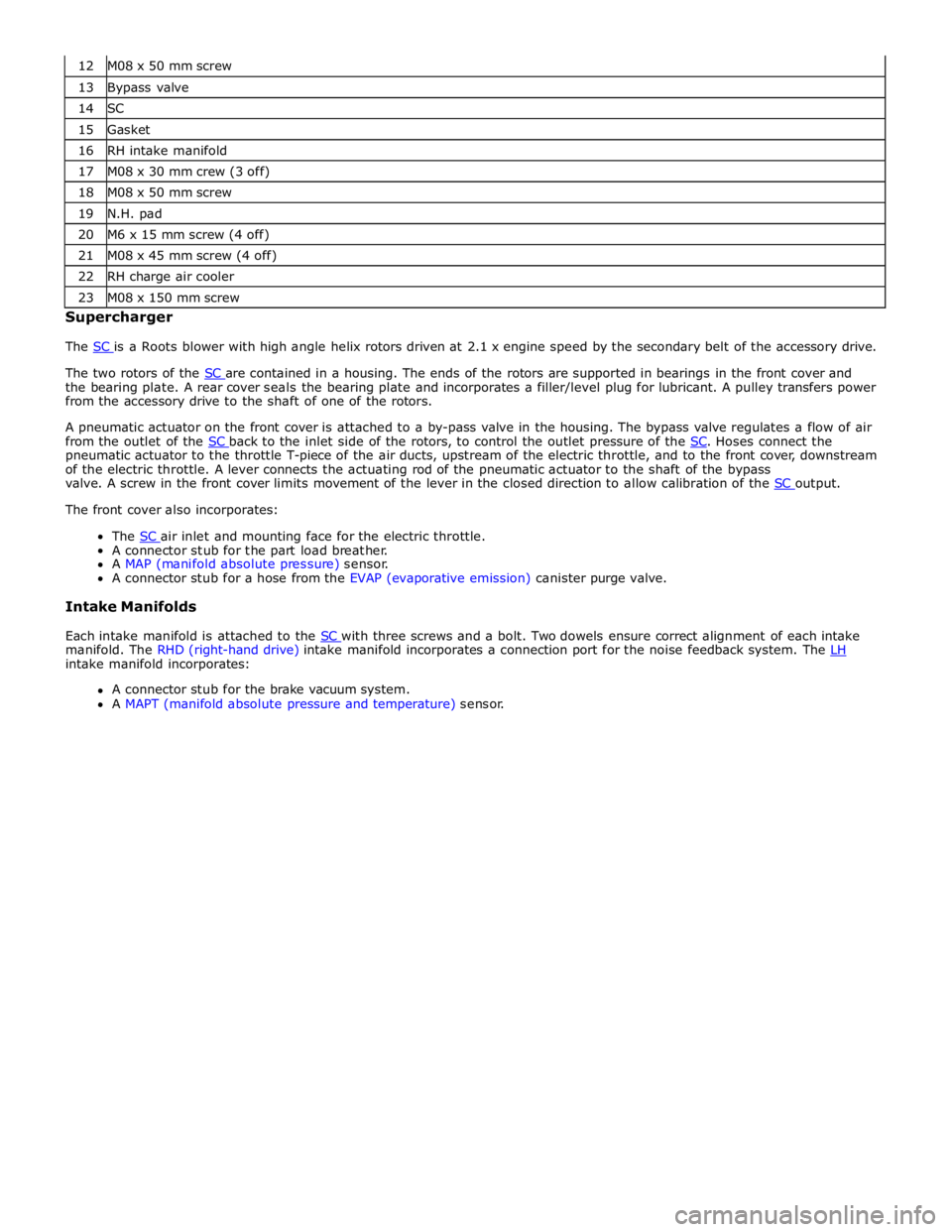
13 Bypass valve 14 SC 15 Gasket 16 RH intake manifold 17 M08 x 30 mm crew (3 off) 18 M08 x 50 mm screw 19 N.H. pad 20 M6 x 15 mm screw (4 off) 21 M08 x 45 mm screw (4 off) 22 RH charge air cooler 23 M08 x 150 mm screw Supercharger
The SC is a Roots blower with high angle helix rotors driven at 2.1 x engine speed by the secondary belt of the accessory drive.
The two rotors of the SC are contained in a housing. The ends of the rotors are supported in bearings in the front cover and the bearing plate. A rear cover seals the bearing plate and incorporates a filler/level plug for lubricant. A pulley transfers power
from the accessory drive to the shaft of one of the rotors.
A pneumatic actuator on the front cover is attached to a by-pass valve in the housing. The bypass valve regulates a flow of air
from the outlet of the SC back to the inlet side of the rotors, to control the outlet pressure of the SC. Hoses connect the pneumatic actuator to the throttle T-piece of the air ducts, upstream of the electric throttle, and to the front cover, downstream
of the electric throttle. A lever connects the actuating rod of the pneumatic actuator to the shaft of the bypass
valve. A screw in the front cover limits movement of the lever in the closed direction to allow calibration of the SC output. The front cover also incorporates:
The SC air inlet and mounting face for the electric throttle. A connector stub for the part load breather.
A MAP (manifold absolute pressure) sensor.
A connector stub for a hose from the EVAP (evaporative emission) canister purge valve.
