2010 JAGUAR XFR battery
[x] Cancel search: batteryPage 2069 of 3039

5 RJB (rear junction box) 6 Battery monitoring system module 7 Rear view camera 8 TCM (transmission control module) 9 Generator 10 Driver's door switch pack 11 Rear door control module 12 Driver's door control module 13 ECM (engine control module) 14 Electronic transmission selector 15 Driver's seat module 16 Driver's seat switch pack 17 Rear door control module 18 Front passenger door control module 19 Clockspring 20 Audio and telephone steering wheel switches 21 Instrument cluster 22 Start control module
Page 2076 of 3039

CAN Harness Architecture
For a detailed description of the CAN Networks and architecture, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section in the
Workshop Manual.
CAN Network Integrity Tests
If a control module is suspected of non-communication, the Network Integrity test application available on the manufacturer
approved diagnostic system can be used to confirm if communication is possible between the control modules on the vehicle
and the manufacturer approved diagnostic system (via the J1962 diagnostic connector ). The results from the test can be used
to determine if either a single module or multiple modules are failing to communicate.
CAN Terminating Modules
If the Network Integrity test indicates that one or more module on one of the CAN networks (HS or MS) are failing to
communicate, there are several checks that can be made. The first step is to identify if both of the CAN terminating modules
on each individual CAN Bus are communicating. If both CAN terminating modules for each individual CAN Bus are
communicating (identified via the Network Integrity test), then it can be confirmed that the main 'backbone' of the CAN
harness is complete. The main 'backbone' of the CAN harness consists of all the modules connected to the CAN harness via a
'loop' configuration and also includes the two terminating modules.
Communication with both CAN terminating modules via the Network Integrity test confirms the physical integrity of the main
'backbone' of the CAN harness (and the harness spur to the J1962 diagnostic connector). This means that there is no
requirement to check the resistance of the CAN Network. This is because the standard check for 60 ohms across the CAN High
and CAN Low lines will not provide any additional information regarding the physical condition of the CAN harness, beyond
what has already been determined from the Network Integrity test.
Non-Communication of a Terminating Module
If a Network Integrity test reveals a terminating module is failing to communicate it can indicate a break in the main
'backbone' of the CAN harness. The first checks should always be to confirm the power and ground supplies to the
non-communicating module are correct. Providing these are correct, the resistance between the CAN High and CAN Low lines at
the J1962 connector can be checked to determine the integrity of the main 'backbone' of the CAN harness. After disconnecting
the battery a reading of 120 ohms would indicate an open circuit in the main 'backbone' of the CAN harness. Alternatively, a
reading of 60 ohms would indicate that there is no open circuit fault with the main 'backbone' of the CAN harness.
It is worth noting that even if one of the terminating modules is disconnected from the CAN harness, communications between
the modules still connected may still be possible. Therefore communication between the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system and the connected modules may also be possible.
Locating CAN Harness Open Circuits
In the case where multiple modules, including a terminating module, are failing to communicate, having first confirmed the
power and ground supplies are correct, the approximate location of the open circuit can be identified from analysis of the
Network Integrity test results and reference to the relevant CAN network circuit diagrams. For example, if an open circuit
existed in a certain position on the CAN harness, any module positioned on the Network between the J1962 connector and the
open circuit should return a response during the Network Integrity test. No responses would be returned from any modules
past the open circuit fault in the Network.
CAN Harness 'Spur' Type Configuration Circuits
If, after the initial checks (Network Integrity test using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system, and power and ground
supplies to the module have been checked and confirmed as correct), a module that is connected to the CAN harness via a
'spur' type configuration is suspected of not communicating, then the physical integrity of the CAN harness 'spur' can be
checked.
This is most easily undertaken by individually checking the continuity of the CAN High and CAN Low lines between the
non-communicating module connector (with the module disconnected) and the J1962 diagnostic connector.
'Lost Communications' DTCs
As well as the methods described so far in this document, which can be used to determine the location of an open circuit in
the CAN harness, 'Lost Communications' DTCs can also be used for this purpose. Lost communication DTCs mean that a
module is not receiving CAN information from another module.