Intake Manifolds
Each intake manifold is attached to the SC with three screws and a bolt. Two dowels ensure correct alignment of each intake manifold. The RHD (right-hand drive) intake manifold incorporates a connection port for the noise feedback system. The LH intake manifold incorporates:
A connector stub for the brake vacuum system.
A MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor.
Page 1297 of 3039
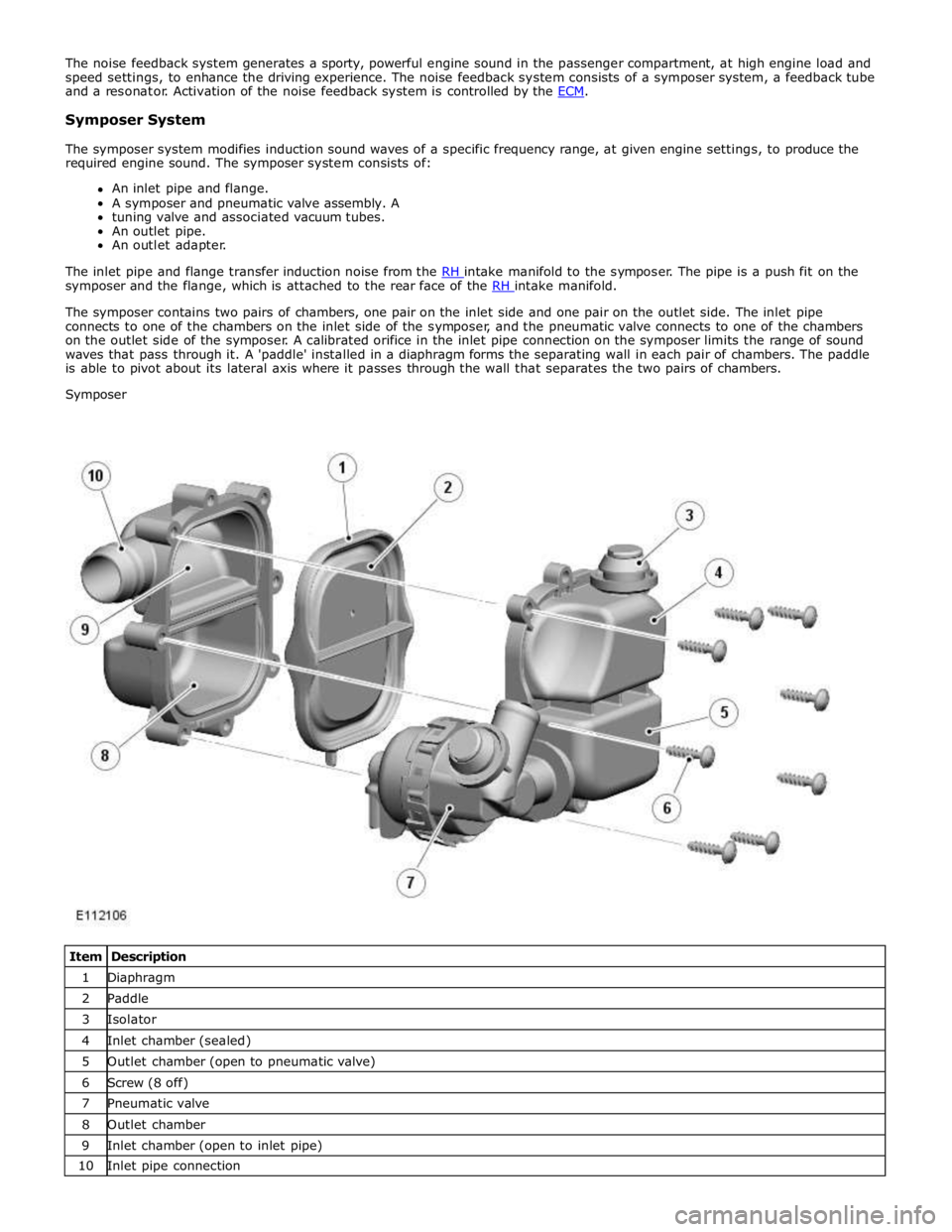
Symposer System
The symposer system modifies induction sound waves of a specific frequency range, at given engine settings, to produce the
required engine sound. The symposer system consists of:
An inlet pipe and flange.
A symposer and pneumatic valve assembly. A
tuning valve and associated vacuum tubes.
An outlet pipe.
An outlet adapter.
The inlet pipe and flange transfer induction noise from the RH intake manifold to the symposer. The pipe is a push fit on the symposer and the flange, which is attached to the rear face of the RH intake manifold.
The symposer contains two pairs of chambers, one pair on the inlet side and one pair on the outlet side. The inlet pipe
connects to one of the chambers on the inlet side of the symposer, and the pneumatic valve connects to one of the chambers
on the outlet side of the symposer. A calibrated orifice in the inlet pipe connection on the symposer limits the range of sound
waves that pass through it. A 'paddle' installed in a diaphragm forms the separating wall in each pair of chambers. The paddle
is able to pivot about its lateral axis where it passes through the wall that separates the two pairs of chambers.
Symposer
Item Description 1 Diaphragm 2 Paddle 3 Isolator 4 Inlet chamber (sealed) 5 Outlet chamber (open to pneumatic valve) 6 Screw (8 off) 7 Pneumatic valve 8 Outlet chamber 9 Inlet chamber (open to inlet pipe) 10 Inlet pipe connection