For example, if a global DTC read were to be carried out, only DTCs stored in the modules that the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system could communicate with would be displayed. If there was an open circuit fault in a certain position on the
CAN harness, the modules that could display DTCs would all be prior to the open circuit on the Network, and these modules
should display 'Lost Communications' DTCs with all the modules located on the Network past the open circuit fault.
'Bus off' DTCs
The references to bus and its condition refer to the network concerned and the modules on that network.
If a module logs a 'Bus Off' DTC, it means that the module has detected CAN transmission errors and has disabled it's own
CAN transmissions and disconnected itself from the network in an attempt to allow the rest of the network to function. At this
point the 'Bus Off' DTC is set. A common cause of 'Bus Off' DTCs can be a short circuit in the CAN network.
Page 2078 of 3039
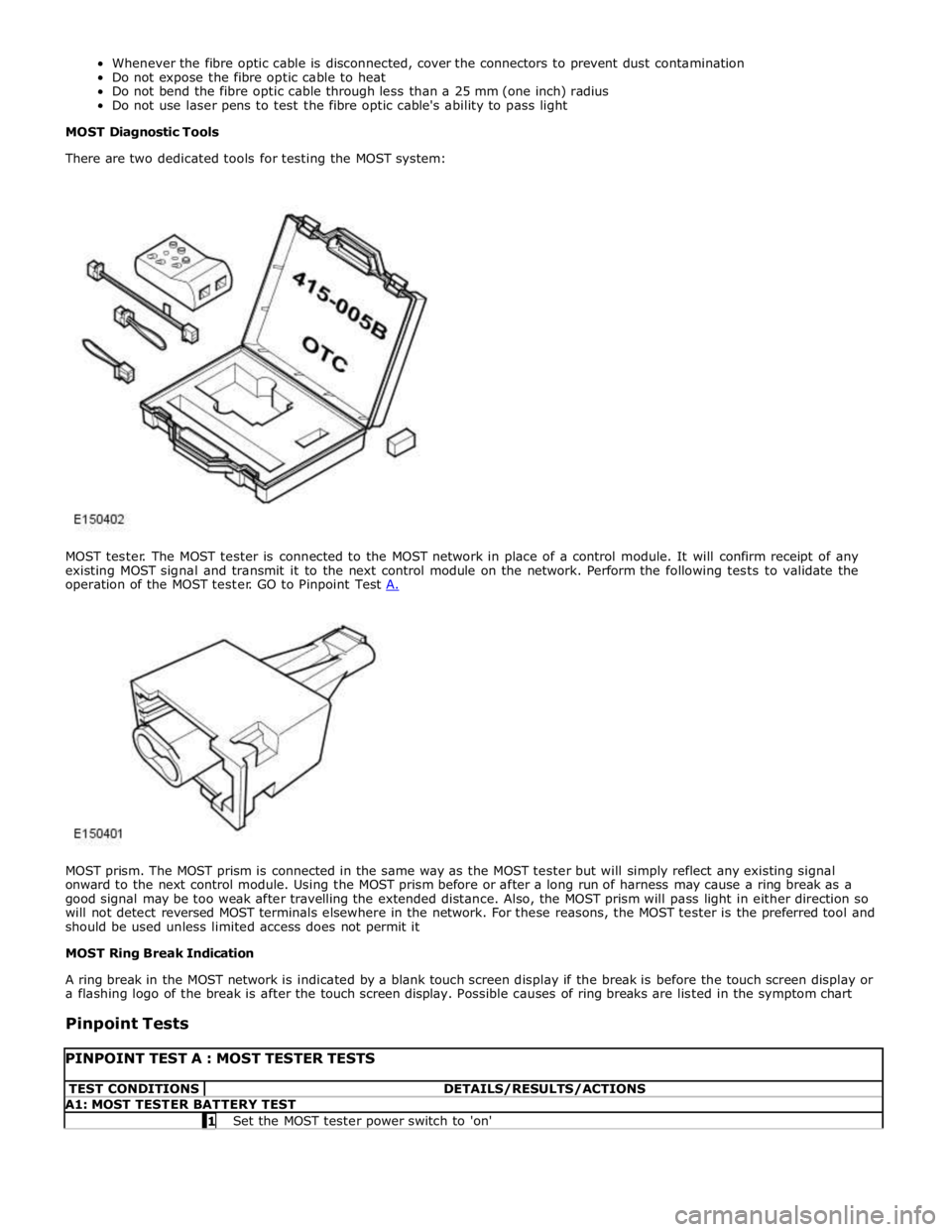
MOST prism. The MOST prism is connected in the same way as the MOST tester but will simply reflect any existing signal
onward to the next control module. Using the MOST prism before or after a long run of harness may cause a ring break as a
good signal may be too weak after travelling the extended distance. Also, the MOST prism will pass light in either direction so
will not detect reversed MOST terminals elsewhere in the network. For these reasons, the MOST tester is the preferred tool and
should be used unless limited access does not permit it
MOST Ring Break Indication
A ring break in the MOST network is indicated by a blank touch screen display if the break is before the touch screen display or
a flashing logo of the break is after the touch screen display. Possible causes of ring breaks are listed in the symptom chart
Pinpoint Tests
PINPOINT TEST A : MOST TESTER TESTS TEST CONDITIONS DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS A1: MOST TESTER BATTERY TEST 1 Set the MOST tester power switch to 'on'
Page 2079 of 3039

Is the power LED illuminated?
Yes
Test passed. GO to A2. No
Test failed. Install a new battery into the MOST tester. GO to A1. A2: 2+0 INPUT/OUTPUT TEST NOTES:
'2+0' indicates that the loop harness connector consists of 2 fibre optic terminals and 0 electrical terminals.
The MOST tester may continue to emit a tone or illuminate the LED after the test switch is released. This does not
indicate a fault. 1 Set the MOST tester power switch to 'on' 2 Set the connector selector switch to '2+0' 3 Set the indication switch to 'beep' or 'LED' 4 Remove the covers from the MOST tester 2+0 connector and the 2+0 loop harness connector 5 Connect the 2+0 loop harness to the MOST tester 2+0 connector 6 Operate the test switch and check the MOST tester beep/LED Did the MOST tester emit a tone or illuminate the LED?
Yes
Test passed. GO to A3. No
Test failed. MOST tester or 2+0 harness fault A3: 2+4 INPUT/OUTPUT TEST NOTES:
'2+4' indicates that the loop harness connector consists of 2 fibre optic terminals and 4 electrical terminals.
The MOST tester may continue to emit a tone or illuminate the LED after the test switch is released. This does not
indicate a fault. 1 Set the MOST tester power switch to 'on' 2 Set the connector selector switch to '2+4' 3 Set the indication switch to 'beep' or 'LED' 4 Remove the covers from the MOST tester 2+4 connector and the 2+4 loop harness connector 5 Connect the 2+4 loop harness to the MOST tester 2+4 connector 6 Operate the test switch and check the MOST tester beep/LED Did the MOST tester emit a tone or illuminate the LED?
Yes
Test passed. GO to A4. No
Test failed. MOST tester or 2+4 harness fault A4: ADAPTER HARNESS AND PRISM TEST
NOTE: The MOST tester may continue to emit a tone or illuminate the LED after the test switch is released. This does
not indicate a fault. 1 Set the MOST tester power switch to 'on' 2 Set the connector selector switch to '2+0' 3 Set the indication switch to 'beep' or 'LED' 4 Remove the covers from the MOST tester 2+0 connector, the prism, and the adapter harness connectors 5 Connect the adapter harness to the MOST tester 2+0 connector 6 Connect the prism to the adapter harness 7 Operate the test switch and check the MOST tester beep/LED Did the MOST tester emit a tone or illuminate the LED?
Yes
Test passed
No
Test failed. MOST tester, adapter harness or prism fault
PINPOINT TEST B : MOST NETWORK INITIAL TESTS TEST
CONDITIONS DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS B1: MOST NETWORK INITIAL TEST 1
Page 2085 of 3039
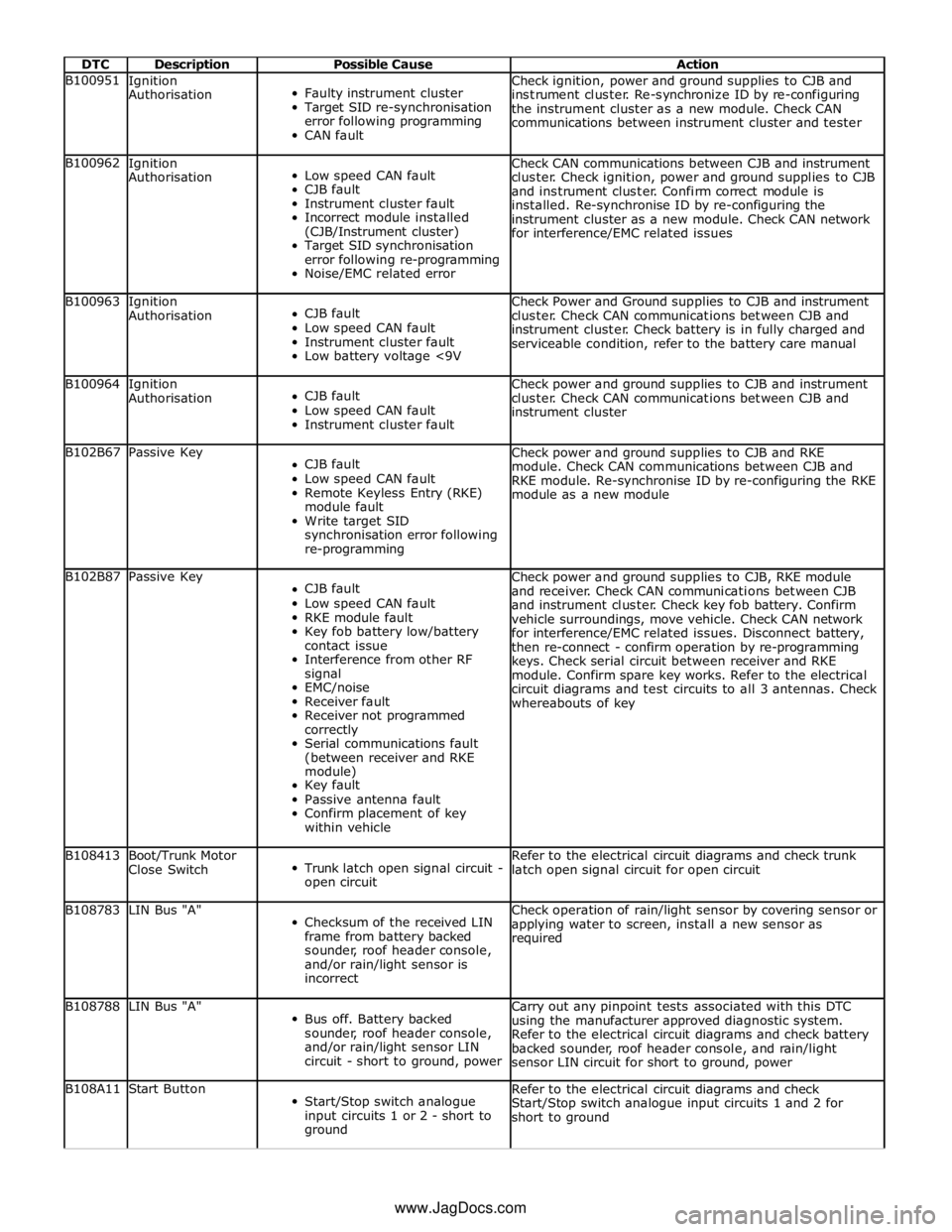
DTC Description Possible Cause Action B100951
Ignition
Authorisation
Faulty instrument cluster
Target SID re-synchronisation
error following programming
CAN fault Check ignition, power and ground supplies to CJB and
instrument cluster. Re-synchronize ID by re-configuring
the instrument cluster as a new module. Check CAN
communications between instrument cluster and tester B100962
Ignition
Authorisation
Low speed CAN fault
CJB fault
Instrument cluster fault
Incorrect module installed
(CJB/Instrument cluster)
Target SID synchronisation
error following re-programming
Noise/EMC related error Check CAN communications between CJB and instrument
cluster. Check ignition, power and ground supplies to CJB
and instrument cluster. Confirm correct module is
installed. Re-synchronise ID by re-configuring the
instrument cluster as a new module. Check CAN network
for interference/EMC related issues B100963
Ignition
Authorisation
CJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
Instrument cluster fault
Low battery voltage <9V Check Power and Ground supplies to CJB and instrument
cluster. Check CAN communications between CJB and
instrument cluster. Check battery is in fully charged and
serviceable condition, refer to the battery care manual B100964
Ignition
Authorisation
CJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
Instrument cluster fault Check power and ground supplies to CJB and instrument
cluster. Check CAN communications between CJB and
instrument cluster B102B67 Passive Key
CJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
Remote Keyless Entry (RKE)
module fault
Write target SID
synchronisation error following
re-programming Check power and ground supplies to CJB and RKE
module. Check CAN communications between CJB and
RKE module. Re-synchronise ID by re-configuring the RKE
module as a new module B102B87 Passive Key
CJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
RKE module fault
Key fob battery low/battery
contact issue
Interference from other RF
signal
EMC/noise
Receiver fault
Receiver not programmed
correctly
Serial communications fault
(between receiver and RKE
module)
Key fault
Passive antenna fault
Confirm placement of key
within vehicle Check power and ground supplies to CJB, RKE module
and receiver. Check CAN communications between CJB
and instrument cluster. Check key fob battery. Confirm
vehicle surroundings, move vehicle. Check CAN network
for interference/EMC related issues. Disconnect battery,
then re-connect - confirm operation by re-programming
keys. Check serial circuit between receiver and RKE
module. Confirm spare key works. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and test circuits to all 3 antennas. Check
whereabouts of key B108413
Boot/Trunk Motor
Close Switch
Trunk latch open signal circuit -
open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check trunk
latch open signal circuit for open circuit B108783 LIN Bus "A"
Checksum of the received LIN
frame from battery backed
sounder, roof header console,
and/or rain/light sensor is
incorrect Check operation of rain/light sensor by covering sensor or
applying water to screen, install a new sensor as
required B108788 LIN Bus "A"
Bus off. Battery backed
sounder, roof header console,
and/or rain/light sensor LIN
circuit - short to ground, power Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check battery
backed sounder, roof header console, and rain/light
sensor LIN circuit for short to ground, power B108A11 Start Button
Start/Stop switch analogue
input circuits 1 or 2 - short to
ground Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
Start/Stop switch analogue input circuits 1 and 2 for
short to ground www.JagDocs.com
Page 2090 of 3039
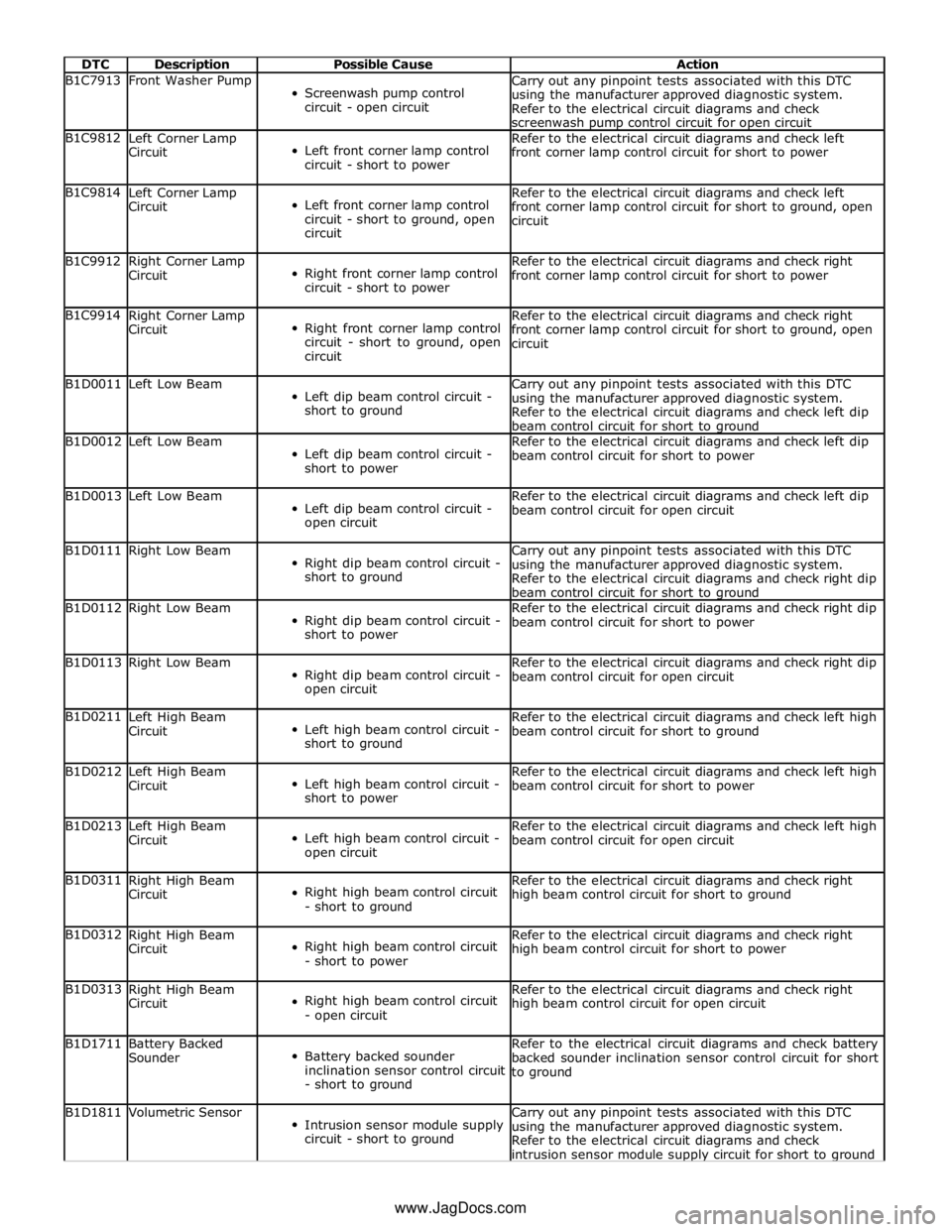
DTC Description Possible Cause Action B1C7913 Front Washer Pump
Screenwash pump control
circuit - open circuit Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
screenwash pump control circuit for open circuit B1C9812
Left Corner Lamp
Circuit
Left front corner lamp control
circuit - short to power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check left
front corner lamp control circuit for short to power B1C9814
Left Corner Lamp
Circuit
Left front corner lamp control
circuit - short to ground, open
circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check left
front corner lamp control circuit for short to ground, open
circuit B1C9912
Right Corner Lamp
Circuit
Right front corner lamp control
circuit - short to power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check right
front corner lamp control circuit for short to power B1C9914
Right Corner Lamp
Circuit
Right front corner lamp control
circuit - short to ground, open
circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check right
front corner lamp control circuit for short to ground, open
circuit B1D0011 Left Low Beam
Left dip beam control circuit -
short to ground Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check left dip
beam control circuit for short to ground B1D0012 Left Low Beam
Left dip beam control circuit -
short to power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check left dip
beam control circuit for short to power B1D0013 Left Low Beam
Left dip beam control circuit -
open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check left dip
beam control circuit for open circuit B1D0111 Right Low Beam
Right dip beam control circuit -
short to ground Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check right dip
beam control circuit for short to ground B1D0112 Right Low Beam
Right dip beam control circuit -
short to power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check right dip
beam control circuit for short to power B1D0113 Right Low Beam
Right dip beam control circuit -
open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check right dip
beam control circuit for open circuit B1D0211
Left High Beam
Circuit
Left high beam control circuit -
short to ground Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check left high
beam control circuit for short to ground B1D0212
Left High Beam
Circuit
Left high beam control circuit -
short to power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check left high
beam control circuit for short to power B1D0213
Left High Beam
Circuit
Left high beam control circuit -
open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check left high
beam control circuit for open circuit B1D0311
Right High Beam
Circuit
Right high beam control circuit
- short to ground Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check right
high beam control circuit for short to ground B1D0312
Right High Beam
Circuit
Right high beam control circuit
- short to power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check right
high beam control circuit for short to power B1D0313
Right High Beam
Circuit
Right high beam control circuit
- open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check right
high beam control circuit for open circuit B1D1711
Battery Backed
Sounder
Battery backed sounder
inclination sensor control circuit
- short to ground Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check battery
backed sounder inclination sensor control circuit for short
to ground B1D1811 Volumetric Sensor
Intrusion sensor module supply
circuit - short to ground Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
intrusion sensor module supply circuit for short to ground www.JagDocs.com
Page 2091 of 3039
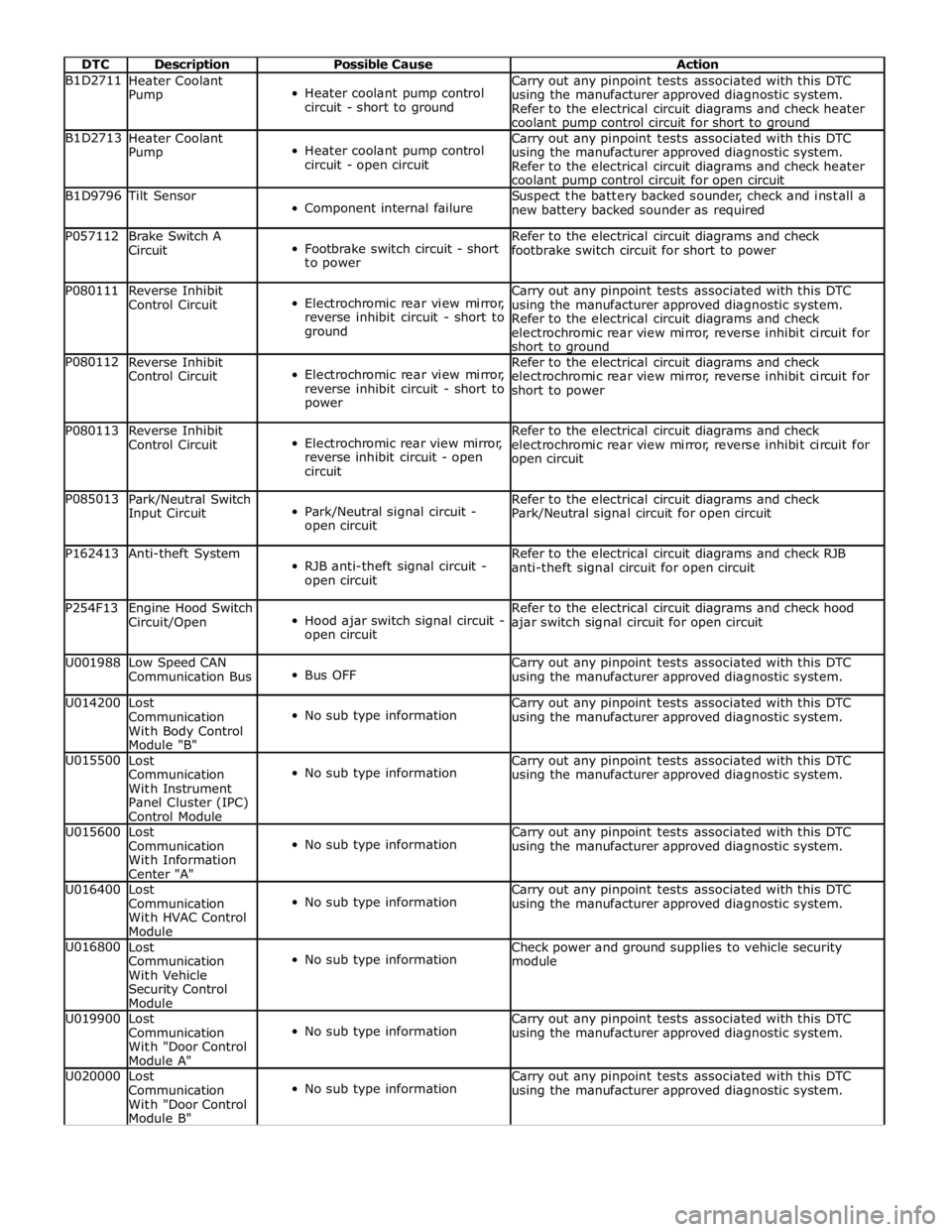
DTC Description Possible Cause Action B1D2711
Heater Coolant
Pump
Heater coolant pump control
circuit - short to ground Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check heater
coolant pump control circuit for short to ground B1D2713
Heater Coolant
Pump
Heater coolant pump control
circuit - open circuit Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check heater
coolant pump control circuit for open circuit B1D9796 Tilt Sensor
Component internal failure Suspect the battery backed sounder, check and install a
new battery backed sounder as required P057112
Brake Switch A
Circuit
Footbrake switch circuit - short
to power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
footbrake switch circuit for short to power P080111
Reverse Inhibit
Control Circuit
Electrochromic rear view mirror,
reverse inhibit circuit - short to
ground Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
electrochromic rear view mirror, reverse inhibit circuit for
short to ground P080112
Reverse Inhibit
Control Circuit
Electrochromic rear view mirror,
reverse inhibit circuit - short to
power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
electrochromic rear view mirror, reverse inhibit circuit for
short to power P080113
Reverse Inhibit
Control Circuit
Electrochromic rear view mirror,
reverse inhibit circuit - open
circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
electrochromic rear view mirror, reverse inhibit circuit for
open circuit P085013
Park/Neutral Switch
Input Circuit
Park/Neutral signal circuit -
open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
Park/Neutral signal circuit for open circuit P162413 Anti-theft System
RJB anti-theft signal circuit -
open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check RJB
anti-theft signal circuit for open circuit P254F13
Engine Hood Switch
Circuit/Open
Hood ajar switch signal circuit -
open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check hood
ajar switch signal circuit for open circuit U001988
Low Speed CAN
Communication Bus
Bus OFF Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system. U014200
Lost
Communication
With Body Control
Module "B"
No sub type information Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system. U015500
Lost
Communication
With Instrument
Panel Cluster (IPC)
Control Module
No sub type information Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system. U015600
Lost
Communication
With Information
Center "A"
No sub type information Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system. U016400
Lost
Communication
With HVAC Control
Module
No sub type information Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system. U016800
Lost
Communication
With Vehicle
Security Control
Module
No sub type information Check power and ground supplies to vehicle security
module U019900
Lost
Communication
With "Door Control
Module A"
No sub type information Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system. U020000
Lost
Communication
With "Door Control
Module B"
No sub type information Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Page 2092 of 3039

DTC Description Possible Cause Action U021400
Lost
Communication
With Remote
Function Actuation
No sub type information Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system. U023100
Lost
Communication
With Rain Sensing
Module
No sub type information Check power and ground supplies to rain sensing module.
LIN circuit fault U030000
Internal Control
Module Software Incompatibility
No sub type information Suspect the CJB. Check and install a new CJB as
required, refer to the new module/component installation
note at the top of the DTC Index U1000-00
Solid State Driver
Protection Active -
Driver Disabled -
No sub type
information
Central junction box output
circuit - Short circuit to ground,
short circuit to power
NOTE: The relevant output is disabled while this
DTC is set. Do not clear the DTC until the fault has been
rectified
Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system, check for other central junction box short
circuit to ground and/or short circuit to power
DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC index for
corrective actions
Once circuit faults have been rectified, clear DTC
and retest U1A1449
CAN Initialisation
Failure
Internal electronic failure Suspect the CJB. Check and install a new CJB as
required, refer to the new module/component installation
note at the top of the DTC Index U200813 Sensor Cluster
Instrument cluster security
signal circuit - open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
instrument cluster security signal circuit for open circuit U201012 Switch Illumination
Switch/interior illumination
PWM supply circuit - short to
power Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
switch/interior illumination PWM supply circuit for short
to power U201014 Switch Illumination
Switch/interior illumination
PWM supply circuit - short to
ground, open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
switch/interior illumination PWM supply circuit for short
to ground, open circuit U210000
Initial Configuration
Not Complete
RJB configuration (parameters)
failure Re-configure the RJB using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system U3000-49
Control Module -
Internal electronic
failure
Central junction box - Internal
failure
NOTE: The relevant output is disabled while this
DTC is set
Using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system, check for other central junction box short
circuit to ground and/or short circuit to power
DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC index for
corrective actions
Install a new central junction box as required.
Clear DTCs and retest U300055 Control Module
Not configured Re-configure the RJB using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system. Check the correct CJB is installed to
vehicle market/specification. Install a new/correct CJB as
required, refer to the new module/component installation
note at the top of the DTC Index U300087 Control Module
Missing message Carry out CAN network integrity test using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check CAN network
between RJB and CJB for short, open circuit. Check RJB
and then CJB for related DTCs and refer to the relevant
DTC Index U300281
Vehicle
Identification
Number
Invalid serial data received Suspect the CJB has previously been installed to another
vehicle. Check and install the original or a new CJB U300317 Battery Voltage
Circuit voltage above threshold Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.